AP U.S. History Political Parties You Must Know
- Minimized government interference with the economy.
Political Parties
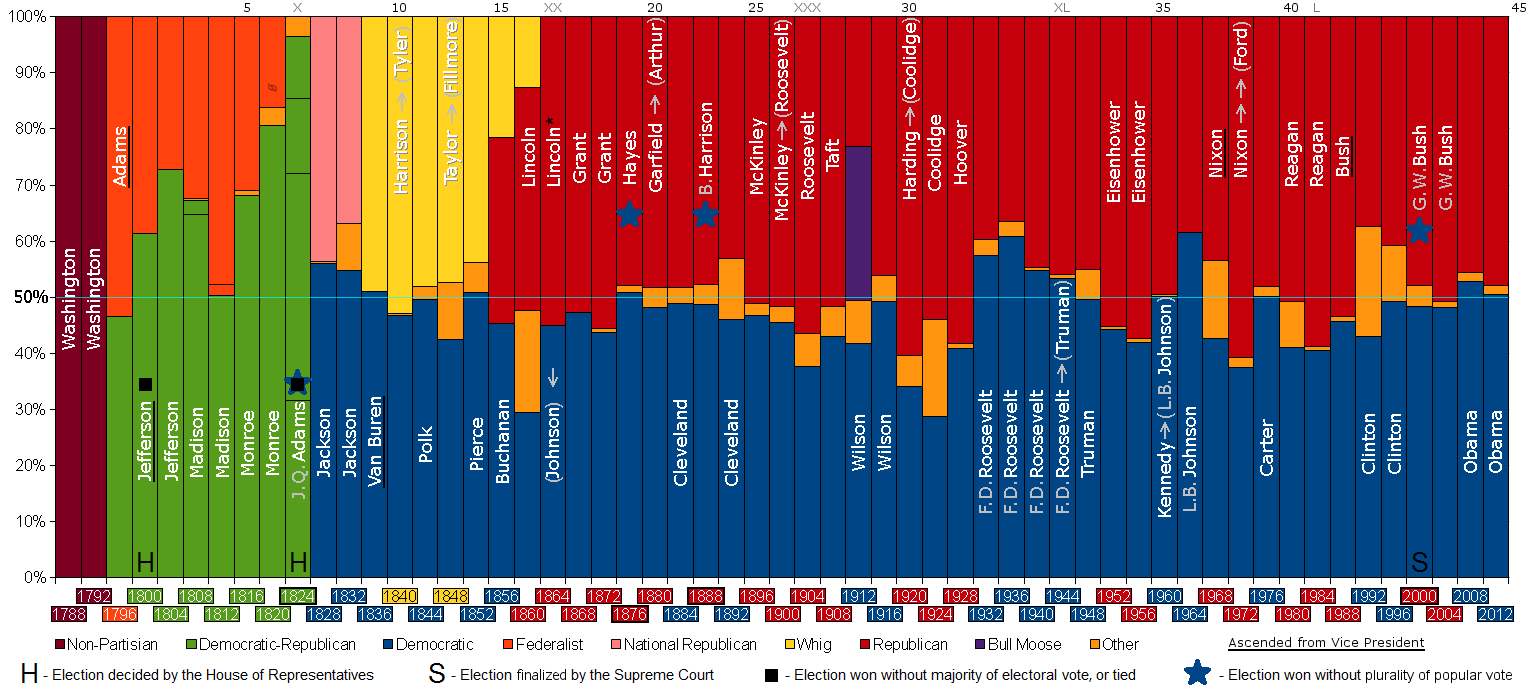
Federalist (1796-1820)
- Northern.
- Weak state government
- Strong centralized government
- Indirect elections
- Longer terms
- Supported the Constitution
- Fought against Antifederalists and Democrat-Republicans
Antifederalists (1787-1789)
- Opposed ratification of the U.S. Constitution.
- Weak centralized government.
- Fought against Federalists.
Democratic Republicans (1796-1824)
- Opposed Federalist party.
- Stronger state government.
- Minimize government interference with the economy.
- Led by Thomas Jefferson.
- Fought against Federalists.
Whigs (1836-1860)
- Protective tariffs.
- National banking.
- Federal aid.
- Power for congress.
- Most were against slavery.
- Fought against Democrats.
Democrats (1828 - Present)
- Weaker national government.
- People power.
- Lower tariffs.
- Expansion
- Minimize government interference with the economy.
- Fought against Whigs, National Republicans, Republicans, Constitutional Union.
Know-Nothings
- Nativist ideas. (American-born).
- Anti-immigrant.
Liberty Party (1840-1860)
- Abolitionist and Anti-slavery.
Free-Soil (1848-1854)
- Merged into republican.
- Anti-slavery.
- Free public land to settlers.
Republicans (1856 - Present)
- Strong military
- Pro-business economic policy.
- Decentralized government.
Progressives / Bull Moose (1912)
- Improve human societies through political action.
- Advance human condition through social reform.
- Advancements in science, technology, economic development, and social organization.
- Commonly called socialists or environmentalists.
Socialists
- Social ownership of the means of production.
- Everyone have an equal share of resources and wealth.
- Similar to communism.