E155 What have we learned about humans in space?
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What aspect of space travel will likely be the most problematic during long-term space travel (e.g. going to Mars) and why?
Ionizing radiation because it damages DNA, proteins and lipids.
Were there any benefits to running on a treadmill for long periods (>200min/week) while in space?
Yes, those who ran on the treadmill for long periods of time experienced less atrophy in space
Maintains gastrocnemius muscle enzymes
Increased fatigue with weightlessness cannot be directly caused by a decline in muscle enzyme capacity
Which fiber types atrophy the most in space? Type I (slow oxidative) or type II (fast glycolytic)?
Type i fibers atrophy the most
What are the effects of microgravity on the heart and blood vessels?
Blood and fluids are pushed upward from legs to core - decrease in blood and fluid in the heat and blood vessels
Swelling in the face and head -> increase brain pressure, hearing loss, brain edema, and eye deformations
Heart becomes the shape of a round ball
What organ systems are affected by microgravity?
Cardiovascular - heart weakens and shrinks
Muscular
Skeletal - bone weakening/ osteoporosis
What were some of the greatest psychological challenges?
Fear and not knowing how your body will react
doing microgravity research on earth
bed rest, head down
psych = comparable to Antartica in winter; simulations
rodents for muscle studies = hindlimb suspension with no ground force (atrophy)
why does microgravity lead to a loss of muscle mass?
No weight bearing activity, reduces mechanical stress on muscles, muscles atrophy in space
less work = disuse = atrophy
mechanical stress → Ca2+ → different pathways → difference in muscle fibers
how do muscle fiber types change in microgravity? does abundance of fast glycolytic fibers increase or decrease?
shift toward type IIA glycolytic fibers from type I fibers (increase in type IIA FG fibers)
there is a decrease in slow oxidative fibers; those that still exist decrease in cross sectional area and diameter
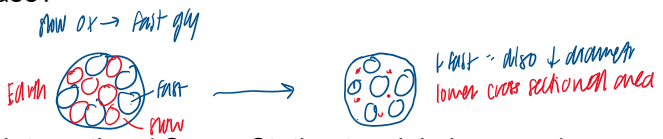
what are astronauts doing on the ISS to minimize muscle loss
exercising (treadmill exercises)
lots of exercise (at least 2 hours/day)
how does the distribution of bodily fluids change in space? why?
Blood flows upward, so fluid accumulates at the head and leaves the legs
fluid to heart and head with no gravity to pull it down
puffy face and chicken legs
what happens to the heart in space? why?
Shrinks and atrophy because the muscles are not used as much
Decrease in arterial pressure
Decrease in blood volume
more round shape, less work load and fluid (decrease CO)
increase blood flow affects hearing, eyes, and edema
what happens to blood vessels in space? why?
May lose some elasticity and responsiveness as they adapt to the lack of gravitational stress; atrophy
walls become thicker (especially in head and neck because of increased blood flow) → less elasticity, atrophy (smooth muscles)
what happens to balance and inner ears in space? why?
Shifts in inner ear fluid and fluid accumulation/pressure causes disrupted balance and sometimes hearing loss
Causes space motion sickness, includes nausea
what happens to skin? why?
Thinning of epidermis and losing elasticity because of degradation of collagen, dehydration, impaired healing
More susceptible to irritation and rashes
drier and ages faster because of radiation and less collagen
what happens to eyes in space?
Edema at the optic nerve can cause visual impairment and change in eye shape (flattening the back of the eye)
swelled optic nerve
space flight neurocular syndrome
optic nerve squished → blind
what happens to bone structure in space? why?
Decrease in bone density -> osteoporosis because of decrease in mech stress
Disrupted balance between osteoclast and osteoblast (osteoclast activity stays the same, but osteoblast decreases)
osteoclast = destroys boen
osteoblast = builds bone
what is a kidney stone? why are astronauts more prone to them while in space?
Kidney stones: salts and minerals that bind together in concentrated urine
Calcium stone, because of the osteoclast activity that releases Ca2+ into the urine
Increased formation in astronauts due to lower amounts of urine volume and higher Ca2+ excretion rate
There is an increase in Ca2+ in the urine due to bone reabsorption -> leads to a negative calcium balance in the body
how are astronauts trying to minimize bone loss? how long does it take to recover bone density after prolonged space travel?
Exercise to minimize bone loss; takes up to 3 years if ever
especially resistance training
Ca2+, VfD supplements, and meds
what are some examples of psych stresses that astronauts endure?
depression, isolation syndrome, home sickness, no privacy
what are some examples of cognitive tests that astronauts have to perform regularly while in space?
winscat = general psych eval
cognition tests = 10 tests
what are some examples of interventions that people are trying to address cognitive and psychological issues?
VR simulation, anti psychotic, flight history has an impact
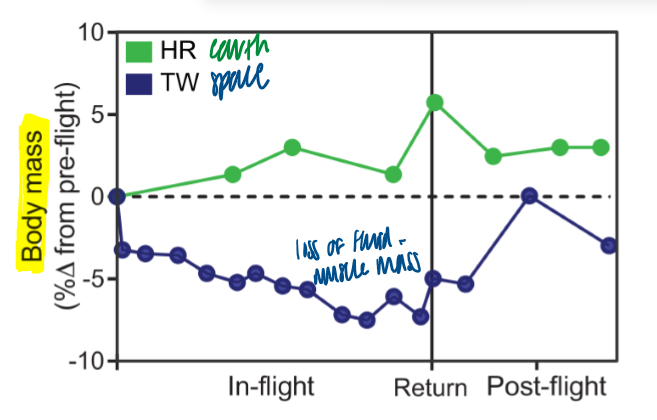
twins in space - body mass
significant loss of fluid and muscle mass
initial spike because of return to fluid
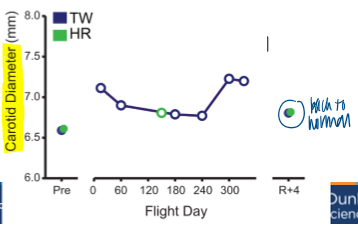
twins in space - carotid diameter
space heart recovered back to normal levels
carotid artery = delivering blood to brain
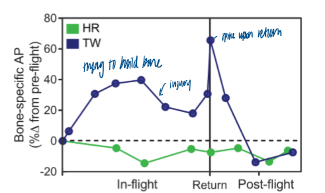
twins in space - bone AP
in space, trying to build bone then drops from injury to system (being in space)
increased AP = more bone building
spike upon return to earth
relatively similar values to norm
telomeres in space
telomeres get longer in space
reason unknown