Chapter 7: Cellular Respiration
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Transfer of Energy Through the Ecosystem
energy flows in as sunlight
leaves as heat
fermentation
partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2
aerobic respiration
consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP
anaerobic respiration
similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2
Stage 1 of Cellular Respiration
glycolysis - cytoplasm
Stage 2 of Cellular Respiration
pyruvate oxidation - mitchondria
Stage 3 of Cellular Respiration
citric acid cycle - mitochondria
Stage 4 of Cellular Respiration
oxidative phosphorylation - mitcochondria
Cellular Respiration - Chemical Formula
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat)
exergonic process
oxidative breakdown of Glucose
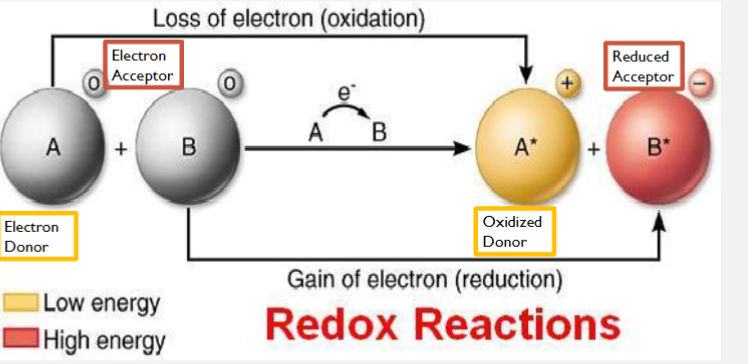
oxidation (OIL)
loss of electron
reduction (RIG)
addition of electrons
Redox Reactions
some do not transfer electrons but change the electron sharing in covalent bonds
Decomposition of Glucose
driven by redox reactions
fuel (glucose) = oxidized
O2 = reduced
abundance of hydrogen = source of high energy electrons
Oxidation of Glucose
NAD+ & FAD electron carriers
energy stored in glucose → harnessed in electron carriers → glucose oxidized into carbon dioxide
Reduction of Oxygen → Water
final electron acceptor in cellular respiration
oxidative phosphorylation
powered by redox reactions
the process that generate almost 90% of ATP
substrate-level phosphorylation
a smaller amount of ATP is formed in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle by…
Gylcolysis
2 sages:
glucose is split into 2 3-C molecules (need energy)
Atom rearrangements generate pyruvate (generates stored chemical E)
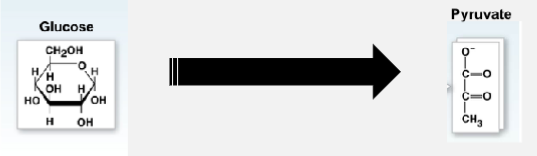
Phase 1: Energy-Consuming Reactions
xxxxxx
Phase 2: Splitting Glucose
xxxx
Phase 3: Energy-Producing Reactions
xxxxx
multienzyme complex catalyzed 3 reactions
oxidation of pyruvate and release of Co2
reduction of NAD+ to NADH
Combination of the remaining two-carbon and fragments and coenzyme A to from acetyl CoA