Week 1- Caring of the Woman during Pregnancy and during the Postpartal Period
1/254
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH 1, 2, 3 (95-107), 10 (323-330), 11, 12, 15, 16, 21 (800-802), and 22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
255 Terms
What is the modern beliefs about childbirth (in relation to historical beliefs)?
return of midwives and doulas; childbirth choices based on what works best for mother, child and family
What is the current practice for maternal and newborn nursing? (4)
complex with increased technology (ex. IVF, 22 week for survival)
Threats of litigation (lawsuits)
Care under time
Economic restraints
what is mortality?
number of people who have died over a specific period
What is the maternal mortality rate? (Definition!)
annual number of deaths from any cause during pregnancy or within 42 days of termination per every 100,000 live births
What race/ethnicity has the highest maternal mortality rate?
African American women
how is the US’s ranking in terms of maternal mortality rate?
Not great based on how technologically advanced medicine is —> ranked 46th
what is the fetal mortality rate? (Definition)
Number of fetal deaths (20 weeks or older) per 1,000 live births
Note: it is a major but often overlooked health problem
what are some maternal factors to the fetal mortality rate? (4)
malnutrition
Disease
Preterm cervical dilation
Comorbidities- ex. gestational or pre-existing diabetes, HTN, etc.
What are some fetal factors to the fetal mortality rate? (2)
chromosomal abnormalities
Poor placental attachment
What is the neonatal mortality rate? (Definition)
number of infant deaths (in the first 28 days) per 1,000 live births
what is the infant mortality rate? (Definition)
number of infant deaths (in the first 12 months) per every 1,000 births
What are some causes of infant mortality? (2)
congenital anomalies = leading cause
Low birth weight and prematurity = significant predictors of infant mortality
What are some causes of low birth weight and prematurity in babies?(4)
alcohol
smoking
Malnutrition
Comorbidities —> HTN/DM
what are some factors that can impact maternal and child health? (8)
family- medical history!! ← especially maternal side!! Can predict complications
Genetics
Society
Global society
Culture- new environments ← for us its the ORs/delivery suites ← can cause a shock
Health status and lifestyle
Access to healthcare- distance?, $, options?
Improvement to diagnosis and treatments
How does someone’s culture impact their experiences in maternal and child health? (3)
immigration = new environment
Spirituality and religion
Changing cultural dynamics due to differing population distributions
How does someone’s health status and lifestyle impact their experiences with maternal and child health?
developmental level- 15 yr old vs. 30 yr old vs. 45 yr old having baby
Nutrition- deficient or excess (obesity)
Lifestyle choices- eating patterns, exercise, tobacco/drugs/alcohol, coping mechanisms, level of stress
Environment- exposure to teratogens, pollution, water/food contamination
Stress and coping- disasters, crises, $$, support systems, violence
what are teratogens and when are they the most problematic?
def = any substance, organism, physical agent, or deficiency state present during gestation that is capable of inducing abnormal postnatal structure or function by interfering with normal embryonic and fetal development AKA anything that can harm the baby during development
Most problematic in beginning of pregnancy when initial development of body systems is taking place
What are some examples of legal and ethical issues in maternal and child health care? (8)
abortion
Substance abuse - criminal implications for mom?
Intrauterine therapy- medical technology advancements (ex. In-utero micro surgeries) vs nature
Maternal- fetal conflict - who to save? Beneficence and autonomy?
stem cell research and use of embryonic stem cells for medical advancement
Umbilical cord blood banking
Informed consent when mother is a minor
refusal of medical treatments vs parental consent ← more of a problem in peds
What is atraumatic care? how can we help to provide it? (3)
Delivery of care that minimizes or eliminates psychological and physical distress experienced by children and families in the health care system
Preventing/minimizing physical stressors
Preventing/minimizing separation
Promoting a sense of control
what is unique about maternal and child health as compared to previous semesters?
family centered care vs patient centered care
More focused on meeting needs of patient and family as they can help to support the patient best
What is discharge planning?
development and implementation of a comprehensive plan from safe discharge from a facility and for continuing safe and effective care in the community and at home
what is case management?
