Septal Closure Devices
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
A congenital deficiency of the interatrial septum leading to an open communication between the right atrium (RA) and left atrium (LA).
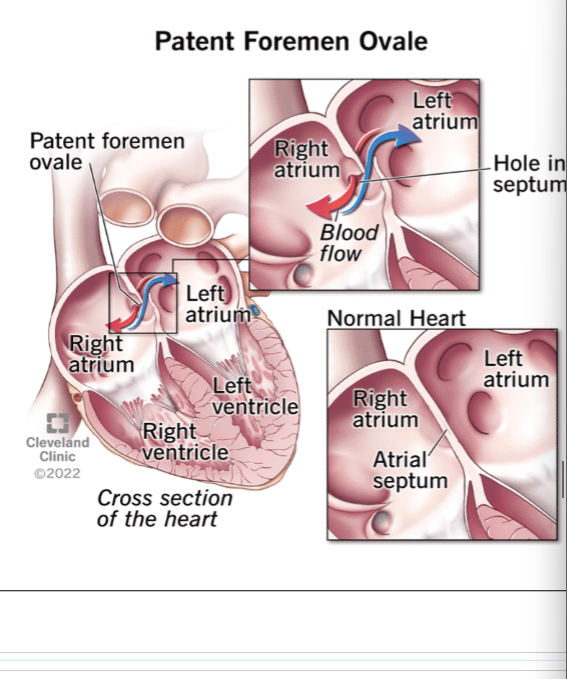
Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) is created by the
Oval fossa
Direction of shunt for fetal circulation
R>L
