Biology H - Evolution | Kowalski (BRHS)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is evolution?
The change in organisms over time
How old is the Earth? Prokaryotes? Eukaryotes? Multicellularity?
4.5 billion
3.5 billion
2.1 billion
700 million
How is fossil evidence used?
Hard body parts preserved in rocks are compared to see ancestors of species
What is strata?
Layers of rock that allow us to estimate how old a fossil is
Top layer - young
Bottom layer - old
How was evolution first proven?
Comparison of reptile fossils to birds served as proof that organisms can give birth to others
What is the Archeopteryx?
An in-between fossil that showed the transition between reptiles and birds.
What is relative and absolute dating?
Relative dating = figure out fossil's age by comparing them to others, not exact
Absolute dating = radioactive carbon dating, exact age
How many total mass extinctions have there been?
Five
How do we know what caused the Cretaceous period mass extinction?
Iridium in Mexico, mostly found in meteorites -> meteors hit Earth -> heat blanket formed over Earth, sun was blocked by dust -> death of most plants & dinosaurs
What happens after a mass extinction?
Remaining species spread out and create new organisms in empty niches
What was the greatest mass extinction?
The Permian where 90% of organisms died
What is continental drift?
The movement of continents across the Earth over time
How is continental drift related to evolution?
When continents move, the climates of the region change, causing organisms to adapt and evolve.
What are homologous structures?
Part with same function and same structure, indicating a common ancestor
What are analogous structures?
Part with same function but a different structure, indicating no common ancestor
What are vestigial structures?
Remnant part with same structure that no longer functions
ex: human tailbone
What do all organisms have in common?
They all use the same biochemical molecules consisting of DNA, ATP and nearly identical enzymes.
Who were Miller & Urey?
Scientists that simulated the conditions of early Earth in an attempt to see if inorganic chemicals can make organic molecules w/o oxygen.
What did Miller & Urey discover?
They discovered that organic material (amino acids) were able to be created by the heating of Earth's original chemical pool
Describe the steps of the Miller-Urey experiment.
1) Water was heated to simulate vaporizing of ocean water into atmosphere
2) The atmosphere consisted of ammonia, methane, water vapor and hydrogen gas, w/ electric sparks mimicking lightning
3) Applied heat + electricity to circulate
4) Formed amino acids + organic acids
How did life form according to Miller & Urey?
Small organic molecules gave rise to larger molecules which finally turned into macromolecules
What does the heterotroph hypothesis say?
That the first cells to exist were heterotrophs (cannot make their own energy) rather than autotrophs
Why do we believe in the heterotroph hypothesis?
Because no rust could be found in early rocks, and oxygen is required for rocks to rust, meaning Earth originally had no oxygen.
What are the five agents of evolutionary change?
1. Mutations
2. Genetic drift
3. Gene flow
4. Nonrandom mating
5. Natural selection
What are mutations?
Chance events that are the only source of new genes in a population
What is genetic drift?
Change in gene frequency due to chance
What is the founder effect?
When a few individuals break off a population and find a new colony. Their gene pool is different from original population.
What is an example of the founder effect?
Polydactyly (extra fingers) more common in Amish because they only reproduce with each other and are "broken off" from population.
What is the bottleneck effect?
When most of the population dies due to a disaster, the gene pool of the few survivors is different from the original population.
What is gene flow?
The movement of genes between populations which keeps the gene pool of said populations similar.
What is nonrandom mating?
When individuals are looking for specific traits in a partner
What does inbreeding do?
Increases frequency of recessive abnormalities (like polydactyly in amish)
What is natural selection?
Survival of the fittest -> favorable traits become more common in successive generations and eventually become present in the whole species.
What shape do most polygenic traits form?
