Lecture 3: Visual Pathways
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Components of the visual pathways
optic nerve, optic chiasm, lateral genicualte nucleus, superios colluculus, visual cortex
The pathways
Rods and cones → (intermediate layers of cells that create excitatory/inhibitory connections) → ganglion cells on the retina → optic nerve → optic chiasm → LGN → V1
Cortical Magnification
the visual field map in V1 in which the fovea takes up a disproportionately large region of V1
Lateral Inhibition
Produced by adjacent receptors that are connected by inhibitory synapses - active neuron inhibits the activity of its neighboring neurons
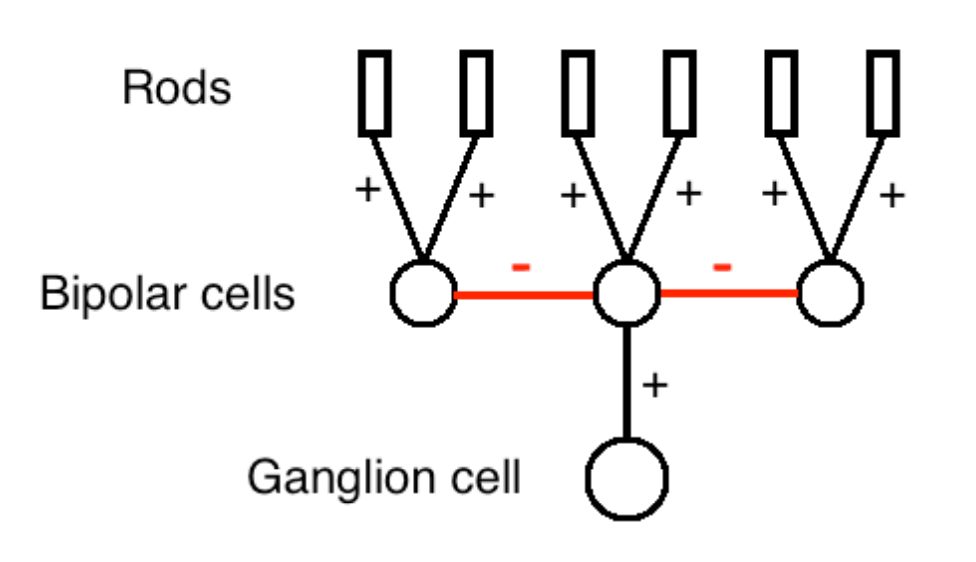
Center-surround receptive fields
act like “contrast detectors”, responding most to visual stimuli with high contrast
Happens in ganglion cells due to the lateral inhibition
Where do ganglion cells go?
most end at the LGN
a bit at the superior colliculus (a region involved in controlling eye movement)
Optic Chiasm
Where signals from each half of the retina meet
Binocular region of the visual field
The are where the view of the left eye and right eye merge
LGN
Organizes info from retina based on: which eye it came from and which type of receptor it came from (rods or cones)
Receives feedback (top-down) signals from cortex
Regulate the signal from retina, sending fewer impulses to cortex
LGN → V1
LGN sends most of its neuron signals to the primary visual cortex (V1), which then move to V2, V3, etc.
V1 physiology
Hubel and Wiesel discoved that V1 neurons respond best to oriented edges.
3 types of neurons in V1: simples cells, complex cells, hypercomplex cells
Simple cells
excitatory and inhibitory areas arranged side by side, sensitive to orientation and position
Complex cells
respond best to orientation, motion, direction
Hypercomplex cells
respond best to orientation, motion, direction, length
Receptive field properties in V1
V1 neurons show a graded response to their preferred stimulus
a simple cell tuned to a vertical edge will also respond to other orientations that deviate slightly from vertical
Orientation tuning curve
measures the relationship between orientation and firing
Retinotopic map
Map of the retina on the cortex
that two points that are close together on an object and on the retina will activate neurons that are close together in the brain
edge enhancement
an increase in perceived contrast at borders between regions of the visual field due to the center-surround receptive field (ex. mach bands)