What is the name of the hole that allows blood to pass between the atrias before birth
Oval fossa
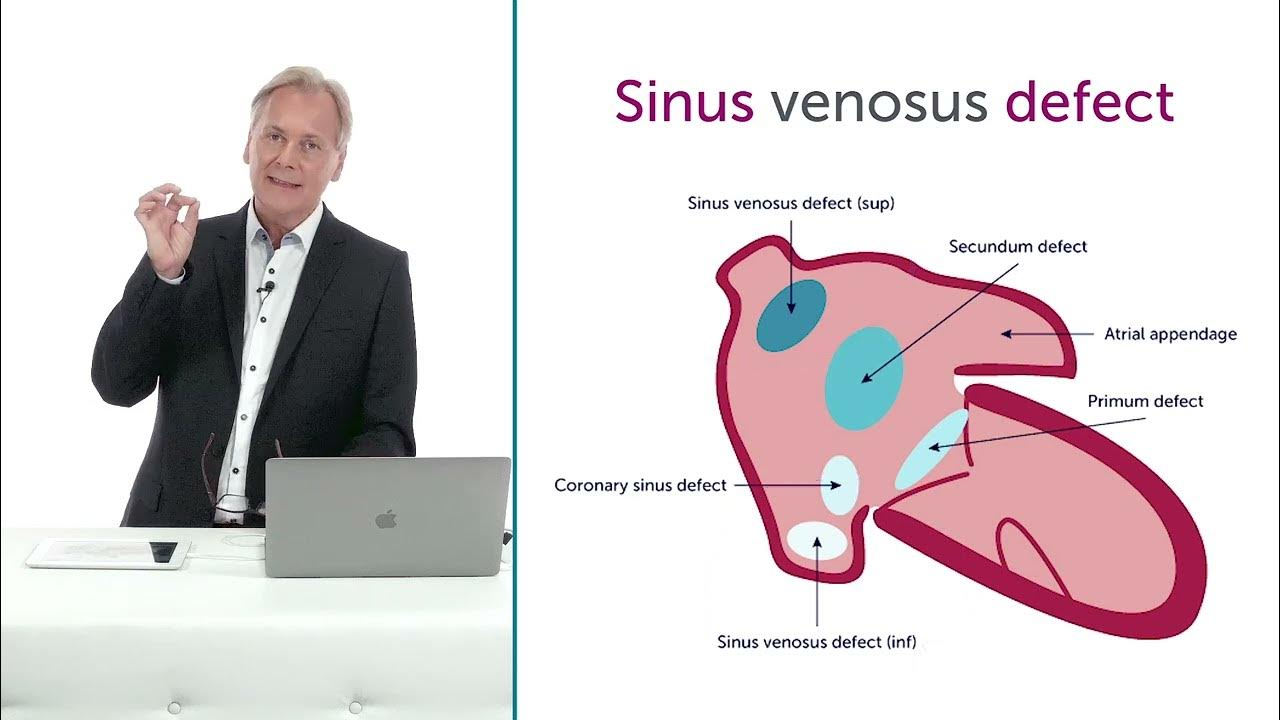
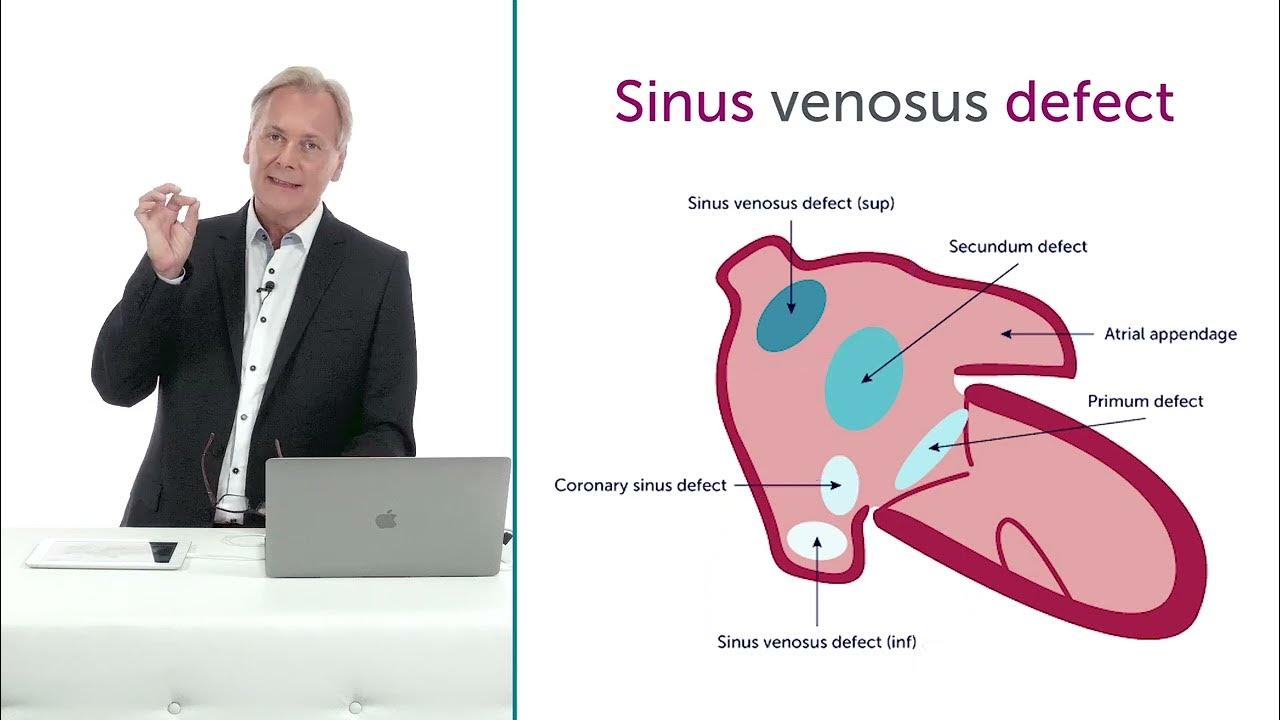
Describe a ostium secundum ASD
gap in the middle, inadequate formation of the septum secundum so that it doesnt completely cover the ostium secundum
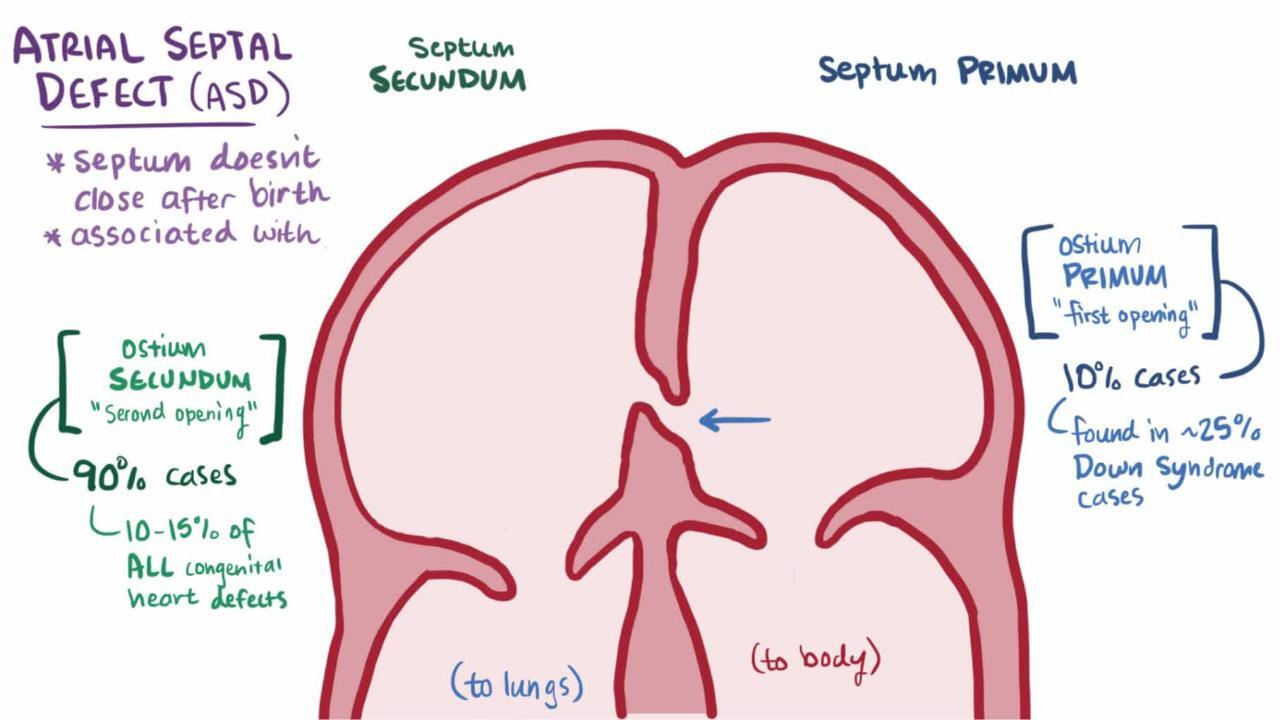
Most common type of ASD
Ostium Secundum
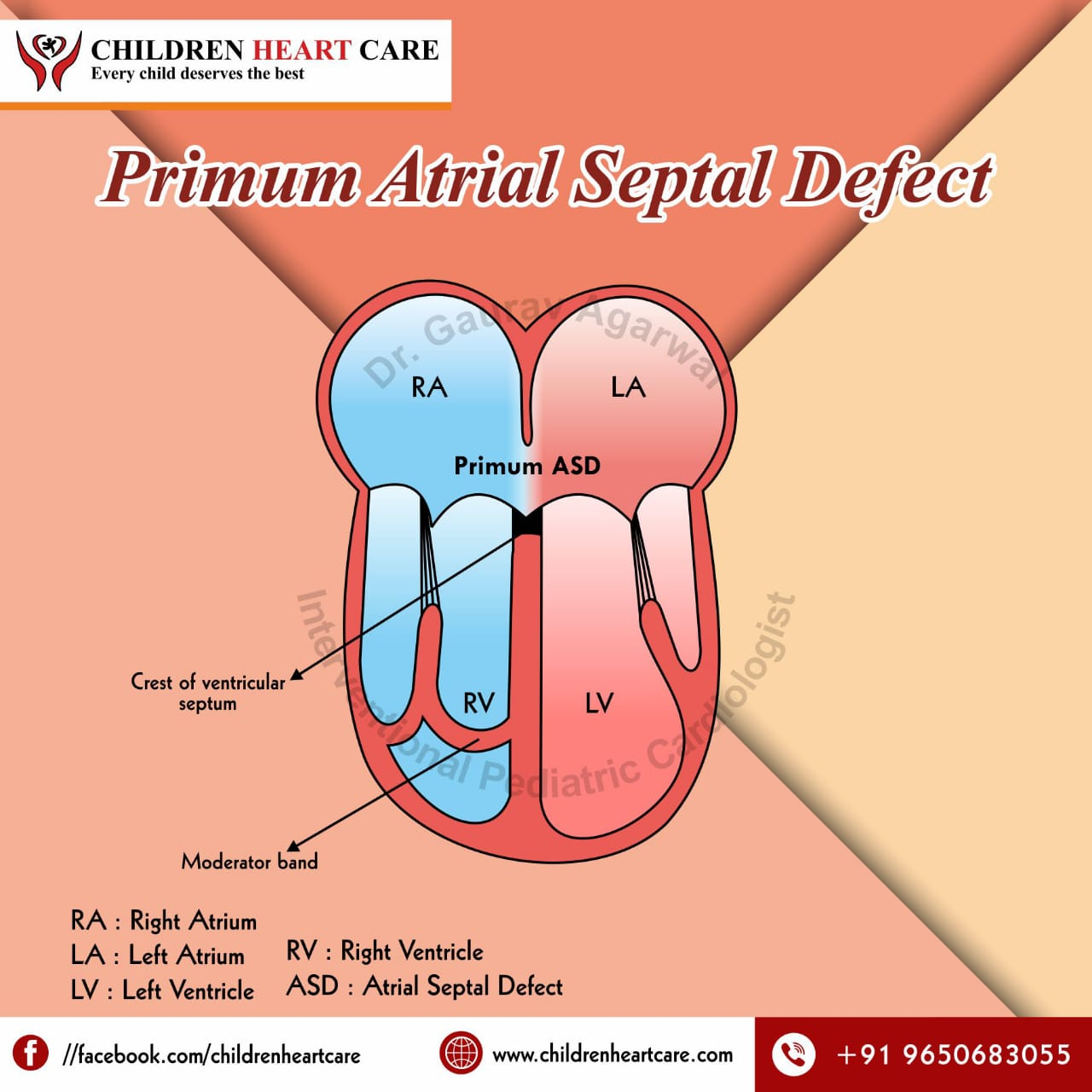
