Automotive Final Corrections
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What does an illuminated engine oil warning light on the dashboard indicate if the engine oil is full?
a. The oil is too hot.
b. The oil pressure is too low.
c. The oil pressure switch is stuck open.
d. The oil pressure relief valve is stuck closed.
If your oil light is on but the oil level is full, it indicates b. The oil pressure is too low, meaning the engine isn't getting proper lubrication, which requires you to stop the engine immediately, as potential causes include a failing oil pump, clogged filter, or faulty sensor, not just low oil.
Light's Purpose: The red oil can light signals a serious pressure problem, not just a low level.
What should the oil pan and valve cover gaskets) be checked for?
a. color
b. leaks
c. hardness
d. corrosion
The correct option is b. leaks
Oil pan and valve cover gaskets should primarily be checked for leaks, which are the most common sign of failure. Gaskets seal the mating surfaces between engine components to prevent oil from escaping, and any seepage or dripping indicates a problem.
When installing a valve cover gasket, what should be done to prevent leaks at uneven surfaces?
a. Apply silicone/gasket marker
b. Apply wheel bearing grease
c. grind down the uneven surfaces
d. Apply spray glue
The correct option is a. Apply silicone/gasket marker (also known as RTV sealant or gasket sealer) at specific points.
Silicone sealant (RTV) is used at corners or seams (such as where a surface transitions from a flat edge to a half-moon shape) that may have slight irregularities or uneven surfaces where the main gasket material might not fully seal.
The primary cause for leaks at uneven surfaces, especially with stamped steel covers, is a warped cover, so an ideal solution is to replace the cover with a less-prone-to-distortion cast aluminum one or attempt to flatten the old one. However, among the provided options, applying a sealant is the correct procedure to address minor imperfections and prevent leaks.
Most modern rubber gaskets are designed to be installed dry, with sealant only applied to specific areas recommended by the manufacturer, as applying too much can cause other issues.
Prior to pressure testing a cooling system for leaks, what should the technician do before removing the cooling system pressure cap?
a. Check the color of the coolant and compare to factory specs.
b. check the coolant for the correct anti-freeze/water mixture.
c. Squeeze the top radiator hose to check for pressure.
d. check the level of the fluid in the coolant reservoir.
The correct option is c. Squeeze the top radiator hose to check for pressure.
Before opening the cooling system pressure cap, a technician should squeeze the top radiator hose to check for pressure.
The primary reason for this step is safety. The cooling system operates under pressure when the engine is warm, and removing the cap while pressurized can cause hot coolant to spray out, leading to severe burns.
Squeezing the hose helps confirm if the system is still pressurized. A soft, easily compressible hose indicates little to no pressure, making it safer to remove the cap.
If pressure is present, the technician must wait until the system is cool and pressure has vented before proceeding with cap removal and the subsequent pressure test.
Before removing a serpentine belt, the technician should do the following...
a. Look up or draw the belt routing/map.
b. Loosen belt tensioner.
c. Align alternator pulley.
d. look up the serpentine belt torque specifications.
The correct option is a. Look up or draw the belt routing/map.
Before removing the serpentine belt, a technician should look up or draw the belt routing/map to ensure the new belt is installed correctly. The serpentine belt often follows a complex path around multiple pulleys (alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, water pump, idler pulleys, and the crankshaft), and having a diagram prevents misrouting, which can cause serious problems. Many vehicles have a diagram on a sticker in the engine compartment or in the owner's manual; taking a picture of this diagram with a phone also serves the same purpose.
Which of the following is the preferred method of checking the wear on a newer-style serpentine belt?
a. Use a belt tension gauge.
b. Visually check for wear.
c. Use a serpentine belt wear gauge.
d. Twist the belt ¼ turn and check for tightness.
The correct option is c. Use a serpentine belt wear gauge.
Modern serpentine belts, made of EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber, do not crack as readily as older belts, making traditional visual inspection less effective for detecting wear.
A serpentine belt wear gauge is specifically designed to measure the depth and profile of the grooves on the belt's ribbed side, providing an accurate assessment of material loss due to wear. The gauge will sit flush with the top of the ribs if the belt is worn out.
When replacing an engines thermostat, you must…?
a. replace the thermostat seal and/or gasket
b. reuse the thermostat seal and/or gasket.
c. apply silicone/gasket maker to the gasket.
d. Replace the engine water pump at the same time.
When replacing an engine thermostat, you must (a) replace the thermostat seal and/or gasket, as reusing an old, compressed gasket risks coolant leaks, and you should clean surfaces thoroughly; while you might use a thin bead of silicone for some older systems if specified, it's often unnecessary and can cause issues if applied improperly, and replacing the water pump isn't always required unless it's failing.

According to the maintenance chart, at which interval is it recommended for the vehicle to have the engine oil and filter changed?
a. 7,500 miles.
b. 3,000 miles.
c. 10,000 miles.
d. 5,000 miles.
Subtract the amounts, of 2 numbers and you can get an answer of a, 7,500 miles.
When checking the engine oil level, which of the following is NOT a step in the procedure?
a. The engine should be at operating temperature.
b. The vehicle should be on level ground.
c. The engine should be running.
d. Remove the dipstick to check the oil level.
The correct option is c. The engine should be running.
Explanation:
To get an accurate measurement of the engine oil level using the dipstick, the engine must be off. When the engine is running, the oil is circulating throughout the engine, which leads to an inaccurate reading of the actual amount of oil in the oil pan. Additionally, checking the oil with the engine running can pose a safety risk.
Which measuring instrument should be used to measure brake rotor parallelism/thickness variation?
a. Micrometer.
b. Feeler gauge.
c. Dial Indicator.
d. Vernier Caliper.
The correct option is a. Micrometer.
Explanation:
A micrometer, specifically a disc brake rotor micrometer, is the correct and most accurate instrument used to measure the thickness of a brake rotor and to check for thickness variation (also known as parallelism) at several points around the rotor's surface. By measuring the rotor in at least four to six locations and comparing the highest and lowest measurements to the manufacturer's specifications, you can determine if the thickness variation is within the acceptable range.
What is the best way to verify a customer’s concern related to a brake noise?
a. Check the vehicle repair history to verify customer concern.
b. Interview the customer yourself to verify customer concern.
c. Test drive the vehicle to verify customer concern.
d. Check the brake fluid level and condition to verify customer concern.
The best way to verify a customer's brake noise concern is c. Test drive the vehicle to verify customer concern, ideally with the customer, to directly experience the noise under relevant conditions, though a thorough initial interview (b) and checking history (a) are also crucial steps before and during diagnosis. You need to replicate the noise to find the root cause, as visual checks (like brake fluid, d) don't always reveal noises, and history only provides context, not the actual sound.
Which of these should a technician use to clean drum brake shows and hardware?
a. Penetrating oil and soapy water.
b. Gasoline or brake fluid.
c. Brake fluid or brake solvent.
d. Brake solvent or soapy water.
The correct option is d. Brake solvent or soapy water.
Technicians should use brake solvent (also called commercial brake cleaner) or soapy water to clean drum brake shoes and hardware.
Brake solvent (cleaner) is an aerosol cleaning agent designed to remove dust, grease, and oil from brake parts. It is a fast and efficient way to clean and degrease all brake components.
Soapy water (or an aqueous cleaner) is an effective and inexpensive alternative that safely removes brake dust and mud. After washing with soap and water, the parts must be thoroughly dried.
Both methods are acceptable ways to prevent hazardous brake dust from becoming airborne and to ensure proper cleaning of components before reassembly and lubrication of contact points.
When inspecting serviceable wheel bearings, Technician A says that wheel bearings in good condition can be replaced with grease and reused. Tech B says that wheel bearings should never be reused. Who is correct?
a. Technician A only.
b. Technician B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is a. Technician A only.
Serviceable wheel bearings (specifically the tapered roller bearing type) that are in good condition (no pitting, spalling, or other damage) can and should be cleaned, inspected, repacked with the correct, fresh grease, and reused. This is a standard automotive maintenance procedure for this type of bearing.
Illumination of the red brake warning light in a vehicle would be caused by which of the following?
a. ABS system failure.
b. Frozen caliper piston.
c. Low fluid level in the master cylinder.
d. An open-wheel speed sensor winding.
The correct option is c. Low fluid level in the master cylinder.
The red brake warning light primarily indicates a problem with the fundamental hydraulic braking system or the parking brake being engaged. A common cause for the light to illuminate is a low brake fluid level in the master cylinder reservoir. This is a critical safety issue, as low fluid can indicate a leak or severely worn brake pads, potentially leading to total brake failure.
Two technicians are discussing brake drum wear. Technician A says if the brake drum has small cracks along its inside lining, it should be replaced. Technician B says if a brake drum has not spots along its inside lining, it may be resurfaced. Who is correct?
a. Technician A only.
b. Technician B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A or B.
c. Both A and B, because cracked drums need replacement for safety, while minor surface imperfections like pitting or heat spots can often be machined smooth (resurfaced) to restore proper function, but deep cracks, excessive scoring, or out-of-round drums require replacement.
Technician A is correct: Small cracks, especially if they're deep or extend significantly, compromise the drum's integrity and can lead to failure, making replacement necessary.
Technician B is correct: Minor pitting (often from heat spots) and light scoring are common and can usually be removed by resurfacing the drum to a uniform diameter, provided the drum doesn't go below its minimum safe thickness.
When bleeding the brake system on a vehicle, which wheel should be bled first?
a. The left-front wheel.
b. The right-front wheel.
c. The wheel closest to the master cylinder.
d. The wheel farthest from the from the master cylinder.
The correct option is d. The wheel farthest from the from the master cylinder.
The general rule for bleeding a conventional brake system is to start with the wheel that has the longest brake line, which is typically the farthest from the master cylinder. This ensures that all the old fluid and any air bubbles are pushed completely through the longest lines first and out of the system, preventing air from being trapped in lines further downstream. The process then proceeds to the next farthest wheel and so on, ending with the wheel closest to the master cylinder.
