RSM483 Lecture 1 + 2
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
How is real estate different from other markets?
Real estate is immobile and durable
Real estate markets are highly regulated and have heavy government involvement
Rules about mortgage terms and tax treatment
Real estate markets are dominated by amateur investors
relationship between interest rates and real estate returns?
As interest rates rise, returns on real estate increase
Why does Just running a regression not give you a home price
Correlation does not equal Causation
Just running a regression does not give you a home price → gives price on average
There may be other variables that impact home price
Real estate is difficult to value because
It is heterogeneous in terms of location and attributes
Views, crime, school quality
There are a lot of unobserved or poorly measured attributes
It is not heavily traded in the market
Not a ton of observations.
What are the 3 approaches to value real estate
1) Cost Approach
2) Income Approach
3) Comparables Approach
Cost Approach
Sum up all the costs to build it
If old home– thing about the cost of building an old-quality building today.
Add up the cost of acquiring all components of a replacement property
Why is it important that markets are competitive?
In competitive markets, economic profits = 0, cost = close to final price
When is Cost approach used best?
Most commonly used for new development of standardized properties in competitive markets
Works best in areas where land values and the cost of all attributes are easily observed and standard
Income Approach
Most commonly used for investment properties
Simple version: the sum of discounted cash flows associated with renting out the property forever
If net income is constant = (Net Income)/r
Implies r = “Cap Rate”= (Net Income) / (Purchase Price)
The simple version ignores risk and expected capital gains/losses
Good when considering use/productivity of asset – especially if hard to sell/no comparables.
Sensitive to interest rate used.
Certain businesses might use higher r’s because their value of future rental streams is lower, leading to lower valuations by income approac
Mostly good for commercial real estate – not homes.
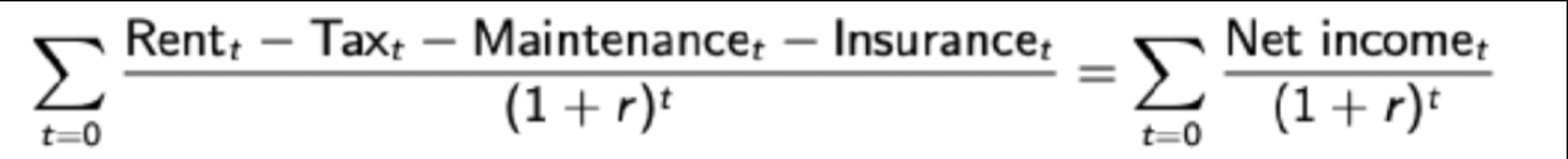
Comparables Approach
Most commonly used for home appraisals and by realtors
Look at recent sales of comparable homes nearby and then use adjustments as needed to the average for differences in home characteristics.
Good when lots of comparable properties and data
Repeat sales approach: when same building is selling again
Use last sale price and apply a home price index to update the price to current time period
Ex: old price x 15% growth in index = current price
Hedonic Pricing –
A more data-driven way to value any house based on any theoretical set of characteristics
Goal here is to find an efficient way to adjust the price of observed sales to account for differences in attributes of houses we hope to value
1) Determine the price of various housing attributes
2) Apply these prices to the house we are trying to value.
What did Rosen Agrue?
Rosen argued that housing price or rent differences must capture differences in a and α across homes, such that identical individuals are indifferent across homes.
Hedonic Price Methology

Using Log in Hedonics
Helps put everything in percents or percent changes
If P(a) = 0.07, a home with 1 more unit of a is has a price that is 7% higher, on average, holding other factors fixed.
Difficulties with Hedonic Pricing
Data may not include some a and α (marble countertops, nice view)
These could be correlated with attributes and amenities that are observed (coefficients estimated incorrectly: correlation # causation!)
Information is on the marginal value of attributes, and may not apply to large changes in attributes
Example: shadow price of 1 garage may not be same as 10 garage.