ACCT 300A - Combined Midterm Material
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Current Assets?
Cash and other assets a company expects to convert into cash, sell, or consume either in one year or in the operating cycle, whichever is longer.
Item - Cash and cash equivalents, what is Basis of Valuation?
Fair value
Item - Short term investments, what is Basis of Valuation?
Generally fair value
Item - Receivables, what is Basis of Valuation?
Estimated amount collectible
Item - Inventories, what is Basis of Valuation?
Lower-of-cost-or-net realizable value/market
Item - Prepaid expenses, what is Basis of Valuation?
Cost
Cash?
Most liquid asset
Standard medium of exchange
Basis for measuring and accounting for all items
Current asset (If unrestricted)
Examples of cash?
Coins
Currency
Available funds on deposit at the bank
Money orders, certified checks, cashier’s checks, personal checks
Bank drafts
Savings accounts
Receivables?
Are claims held against customers and others for money, goods, or services.
Receivables as are identified in the Balance Sheet as?
Current
Non-current
Trade
Non-trade
Trade Receivables?
Refers to receivable generated by selling a product or
providing a service to a customer.
What do trade receivables include?
Accounts receivables
Notes Receivables
Note receivables arising from other transactions like financing?
Are not trade receivables.
What does the Accounts Receivable Turnover evaluate?
The liquidity of accounts receivable.
Accounts Receivable Turnover?
Measures number of times, on average, a company collects receivables during the period.
How to increase A/R turnover?
Do a better job at collecting receivables
Give rewards for consistent payment from customers (time)
Don’t choose customers with bad credit scores
Less strict policies
Average Days to Collect Receivables?
General rule is that the average collection period should not greatly exceed the credit term period.
Liquidity Ratios?
Measures of the company's short-term ability to pay its maturing obligations.
Activity Ratios?
Measures of how effectively the company uses its assets.
Profitability Ratios?
Measures of the degree of success or failure of a given company or division for a given period of time.
Coverage Ratios?
Measures of the degree of protection for long-term creditors and investors.
Basic Format of Cash Flow Statement?
Cash flows from operating activities
Cash flows from investing activities
Cash flows from financing activities
Net increase (decrease) in cash
Cash at beginning of year
Cash at end of year
Cash flows from operating activities - Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities (Orange slide #1)? - Know how to calculate - 3 adjustments
+ Depreciation/depletion/amortization expense
+ Loss on sale of long-term assets
- Gain on sale of long-term assets
- Increases in current assets other than cash
+ Decreases in current assets other than cash
+ Increases in current liabilities
- Decrease in current liabilities
= Net cash provided by (used for) operating activities
Cash Flow from Investing Activities? (Orange slide #2)
+ Sales of long-term assets
- Purchases of long-term assets
+ Sale of investments
- Purchase of investments
+ Collections of notes receivable
- Loans to others
= Net cash provided by investing activities
Cash Flow from Financing Activities? (Orange slide #3)
+ Issuance of shares
- Repurchase of shares
+ Borrowing
- Payment of notes and bonds payable
- Payment of dividends
= Net cash provided by financing activities
Significant financing and investing activities that do not affect cash are reported in?
Either a separate schedule at the bottom of the statement or cash flows or in the notes
Examples of significant non-cash activities include?
Issuance of common stock to purchase assets
Conversion of bonds into common stock
Issuance of debt to purchase assets
Exchanges of long-lived assets
Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity - Present value of a series of equal rents to be withdrawn or received at?
Equal intervals
When do periodic rents in the Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity occur?
At the end of the period
When it comes to frequency of compounding, the greater the frequency?
The greater the effective interest rate or yield
Future Value of a Single Amount formula?
FV = PV (FVFni)
FVFni = (1+i)^n
Present Value of a Single Amount formula?
PV = FV (PFVni)
PVFni = 1/(1+i)^n
Factor most likely given
What is the present value of $73,466 to be received or paid in 5 years discounted at 8% compounded annually?
Factor = .68058
Look at table (n = 5 years, i = 8%)
PV = FV(.68058)
$73,466 × 0.68
= $50,000
On January 1, 2020, Gore Co. sold to Cey Corp. $900,000 of its 10% bonds for $796,766 to yield 12%. Interest is payable semiannually on January 1 and July 1. What amount should Gore report as interest expense for the six months ended June 30, 2020?
Principal = $796,766 (What it sold for)
Interest rate = 12%
796,766 × 12%/2 (b/c semiannual)
$47,806
Interest expense formula?
Principal * Interest rate
The following information is available for Swifty Corporation:
Allowance for doubtful accounts at December 31, 2019: $23,000
Credit sales during 2020: $1,110,000
Accounts receivable deemed worthless and written off during 2020: $29,000
As a result of a review and aging of accounts receivable in early January 2021, it has been determined that an allowance for doubtful accounts of $16,000 is needed at December 31, 2020. What amount should Swifty record as "bad debt expense" for the year ended December 31, 2020?