Disc brake pads are being replaced. What should the technician do after removing the retaining bolts from the caliper?
a. Check brake pedal height.
b. Start to install the on-car brake lathe.
c. Hang the caliper on a piece of wire or hook.
d. Manually bleed the brake system.
After removing caliper retaining bolts, a technician must securely hang the caliper on a piece of wire or hook (option c) to avoid stressing the flexible brake hose, then use a tool to compress the piston, install new pads, and reassemble, finally checking fluid and pumping the pedal before driving.
What will occur as a result of an out-of-round or eccentric brake drum?
a. A loss brake fluid.
b. Brake pedal pulsation.
c. The brake warning light will come on.
d. The ABS light will come on.
The correct option is b. Brake pedal pulsation.
An out-of-round or eccentric brake drum is one that is no longer perfectly circular or balanced. When the brakes are applied, this uneven surface causes the brake shoes to make intermittent contact with the drum as it rotates, rather than constant, even contact. This rapid movement of the brake shoes results in a pulsating or vibrating sensation that can be felt through the brake pedal.
During a test drive, the brakes on a vehicle are hard to apply, with little or no braking effect. Which of these could be the cause?
a. Low brake fluid level.
b. Leaking wheel cylinder.
c. Faulty brake booster.
d. Worn out brake pads.
The correct option is c. Faulty brake booster.
A faulty brake booster causes the brake pedal to be hard to press, requiring extra force from the driver to achieve little or no braking effect. The booster uses engine vacuum (or hydraulic pressure in some systems) to assist the driver in applying the brakes; without this assistance, the braking power is significantly compromised.
When performing a vacuum brake booster test, the technician should begin the test by pumping the brake pedal several times. What else should be true?
a. The engine should be off.
b. The engine should be running.
c. The master cylinder should be removed.
d. The technician should be driving the vehicle slowly.
The correct option is a. The engine should be off.
The initial part of the vacuum brake booster test involves depleting any stored vacuum by pumping the brake pedal several times with the engine off. This makes the pedal feel hard. After this initial step, the technician applies the pedal and holds it while starting the engine. If the booster is working correctly, the pedal will sink slightly toward the floor as engine vacuum provides the power assist.
Which of these could result from a broken drum brake return spring?
a. The brake shows may drag.
b. The brake pad will fail to retract.
c. The brake rotor will emit a scraping sound.
d. The brake pedal will fail to return to its rest position.
A broken drum brake return spring could result in the brake shoes may drag (option a). The return springs are responsible for pulling the brake shoes back to their resting position when the brake pedal is released.
Under which of the following circumstances MUST a brake system be bled?
a. Whenever the brake fluid level is low.
b. During routine maintenance inspections.
c. Whenever you change the brake pads.
c. When any hydraulic component is replaced.
The correct option is d. When any hydraulic component is replaced.
Bleeding a brake system is the process of removing trapped air from the brake lines. Air in the system is compressible, which makes the brake pedal feel soft or "spongy" and reduces braking effectiveness, a significant safety hazard. When any part of the hydraulic fluid circuit is disassembled, removed, or replaced (such as the master cylinder, a brake line, a caliper, or a wheel cylinder), air inevitably enters the system and must be removed by bleeding the brakes to ensure proper function and safety.
Which of these would result from a seized sliding/floating caliper?
a. Brake pedal pulsation.
b. Uneven brake pad wear.
c. Inoperative parking brake.
d. Malfunctioning ABS system.
The correct option is b. Uneven brake pad wear.
A seized sliding/floating caliper (specifically the guide pins) prevents the caliper body from moving laterally. In this system, the piston pushes the inner pad against the rotor, and the caliper body is supposed to slide inward to pull the outer pad into contact with the other side of the rotor.
If the caliper is seized on its pins, it cannot slide. This results in clamping force being primarily, or solely, applied by the piston side.
This causes the inner pad (piston side) to wear down much faster than the outer pad (caliper body side), leading to a significant uneven brake pad wear pattern across the axle.
A seized caliper also causes constant dragging, generating immense heat, which can warp the rotor over time. A warped rotor is the primary cause of brake pedal pulsation.
During a brake inspection, Technician A finds that the brake pad wear indicator is rubbing the rotor and recommends pad replacement. Technician B notices that the brake pad wear indicator light is illuminated on the instrument panel and recommends a brake fluid flush? Which technician recommendation is correct?
a. Technician A only.
b. Technician B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Technician A is correct, because a brake pad wear indicator rubbing the rotor directly signals worn pads needing replacement, while Technician B's recommendation for a fluid flush for an illuminated wear light is incorrect; an illuminated wear light (from the sensor) also means pads need replacement, and a flush is for old fluid, not pad wear, although low fluid can trigger a different brake light. So, the answer is a. Technician A only.
Wear Indicator: A metal clip or sensor touching the rotor creates a squealing sound or triggers a dashboard light (depending on type), indicating the pad material is low and needs replacement to prevent rotor damage.
What is the next step after marching an cleaning a brake rotor?
a. Using a micrometer to measure thickness.
b. Using a micrometer to measure diameter.
c. Use a dial indicator to measure the diameter.
d. Use a dial indicator to measure thickness.
The correct option is a. Using a micrometer to measure thickness.
After cleaning a brake rotor (whether new or resurfaced), the next critical step in a brake job is to measure its thickness with a micrometer to ensure it is within the manufacturer's specifications (above the minimum discard thickness or within the allowable refinish thickness).
Most manufacturers recommend that rotors that have been machined should be cleaned with…?
a. soap and water.
b. throttle body cleaner.
c. compressed air.
d. shop towel or rag.
The correct answer is a. soap and water.
Most manufacturers and industry experts recommend cleaning newly machined (resurfaced) brake rotors with mild soap and hot water.
Why soap and water? Machining a rotor leaves behind tiny metal particles embedded in the surface valleys. A water-based cleaning solution, combined with scrubbing, effectively lifts and removes these microscopic metal fragments. This prevents the particles from becoming embedded in the new brake pads, which can cause noise, reduce braking efficiency, and lead to premature wear.
Brake fluid is observed leaking from the rear of the master cylinder and flowing down the front of the vacuum brake booster assembly. Which of the following is the cause?
a. A leaking brake line.
b. A bent master cylinder push-rod.
c. A leaking rear seal in the master cylinder.
d. The vacuum booster is leaking.
The correct option is c. A leaking rear seal in the master cylinder.
Brake fluid leaking from the rear of the master cylinder, where it mounts to the vacuum brake booster, is a classic symptom of a failed rear piston seal inside the master cylinder. This seal is designed to prevent fluid from passing into the area where the master cylinder push-rod operates. When it fails, brake fluid can leak past the seal and run down the front of the vacuum booster assembly. The fluid can also accumulate inside the booster itself, potentially damaging its internal diaphragm and seals over time.
A digital multimeter (DMM) set to ohms is being used. What does “OL” on the display indicate?
a. The circuit is open.
b. The circuit has a short to voltage.
c. The DMM internal battery is low.
d. The meter function is incorrectly set.
The correct option is a. The circuit is open.
When a digital multimeter (DMM) set to measure ohms (resistance) displays "OL" (Overload or Open Line), it means the measured resistance value is higher than the meter's maximum measurement range, essentially indicating infinite resistance. An open circuit (or a broken wire/component) has theoretically infinite resistance, meaning no continuity and current cannot flow through it.
What statement is true about the amperage is a series circuit?
a. Amperage is never the same in two places in a circuit.
b. Amperage is the same throughout the entire circuit.
c. Amperage is divided between the number of loads.
d. Amperage drops to zero after going through the load.
The correct option is b. Amperage is the same throughout the entire circuit.
In a series circuit, there is only one path for the electrical current (amperage) to flow. As a result, the same amount of current must pass through every component and at every point in the circuit, following the principle of conservation of charge. Ammeters placed at different points within a series circuit will all show the same reading.
In a series circuit with three bulbs, if the middle bulb is burned out and not functioning, then what would happen within the circuit?
a. Only the first bulb would light.
b. Only the third bulb would light.
c. Both the first and third bulbs would light.
d. None of the bulbs would light.
The correct option is d. None of the bulbs would light.
In a series circuit, components are connected along a single, continuous path. The electric current must flow through each component sequentially to complete the circuit.
If the middle bulb burns out or is removed, it creates an open circuit, which is like an open switch.
This break interrupts the flow of current to all other components in the series, regardless of their position relative to the power source.
As a result, no current can flow through the first or third bulbs either, and the entire circuit stops operating.
While reading a digital multimeter, the meter displays 631 mA. How many amps is that equal to?
a. .631 amps.
b. 16.31 amps.
c. 0.001631 amps.
d. 0.0001631 amps.
631 mA is equal to 0.631 amps.
Divide (mA) by 1000 to convert.
Which of these could cause current flow to be below specifications?
a. High voltage.
b. A short circuit.
c. Low resistance.
d. High resistance.
The correct option is d. High resistance.
According to Ohm's law, current (I) is directly proportional to voltage (V) and inversely proportional to resistance (R) (expressed as I = V/R). An increase in high resistance will cause a decrease in the current flow, potentially making it fall below specifications.
Technician A recommends the replacement of a flexible brake line when damage is found. Technician B recommends the repair of a flexible brake line when damage is found. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is a. A only.
Technician A is correct because a damaged flexible brake line (hose) must always be replaced, not repaired. Brake systems operate under extremely high pressure, and any repair to a flexible hose would be unsafe and highly likely to fail, leading to total brake failure. Automotive safety standards and best practices require the installation of a new, approved brake hose assembly.
Which of these statements is true regarding a series circuit?
a. Total resistance is the same as the source voltage.
b. Total resistance is the sum of all resistances.
c. Current flows through the path of greatest resistance.
d. Total resistance is less than the lowest of the individual resistances.
