ib econ - 2.7: the role of governments in microeconomics
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/microeconomics/2-7-role-of-government-in-microeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
why does the government intervene in markets?
because it wants to influence market outcomes in order to:
earn government revenue
support firms
support household on low incomes
influence the level of production or consumption
correct market failures
promote equity
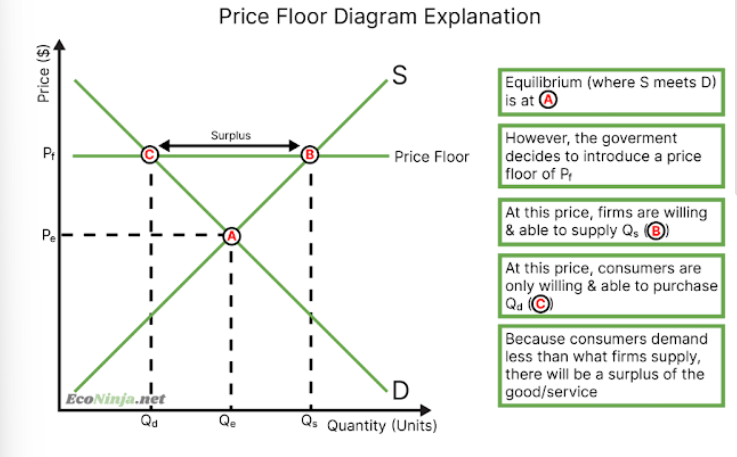
what is a price floor?
minimum prices set by the government when (often goods and services like labour). equilibrium price is below the set price, leading to a surplus of the good or service
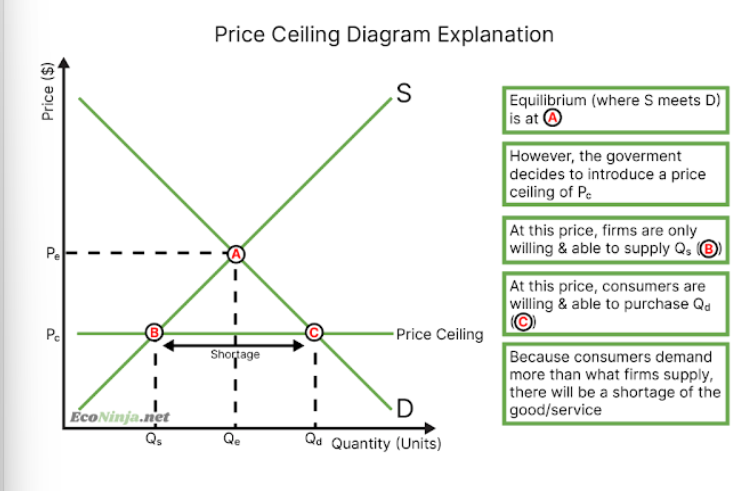
what is a price ceiling?
maximum prices set by the government (often goods and services like housing rent). equilibrium price is above the set price, leading to a shortage of the good or service
draw a price floor diagram
draw a price ceiling diagram
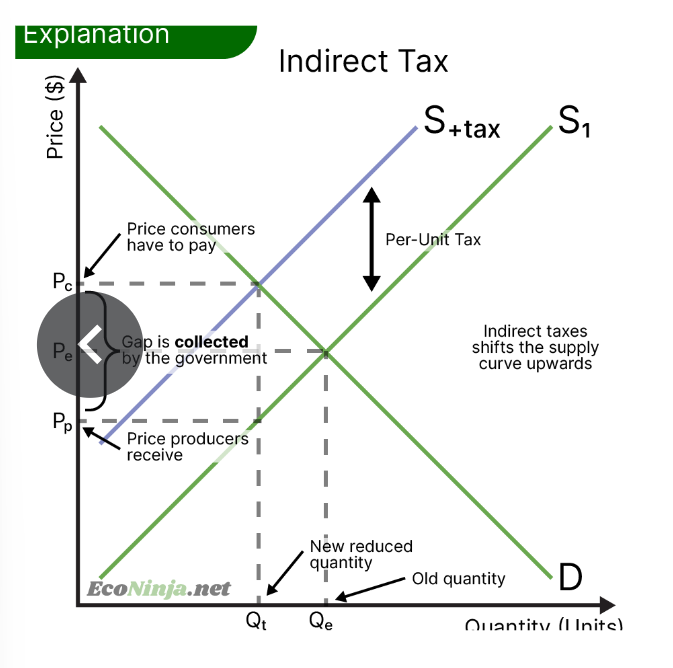
what is an indirect tax?
taxes on consumption rather than on income- imposed on the producer of goods/services. make goods and services more effective.
