Gov Vocab Units 1-3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
constitution
the supreme law of the US outlining the three branches and checks & balances
natural rights
rights that people have by nature and that cannot be taken away by a government or any other authority (Locke)
Social Contract Theory
an implicit agreement among the members of a society to cooperate for social benefits, for example by sacrificing some individual freedom for state protection (Hobbes, Locke, Rousseau)
Declaration of Independence
document that was adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, that established the United States as an independent nation and severed political ties with Great Britain.
Consent of the Governed
a government's legitimacy and moral right to use state power is justified only when consented to by the society over which that political power is exercised
Limited Government
a theory of governance that limits the power of the government and protects the rights of individuals
Articles of Confederation
first constitution of the US, establishing the country's national government after it declared independence
Shays’ Rebellion
series of violent attacks on courthouses in Massachusetts by mostly ex-Revolutionary War soldiers-turned farmers who opposed state economic policies causing poverty and property foreclosures
Constitutional Convention
A convention of delegates in 1787 in Philadelphia - at this meeting it was decided to set aside the Articles of Confederation and write a new constitution.
Thomas Hobbes
Hobbes was an English philosopher, best known for his 1651 book Leviathan, and develops Social Contract 1.0
Factions
conflicting groups within government
Virginia Plan
a proposal that proportioned each state’s representation based on population
New Jersey Plan
a proposal that gave each state equal representation
Great Compromise (Connecticut)
created a bicameral legislature with one house that give representation on population and another (the senate) which gave each state equal representation
3/5s Compromise
determined that three out of every five slaves were counted when determining a state's total population for representation and taxation
Charles Beard’s Critique
the U.S. Constitution was adopted in order to protect the rights and interests of the Founding Fathers - the wealthy, upper-class members of society
Writ of Habeas Corpus
(lawful and speedy trial) - a person under arrest must be brought before a court to secure the person's release unless lawful grounds are shown for their detention.
Bill of Attainder
A bill of attainder is a piece of legislation that punishes a person or group of people without a judicial trial - these were banned in the Constitution
Ex Post Facto
criminalizing conduct that was legal when originally performed
Madisonian Model
governmental scheme so that the power and influence of each branch would be balanced by those of the others. The separation of powers is a result of Congress passing laws, the president enforcing laws, and the courts interpreting the laws.
“If men were angels”
“no government would be necessary” (Federalist 51 by James Madison)
Limiting the Majority
limit direct democracy as much as possible (republicanism, electoral college, etc)
Separation of Powers
a constitutional principle that divides the government into three branches, each with its own specific duties: Legislative makes the laws, Executive enforces the laws, and Judicial interprets the laws
Checks and Balances
each branch can check the power of the others
Diagram of Checks
..
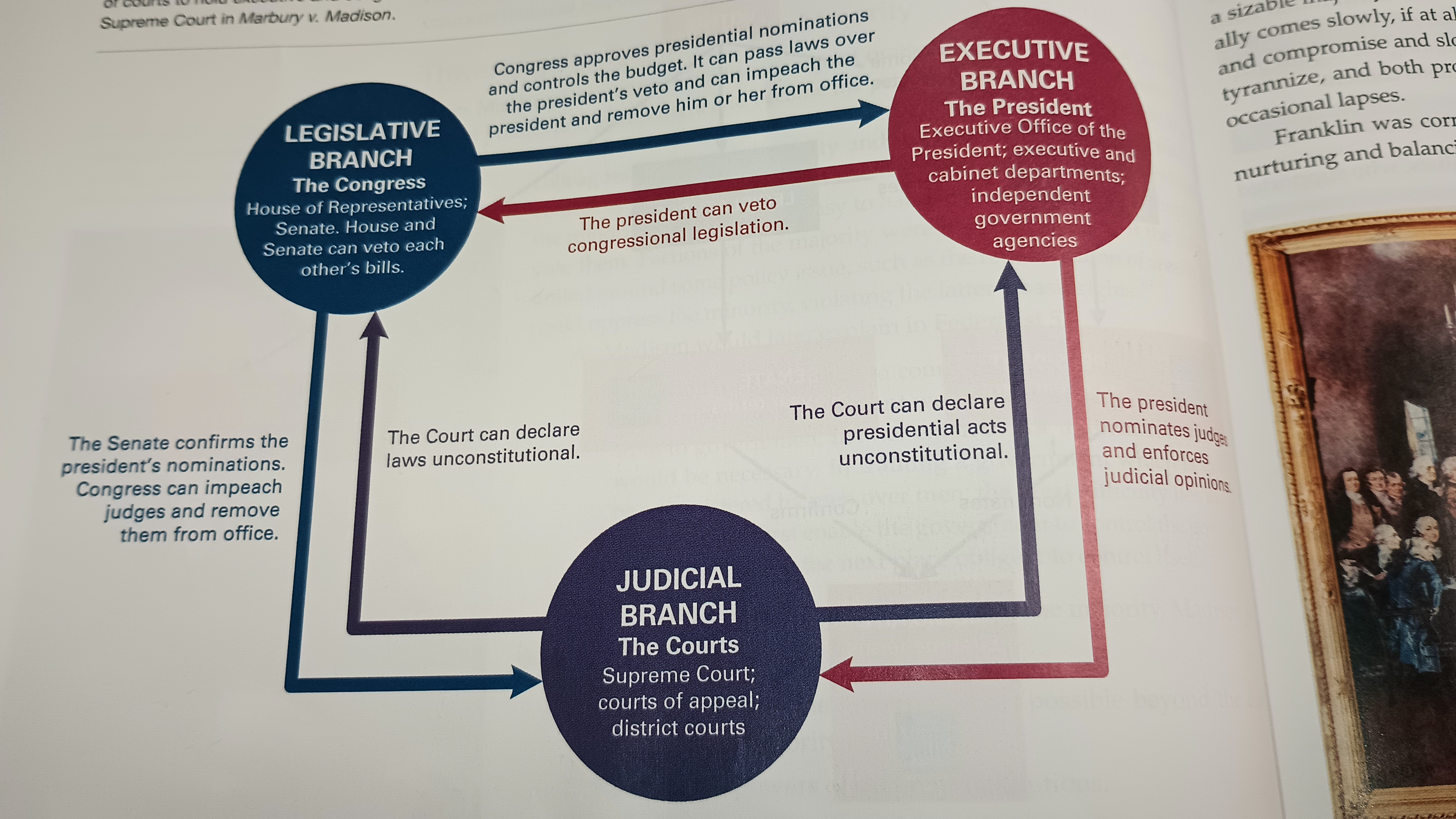
Judicial Review
power of the courts of a country to examine the actions of the other branches and determine constitutionality
Republic
supreme power is held by the people and their elected representatives
federalist
early US political party advocating a strong central government, initially pro-constitution
anti-federalist
people opposing federalist party (opposing the constitution)
Federalist Papers
series of 85 essays designed to convince New York to vote for the constitution
Coalition
an alliance for combined action, especially a temporary alliance of political parties
Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights is the first 10 Amendments to the Constitution. It spells out Americans' rights in relation to their government.
Amendment
a change to the Constitution
Amendment Process
amendment may be proposed by a two-thirds vote of both Houses of Congress, or, if two-thirds of the States request one, by a convention called for that purpose. The amendment must then be ratified by three-fourths of the State legislatures, or three-fourths of conventions called in each State for ratification.