The correct option is b. Total resistance is the sum of all resistances.
In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, creating a single path for the current to flow. To find the total or equivalent resistance of the circuit, you simply add the individual resistances of each component together:
Rtotal=R1+R2+R3+…
In an automotive electrical circuit, a relay is used so that which of the following can happen?
a. A higher-current/amperage circuit can control lower-current/amperage circuit.
b. A higher-voltage circuit can control lower-voltage circuit.
c. A lower-voltage circuit can control a higher-voltage circuit.
d. A lower-current/amperage circuit can control a higher-current/amperage circuit.
The correct option is d. A lower-current/amperage circuit can control a higher-current/amperage circuit.
A relay is an electrically operated switch that allows a low-current control circuit (e.g., from a small switch on a dashboard) to activate a high-current load circuit (e.g., a fuel pump, headlights, or a fan motor). This design is used to:
Protect sensitive control switches from the damage that would be caused by high current flow.
Allow the use of thinner, lighter, and less expensive wiring for the control circuit.
Route the heavy-gauge wiring needed for the high-current load over the shortest possible distance to reduce voltage loss, typically positioning the relay in the engine compartment close to the load.
A technician is testing a non-operational dome light using a multimeter. The technician finds there is 12.6 volts on both the (+) power and (-) ground side of the blub. What does this indicate?
a. A short-to-ground in the power side of the circuit.
b. A corroded bulb socket.
c. A defective (open) bulb.
d. An open in the ground side of the circuit.
This indicates d. An open in the ground side of the circuit.
Here is the explanation:
A complete circuit requires a path for current to flow from the power source through the load (the bulb) and back to the ground.
The reading of 12.6 volts on the power side indicates that power is successfully reaching the bulb socket.
The reading of 12.6 volts on the ground side means there is no potential difference (voltage drop) across the bulb, which suggests the circuit is not completed to the actual ground source. The voltage is "backed up" or "floating" on the ground wire because there is a break (an open) preventing it from returning to the chassis ground [1].
Therefore, the bulb does not illuminate because no current is flowing through it, and the issue lies in the return path (the ground side) of the circuit [1].
The fuse to the auxiliary/power outlet keeps blowing whenever the phone charger is plugged in. What is the MOST LIKELY cause?
a. Low resistance in the phone charger.
b. Poor ground on the auxiliary/power outlet.
c. Corrosion on the electrical connector to the auxiliary/power outlet.
d. High resistance in the phone charger.
The correct option is a. Low resistance in the phone charger.
A fuse is a safety device designed to melt and open a circuit when the current flowing through it exceeds a safe level. This excessive current is typically caused by a short circuit or an overloaded circuit.
A low resistance in the phone charger (specifically, an internal short circuit) would cause a large amount of current to flow through the circuit, exceeding the fuse's amperage rating and causing it to blow immediately. This is the most likely cause because the fuse blows whenever that specific charger is plugged in, suggesting the fault lies within the charger itself.
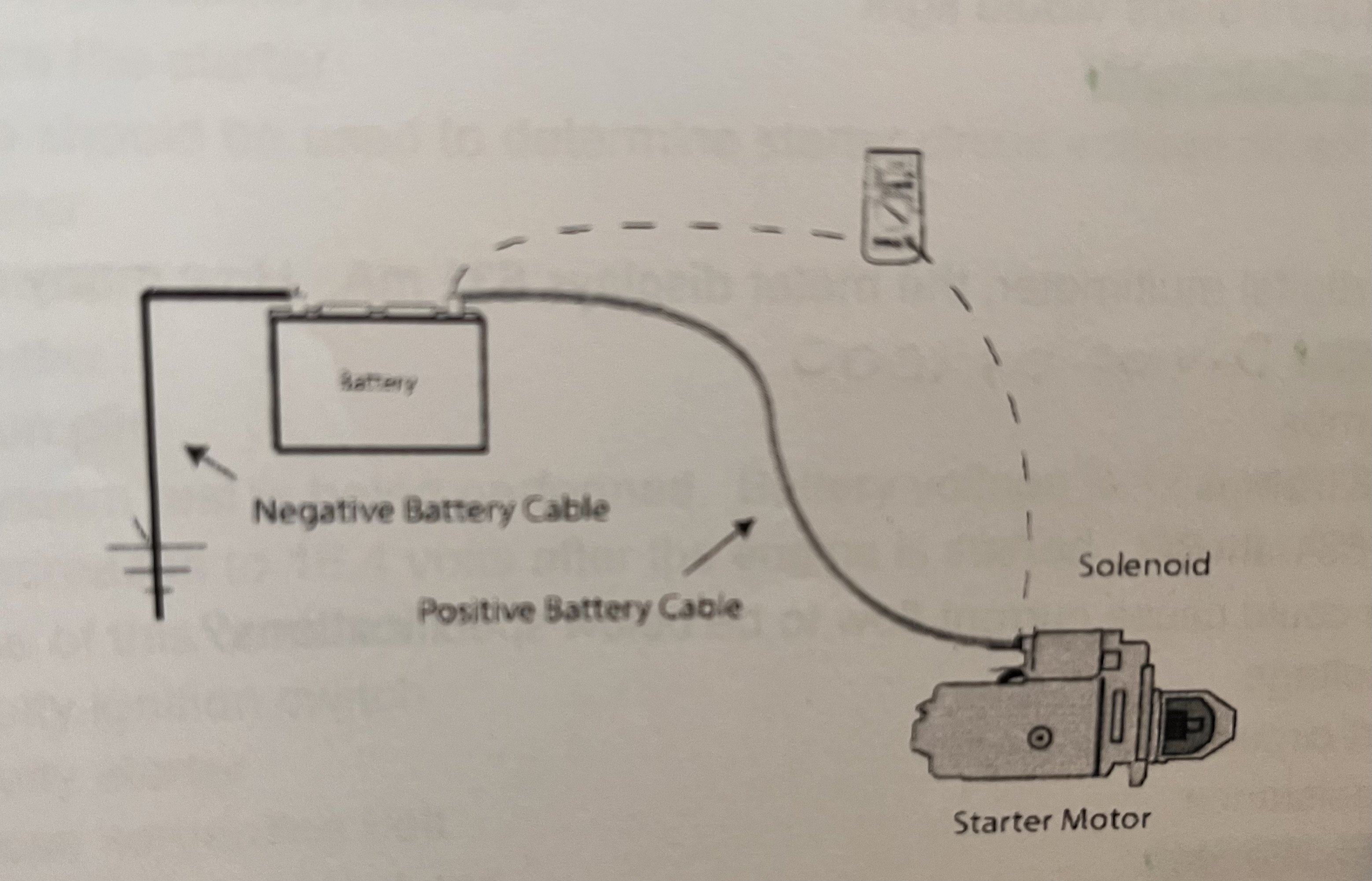
While performing a voltage drop test on a starter circuit, the meter indicates 00.06 volts on the DMM display when the starter is working. Which of the following describes the results on the meter display?
a. Normal condition.
b. It is an open circuit.
c. Indicates high resistance.
d. Terminals are corroded.
A meter reading of 0.06 volts during a voltage drop test on a starter circuit indicates a normal condition.
Acceptable voltage drop readings for specific segments of the starter circuit are generally 0.2 volts or less for the cables and connections on either the positive or negative side, with a total circuit drop ideally between 0.2 and 0.5 volts. A reading of 0.06 volts is well within this normal, low-resistance range.
The driver and passenger side airbags and being disabled a protection against the possibility of accidental deployment. The technician should look for electrical connectors that are what color?
a. Red.
b. Black.
c. Green.
d. Yellow.
The electrical connectors for airbags and related safety restraint systems are typically yellow in color across most vehicle manufacturers [1]. This standardized color-coding is used to alert technicians to the high-voltage, pyrotechnic nature of the circuit and to exercise extreme caution to prevent accidental deployment [1].
Therefore, the correct answer is d. Yellow.
A power antenna is inoperative. The technician replaces the recommended 15 amps fuse and the fuse element melts immediately. Technician A says this could be caused by a short to ground. Technician B says to use a 20 amp fuse to protect this circuit. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
A. Technician A is correct, because an immediately blown 15A fuse after replacement indicates a severe overload, likely a short to ground or internal fault in the antenna motor, while Technician B is wrong for suggesting a higher amperage fuse which would dangerously overload the circuit wires, leading to potential fire.
Why Technician A is correct:
Immediate Blow: When a fuse blows immediately, it means an excessive amount of current (far beyond 15 amps) is trying to flow, overwhelming the fuse's element instantly.
Short to Ground: A short to ground creates a near-zero resistance path, allowing massive current to flow, thus blowing the fuse immediately.
Action: The correct action is to diagnose the short circuit (check wiring, motor) not replace the fuse with a higher rating.
When jump-starting a vehicle, which of these needs to be done last?
a. Connect the positive terminal of the running vehicle’s battery to the positive terminal on the vehicle with the dead/discharged battery.
b. Connect the negative terminal of running vehicle’s battery to an engine ground on the vehicle with dead/discharged battery.
c. Connect the negative terminal of the dead/discharged battery to the positive terminal of the running vehicles battery.
d. Connect the positive terminal of the dead/discharged battery to a ground of the dead/discharged battery.
The correct option is b. Connect the negative terminal of running vehicle’s battery to an engine ground on the vehicle with dead/discharged battery.
Explanation:
The final connection in the jump-starting process is to connect the black negative clamp to an unpainted metal surface on the car with the dead battery, such as the engine block or chassis ground. This is done to minimize the risk of a spark occurring near the battery, which can produce flammable hydrogen gas and potentially cause an explosion. The options provided in the question are slightly misworded compared to the standard, safest practice of connecting to a ground away from the dead battery, but the intent is for the last connection to be the negative/ground connection on the vehicle being jumped. Option b describes connecting to an "engine ground on the vehicle with dead/discharged battery", which is the correct final step.
