AP Human Geo: Unit 7 Flashcards
1/77
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Primary Sectors
Refers to industries that extract natural resources from the environment.
Ex: Fishing, hunting, farming, logging, oil extraction
Secondary Sector
Refers to industries that process the raw materials extracted by primary industries, transforming them into finished, usable forms.
Ex: Furniture Manufacturing or Automobile Manufacturing
Tertiary Sector
Dedicated to providing services to businesses and consumers including the movement and delivery of goods and resources.
Ex: checkout clerks at the supermarket, lawyers, college professors
Quaternary Sector
Includes the intellectual and informational services. This is the sector of innovation and invention, and much of the work is scientific and research and development that leads to the patenting of new procedures and goods.
Ex: Computer Software Development, Biomedical Research
Quinary Sector
The highest-level of management decisions in the areas of business, government, education and science are made in this sector.
Ex: Chief executive officer (CEO)
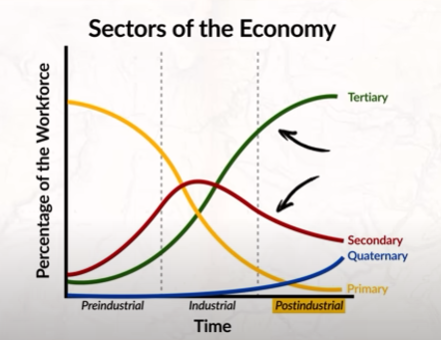
Economic Sectors
Grouping of industries based on what is produced and the activities of the workforce.
Cottage Industry
Small-scale business typically operated out of a person’s home (Individuals typically use traditional techniques and tools to produce custom goods by hand)
Enclosure Movement
A movement in England which took agricultural land that was publicly owned by the community and privatized it. (Countered the tragedy of the commons and increased food production)
Value-Added Products
Products that have been processed in a way that increases their overall value. (Final product can be sold for higher price than the original raw materials used to make it.)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period of time.
(GDP = Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + (Exports - Imports) )
When GDP is increasing:
Businesses are expanding
Jobs are being created
Economy is growing
Indicates there is more consumer and government spending
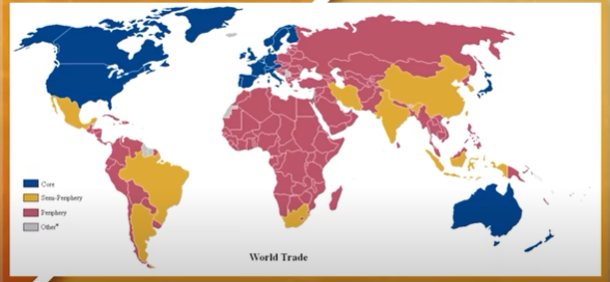
Core Countries
Countries with the most advanced economies and highest standard of living.
Typically have a degree of political and economic influence over other countries and regions in the world.
Ex: United States, Japan, Germany
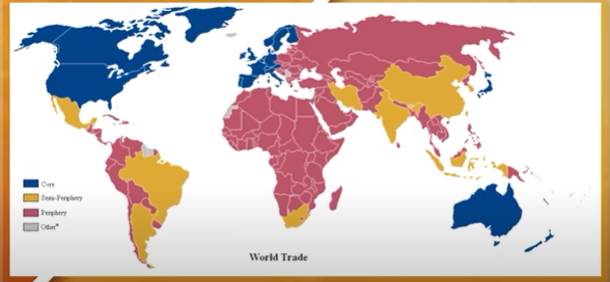
Semi-periphery Countries
Countries that have emerging economies that are industrializing.
Located between core countries and periphery countries in term of development
Ex: Brazil, India
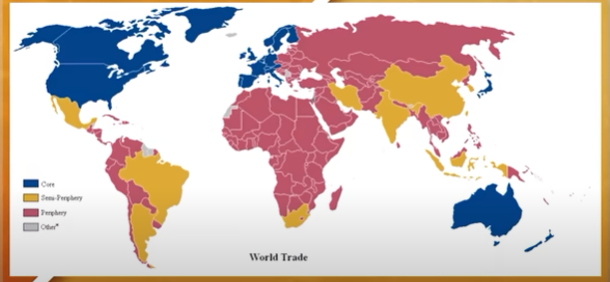
Periphery Countries
Countries that still reply heavily on the exportation of raw resources to more economically developed countries.
Typically these countries are the least economically developed and have a lower standard of living.