Where is the whole in ostium primum
ASD that occurs near the bottom part of the septum, close to valves
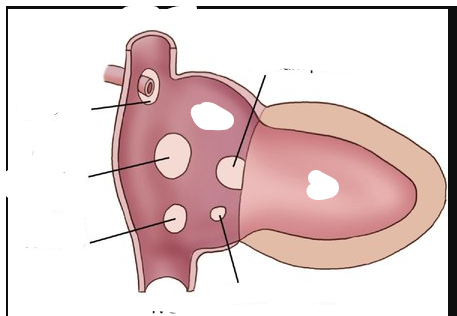
Identify each of these ASD
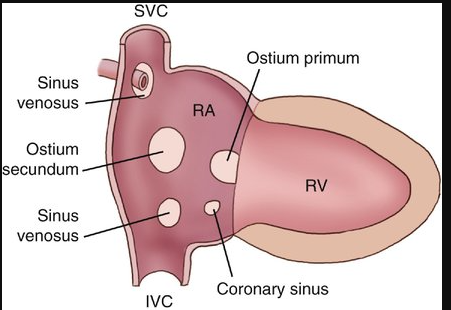
Describe Sinus Venosus and where it is located
A rare type of ASD located near the entrance of the superior vena cava into the right atrium. RARELY at entry of the IVC into RA
When theres a hole in the septum it disrupts the system in 3 main ways
disrupts the pressure gradient from L (02) to R (<02)
Overload the right
mix oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Coronary Sinus Defect
Another rare type, involving the vein that drains the hearts blood
What occurs in a Left-to-Right Shunt and why is it bad
A condition where blood flows from the left atrium to the right atrium, leading to volume overload of the right heart.