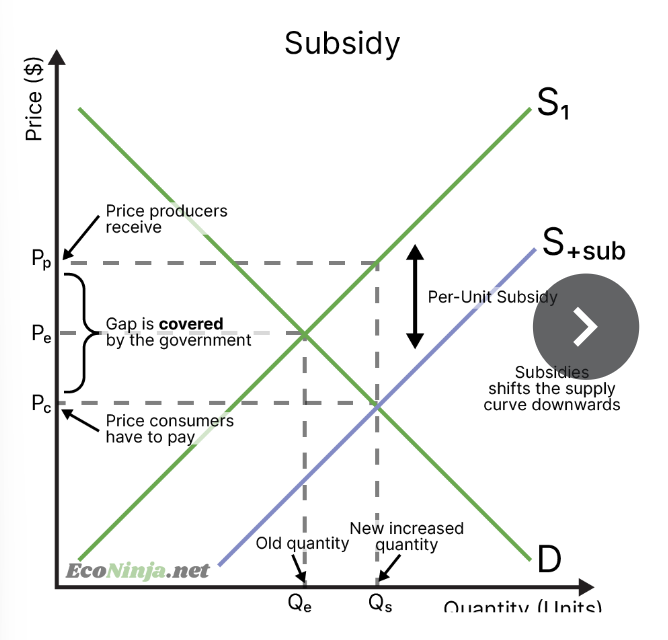
what is a subsidy?
forms of monetary governmental assistance for firms or an industry. the government may pay firms to produce a certain product or encourage healthier alternatives. subsidies make goods and services cheaper.
draw an indirect tax diagram
draw a subsidy diagram
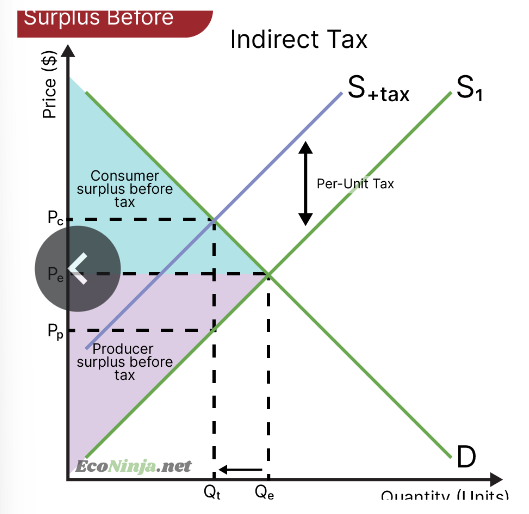
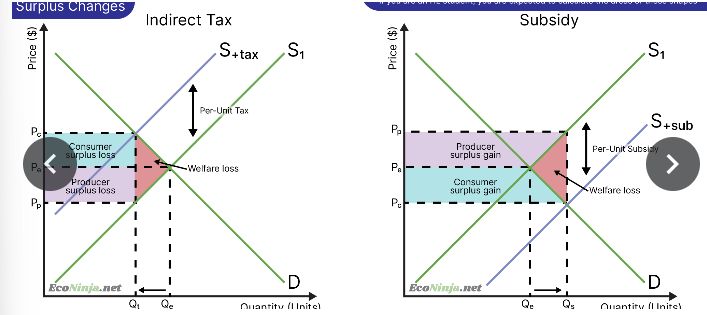
draw a diagram showing producer and consumer surplus after an indirect tax is imposed
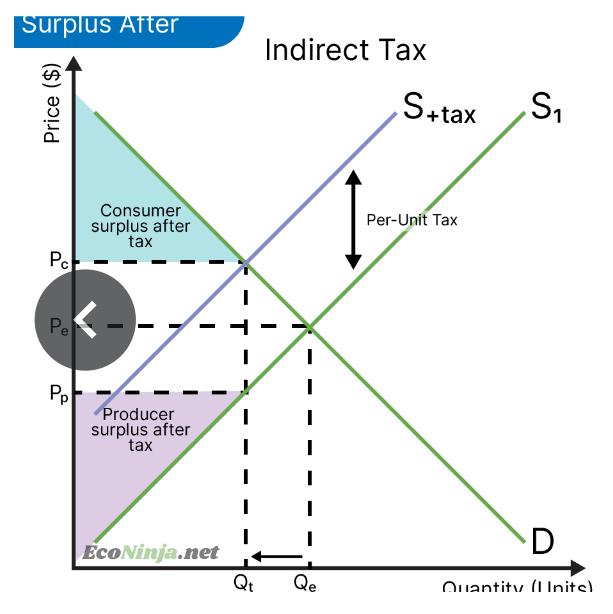
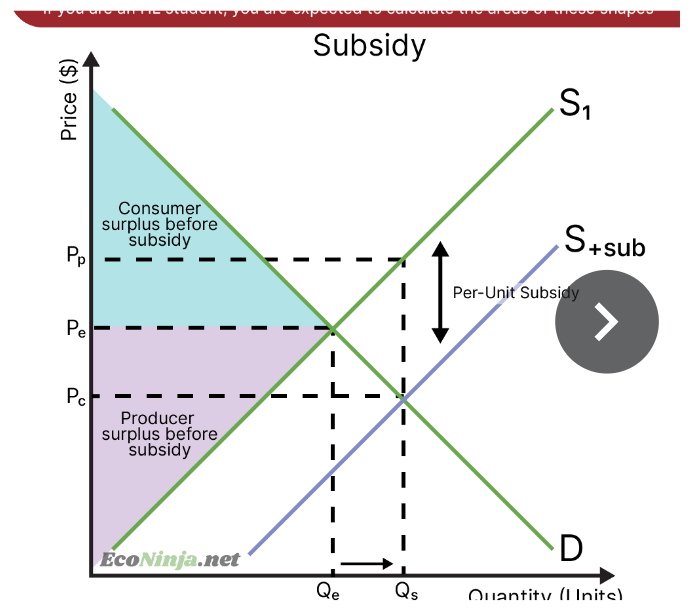
draw a diagram showing consumer and producer surplus after a subsidy is imposed
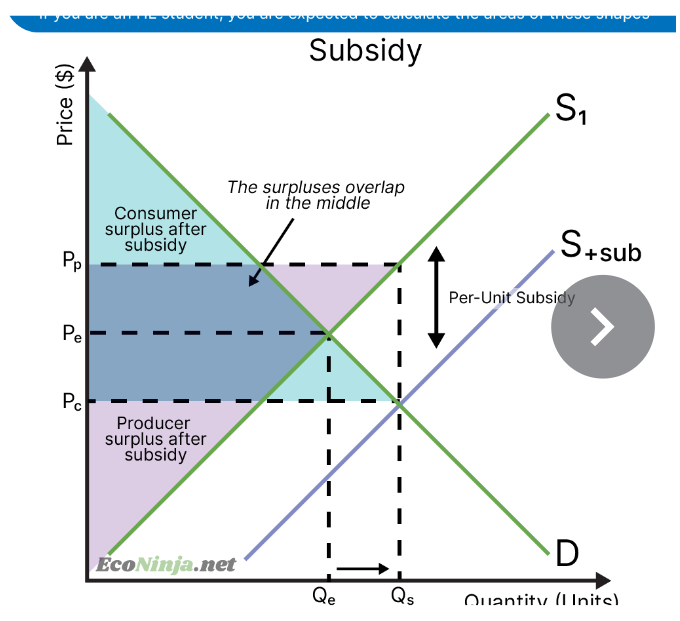
draw diagrams showing the welfare loss caused by the imposition of an indirect tax and a subsidy respectively
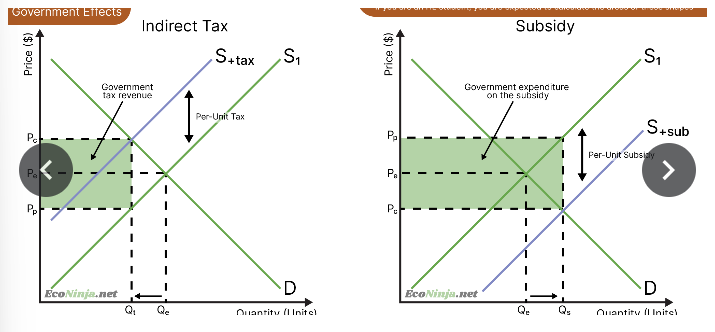
draw diagrams showing the effects on the government of the imposition of an indirect tax or subsidy
why might governments decide to directly provide services?
reduces reliance on the private sector if services may not be supplied without the government. (for example, libraries wouldn’t exist if the government didn’t provide them)
what is command and control regulation and legislation?
banning or restricting some products by law instead of letting private entities figure it out, allowing easy intervention.
what are the intended positive consequences of any government intervention?
usually promotes general economic wellbeing’
can maximise social welfare as it reduces negative externalities and promotes positive ones
however, government intervention is not always successful, leading to government failure
what are the consequences of price ceilings?
on markets: prices will be lower than in a free market, but a shortage of supply will arise
on stakeholders: consumer surplus increases, but producer surplus decreases and the government may have to supply the product itself to decrease the shortage
what are the consequences of price floors?
on markets: price will be higher than in a free market, and a surplus of supply will arise.
on stakeholders: consumer surplus decreases, but producer surplus increases. governments may have to buy the product to decrease the surplus
what are the consequences of indirect taxation?
on markets: prices will be higher than in the free market, the quantity demanded will decrease
on stakeholders: consumer and producer surplus decreases, but the government increases its tax revenue
what are the consequences of subsidies?
on markets: the price will be lower than in the free market, but the quantity demanded will increase
on stakeholders: consumer and producer surplus increases, but governments have to spend more to finance the subsidy