Ex: Haiti
Break Of Bulk Point
A location where goods are transferred from one mode of transportation to another.
Weber’s Least Cost Theory (Theory of Industrial Location)
The optimal location of an industry is determined by various factors such as labor and transportation cost. Suggests that businesses will choose a location that minimizes their total transportation costs for raw materials and finished goods.
The location is determined by 3 factors:
Transportation Costs (minimize)
Labor Costs (minimize)
Agglomeration (maximize)
Agglomeration
The clustering of different economic activities and industries in a specific geographic area. Allows business to reduce transportation costs and infrastructure cost
Bulk Reducing Good
A product that becomes lighter and easier to transport as production occurs.
Have heavy and bulky raw resources that are used in the production of the good.
The final product is often lighter and more maneuverable.
Bulk Gaining Good
A product that becomes heavier and more difficult to transport as production occurs.
Often are made up of resources that are actually lighter and more maneuverable compared to the final product.
Criticisms of Weber’s Least Cost Theory
Oversimplifies the factor that influence location of production.
Fails to consider factors such as
Government policies
Cultural preferences
Environmental concerns
Formal Economy
Economic activities that are recognized by law and are overseen by the government.
Ex: Doctor, Server, Teachers
Informal Economy
Economic activities and jobs that are not regulated or protected by the government.
Ex: Street vendors, domestic work, or unregistered small businesses.
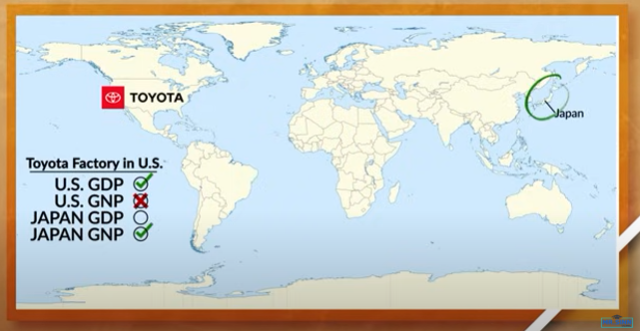
Gross National Product (GNP)
The total economic output produced by a country’s residents and businesses, regardless of their location, during a specific period of time.
Different from GDP because it factors in both domestic production and production of a country’s citizens who are living abroad.
If a country’s GNP is higher than their GDP, it could mean the following:
There is a lot of significant amount of citizens living abroad and no longer.
Lots of foreign investments and production happening inside the countries boundaries.
Gross National Income (GNI)
The total amount of income generated by a country’s residents and businesses, both domestically and abroad, in a given year.
Different from GNP because it focuses on the income generated by a country’s citizens and company while GNP focuses on production.
GNI per capita
Often used as a way to better understand a country’s standard of living.
GNI/total population = GNI per capita
Higher= better standard of living
Doesn’t factors in for the following:
Income inequality
Quality of life
Other social aspects
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
A composite index that measures gender-based inequalities in health, education and economic participation.
Measures it in three different areas:
Reproductive health
measured by the maternal mortality ratio: a measure of the number of maternal deaths per 100,000 live births that occur due to pregnancy or childbirth-related complications.
also measured by adolescent fertility rate: the number of live births per 1,000 women aged 15-19 years old in a specific year.
Empowerment
measured by the amount of government positions held by each gender and the amount of secondary and higher education levels obtained by each gender.
Labor Market
measured by the women’s participation in the workforce.
Higher GII = more inequalities in the country (ranges from 1-10)
0= no inequalities in the country
Human Development Index (HDI)
An index that is used to measure the social and economic development of a country.
Determined by analyzing a country’s life expectancy, expected year of schooling and gross national income per capita.
Higher the score = the better the country’s human development (ranges from 1 to 10)
Global Gender Gap Index
Uses four benchmarks to measure the index:
Economic Participation and Opportunity
Educational Attainment
Health and Survival
Political Empowerment
Microloans
Small loans provided to individuals or small businesses who are typically excluded from traditional banking services.
Risks:
If the person is not able to pay the loan back, they will go into debt and the loan will act opposite of what it was suppose to do.
Microfinancing
A category of financial services that are for individuals and small businesses who lack access to traditional banking services.
Often includes access to a saving account, insurance, or money transfer services.