All of these can cause over-heating of a battery EXCEPT:
a. A battery discharging rapidly.
b. An alternator undercharging the battery.
c. An alternator overcharging the battery.
d. A battery charger set to a fast/rapid changing rate.
The correct option is b. An alternator undercharging the battery.
Explanation
Undercharging the battery does not cause it to overheat; instead, it results in a discharged or sulfated battery that may not start the vehicle or charges very quickly and produces a low amperage discharge rate. An undercharged battery is cool.
When using a battery analyzer, the technician finds that the voltage is below the manufacturer’ s specifications. Which action should the technician perform?
a. Replace the battery.
b. Replace the alternator.
c. Replace the battery cables.
d. Replace the starter.
The correct option is a. Replace the battery.
Explanation:
If a battery analyzer (specifically when performing a load test, as implied by the diagnosis of low voltage under testing conditions) finds that the voltage drops below specifications, it indicates the battery is faulty and needs replacement. The battery cannot hold a charge or deliver the necessary power under load. A normal battery, even if discharged, can often be recharged and retested if it's otherwise healthy, but a failure on a proper analyzer (such as a load test) usually means an internal defect, such as a bad cell.
Which of these should be used to determine starter circuit voltage drop?
a. Ammeter.
b. Ohmmeter.
c. Voltmeter.
d. Carbon pile.
The correct option is c. Voltmeter.
Explanation:
A voltmeter (or digital multimeter set to measure DC voltage) is used to determine the starter circuit voltage drop. A voltage drop test measures the difference in electrical potential (voltage) between two points in a circuit while the circuit is under load (e.g., while cranking the engine) to identify excessive resistance in wires or connections.
A charging system test is being performed. Battery voltage is 12.6 volts before starting the engine and increase to 16.4 volts after the engine started. Which of these is the MOST LIKELY cause of this condition?
a. A faulty ignition switch.
b. A faulty starter.
c. A loose serpentine belt.
d. A faulty voltage regulator.
The correct option is d. A faulty voltage regulator.
Explanation:
A healthy charging system typically operates between 13.5 and 14.5 volts with the engine running. A voltage reading of 16.4 volts indicates that the alternator is overcharging the system. The component responsible for controlling the alternator's output voltage is the voltage regulator, which is usually an internal part of the alternator in modern vehicles. A faulty or stuck voltage regulator can fail to limit the voltage output, leading to an overcharge condition that can damage the battery and other electrical components in the vehicle.
Safety glasses need to be worn in all the following circumstances, EXCEPT:
a. While using an air tool.
b. While using the brake lathe.
c. While working on a vehicle.
d. While in a class discussion.
The correct option is d. While in a class discussion.
Explanation:
Safety glasses are required whenever there is a potential for eye injuries from flying debris, chemicals, or other hazards, which is a constant risk in a workshop environment when using tools and working on vehicles. A class discussion, however, is a theoretical setting where these physical hazards are not present, so eye protection is not necessary.
When using a dry chemical (Multi-purpose ABC fire extinguisher), Technician A aims the nozzle of a fire extinguisher at the top of the fire. Technician B uses a sweeping motion at the base of the fire. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Technician B is correct (option b.). The proper technique for using a dry chemical fire extinguisher is to follow the P.A.S.S. method, which involves aiming the nozzle at the base of the fire and using a sweeping motion. Aiming at the flames or the top of the fire is ineffective as the extinguishing agent will not reach the fuel source.
The P.A.S.S. Method:
Pull the pin to release the locking mechanism.
Aim the nozzle low, pointing it at the base of the fire.
Squeeze the handle to release the extinguishing agent.
Sweep from side to side at the base of the fire until it is completely out.
Technician A says carbon monoxide has a distinctive smell. Technician B says when starting/ running an engine in the lab, the exhaust fan hoses need to be connected. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Technician B is correct. Carbon monoxide is an odorless, colorless, and tasteless gas, so Technician A is incorrect. When running an engine in a lab, proper ventilation, such as connecting exhaust fan hoses, is critical for safety to prevent the buildup of deadly carbon monoxide fumes.
Technician A says a micrometer can be used to measure the outside diameter of the value stem. Technician B says a micrometer can be used to measure the piston ring gap. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Both Technicians are correct: Technicians use outside micrometers for valve stem diameters and specialized micrometers (like bore gauges with an outside micrometer) for piston ring gaps, making c. Both A and B the right choice, as micrometers measure outside dimensions, including stem diameter, and can be adapted for precise gap measurements.
Technician A (Valve Stem): Correct. An outside micrometer measures the external diameter or thickness, perfect for a valve stem.
Technician B (Piston Ring Gap): Correct. While you measure the gap inside a cylinder, you often use a feeler gauge in the cylinder (at spec) and then measure the gap with an outside micrometer by closing the ring and measuring the ends, or use a bore gauge with an outside micrometer for precision.
Therefore, both statements describe valid applications for micrometers in an automotive context
What must be done with gloves that have been used in the clean-up of blood after an accident?
a. They must be burned.
b. They must be sterilized.
c. They must be thrown in the trash can.
d. They must be placed in a hazardous waste container.
The correct option is d. They must be placed in a hazardous waste container.
Explanation:
Gloves and other disposable items contaminated with blood or other potentially infectious materials (OPIM) are considered biohazardous waste and must be disposed of in designated, properly labeled biohazard bags or containers (often red) according to OSHA standards. This prevents the spread of infection and ensures safe handling by waste management personnel.
What type of wrench should be used to loosen or tighten brake lines or tubing fittings?
a. Box-end wrench.
b. Open-end wrench.
c. Line/Flare Nut wrench.
d. Combination Wrench.
The correct wrench to use for brake lines and tubing fittings is a c. Line/Flare Nut wrench, because it's designed with a split opening to slip over the line but grip the nut on multiple faces, preventing the common rounding and damage that occurs with standard open-end or box-end wrenches.
What is the color of the high-voltage electrical cables on a hybrid vehicle?
a. Red.
b. Pink.
c. Green.
d. Orange.
The color of high-voltage electrical cables on a hybrid vehicle is typically (d) Orange, a standard color-coding used internationally to signify high-voltage lines and alert technicians to potential danger for safety reasons, although some manufacturers might use blue as an alternative.
Why Orange?
Safety: The bright orange color stands out, clearly indicating that the cable carries dangerous, high voltage.
Standardization: Federal standards and industry practices require orange for high-voltage components outside protective barriers in EVs and HEVs.
Contrast: It differentiates them from lower-voltage automotive wiring, which uses colors like red, black, or green/yellow for standard functions.
Which of the following is NOT a good tip when dressing for work ad an automotive technician?
a. Secure long hair.
b. Secure loose clothing.
c. Wear jewelry.
d. Wear appropriate foot wear.
The correct option is c. Wear jewelry.
Explanation:
Wearing jewelry is a major safety hazard for an automotive technician. Jewelry can easily get caught in moving parts of machinery or equipment, which can lead to severe injuries such as entanglement, electrical shock (as perspiration and moisture make the body a better conductor of electricity), or lacerations. Safety guidelines universally recommend against wearing jewelry in a shop environment
If a chemical gets in your your eyes, where would someone find information on how to properly treat your eyes?
a. The safety data sheets (SDS).
b. Vehicle repair manual.
c. Your peers.
d. The chemical label.
The correct option is a. The safety data sheets (SDS).
Explanation:
Safety data sheets (SDS) are specifically designed to provide detailed occupational safety and health information about a chemical product, including hazards, safe handling procedures, and emergency first aid measures.
Section 4 of the SDS specifically outlines the necessary first aid instructions for various exposure routes, including eye contact, skin contact, inhalation, and ingestion.
If a vehicle is starting to fall from the lift, what should you do?
a. Continue raising the vehicle.
b. Immediately get out of the way.
c. Hold up the falling end and yell for help.
d. Use a supplementary stand to support the vehicle.
The correct option is b. Immediately get out of the way.
If a vehicle is starting to fall from a lift, the primary concern is personal safety. Safety protocols mandate that human life is prioritized over property or equipment. The structure of a falling vehicle on a lift is unstable, and any attempt to intervene manually or use additional equipment on the spot poses a high risk of serious injury or death.
Evacuate the area immediately to ensure personal safety.
Alert others nearby to the potential danger.
Do not attempt to stabilize the vehicle yourself.
Notify trained personnel or emergency services to handle the situation safely.
Each of the following can be used to determine 12-volt battery condition on a maintenance-free battery EXCEPT:
a. Hydrometer.
b. Capacitance tester.
c. Voltmeter.
d. Load tester.
The correct option is a. Hydrometer.
A hydrometer cannot be used to determine the condition of a maintenance-free battery because these batteries are sealed and do not have removable caps to access the liquid electrolyte for specific gravity testing. The specific gravity test works by measuring the density of the sulfuric acid and water mixture, which changes with the battery's state of charge. Maintenance-free batteries are designed to never need the electrolyte level checked or refilled, making them inaccessible for this type of test.
Under average conditions, which of the following is the most ideal ratio of anti-freeze and water?
a. 20%-80%
b. 40%-60%
c. 50%-50%
d. 70%-30%
The correct option is c. 50%-50%.
For average conditions and most climates, a 50/50 mixture of antifreeze (coolant concentrate) and distilled water is the standard and widely recommended ratio. This balanced ratio offers several benefits:
Freeze Protection: It lowers the freezing point of the liquid to approximately -34°F (-37°C), protecting the engine in cold weather.
Boil-over Protection: It raises the boiling point of the water to around 223°F (106°C), preventing the engine from overheating.
Corrosion Inhibition: The antifreeze contains additives that protect the internal metal components of the cooling system from rust and corrosion, which pure water alone would cause.