Coordinating health care services while balancing quality and cost outcomes
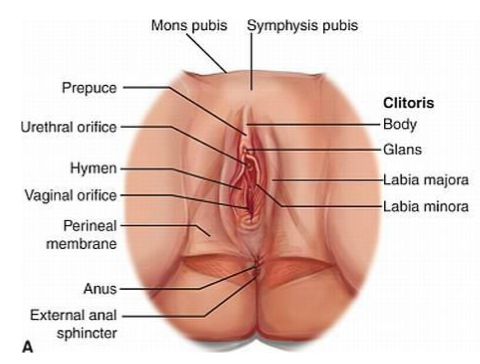
What is the function of the external female reproductive organs? (2) What is it called?
AKA vulva
Protects urethra and vaginal openings
Highly sensitive to touch to increase female’s pleasure during sexual arousal
What are the components of the vulva? Functions? (6)
Mons pubis- fatty tissue to protect the pubic symphysis
Labia majora- contains sweat and sebaceous glands and protects vaginal opening
labia minora- highly vascular and abundant nerve supply; lubricates vulva and swells with stimulation
Clitoris- small cylindrical mass of erectile tissue and serves; function = sexual stimulation
Vestibular structures- urethra, vagina, 2 sets of glands (secrete mucus to keep opening moist)
Perineum = vagina ←> anus
what are the internal female reproductive organs? Functions? (5)
Vagina- pathway to external environment from uterus
Uterus- home to fetus
Cervix- opening to uterus (note: should be closed until labor begins)
Fallopian tubes- connect the uterus to the ovaries
Ovaries- produce eggs
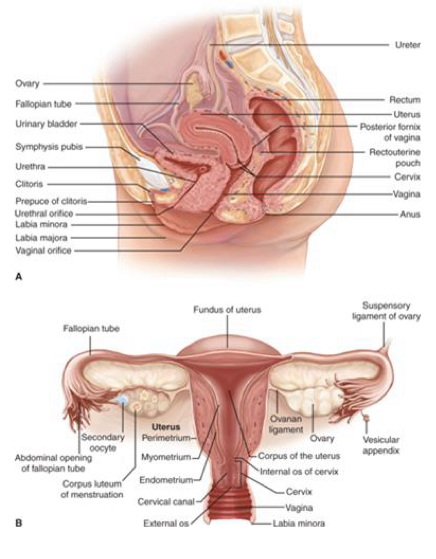
What are the layers of the uterine wall? (3)
Endometrium- lines the uterine cavity in nonpregnant women
Myometrium- majority of uterus- contracts during labor
Perimetrium- covers body of the uterus
What is menstruation?
expulsion of inner uterine lining occurring monthly
Marks the beginning and end of each menstrual cycle
what is menarche?
establishment of menstruation in females; occurs around 12-14 yrs old
what is menopause?
naturally occurring cessation of regular menstrual cycles
what is the frequency of menstruation?
21-36 days ← variable
what are the 3 stages of the ovarian cycle? Timeline?
Follicular phase = day 1 through ovulation (days 10-14)
Ovulation = day 14 of a 28 day cycle
Luteal phase = day 15 through 28 of a 28 day cycle
What are the 4 phases of the uterine cycle?
Menstrual
Proliferative
Secretory
Ischemic
What happens during the follicular phase? (Hormones! -2)
FSH stimulates follicle development
Estrogen rises → endometrial proliferation
What happens during ovulation? (2)
LH surges to trigger the release of the ovum
Cervical mucus becomes thin and stretchy
What happens during the luteal phase? (3 → hint include the outcome when fertilization occurs and when it doesn’t)
Corpus luteum secretes progesterone
Prepares endometrium for implantation
If no fertilization the corpus luteum regresses → progesterone decreases → menstruation occurs
What is the role of GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone)?
stimulates the release of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary
What is the role of FSH? (2)
Follicle growth
Estrogen secretion
What is the role of LH? (2)
Ovulation
Forms corpus luteum
What is the role of estrogen? (2)
Develops endometrium
Secondary sex characteristics - breast development, fat distribution
What is the role of progesterone? (2)
Maintains uterine lining
Relaxes uterine muscle - prevents contractions
What is the role of prostaglandins? (2)
Influence ovulation
Cause uterine contractions and cramps
When are LH levels at their highest during the menstrual cycle?