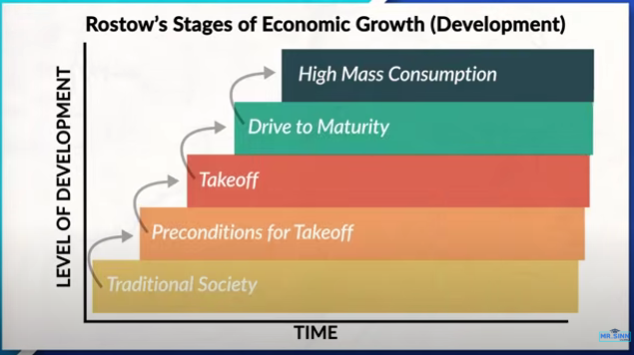
Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth (Development)
Five stages of development that countries generally go through as they develop economically.
Five Stages:
1) Traditional Society
2) Preconditions for takeoff
3) Takeoff
4) Drive to maturity
5) High Mass Consumption
Traditional Society (Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth)
Economy mainly subsistent with majority of the population being engaged in the primary sector such as subsistence farmers. Slow economic growth and have little specialization and often lack modern technology.
Preconditions for takeoff (Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth)
Economy begins to grow due to more investment in infrastructure and education as time goes on productivity starts to increase as new industries start to emerge. New industries allow for more jobs to open up in the secondary sector of the economy as more jobs start to be centered around manufacturing.
Takeoff (Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth)
Rapid economic growth occurs during this stage. Jobs start to transition out of traditional agricultural based activities and into industrial activities. Has increased urbanization as more jobs and opportunities continue. States in this stage gets exploited by foreign states as they seek to take advantage of their raw resources.
Drive to maturity (Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth)
When a state starts to specialize more and participates more in global trade all of which helps diversify the economy and create new opportunities for citizens in the tertiary sector. During this stage, we start to see a shift from heavy industrial industries to more consumer goods as economic growth continues to occur and the economy stabilizes. Starting to become more independent.
High Mass Consumption (Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth)
In this stage, economy becomes full fully developed. Society makes products that not only meet the society’s basic needs but their wants as well. Majority of jobs are in the tertiary sector of the economy. The state is now fairly independent from outside influences. They have developed a consumer culture. Economy is centered around consumption rather than manufacturing.
Dependency Theory
A theory that suggests that developing countries are dependent on developed countries for their economic growth.
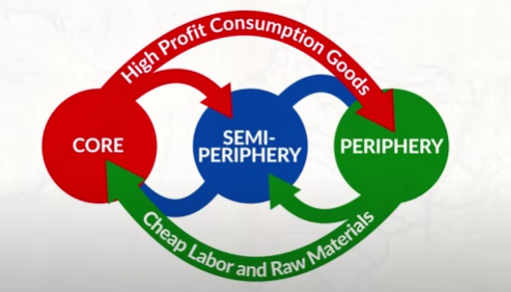
Wallerstein’s World System Theory
Core, semi-periphery, and periphery are all interdependent on each other.
Criticisms of Wallerstein’s Theory:
Fails to account for nongovernmental organizations that offer microfinancing for individuals in developing countries.
Fails to consider programs such as microloans that seek to support individuals in semi-periphery and periphery allowing them to become independent and self-reliant.
Commodity Dependence
When a country has more than 60% of its total exports made up of just commodities (raw materials or agricultural products)
Ex: Venezuela’s petroleum
Globalization
The process by which countries, economies, cultures, businesses, and other people become interconnected and interdependent on one another.
Capital Investment
The funds or resources that a company or individual put into an activity, project, or business with the expectation of generating future profits.
Complementarity Index Score
A measure used in economics and trade to assess the compatibility between the product and the services that two countries produce and trade with each other.
Higher score indicates a more favorable trade relationship between the countries. It is on a scale of 0 to 100.
Comparative Advantage
The ability of a country, individual or organization to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another country, individual, or organization.
Tariff
A tax or duty imposed by a government on goods and services that are imported into the country.
Trade Deficit
A situation where a country imports more goods and services than it exports (Occurs when a country spends more on imports than it earns on its exports)
Neoliberalism
A political and economic philosophy that emphasizes free markets, privatization, and limited government intervention in the economy.
Policies often focus on:
Private ownership
Free trade
Individual freedom over government controlled businesses
World Trade Organization
Is an international organization whose primary purpose is to open trade for the benefit of all.