Optimal Performance: This mix provides a good compromise between heat transfer efficiency (water is a better coolant than pure antifreeze) and the protective properties of the antifreeze.
Two technicians are discussing wiring repairs. Technician A says that using a wire nut is a proper repair. Technician B says using heat shrink and solder is a proper repair. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is b. B only.
Technician A is incorrect because a wire nut (twist-on connector) is generally not considered a proper repair method for automotive wiring, especially in exposed environments subject to vibration, temperature changes, and moisture. They are more common for residential or commercial building wiring and are less reliable in demanding conditions compared to methods designed for a more robust connection.
Technician B is correct because using solder and adhesive-lined heat shrink tubing is a widely accepted and proper method for electrical repairs, particularly in automotive applications where a durable, secure, and environmentally sealed connection is needed. The solder provides a strong electrical connection, while the adhesive-lined heat shrink provides insulation and a waterproof seal, protecting the joint from corrosion and the elements
How is Ohm’s law formulated?
a. Amperage is equal to Resistance multiplied by voltage (A = Ω x V)
b. Resistance is equal to Amperage multiplied by Voltage (Ω = A x V)
c. Voltage is equal to Amperage divided by Resistance (V = A/Ω)
d. Voltage is equal to Amperage multiplied by Resistance (V = A x Ω)
The correct formulation of Ohm's law from your options is d. Voltage is equal to Amperage multiplied by Resistance (V = A x Ω), as Ohm's Law states voltage (V) is the product of current (I or A for Amperage) and resistance (R or Ω for Ohms), often written as V = I R or V = A x Ω.
Here's a breakdown of the common forms:
Voltage (V): V = I x R (or A x Ω)
Current (I or A): I = V / R (or A = V / Ω)
Resistance (R or Ω): R = V / I (or Ω = V / A)
Technician A says that damaged external threads can be repaired using a tap. Technician B says a thread insert could be used when internal threads are damaged beyond repair. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Bothe A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is b. B only.
Technician A is incorrect. A tap is a tool used to cut or repair internal threads (in holes). It is not used for external threads (on a bolt or rod). Damaged external threads are typically repaired using a die or a thread file.
Technician B is correct. A thread insert, such as a Heli-Coil or Time-Sert, is specifically designed to repair internal threads that are severely damaged or stripped beyond repair. The process involves drilling and tapping the hole to a larger size, and then installing the insert to provide new threads of the original size.
The charging system warning light comes on while driving down the road. What does this condition mean?
a. This condition is normal.
b. There is secondary ignition system.
c. There is a charging system problem.
d. There is a timing belt problem.
When the charging system warning light comes on while driving, it means there's a problem with your vehicle's electrical charging system, likely the alternator, battery, or related wiring/belts, indicating the battery isn't recharging, and you should get it checked immediately to prevent a breakdown. Therefore, option c. There is a charging system problem is the correct answer.
Gaskets must have all the following characteristics, EXCEPT:
a. Maintain a tight seal during the normal rates of thermal expansion.
b. Fit loosely along the mating surfaces.
c. Remain flexible and not shrink or compress over time.
d. Maintain a good seal when subjected to normal operating conditions.
The correct option is b. Fit loosely along the mating surfaces.
A gasket is a mechanical seal that fills the space between two or more mating surfaces to prevent leakage. It is designed to be a yielding or deformable material that can be compressed to tightly fill any irregularities in the surfaces and create a secure seal. Therefore, for a gasket to be effective, it must fit snugly and be under compression, not loosely, along the mating surfaces.
A vehicle was brought in with the customer complaining about an oil leak. While doing an inspection, the source of the leak was not visibly noticeable. Which of the following would be a good method to pinpoint the leak?
a. Install a fluorescent dye in the engine oil and operate the vehicle.
b. Overall the crankcase by adding two extra quarts and force the leak to get larger.
c. Run the engine long enough for the leak to become visible.
d. Inform the customer to bring it back when it starts leaking again.
The correct option is a. Install a fluorescent dye in the engine oil and operate the vehicle.
Fluorescent dye testing is a common and effective diagnostic method for finding oil leaks that are difficult to locate visually.
The dye is added to the engine oil and circulated through the system by operating the vehicle.
Later, a UV or black light is used to inspect the engine bay; the dye will fluoresce and glow brightly under the light, pinpointing the exact source of the leak, even if it's small or in a hard-to-see location.
During a vacuum-assisted power booster test. Technician A says a faulty booster will result in a dropping pedal when the engine is started. Technician B says a faulty booster will result in a hard/solid pedal when the engine is started. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Technician B is correct; a faulty vacuum booster typically causes a hard/solid pedal, especially when starting the engine after depleting vacuum, as the booster can't provide assist, while a soft/dropping pedal usually indicates a hydraulic issue (like air or fluid leak) rather than a booster problem, making Technician A incorrect.
Explanation:
Technician A (Dropping Pedal): A soft or sinking pedal under pressure (with the engine running) generally points to a hydraulic system problem, such as air in the lines, a master cylinder issue, or a leak, not a vacuum booster failure.
Technician B (Hard Pedal): A faulty booster fails to create the vacuum assist needed, making the pedal feel stiff, solid, or requiring much more force to press, which is the classic symptom of a bad booster (or vacuum supply).
During a brake inspection, an area of the vacuum brake booster below the master cylinder is wet. Technician A says that is normal condition. Technician B says that the master cylinder should be inspected for leaks. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is b. B only.
A wet area on the vacuum brake booster below the master cylinder indicates a leak that needs addressing, not a normal condition.
Technician B is correct because the area below the master cylinder, specifically where it mates with the vacuum booster, should be dry. Any presence of brake fluid in this area is a strong indication of an external leak from the master cylinder's rear piston seal. This leak allows brake fluid to seep into the booster assembly, which can eventually damage the internal diaphragm and potentially lead to a loss of power assist.
The rear drum brakes are being inspected on a rear-wheel-drive vehicle. Two brake drums stamped MAX ID 9.50 inches are being measured. The left drum is 9.60 inches and the right drum is 9.75 inches. Technician A says to machine the left drum and to replace the right drum. Technician B says to machine both drums. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Technician A is correct (a. A only).
Left Drum: The measured inside diameter of 9.60 inches exceeds the maximum allowable internal diameter (MAX ID) of 9.50 inches. This indicates the drum is beyond the acceptable service limit for standard use and requires replacement, not just machining, as machining it further would thin the wall even more past the safe limit. The initial statement of the problem has a slight contradiction (saying to "machine" a drum that is already over max ID) but based on standard automotive practice, a drum over the MAX ID must be replaced.
Right Drum: The measured inside diameter of 9.75 inches also exceeds the maximum allowable internal diameter (MAX ID) of 9.50 inches. This drum is even further past the service limit than the left one and clearly must be replaced.
Technician A correctly advises to replace the drum that is significantly over the limit (right drum) but incorrectly suggests machining the left drum (which is also over the limit). Technician B incorrectly advises machining both drums, which are both beyond safe service limits.
Therefore, Technician A is closer to the correct action for both, as both drums must be replaced according to safety standards, and Technician A at least correctly identifies the need to replace the most worn one.
Technician A says a fully charged automotive battery has a measured voltage of 12.6 volts. Technician B says when replacing a battery, always disconnect the negative terminal first. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is C. Both A and B.
Explanation
Technician A is correct because a fully charged 12-volt lead-acid automotive battery, when rested (engine off), typically has a measured open-circuit voltage of 12.6 volts or higher.
Technician B is correct because when replacing (removing) a battery, the negative (or ground) terminal should always be disconnected first. This prevents accidental short circuits or sparks if a tool used on the positive terminal simultaneously touches any grounded metal part of the vehicle's chassis.
An acceptable key-off battery drain (parasitic draw) with a vehicle having multiple computers is…?
a. 2-5 A.
b. 150-300 mA.
c. 20-50 mA.
d. 20-50 A.
The correct option is c. 20-50 mA.
An acceptable key-off battery drain (parasitic draw) for a vehicle with multiple computers typically falls within the range of 20 to 50 milliamperes (mA).
Modern vehicles have many electronic control modules (computers, security systems, clocks, memory settings, etc.) that need a small, continuous amount of power to retain memory and perform essential background functions even when the vehicle is off.
The systems are designed to "go to sleep" after a certain period (usually around 15-45 minutes), at which point the current draw should drop to this low, acceptable range. A draw higher than this can indicate a problem, as it will drain the battery over a few days or weeks if the car is left unused.
Technician A says a battery test should be done after a starter had failed the current draw test. Technician B says if during a starter current draw test the amperage is higher than specifications, it could be caused by a defective starter. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Bother A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Only Technician B is correct; high current draw in a starter usually points to a faulty starter (like worn bushings, shorts) or mechanical drag, while a weak battery causes low voltage and potentially low cranking speed, not high amperage, so testing the battery first after a high draw is less logical than suspecting the starter itself.
Technician B is correct:
High Amperage = Starter Issue: An amperage reading above specifications indicates excessive current, often from internal starter problems (worn brushes, shorts, bad bearings) or mechanical binding in the engine, requiring starter/engine diagnosis.
When removing an air bag from a supplemental restraint system (SRS) what is the first step the technician needs to perform?
a. Leave ignition off for 15 minutes.
b. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
c. Remove air bag retaining fasteners.
d. Disconnect the yellow air bag electrical connector.
The correct option is b. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
Explanation:
The very first step a technician needs to perform when working on any part of the SRS system is to disconnect the negative battery cable. This is a critical safety measure to remove all power to the system, thus preventing accidental deployment of the airbag. After disconnecting the battery, it is also recommended to wait for a specific period (typically 10 to 90 seconds, but some sources mention up to 15 minutes) to allow the system's backup power source (capacitors) to discharge completely.
An alternator could fail a charging system output test and yet still be okay, if:
a. The battery is weak or defective.
b. The engine speed is not high enough during testing.
c. The drive belt tensioner is weak.
d. All the above.