Ovulation
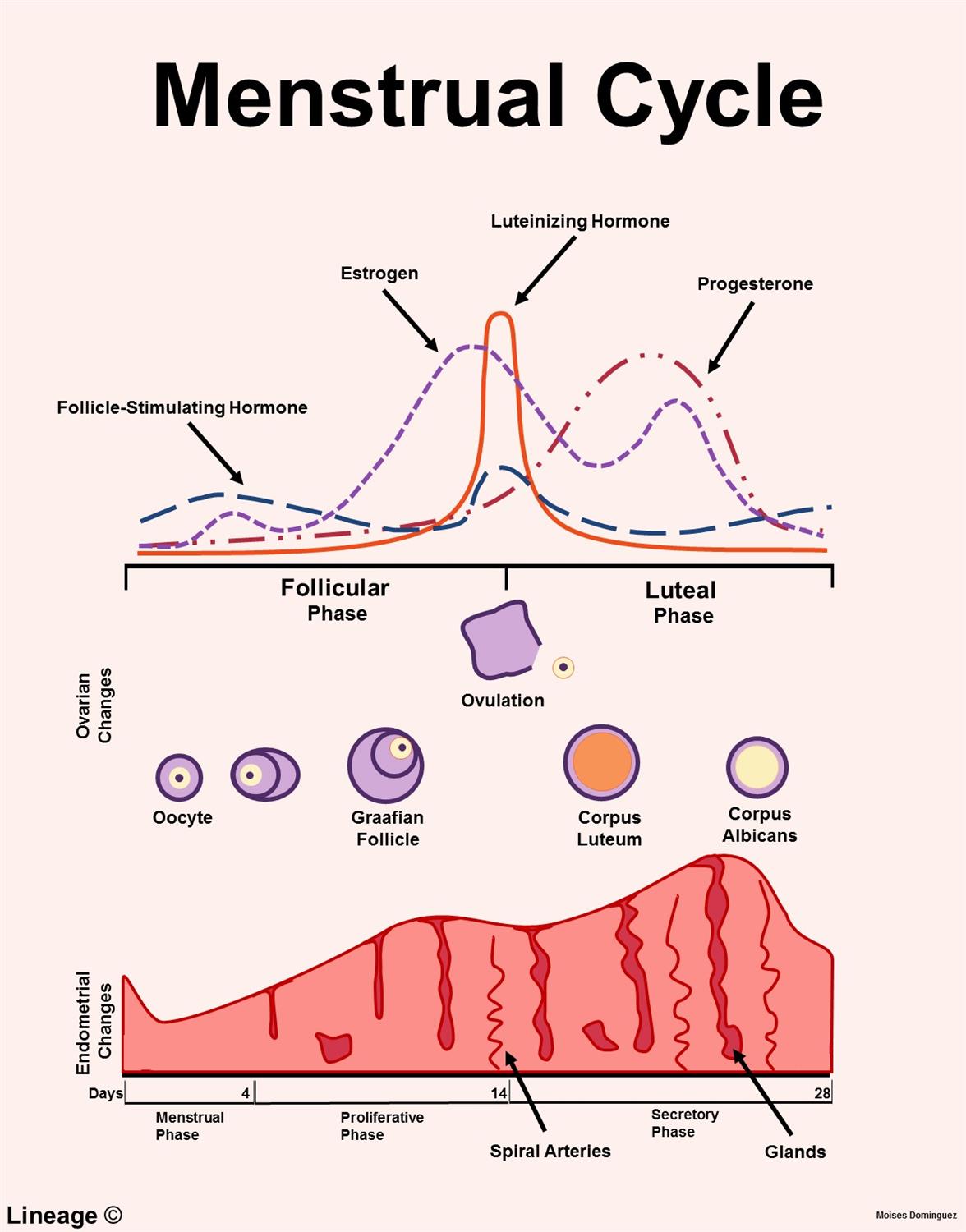
When are FSH levels at their highest during the menstrual cycle?