International Monetary Fund
Three Critical Missions:
Furthering international monetary cooperation
Encouraging the expansion of trade and economic growth
Discouraging policies that would harm prosperity
Mercosur
A South American trade bloc, aimed at promoting free trade and the fluid movement of goods, people, and currency. Its purpose is to create a common market, encourage economic development, and strengthen democratic cooperation among member countries.
European Union
Goals:
Establish an internal market
Achieve sustainable development based on balance economic growth and price stability and a highly competitive market economy with full employment and social progress.
Enhance economic, social and territorial cohesion and solidarity among EU countries.
Establish an economic and monetary union whose currency is the euro.
OPEC
Objective is to co-ordinate and unify petroleum policies among member countries, in order to secure fair and stable prices for petroleum producers.
NAFTA/USMCA
Trade agreement between Canada, the United States, and Mexico, aimed to eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers between the three countries.
Free Trade
International trade where there are no restrictions or barriers that increase the cost of trade or prevent trade from occurring.
Criticisms of Neoliberal Policies
Prioritize the need for wealthier corporations and states over developing regions which often increases economic inequality.
Deregulation of different markets can lead to less accountability and government oversight which may increase in unethical behavior by different institutions.
Economic Restructuring
A significant shift in production, employment, investment, trade patterns, or underlying economic systems and process (Often driven by technological change, globalization, consumer preferences, or government policies)
Offshoring
The process of relocating a business process or service to a foreign country.
Ex: Company A moves it manufacturing centers out of the core country into a semi-periphery country to take advantage of lower labor costs.
Advantages:
Lower labor costs
Tax incentives
Favorable economic conditions
Outsourcing
When a business contracts out a service or job to an external provider in order to reduce their costs and increase their efficiency.
Ex: Company A outsources their bookkeeping to a professional accounting firm to take advantage of the accounting firm experts.
Economies of Scale
As a company grows, it is able to reduce the average cost to produce its product.
As companies get larger they have access to more capital, which allows them to scale up production and produce more at a cheaper rate.
International Division of Labor
A concept that describes how countries utilize their comparative advantage to specialize in different economic activities, resources, and capabilities.
Often results in a hierarchy of countries, with some countries becoming more dominant in the global market.
Urban Blight
Homes that hold close to no value due to being abandoned, vandalized and/or stripped.
Deindustrialization
Loss of industrial activity in one region, usually because of relocation to developing countries with cheaper labor and low economic standards. Example: Rust Belt of US is debilitated due to deindustrialization.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
Regions within a country that provide different economic incentives with the objective of attracting foreign investment and promoting economic growth.
Free Trade Zones (FTZ)
A region within a country where imported goods can be stored and processed without being subject to tariffs or trade barriers.
Export Processing Zones (EPZs)
Regions within a country’s borders that offer special economic regulations and incentives to promote the production of goods and services for export.
Multiplier Effect
A phenomenon where an original investment by an individual, business, government or organization leads to a chain reaction of spending and increased economic activity.
Fordism
A system of production that emphasizes mass production of standard goods.
Post-Fordism
A system of production that emphasizes more flexible production methods where workers are trained in multiple tasks and produce custom goods.
Just-In-Time Delivery
A production and inventory control system where products and materials are delivered to the manufacturing plant precisely when they are needed in the production process.
Growth Poles
Specific regions, cities or economic sectors that are considered centers of economic growth and development.
Sustainability
The use of the Earth’s resources in a way that ensure those resources will still be available in the future.
Resource Depletion
Refers to the depletion or exhaustion of natural resources as a result of unsustainable practice and excessive consumption.
Degradation
Refers to deterioration or decline in quality of natural resources or ecosystem due to human activities.
Ecotourism
A form of tourism that focuses on responsible travel to natural areas that conserve the environment and improve the well-being of the local people.
Characteristics of Ecotourism:
Guided tours that provide information about the local culture and environment.
Activities that promote conservation
Tours that are often run by small-scale low impact operations
United Nations Sustainable Goals
List of 17 goals that focus on a sustainable world by reducing inequalities.
Mercantilism
An economic system where a country tries to become rich and powerful by selling more goods to other countries than it buys, and by accumulating gold and silver
Protectionism
An economic policy where governments restrict international trade to protect domestic industries and jobs.
Containerization
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers with standardized dimensions, that has dramatically reduced the time and cost necessary for shipping.
Point Source Pollution
pollution that originates from a single, identifiable, and confined location.
A trade bloc
An intergovernmental agreement, often part of a regional organization, where participating states reduce or eliminate trade barriers like tariffs and quotas