The correct option is d. All the above.
Explanation:
An alternator may produce a lower-than-normal output reading during a charging system test, even if it is mechanically sound, due to any of the following conditions:
A weak or defective battery: The alternator works in conjunction with the battery to manage the charging system. A weak or defective battery can cause inaccurate test results or put an excessive load on the system, making the alternator appear faulty during testing.
Insufficient engine speed: Alternators typically need to be spun at a sufficient RPM to produce their full-rated output. If the engine speed is not high enough during the test (e.g., only at idle), the output may be low even if the alternator is good.
A weak drive belt tensioner/loose belt: If the drive belt tensioner is weak or the belt is loose, the belt can slip on the alternator pulley, preventing the alternator from spinning fast enough or consistently enough to generate adequate power, especially under load.
Technician A says a voltage drop can be caused by high resistance in a circuit. Technician B says there should be a 2 volt drop across a harness connector. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is a. A only.
Explanation:
Technician A is correct: According to Ohm's law and principles of electricity, high resistance in a circuit causes a voltage drop (V=IR). The higher the resistance across a component or a poor connection, the greater the voltage drop.
Technician B is incorrect: A 2 volt drop across a single harness connector is considered excessive and indicates a problem, such as corrosion or a loose connection. The ideal voltage drop across a good connector or wire should be minimal, typically less than 200 millivolts (0.2 volts), or even lower.
Technician A says the vehicle’s owner manual includes alternator removal instructions. Technician B says the vehicle’s owner’s manual includes infotainment instructions. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
The correct option is b. B only.
Explanation:
Technician B is correct because modern vehicle owner's manuals often include instructions for using the infotainment system, such as pairing a phone, setting the clock, and using various features.
Technician A is incorrect because the vehicle owner's manual provides general operation, safety, and basic maintenance information (like changing a tire or checking fluid levels), not detailed repair instructions like how to remove an alternator. Complex repair procedures, such as alternator removal, are found in detailed factory service manuals or aftermarket repair manuals, which are intended for trained technicians.
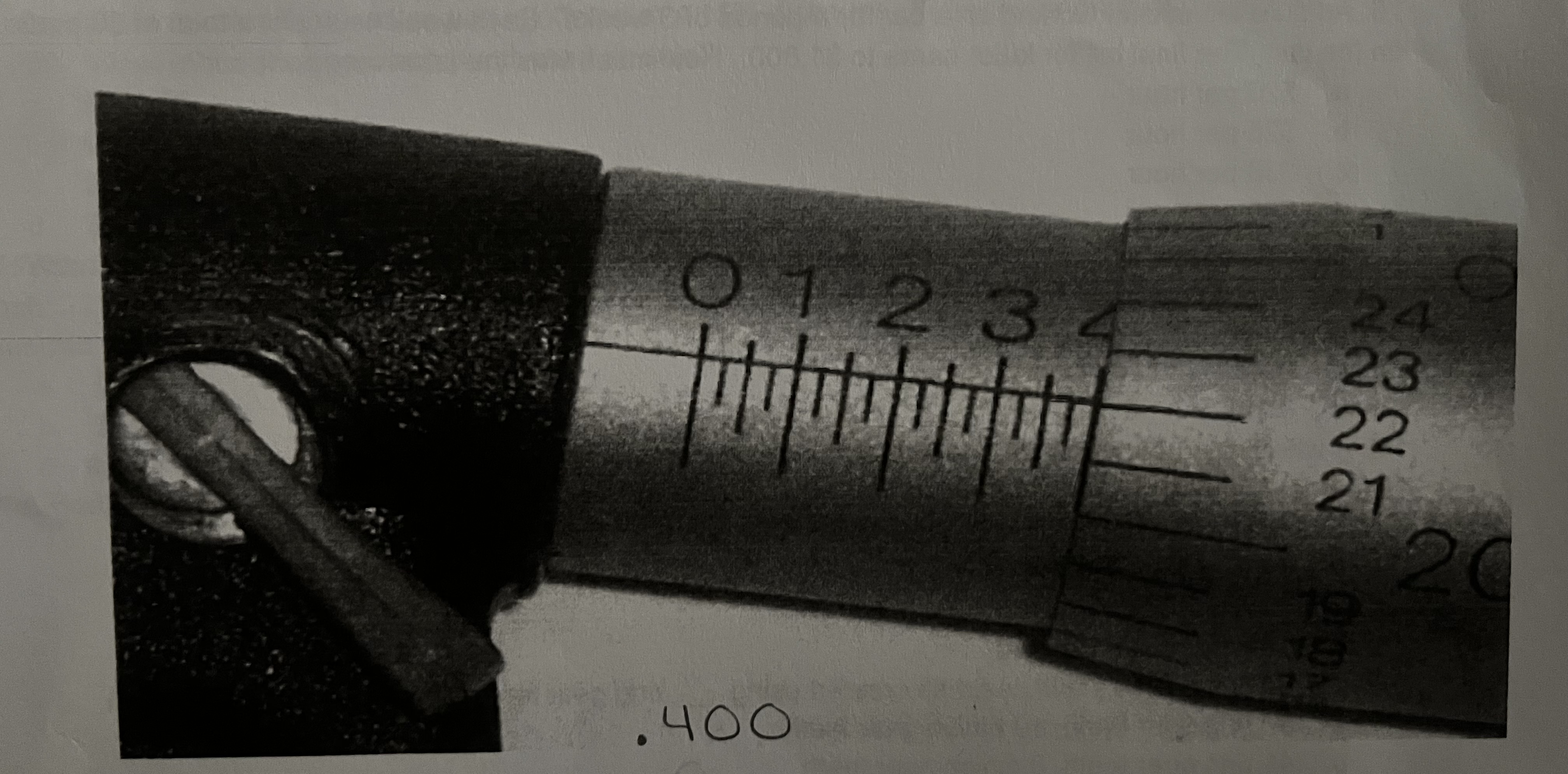
What is the reading of this micrometer?
a. 4.220”
b. .497”
c. .422”
d. .387”
Step 1: Identify the micrometer type
This is a standard inch micrometer:
Each number on the sleeve = 0.100"
Each small line on the sleeve = 0.025"
Each number on the thimble = 0.001"
Step 2: Read the sleeve (main scale)
Looking at the sleeve:
You can clearly see 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
The last fully visible number is 4
That gives:
0.400"
Now look carefully past the 4:
There are no extra .025 lines visible beyond the 4
So the sleeve reading is:
0.400"
✅ This part is correct (you even wrote “.400” on the paper)
Step 3: Read the thimble
Now look at the thimble on the right:
The reference line on the sleeve lines up with 22 on the thimble
That means:
0.022"
Step 4: Add them together 0.400"+0.022"=0.422"
✅ Correct answer
c. .422”
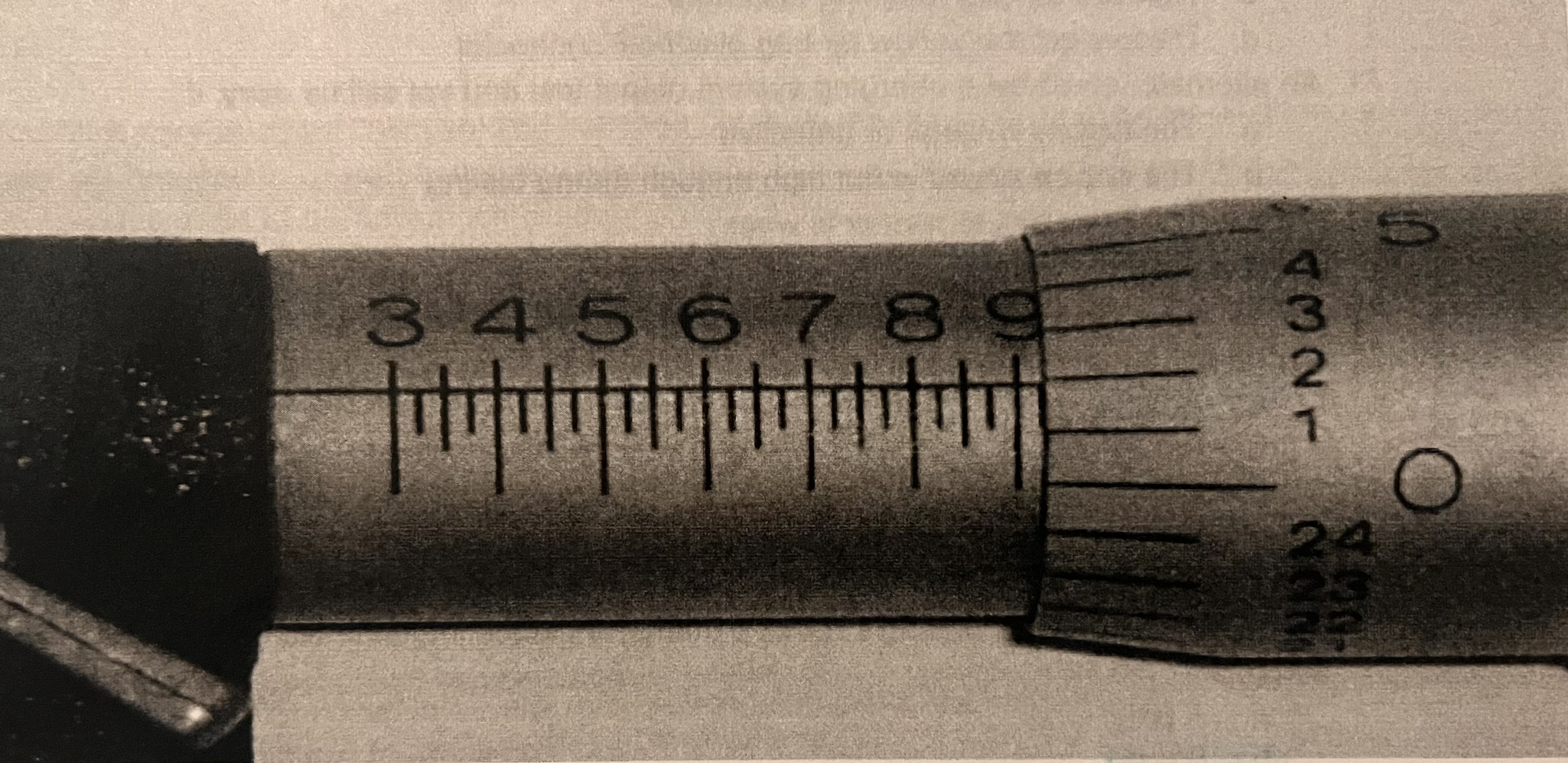
A rotor with a minimum/discard thickness of 0.940 inches is being measured. Technician A says a micrometer reading of 0.927 inches would indicate the rotor needs to be replaced. Technician B says a micrometer reading below the minimum/discard thickness specification would indicate the rotor could be machined and reused. Who is correct?
a. A only.
b. B only.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
Final answer (confirmed by the image)
a. A only
Technician A is correct.