During the first week of the follicular phase
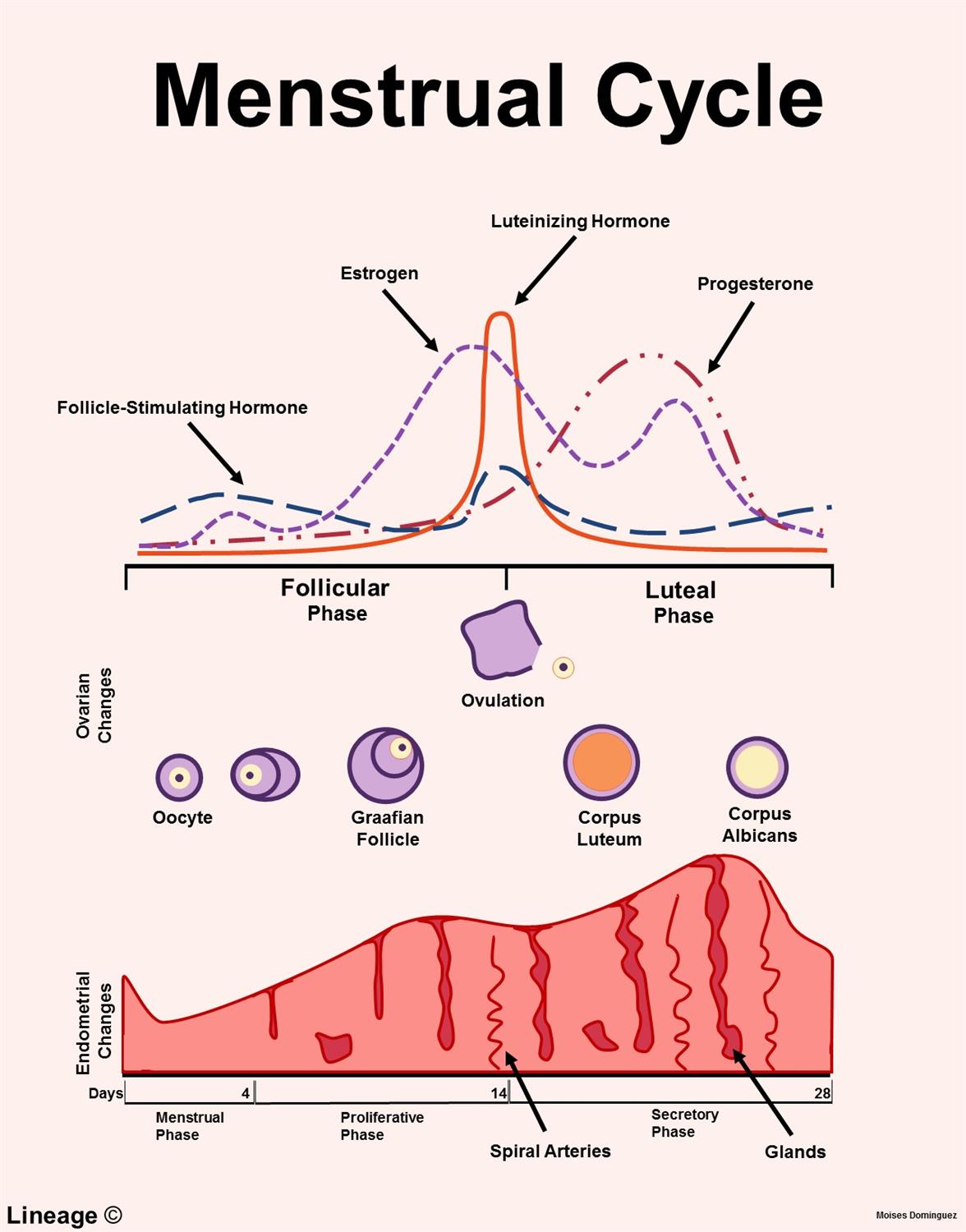
When are estrogen levels at their highest during the menstrual cycle?