A bell-shaped curve (no selection)
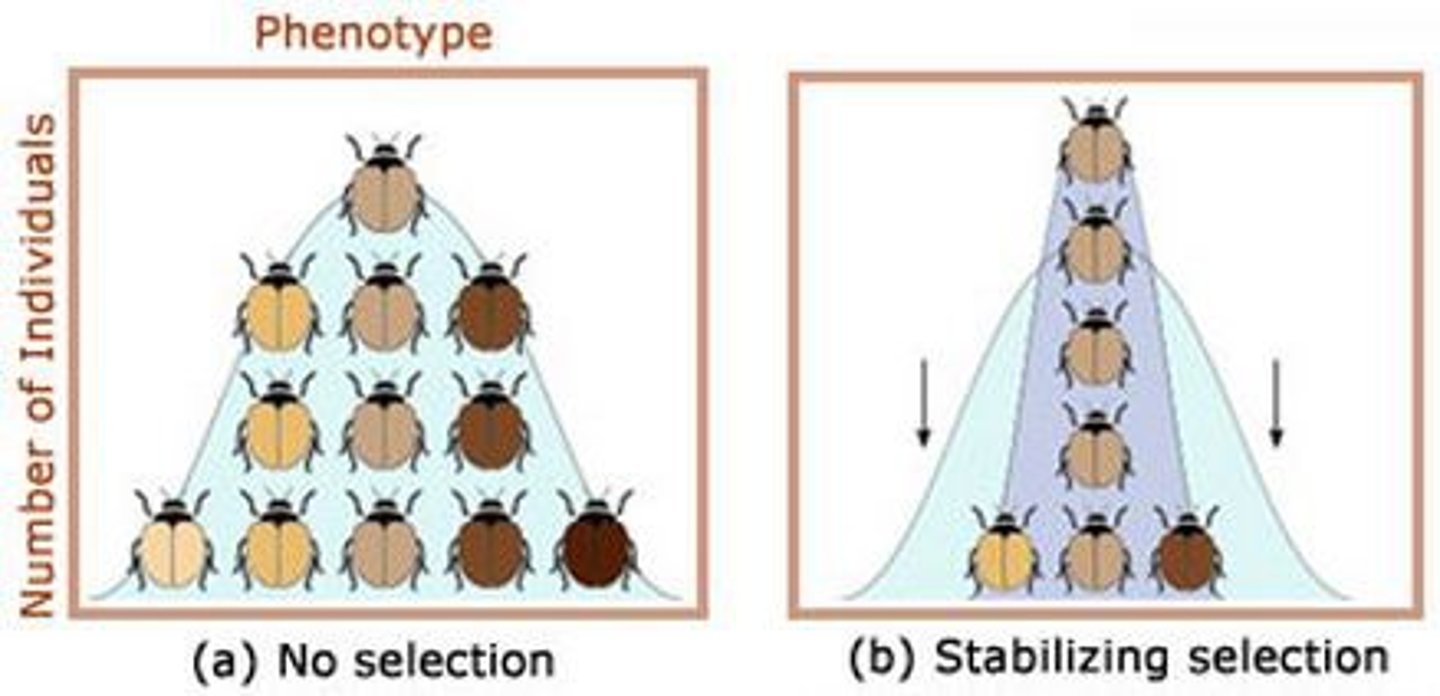
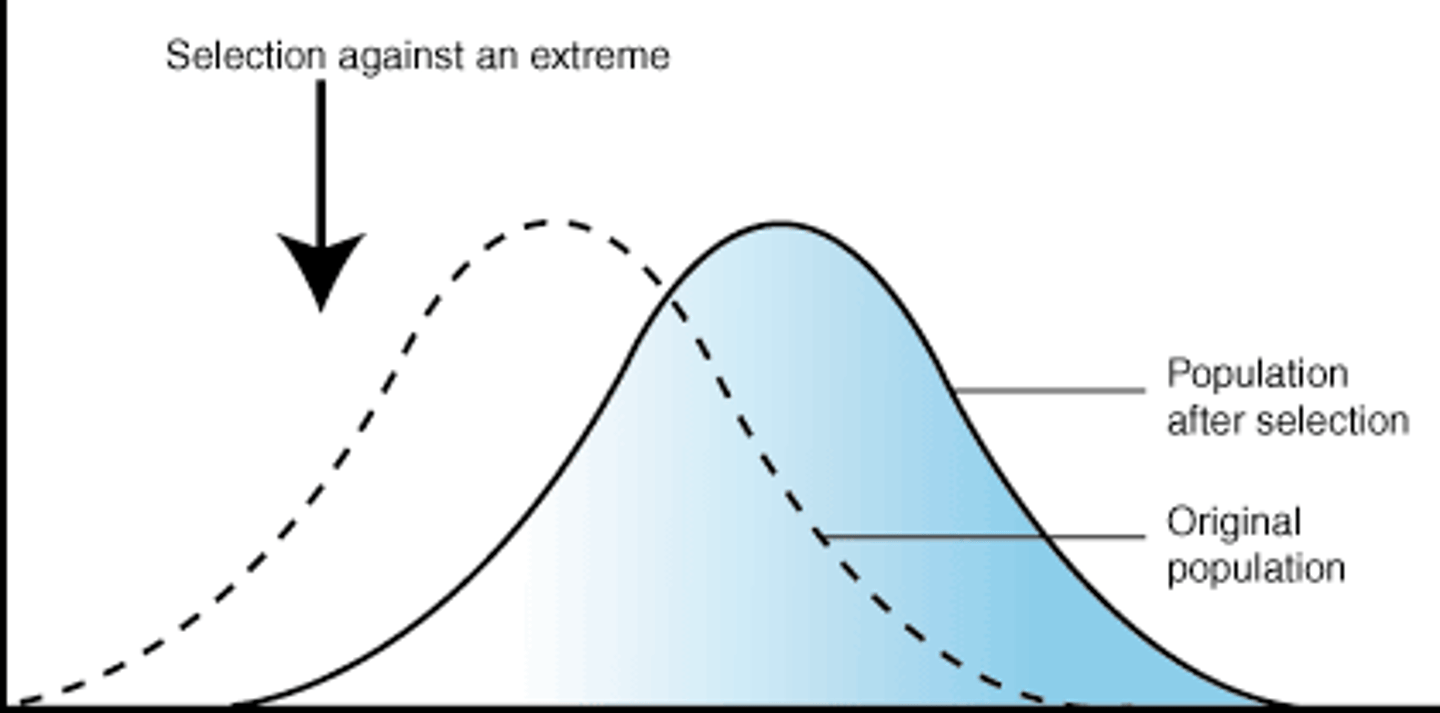
What is directional selection?
When an extreme phenotype is favored, the bell curve shifts in the direction of the extreme (moves left/right)
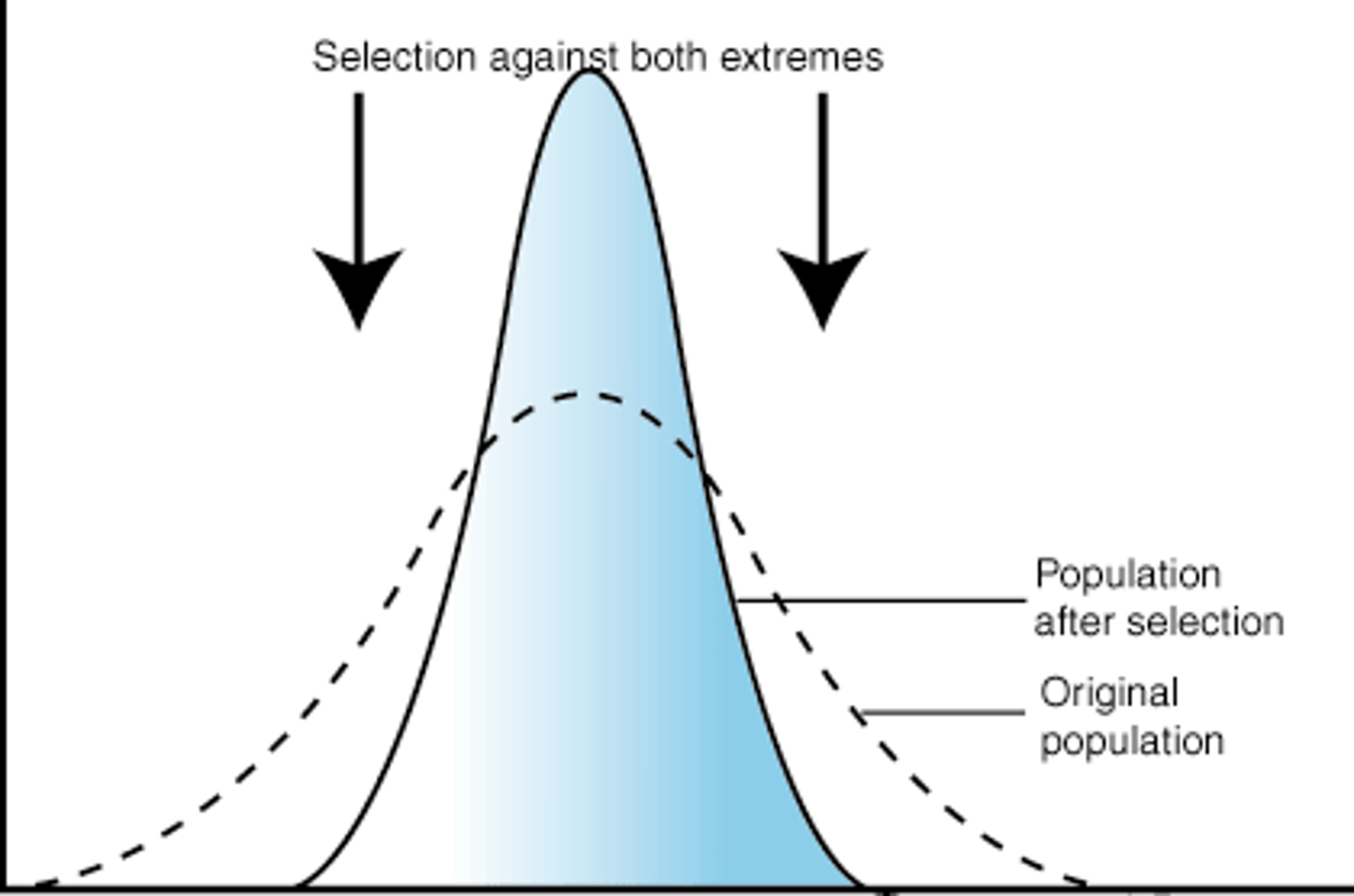
What is stabilizing selection?
When an intermediate phenotype is favored, the curve squishes more near the middle
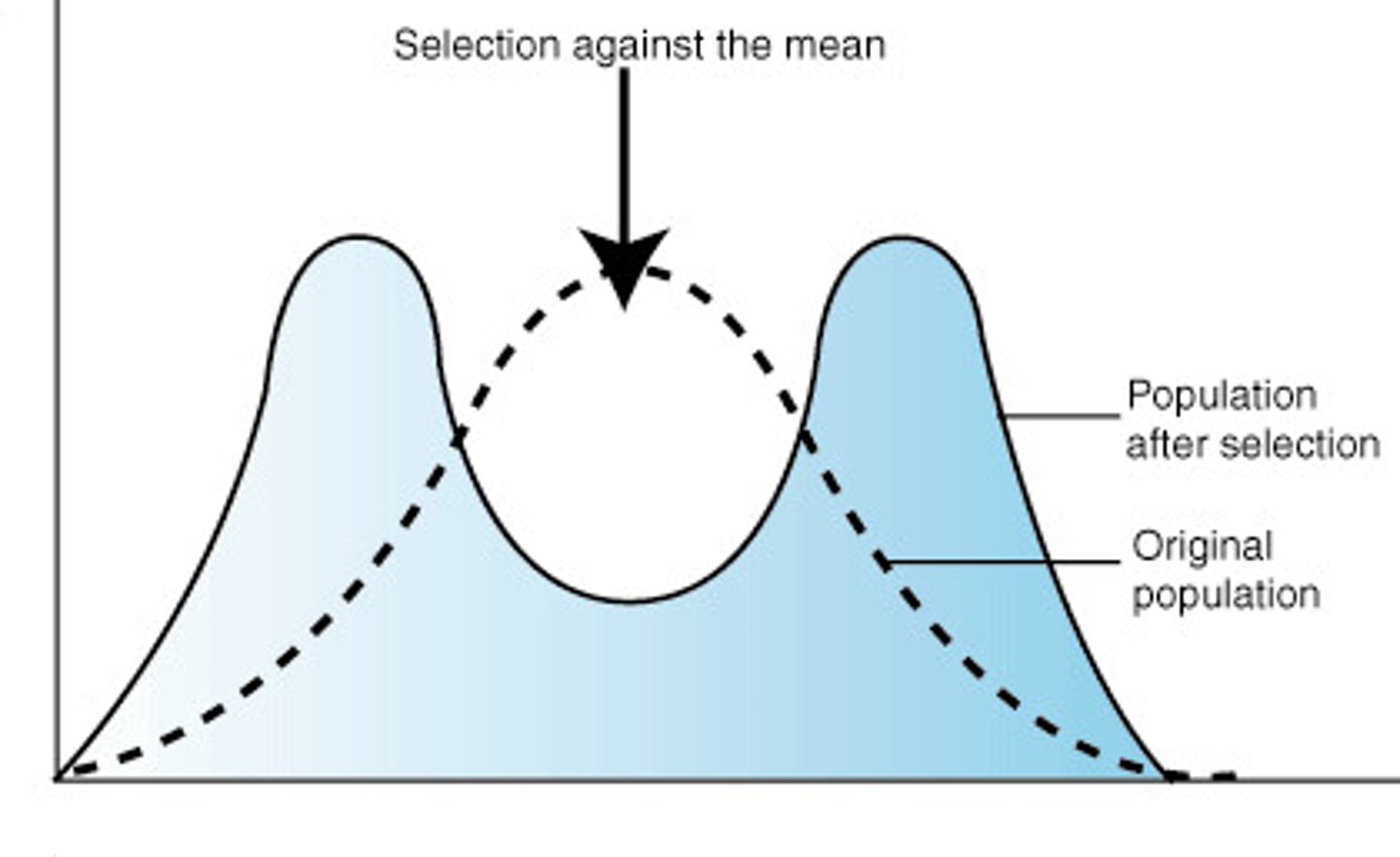
What is disruptive selection?
When two or more extreme phenotypes are favored over intermediate phenotype
What is microevolution?
A change in gene frequencies within a specific population
Define gene frequency and gene pool