Technician B is incorrect.
Step 1: Read the sleeve (main scale)
On the sleeve we can see the numbers:
3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Each number = 0.100 in
The last fully visible number is 9, which means:
0.900"
Now check for extra .025 marks past the 9:
There are no additional .025 marks visible past 9
So the sleeve reading is:
0.900"
Step 2: Read the thimble
Look at the reference line on the sleeve and where it lines up on the thimble:
It lines up with 27 (between 25 and 30, exactly on 27)
Each thimble division = 0.001 in
So:
0.027"
Step 3: Add them together 0.900"+0.027"=0.927"
✅ This matches the value mentioned in the question.
Step 4: Apply the specification
Minimum / discard thickness = 0.940 in
Measured thickness = 0.927 in
Since:
0.927<0.940
➡ The rotor is below discard thickness
➡ It must be replaced
➡ It cannot be machined
An auto technician worked on a car for a period of 3 weeks. Each week he spent a total of 20 hours on the car. The final bill for labor came to $1,800. How much was the labor rate per hour?
a. $20 per hour.
b. $25 per hour.
c. $30 per hour.
d. $35 per hour.
The labor rate per hour was
c. $30 per hour.
Here is the calculation:
Calculate the total hours worked:
3 weeks × 20 hours/week = 60 hours total
Calculate the labor rate per hour:
Total bill / Total hours = Labor rate1,800/60 hours = $30 per hour
A measurement should be 0.1” plus or minus 0.05. Which measurement would be within tolerance?
a. 0.18”.
b. 0.04”.
c. 0.2”.
d. 0.12”.
Minimum acceptable value:
0.1" − 0.05" = 0.05"
Maximum acceptable value:
0.1" + 0.05" = 0.15"
A measurement is "within tolerance" if it is greater than or equal to 0.05" and less than or equal to 0.15”.
Therefore, the correct answer is d. 0.12”
A wheel alignment machine goes through a self-check to see that the interior angles for the four cameras from a true parallelogram. If two of the angles are 75 deg what are each of the opposites angles?
a. They are both 75 deg.
b. They are both 90 deg.
c. They are both 105 deg.
d. They are both 180 deg.
The two opposite angles are both 105 deg.
A parallelogram has two pairs of equal opposite angles, and consecutive angles are supplementary, meaning they sum to 180 degrees. If two angles in the parallelogram are 75 degrees, they must form an opposite pair to be valid within the 360 degree circle total sum.
The other two angles are consecutive to the 75 degree angles. The measure of each consecutive angle (which are also opposite each other) can be calculated as:
180 degrees - 75 degrees = 105 degrees
The angles in the parallelogram are 75, 105, 75, and 105. Therefore, the other pair of opposite angles are both 105, which corresponds to option c.
A 4.10:1 rear differential could be created using __ ring gear teeth and __ pinion gear teeth.
a. 37 ring gear teeth, 10 pinion gear teeth.
b. 41 ring gear teeth, 8 pinion gear teeth.
c. 31 ring gear teeth, 8 pinion gear teeth.
d. 41 ring gear teeth, 10 pinion gear teeth.
A 4.10:1 rear differential uses 41 ring gear teeth and 10 pinion gear teeth, as the ratio is calculated by dividing the ring gear teeth by the pinion teeth (41 / 10 = 4.10), making option (d) the correct answer.
Here's why:
Gear Ratio Formula: Gear Ratio = Ring Gear Teeth / Pinion Gear Teeth.
Testing Option (d): 41 teeth (ring) / 10 teeth (pinion) = 4.10:1.
The owner of a repair shop received a service bulletin saying that the probability of part A failing is 1/100, the probability of part B failing is 1/50, the probability of part C failing is 1/33, and the probability of part D failing is 1/25. Which part has the smallest probability of failing?
a. Part A.
b. Part B.
c. Part C.
d. Part D.
Part A has the smallest probability of failing.
To determine which part has the smallest probability, we compare the given fractions:
When comparing fractions with the same numerator, the fraction with the largest denominator is the smallest in value. The denominators are 100, 50, 33, and 25, so
1/100 is the smallest probability value.
Comparing the decimal values, 0.01 is the smallest. Therefore, Part A has the smallest.
An automotive service department sold 36 batteries, 24 tires, and 112 quarts of motor oil during a week. If they are required to charge a disposal fee of 85 cents for each battery, 75 cents for each tire, and 2 cents for each quart of oil, how much did they collect in disposal fees that week?
a. $3.60.
b. $48.12.
c. $50.84.
d. $117.00.
The total amount collected in disposal fees that week was c. $50.84.
An automotive repair technician worked 42 hours at $16.00 per hour and overtime of 6 hours as a rate of 150% of his normal hourly rate. How much did they earn that week, before taxes?
a. $720,00.
b. $768.00.
c. $816.00.
d. $864.00.
The technician earned a total of $816.00 that week before taxes [1].
If 11 out of 43 cars you serviced in a week took less than 30 minutes to repair, what percentage of cars took longer than 30 minutes to repair?
a. 26%
b. 32%
c. 54%
d. 74%
The calculated percentage is approximately 74%.
The correct option is d. 74%
On sale, a re-manufactured engine is offered at a 15% discount. The regular price of the engine is $1,250. What is the savings when purchased on sale?
a. $150.00.
b. $187.00.
c. $1,062.00.
d. $1,437.50.
The savings when purchased on sale is $187.50.
What is the total cost of these items: 4 large tool boxes at $39.99 each; 120 spark plugs at $1.55 each; 22 distributer caps at $12.44 each; 100 spark plug gauges at $0.99 each, including 9% tax, rounded to the nearest penny?
a. $717.64.
b. $759.92.
c. $767.36.
d. $783.32.
d. $783.32
Multiply everything by 4, than add, then calculate the Tax and add it to the main total, and you will get the total.
(REQUIRES READING OF DESCRITION OF OBDII DRIVE CYCLE) According to the article, what does PCM stand for?
a. Process control module.
b. Power converter module.
c. Powertrain control module.
d. Powertrain control modem.
Answer: c. Powertrain control module
(REQUIRES READING OF DESCRITION OF OBDII DRIVE CYCLE) According to the article, which monitor can only operate during the first 30 minutes of engine operation?
a. EGR Monitor.
b. EVAP Monitor.
c. Oxygen sensor monitor.
d. Misfire and fuel monitors.
Answer: d. Misfire and fuel monitors
(REQUIRES READING OF DESCRITION OF OBDII DRIVE CYCLE) Which of the following conditions will NOT allow the EVAP monitor to run?
a. IAT is within 40-100 degree’s Fahrenheit.
b. Fuel tank level 50%.
c. IAT is within 40-100 degree’s Fahrenheit and the altitude is over 8000 feet.
d. IAT is within 40-100 degree’s Fahrenheit and the altitude is under 8000 feet.
Answer: c. IAT is within 40–100°F and the altitude is over 8000 feet
(REQUIRES READING OF DESCRITION OF OBDII DRIVE CYCLE) Based on this article, how is the Catalyst monitor executed?
a. By cruising at 40 MPH for up to 4 minutes.
b. From a stop, accelerate to 40 MHP at ½ to ¾ throttle.
c. Driving in stop and go traffic, ranging from 25-45 MPH for 10 minutes.
d. From a stop, accelerate to 65 MPH, then decelerate at closed throttle.
Answer: b. From a stop, accelerate to 40 MPH at ½ to ¾ throttle
(REQUIRES READING OF DESCRITION OF OBDII DRIVE CYCLE) Where does the article say to find each described function of the OBDII Drive Cycle?
a. Owner’s manual.
b. Instruction manual.
c. Technical Service Bulletins.
d. On the Driver’s side door placard.
Answer: a. Owner’s manual
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) According to the article, what are the two common types of mass airflow sensors used in automotive engines?
a. Vane meter and hot wire.
b. Intake air sensor and vane meter.
c. Hot wire sensor and cold wire sensor.
d. Pulse-Width modulation sensor and cold wire sensor.
Answer: a. Vane meter and hot wire ✅
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) According to the article, what is a characteristic of MAF (mass air flow) sensors?
a. Outputs a pulse-width modulated signal to to EFI.
b. Outputs a 0.0v-5.0v or a pulse width modulated signal.
c. Output a 0.0v-5.0v signal that is not proportional to the air mass flow rate.
d. The output frequency is inversely proportional to the air mass entering the engine.
Answer: b. Outputs a 0.0v–5.0v or a pulse width modulated signal ✅
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) According to the article, what is the difference between a hot film MAF sensor and a hot wire MAF sensor?
a. Hot wire MAF sensors is a pulse width modulated frequency sensor.
b. Hot wire MAF sensors can only detect air temperature, not air density.
c. Hot film MAF sensors output a frequency signal instead of a 0.0v5.0v signal.
d. Hot film MAF sensors cannot convert the proportional measurement into a calibrated signal for the ECU.