just before ovulation
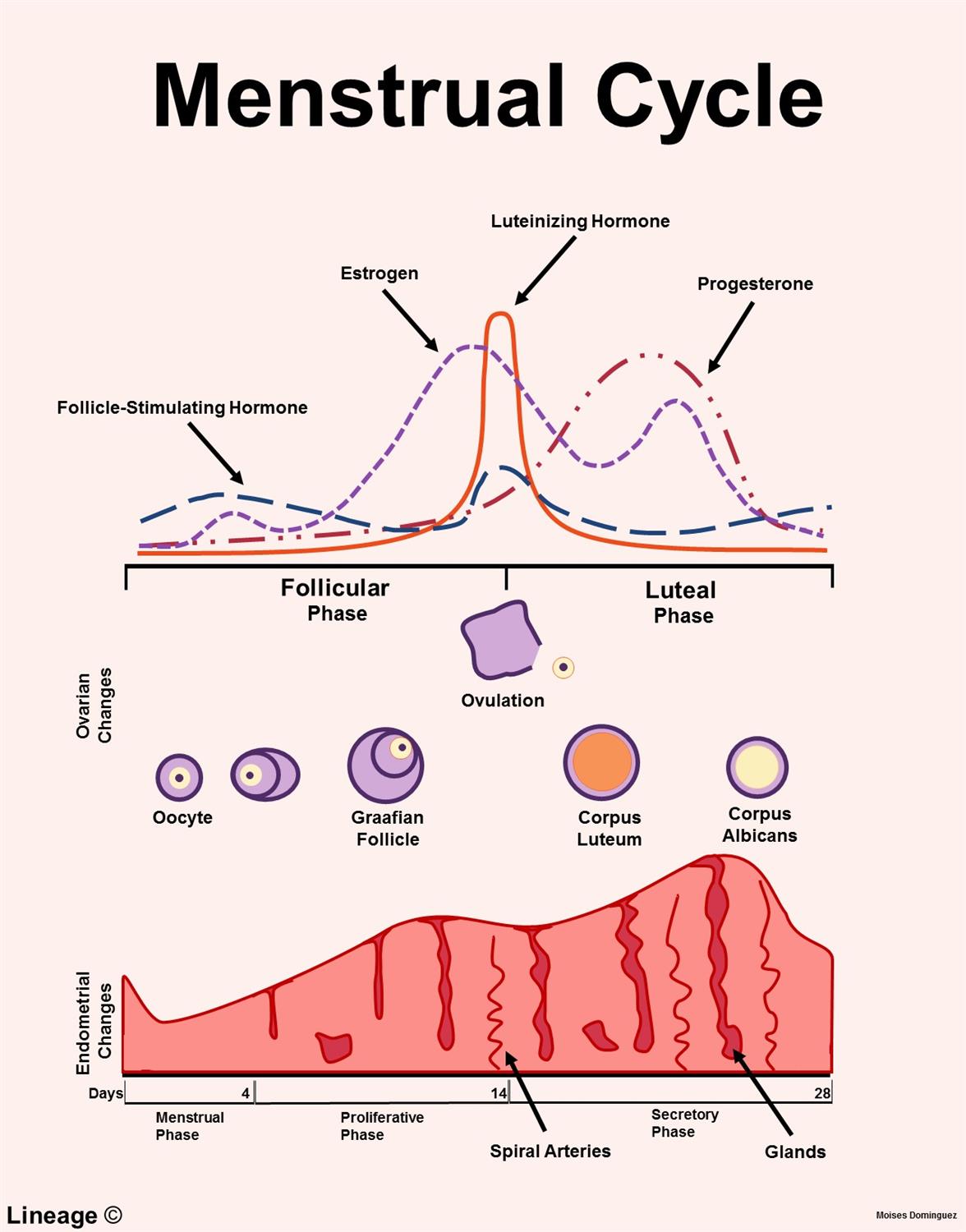
When are progesterone levels at their highest during the menstrual cycle?
5-7 days after ovulation during the luteal phase
What are the stages of fetal development? (4)
Zygotic stage
Blastocyst stage
Embryonic stage
Fetal stage
What occurs during the zygotic stage?
Fertilization of sperm and egg AKA conception
what occurs during the embryonic stage of development?
Basic structures of major body organs and main external features
what occurs during the fetal stage?
differentiation and structures specialize
When is the embryonic stage of development?
end of 2nd week through the 8th week
When is the fetal stage of development?
End of 8th week until birth
What does the placenta do for the fetus? (3)
Protection from mother’s immune system
Removing waste products from the fetus
Inducing mother to bring more food to the placenta to ensure the fetus is supplied with nutrients and oxygen
what are the components of the umbilical cord? (3)
One large vein
2 small arteries
Wharton jelly that surrounds the vessels to prevent compression
What are the roles of the amniotic fluid? (5)
Helps maintain constant body temp for fetus
Permits symmetrical growth and development
Protects/cushions fetus from trauma
Allows umbilical cord to be relatively free of compression
Promotes fetal movement to enhance the development of the musculoskeletal systems
What is the risk associated with too LITTLE amniotic fluid?
can compress umbilical cord
What is the risk associated with too MUCH amniotic fluid?