Suppose that Bishop Company does not record as a purchase certain goods that it owns and does not count them in ending inventory - Balance Sheet - Inventory?
Understated
Suppose that Bishop Company does not record as a purchase certain goods that it owns and does not count them in ending inventory - Balance Sheet - Retained earnings?
No effect
Suppose that Bishop Company does not record as a purchase certain goods that it owns and does not count them in ending inventory - Balance Sheet - Accounts payable?
Understated
Suppose that Bishop Company does not record as a purchase certain goods that it owns and does not count them in ending inventory - Income Statement - Purchases?
Understated
Suppose that Bishop Company does not record as a purchase certain goods that it owns and does not count them in ending inventory - Income Statement - Cost of goods sold?
No effect
Suppose that Bishop Company does not record as a purchase certain goods that it owns and does not count them in ending inventory - Income Statement - Net income?
No effect
Suppose that Bishop Company does not record as a purchase certain goods that it owns and does not count them in ending inventory - Income Statement - Ending inventory?
Understated
The understatement does not affect cost of goods sold and net income because the errors offset one another.
Cost of goods sold
Net income
LIFO Reserve formula?
Ending Inventory FIFO - Ending Inventory LIFO
What are the LIFO reserves for the current year and the previous
Note 1 (partial): Inventories. Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market determined principally by the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method. If the first-in, first-out (FIFO) cost method had been used, inventories would have been $11,709 higher in the current year and $13,424 higher in the previous year.
LIFO Reserve
Ending Inventory FIFO - Ending Inventory LIFO
13,424 - 11,709 = $1,715
Crest Textiles, Inc. factors $500,000 of accounts receivable with Commercial Factors, Inc., on a WITH recourse basis. Commercial Factors assesses a finance charge of 3 percent of the amount of accounts receivable and retains an amount equal to 5 percent of the accounts receivable (for probable adjustments). Crest Textiles determines that this recourse obligation has a fair value of $6,000. Crest Textiles and Commercial Factors make the following journal entries for the receivables transferred without recourse.
How much is the loss from sales?
$500,000 × 3% + 6,000
$21,000
Crest Textiles, Inc. factors $500,000 of accounts receivable with Commercial Factors, Inc., on a WITHOUT recourse basis. Commercial Factors assesses a finance charge of 3 percent of the amount of accounts receivable and retains an amount equal to 5 percent of the accounts receivable (for probable adjustments). Crest Textiles determines that this recourse obligation has a fair value of $6,000. Crest Textiles and Commercial Factors make the following journal entries for the receivables transferred without recourse.
How much is the loss from sales?
$500,000 × 3%
$15,000
Crest Textiles, Inc. factors $500,000 of accounts receivable with Commercial Factors, Inc., on a WITH recourse basis. Commercial Factors assesses a finance charge of 3 percent of the amount of accounts receivable and retains an amount equal to 5 percent of the accounts receivable (for probable adjustments). Crest Textiles determines that this recourse obligation has a fair value of $6,000. Crest Textiles and Commercial Factors make the following journal entries for the receivables transferred without recourse.
What are the journal entries?
Dr. Cash $460,00
Dr. Due from factor $25,000
Dr. Loss on Sales of Receivable $21,000
Cr. Accounts (Notes Receivable) $500,000
Cr. Recourse Liability $6,000
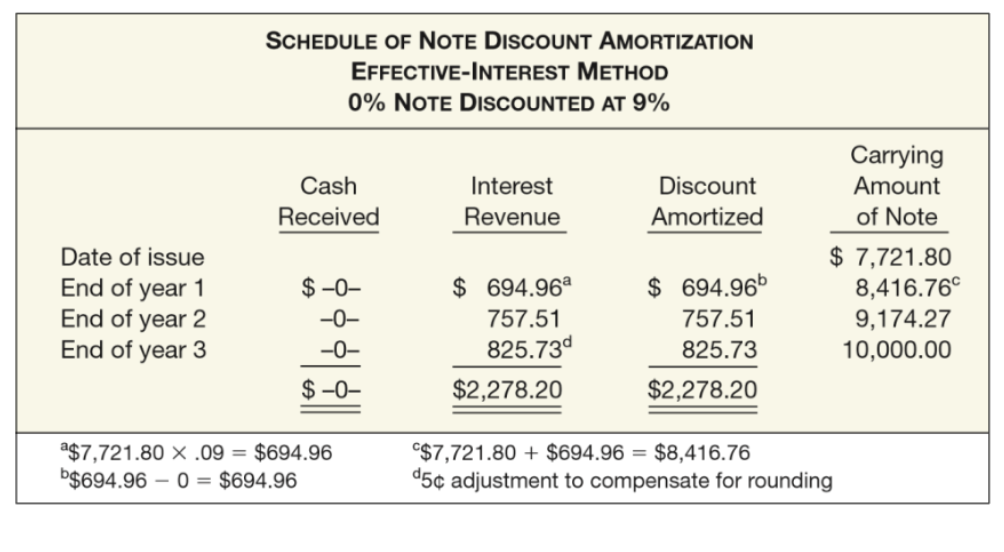
Check image - Prepare the journal entry to record the interest revenue at the end of the second year
Dr. Discount on Notes Receivable $757.51
Cr. Interest revenue $757.51
What is a LIFO layer?