Answer: c. Hot film MAF sensors output a frequency signal instead of a 0.0–5.0V signal ✅
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) According to the article, an engine’s air/fuel ratio can be controlled very accurately when a MAF sensor is used in conjunction with which of the following sensors:
a. IAT sensors.
b. MAP sensor.
c. PWM Sensor.
d. Oxygen sensor.
Answer: d. Oxygen sensor ✅
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) Which statement best describes the operation of a hot wire mass airflow sensor?
a. The hot wire’s electrical resistance decreases as the wire’s temperature increases.
b. The current increase or decrease is proportional to the mass of air flowing past the wire.
c. This sensor utilizes a hot film grid that produces a pulse width modulated frequency signal.
d. When air flows past the hot wire, the wire cools, increasing its resistance, which in turn allows more current to flow.
Answer: b. The current increase or decrease is proportional to the mass of air flowing past the wire ✅
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) According to the article, which sensor tends to cause intermittent problems due to internal electrical failure?
a. IAT sensors.
b. MAP sensors.
c. Hot film MAF sensor.
d. Hot wire MAF sensor.
Answer: d. Hot wire MAF sensor ✅
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) According to the article, how is the hot wire MAF sensor kept clean?
a. Utilize MAF cleaning spray.
b. By use of an oscilloscope.
c. By the use of a burn off cleaning circuit.
d. Blowing the hot wire off with compressed air.
Answer: c. By the use of a burn off cleaning circuit ✅
(REQUIRES READING OF MASS AIRFLOW SENSORS) In a hot wire MAF sensor, what will denser air flowing past the sensor do?
a. Remove more heat from the wire indicating a lower mass airflow.
b. Remove less heat from wire indicating a higher mass airflow.
c. Remove more heat from the wire indicating a higher mass airflow.
d. Create an output frequency that is directly proportional to the air mass entering the engine.
Answer: c. Remove more heat from the wire indicating a higher mass airflow ✅
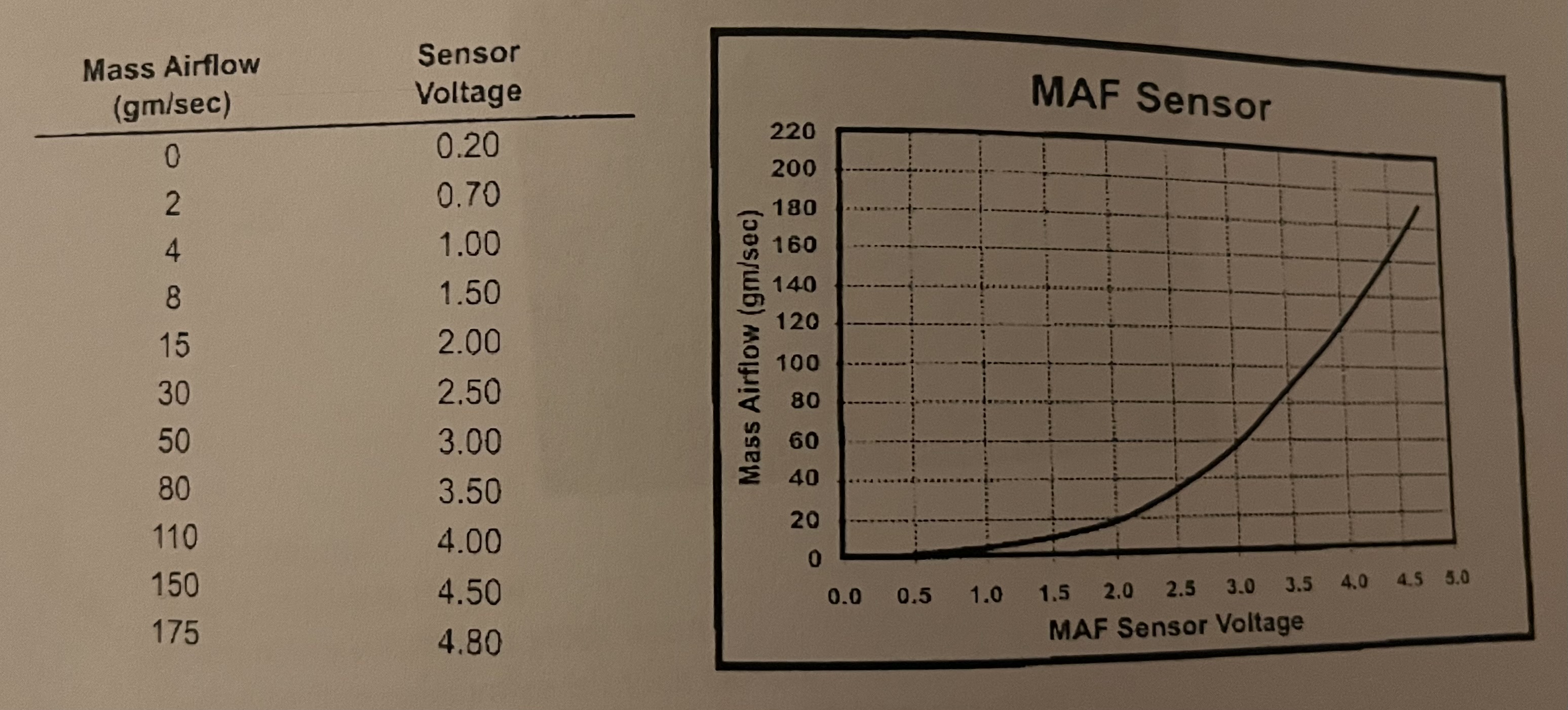
Using the diagram, if the MAF sensor voltage is outputting 2.5 volts, how mush air is entering the engine?
a. 8 gm/sec
b. 15 gm/sec
c. 30 gm/sec
d. 50 gm/sec
✅ Answer: c. 30 gm/sec
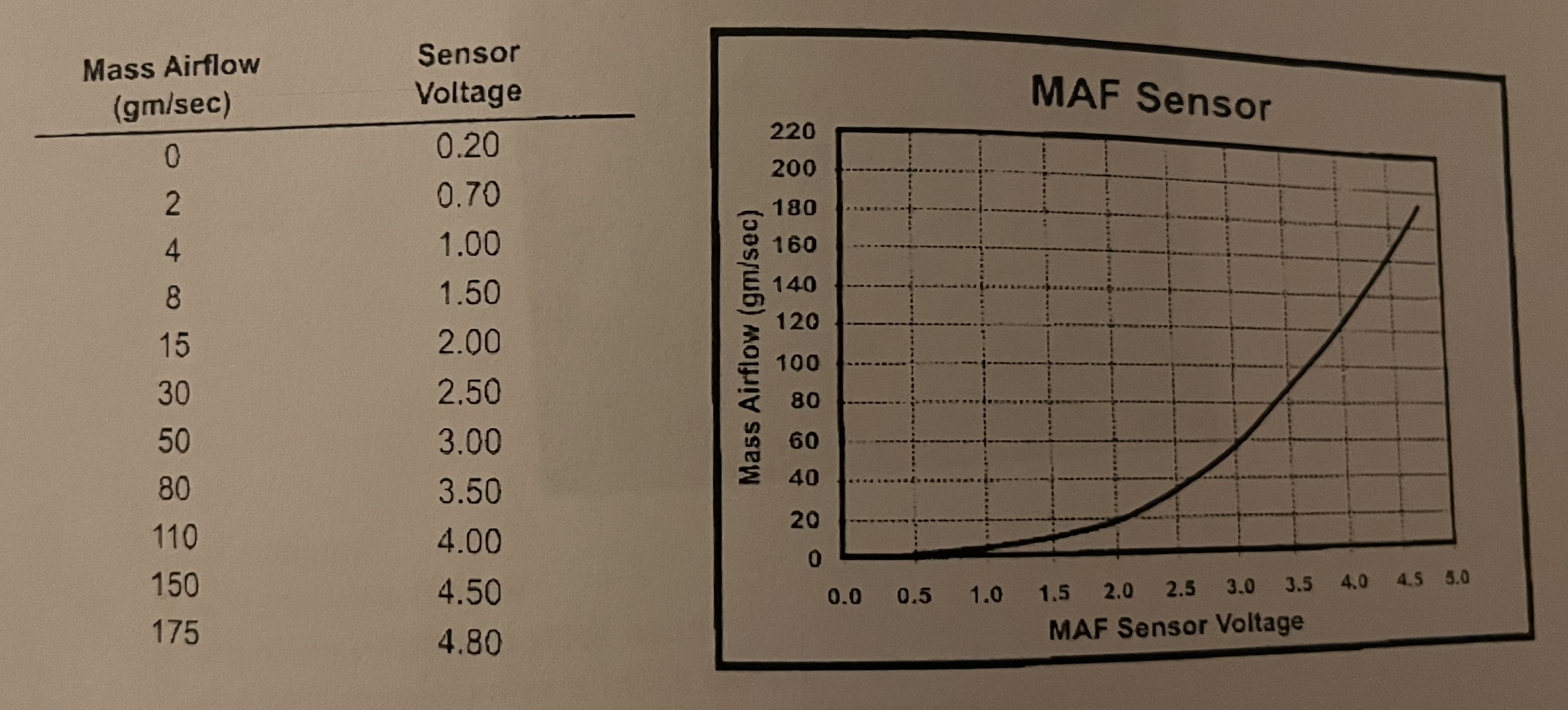
If the engine is intaking 130gm/sec of air, how much voltage should the MAF sensor be sending to the engine control unit (ECU)?
a. 4.00v
b. 4.20v
c. 4.50v
d. 4.90v
✅ Answer: b. 4.20 V