Coronary Artery Disease and Acute Coronary Syndrome
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Non-modifiable risk factors
Age
Sex
Family history/ genetics
Ethnicity
Modifiable
Elevated serum lipids
Hypertension
Smoking
Physical inactivity
Obesity
Nutrition
Comorbid Conditions
Angina
Clinical manifestation of ischemia
Results from imbalance of supply of blood to heart and O2 demand
Supply
Heart rate
Coronary Perfusion Pressure
Pressure that drives blood forward for coronary perfusion
O2 concentration
Coronary vessel diameter
Demand
Basal requirements
Heart rate
Preload/afterload
Force that stresses the cardiac muscle prior to contraction. This is the volume of blood that fills the heart from venous return
The amount of pressure the heart needs to exert to eject the blood to circulation
Contractility
Location of pain
May present differently in female pt and those with diabetes
PQRST
P - Precipitating events
What were you doing when it started?
Q- Quality of Pain
What does it feel like? Pressure/dull/sharp/ squeezing
R- Region
Where is it located? Can you point to it? Does it radiate?
S- Severity of pain
Scale of 0-10 how bad is it?
T - Timing
When did it start? Has it changed (better/ worse)? Have you had this before?
Stable Angina
Typically provoked by exertion or stress
Reversible
Last 5-10 minutes
Relieved by rest and NTG ( Nitroglycerin)
No change in frequency, duration, or precipitation factors in preceding 60 days
Associated with a stable atherosclerotic
Unstable angina
Occurs at rest or awakens the pt from sleep
Longer duration >15 minutes
Frequency and intensity of pain increases
Unpredictable Pattern
associated with rupture of a plaque, results in platelet aggregation, clot formation, and vasoconstriction
Stable Angina Tx
Modification of risk factors
Revascularization (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention, Coronary Artery Bypass Graft)
Medications
Antiplatelet
Asprin
Clopidogrel
Nitrates
SL NTG/Long acting
NTG patch
Make sure to remove old patches/ paste each evening and make sure to wear gloves when handling
Tolerance to long nitrates can develop and pt should have a nitrate free period
ACE/ ARBS, BB, CCB
Lipid Lowering medications
Medication teaching for NTG
Keep in original bottle
Protect from light
Replace every 6 months
Avoid storing in temp extremes
Take 1 if pain not relieved in 5 mins, seek further evaluation and can take up for 3 times. Should tingle under tongue and keep with you at all times
Ischemia
ST depression
Decreased perfusion
Injury
ST segment elevation
Will resolve in hours to days with development of inverted T waves or pathologic Q waves if reperfusion is not done quickly. Inverted T waves may resolve, Q waves will always be here if they develop
Damage to cells causing elevated troponin
Troponin
Released by damaged heart muscle, increased with more damage - heart specific
CK-MB
Creatine kinase-MB distinguishes between heart and skeletal muscle damage (CK level)
Chest pain - What to do
Assess Client including vital signs
Administer NTG as ordered
Notify provider if pain persists ( or if no new onsent/ no NTG order)
Obtain 12 lead EKG stat if pain unrelieved or changed
Code chart to client’s bedside
Common medication orders
NTG 0.4 mg sublingual q 5 min x 3 dpses prn if systolic BP>100
If no chest pain relief morphine 2 mg IV q 5 min prn to a max of 10mg over 2 hrs
STEMI
Caused by occlusive thrombus
ST elevation in leads facing infarct
Elevation of cardiac markers
Development of pathologic Q wave if not treated quicklu
TX
Urgent PCI or antithrombolytics
Goal is to revascularize within 90 mins
NON-STEMI