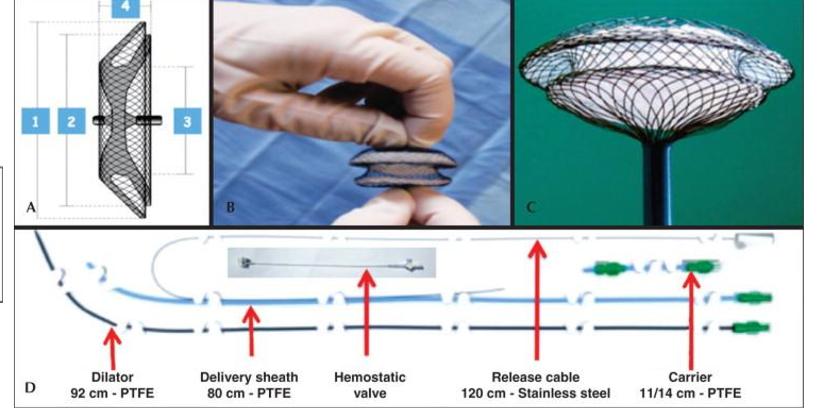
Amplatzer Septal Occluder is made of
A device used for the percutaneous closure of ASDs, made of a nitinol wire mesh with polyester fabric.
What is special about Gore HELEX Septal Occluder
A device designed for ASD closure that features independent discs and petals for better conformability.
Complications of ASD Closure any 2
persistent dysrhythmia or potential lethal intraprocedural arrhythmia requiring cardioversion
death
cardiac or respiratory arrest
device erosion
device embolization
2 most common signs of right sided heart failure
peripheral edema
pedal edema
common symptoms of a large symptomatic ASD
right sided heart failure
pulmonary HTN
^ CO
fluid build up
What is eisenmenger syndrome and why is it a contraindication for a ASD closure
L 2 R shunt reverse to R 2 L due to prolonged pressure overload. closing ASD could worsen p’s condition by trapping the blood flow and ^ pressure in the lungs
what does TEE and TTE stand for
Transesophageal Echocardiography
Transthoracic echocardiography
Which has higher quality image
TEE
or
TTE
TEE
what does ICE stand for
Intra-cardiac echocardiography
Key indication for PFO closure
cryptogenic stroke, stroke prevention RESPECT, REDUCE, CLOSE, and DEFENSE-PFO trials show reduced risk of recurrent stroke in these pt’s
key indication for ASD closure
Significant left to right shunt
significant RH enlargement due to volume overload
R2L shunt causing hypoxemia & or embolism
secundum defect greater than 5mm
Contraindications for ASD closure
small defect
no RV volume overload
describe the anatomy of a PFO
tunnel like passageway between the septum primum and septum secundum
describe the anatomy of a ASD
hole in the atrial septum caused by congenital failure in overlap between the septum primum and secundum

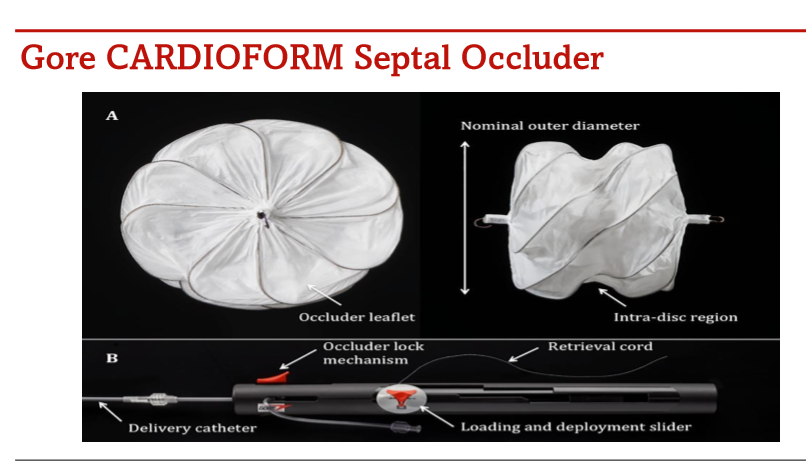
Name these devices
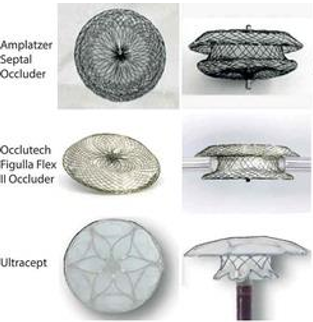

name these devices

which is the ASD
which is the PFO device
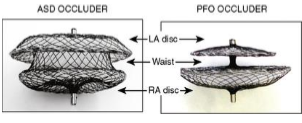

pfo or ASD?