A LIFO layer refers to a distinct unit of inventory that is costed under the Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) inventory accounting method. LIFO assumes that the most recently acquired inventory items are sold first. A LIFO layer represents inventory costs accumulated during a specific period under this method.
In other words, a new layer of inventory is added to the cost of ending inventory
Gross Corporation adopted the dollar-value LIFO method of inventory valuation on December 31, 2019. Its inventory at that
date was $1,100,000
‘??and the relevant price index was 100. Information regarding inventory for subsequent years is as
follows:
Dates:
Dec. 31 2020
Dec. 31 2021
Dec. 31 2022
Inventory at current prices:
$1,296,000
$1,450,000
$1,750,000
Current price index:
108
125
140
Find cost of ending inventories for all 3 dates
1,208,000
1,164,800
1,290,800
Sunflower Corp. is purchasing new equipment with a cash cost of $425,000 for a production line. The manufacturer has offered to accept $98,500 payment at the end of each of the next six years. How much interest will Sunflower Corp. pay over the term of the loan?
Payment x Periods
98500 × 6 = $591,000
$591,000 - 425,000 = $166,000
White Corporation uses the FIFO method for internal reporting purposes and LIFO for external reporting purposes. The balance in the LIFO Reserve account at the end of 2020 was $340,000. The balance in the same account at the end of 2021 is $520,000. White's Cost of Goods Sold account has a balance of $2,450,000 from sales transactions recorded during the year. What amount should White report as Cost of Goods Sold in the 2021 income statement?
COGS here: LIFO Reserve 2021 - LIFO Reserve 2020 + COGS Balance
520,000 - 340,000
$180,000
2,450,000 + 180,000
2,630,000
Mountain Roads sold $150,000 of goods and accepted the customer's $150,000 8%, 1-year note receivable in exchange. Assuming 8% approximates the market rate of return, what would be the debit in this journal entry to record the sale?
Dr. Notes Receivable $150,000
Cr. Sales Revenue $150,000
Assume Valleyview Corp., an equipment distributor, sells a piece of machinery with a list price of $890,000 to Harrison Inc. Harrison will pay $950,000 in one year. Valleyview Corp. normally sells this type of equipment for 95% of list price. How much should be recorded as sales revenue?
95% x list price
$890,000 × 0.95
845500
If a potential investor wants to assess the ability of a company to take effective actions to alter the amounts and timing of cash flows so it can respond to unexpected needs and opportunities, the investor is assessing?
Financial flexibility
On a classified balance sheet, which of the following should a company report separately?
Assets that differ in their type or expected function
Assets and liabilities with different implications for the company’s financial flexibility
Assets and liabilities with different general liquidity characteristics
The cash debt coverage ratio is often used to assess?
Financial flexibility (2)
Which of the following pairings of an item and a basis of valuation is incorrect?
Receivables
Lower-of-cost or market
Which of the following is included in an owners equity section reported in the balance sheet?
Additional paid-in-capital
Payment of dividends would come under which activity on the statement of cash flows
Financing
Major limitations of the balance sheet include all of the following except?
Only amounts known with absolute certainty are reported
Receipt of interest from a Note Receivable would be reported as a cash inflow in which of the following sections?
Operating
Which of the following describes the use of present value concepts applied to environmental liabilities
Determining the fair value of future obligations for asset retirements
In solving single-sum problems, which of the following values can be calculated?
Future value
Present value
Number of periods
Interest rate
When the future value of an annuity due is computed, the number of compounding periods will always be
Equal to the number of rents
On December 1, 2021, Doreen Company sold land to McKnight Company. The two companies entered into an installment sales contract at a predetermined interest rate. The contract required five equal annual payments with the first payment due on December 1, 2021, the date of the sale. What present value concept is appropriate for this situation?
Present value of an annuity due 1 for five periods
A deferred annuity is one in which the rents begin?
After a specified number of periods
Which of the following has an impact on the dollar amount of the interest related to any financing transaction?
Principal
Interest rate
Time
Future value of an interest-bearing transaction is?
Always greater than the present value
Which of the following statements related to an annuity is correct?
The periodic payments must always be the same amount
Sandhill Tag makes an investment today (January 1, 2023). Sandhill will receive $40000 every December 31st for the next six years (2023 - 2028). If Sandhill wants to earn 8% on her investment, what is the most she should invest on January 1, 2023?
Time periods | Factor | |
PV Annuity due | 5 | 4.31213 |
PV Annuity due | 6 | 4.99271 |
PV Ordinary annuity | 5 | 3.99271 |
PV Ordinary annuity | 6 | 4.62288 |
Ordinary annuity = Payment due at the end of each period
Annuity due = Payment due at the start of each period
$40,000 × 4.62288
$184,915