Can increase risk of cord wrapping around baby neck
What is pharmacogenomics?
study of genetic and genomic influences on pharmacodynamics and pharmacotherapeutics
Includes testing for genetic disorders and gene therapy
IDEALLY when should new parents receive genetic evaluations and counseling?
before conception
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Fatigue (12 weeks)
Presumptive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Breast tenderness (3-4 weeks)
Presumptive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
N/V (4-14 weeks)
presumptive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Amenorrhea (4 weeks)
Presumptive
Note- it is the absence of menstrual cycle
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Urinary frequency (6-12 weeks)
presumptive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Hyperpigmentation of skin (16 weeks)
Presumptive
What is quickening?
fetal movements
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Quickening (16-20 weeks)
presumptive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Uterine enlargement (7-12 weeks)
presumptive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Breast enlargement (6 weeks)
presumptive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Braxton Hicks contractions (16-28 weeks)
probable
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Positive pregnancy test (4-12 weeks)
probable
Note: HcG can also indicate cancer
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Abdominal enlargement (14 weeks)
probable
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Ballotment (16-28 weeks)
Probable
What is ballotment?
gently pushing on the uterus through the abdominal wall or vagina to displace the fetus. If the fetus is present, it will rebound and tap against the examiner's fingers
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Goodell sign (5 weeks)
probable
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Chadwick sign (6-8 weeks)
probable
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Hegar sign (6-12 weeks)
probable
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Ultrasound verification of embryo or fetus (4-6 weeks)
positive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Fetal movement felt by experienced clinician (NOT THE PT) (20 weeks)
positive
What is the following sign of pregnancy?
Auscultation of fetal heart tones via doppler (10-12 weeks)
positive
what is a presumptive sign of pregnancy?