asd
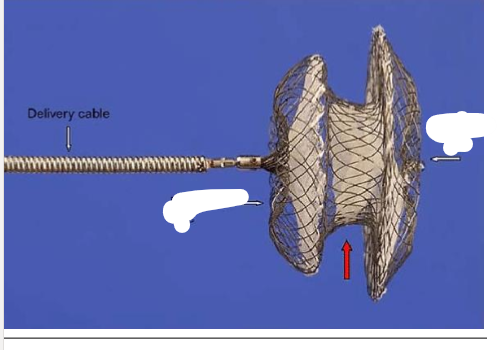
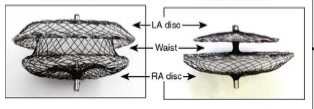
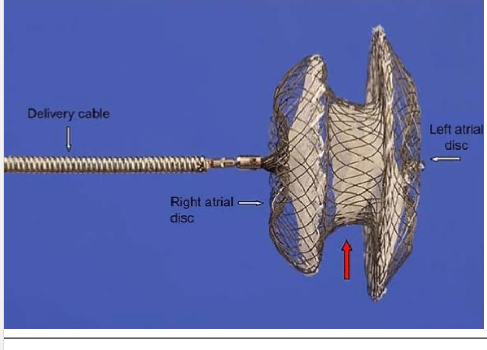
What side is this disc supposed to go on
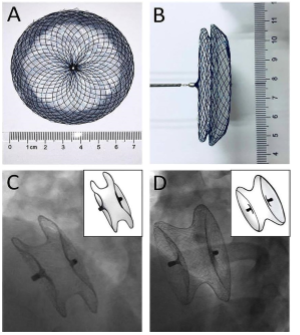
What device is this
Amplatz septal occluder
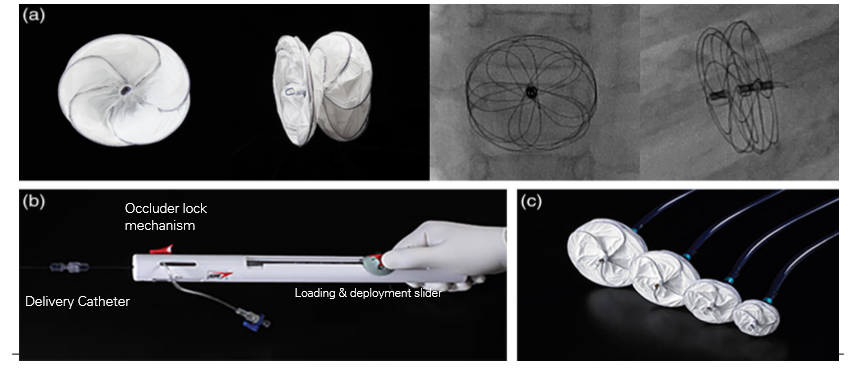
What device is this
Gore HELEX Septal Occluder
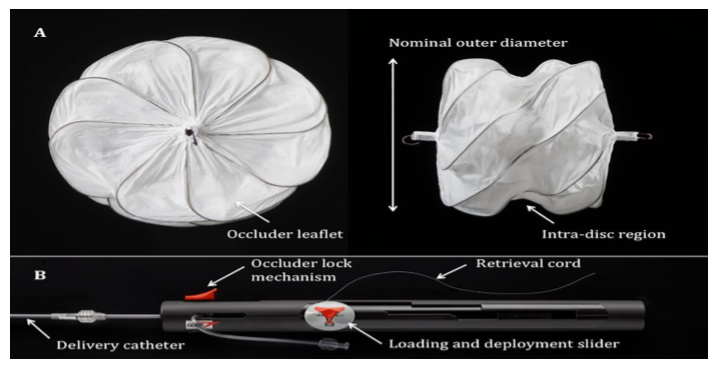
What device is this