Caused by non-occlusive thrombus
No ST elevation
May see ST depression or T wave inversion
Elevation of cardiac markers
Tx
Cardiac cath within 12-72 hours Tx as needed
Complications of Acute MI
Dysrhythmias
Heart failure
Cardiogenic Shock
Pericarditis
LV wall aneurysm
Papillary Muscle Dysfunction or rupture
Ventricular- Septal Wall Rupture
LV Free wall rupture
Tx for MI
Fibrinolytics - STEMI only
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
With or without stent
Heparin or IIB/IIA inhibitors (eptifibatide)
Coronary artery bypass graft
Fibrinolytc therapy
Only for STEMI MI and no access to PCI
Clot busters
Tenecteplase, alteplase; give IV
Indications: CP <12 hours, STEMI
Contraindications
Severe HTN
H/O ICH
Intracranial surgery <2 months
Ischemic stroke < 2 months
Aortic dissection
Brain tumor
Active bleeding
Markers of reperfusion
Significant relief of pain
Reduction of ST segment elevation
Abrupt increase in cardiac enzymes
Rescue PCI if thrmobyltics fail
Major complication is bleeding
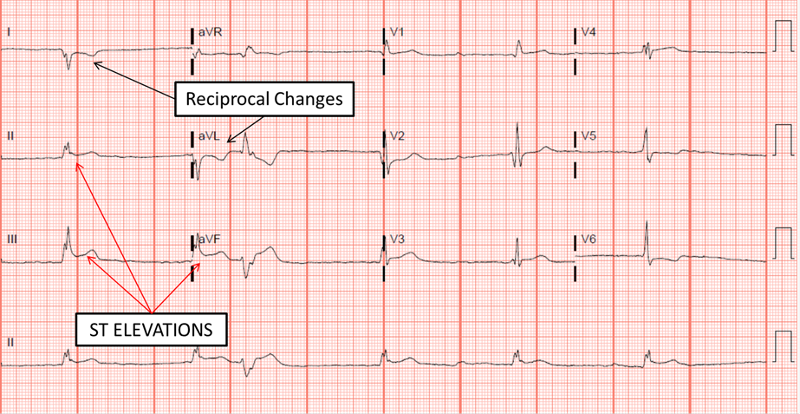
Reciprocal changes
ST elevation in one sets of lead are accompanied by ST- segment depressions in the opposite (reciprocal) leads
Contiguous leads
ECG leads that are anatomically next to each other and reprsent the general area of the heart
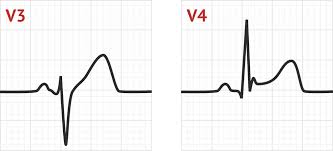
ST elevation
STEMI
ST depression
Myocardial ischemia
NON STEMI
LDL
Delivers cholesterol
HDL
Removes cholesterol from the bloodstream
“Good cholesterol”
MI S/S
Heart palpitations
Chest pain that radiates to left arm
SOB
Nausea
Ashy, clammy, and cool skin
Initial increase in HR and BP followed by decrease
Crackles in lungs
Jugular vein distension
Fever
Weakness
Anxiety
Statins
Thought to be associated with plaque stabilization, showed decrease in major adverse cardiac event post MI
Medications
Morphine
NTG
Antiplatelets
Beta Blockers
Ace inhibitors
Stool softeners
PCI pre- procedure
Baseline assessment
Allergies
Shellfish
Contrast dye
Precautions with metformin
NPO
Informed Consent
Teaching
Access radial versus femoral artery
Goal is to reopen artery within 90 minutes of presentation
Cardiac Catheterization
Look at arteries and figure out what is needed
PCI
Angioplasty
Treating blockages
PCI - Post Procedure
V/S q15 min for 1 hours, then q30 for 1 hour then every hour
Assess pain
May still have some chest pain after
Monitor puncture site/compression device
Circulation to extremity
Hydration
Bedrest 2-8 hours, extremity straight
Caution with bending after BR
Monitor ECG
For improving ST elevation and decreasing cardiac enzymes
Anticoagulation - ASA/ Clopidogrel
Low-dose aspirin and antiplatelet 1-12 months depending on type of stent
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) - Revascularization Surgery
Indications
failed medical management
Continued chest pain after PCI
Presence of 3 vessel disease
Disease of the left main coronary artery
CABG Post-op nursing care
V/S
Heart rhythm
Surgical sites
Chest tube output
Pain
Cognitive status
Fluid volume management
Pulmonary toileting
Early ambulation
Sternal precautions
Usually ICU for 24-48 hours
Hospitalized 3-5 days
Sternal Precautions
No tub baths x 4-6 weeks
Do not use arms to push up from chair
Do not lift > 4-10lbs for 4-6 weeks
Do not push/pull
Avoid driving x 4-6 weeks
Discharge planning
Pt and family teaching
Medications
Do not stop antiplatelets untill instructed by provider
Sternal precautions
Exercise
Resumption of sexual activity
Do not take erectile dysfunction drugs ex sildenafil with nitrates for a risk of hypotension
Coping with anxiety
Cardiac rehabilitation
Reduction of risk factors