Gene frequency - how often we see a gene in a population
Gene pool - the sum total of all alleles of all genes in a population
What is the equation to calculate the genotype and allele frequencies of a population?
Hardy-Weinberg
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
What does each part in the Hardy-Weinberg equation refer to?
p² = frequency of homozygous dominant individuals
2pq = frequency of heterozygous individuals (p+q=1)
q² = frequency of homozygous recessive individuals
p = frequency of dominant allele
q = frequency of recessive allele
What does the Hardy-Weinberg principle state?
That allele frequencies in a population should remain constant as long as no evolutionary change happens (practically impossible)
What is speciation?
The formation of a new species
What is a species?
A group of organisms that can reproduce AND produce fertile offspring.
What are isolation mechanisms?
Things that cause reproduction to never be attempted
List the four isolation mechanisms
Habitat isolation - organisms live in different habitats and never meet
Temporal isolation - organisms reproduce in different seasons, never breed at same time
Behavioral isolation - organisms have different mating rituals (calls, displays, dances, etc.)
Mechanical isolation - organisms have different reproductive parts that cannot fit the other
What is allopatric speciation?
When geographical barriers separate a population into different groups
What is sympatric speciation?
When populations become reproductively isolated without geographical barriers (VERY rare)
What are the two paces of speciation?
Phyletic gradualism - slow change but steady before and after a divergence
Punctuated equilibrium - periods of no change and then rapid change
What is classification?
The assignment of species to a hierarchy of categories
What are the categories from general to specific?
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
What are the three domains?
Bacteria (monera), Archaea (ancient bacteria), Eukarya (eukaryotes)
What are the five kingdoms?
Monera (bacteria), protista (algae, kelp), fungi (mushrooms), plantae, animalia