subjective feelings a women feels that can occur during pregnancy but can also occur without a pregnancy
what is a probable sign of pregnancy?
Objective signs of a pregnancy that can be measured by others or proven to others but can also occur without a pregnancy
what is a positive sign of pregnancy?
Signs of pregnancy that are observed by trained professionals that are able to prove that a pregnancy is taking place
What is Chadwick’s sign?
bluish-purple discoloration of the cervix, vagina and vulva

What causes Chadwick’s sign? (2)
increased vascularity
congestion of pelvic blood due to rising estrogen levels
What is goodell’s sign?
softening of the cervix from firm (tip of nose) to soft (earlobe consistency)
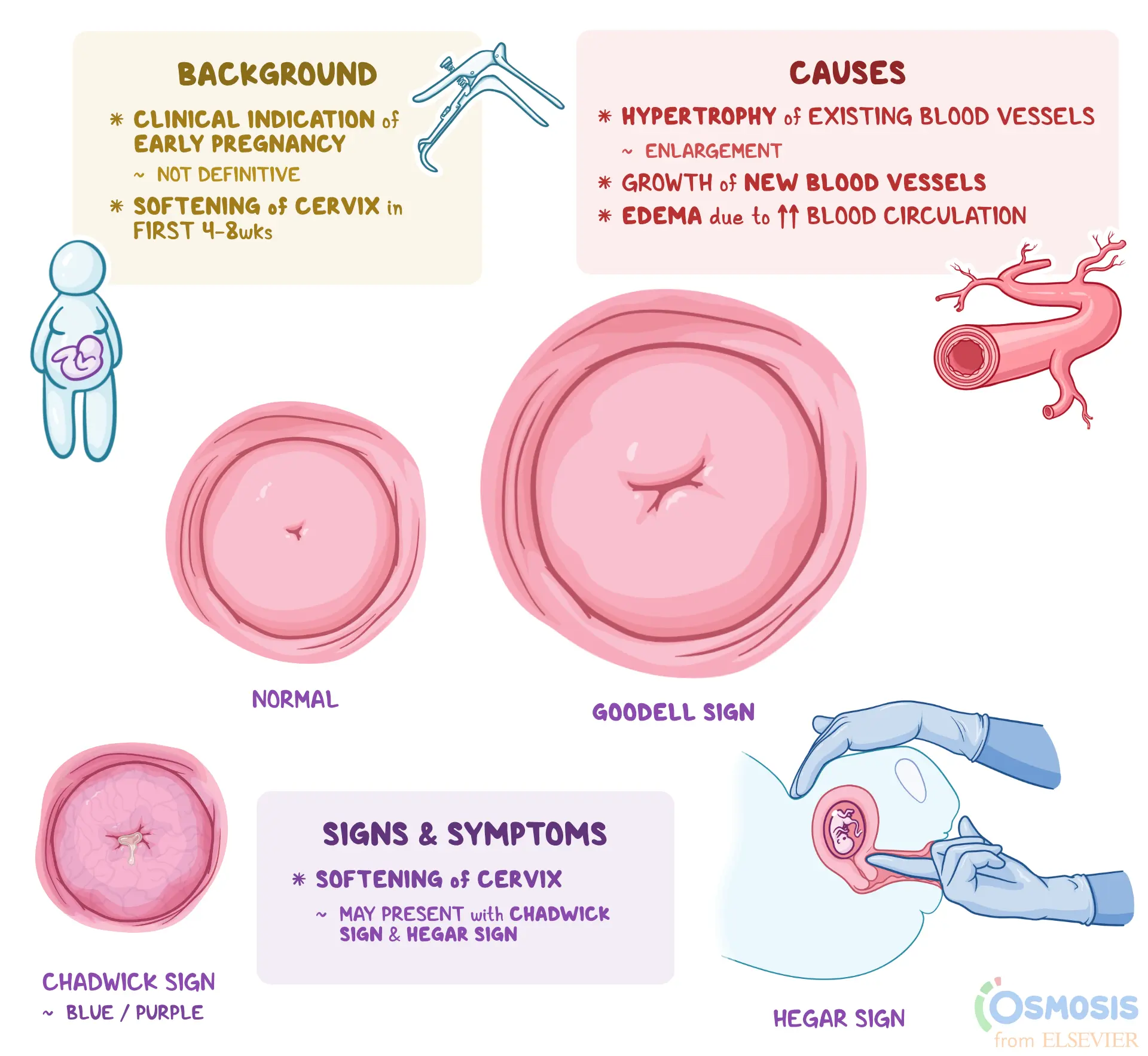
What causes goodell’s sign? (3)
increased vascularization
Edema
Hyperplasia of cervical tissues
Under influence of estrogen and progesterone
what is hegar’s sign?
softening and compressibility of the lower uterine segment (isthmus) just above the cervix
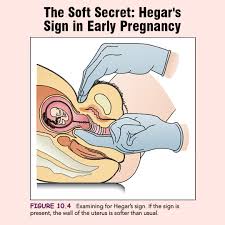
what is the cause of hegar’s sign?
hormonal (estrogen and progesterone) effects cause relaxation of uterine muscles and increased blood supply
How do you measure fundal height?
measuring from where the fundus is palpated to the pubic symphysis
when is fundal height a reliable determination of gestational age until?
36 weeks
what is ripening of the cervix?
softening and thinning
What is leukorrhea?
Vaginal secretions that are more acidic, white, and thicker than usual
Does ovulation continue during pregnancy?
No
what is colostrum?
Antibody-rich, yellow fluid that can be expressed after the 12th week; the conversion to more mature milk about 3 days after delivery
What is ptyalism?
Excess spit AKA excessive salivation
what happens to the blood supply during pregnancy? What can this cause? (2)
A 50% increase in pre pregnancy levels of blood volume and cardiac output increases
Can cause underlying cardiac issues to surface
Hypercoaguable states due to increased blood clotting components
What is the mask of pregnancy or facial melasma?
Sun spots
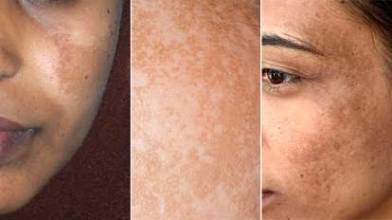
what is Linea nigra?
Brown line through belly to pubic symphysis
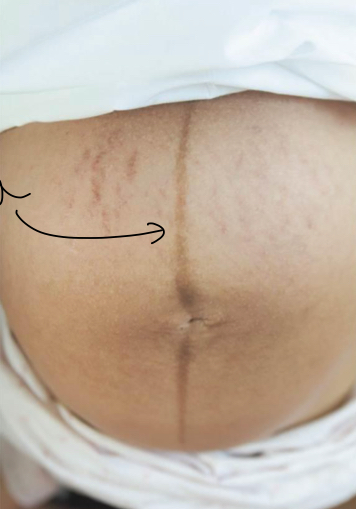
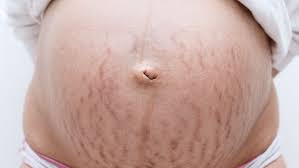
what is striae grivadarum?
stretch marks
What are the nutritional needs of pregnancy? (3 but 1 of the 3 has 4 parts)
Vitamin and mineral supplements daily
Increase in…
Protein
Iron
Folate
Calories
Avoidance of some fish due to mercury content