AP Art History 12-47 Form, Function, Content, Context
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
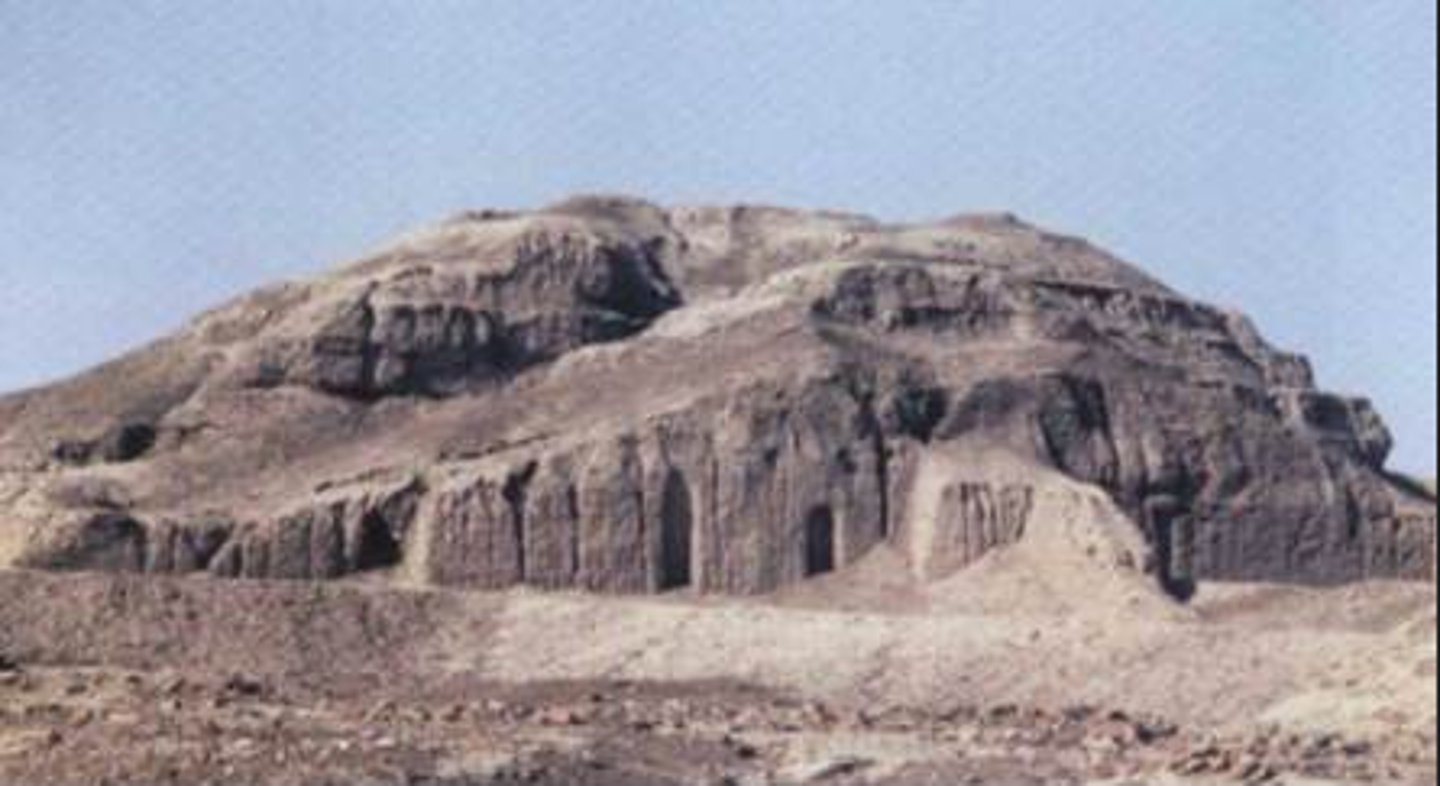
White Temple and its ziggurat
Form:
- mud brick
-collosal scale
-built to resemble mountain
Content:
- sloping walls, bent access (ramp up to enter the altar), 3 entrances
-mosaic surface
Function:
- temple that is a meeting place for humans and gods in the center of the city
-votive figures and dedicated to Anu the sky god
-top temple was only for royals or clergy to enter
Context:
- Uruk; Modern day Warka, Iraq
-Sumerian
- 3500-3000 BCE

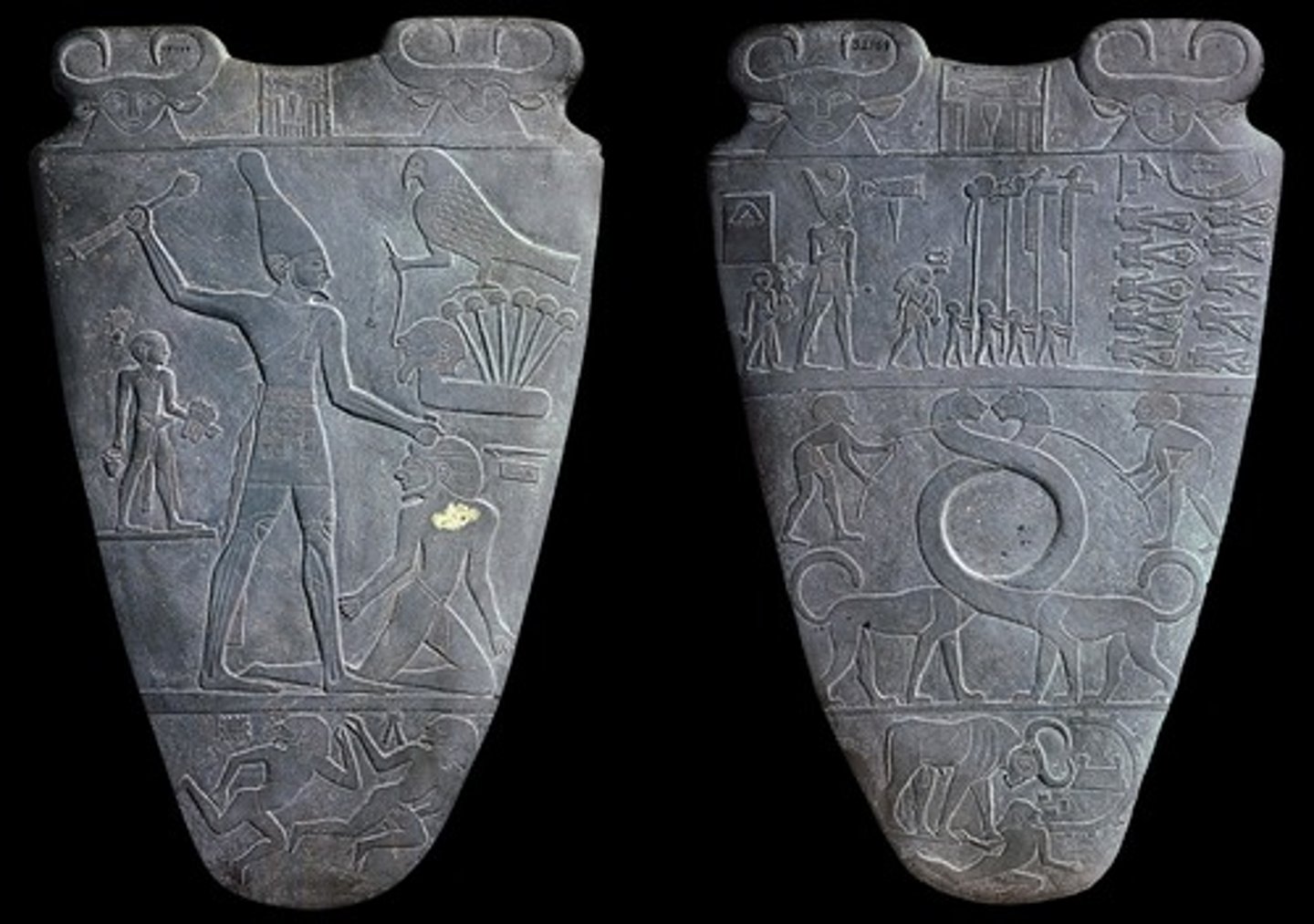
Palette of King Narmer
Form:
-greywacke
-organized in registers
-hierarchic scale
-low relief, twisted perspective
Content:
-Front: Narmer (on large scale) looking on the beheaded bodies of his enemies wearing crown of lower Egypt, harnessed lionesses (symbol of unification), bull knowcking down a city fortress (Narmer knocking over enemies)
-Back: Hawk=Horus, Narmer wearing bowling pin crown (symbol of unification), stands barefoot (he is a divine king), palette for eye makeup, hieroglyphics
Function:
-represents the unification of Egypt and country's growth as a powerful nation
Context:
-found in temple of Horus
-Old Kingdom of Egypt
-3000 BCE

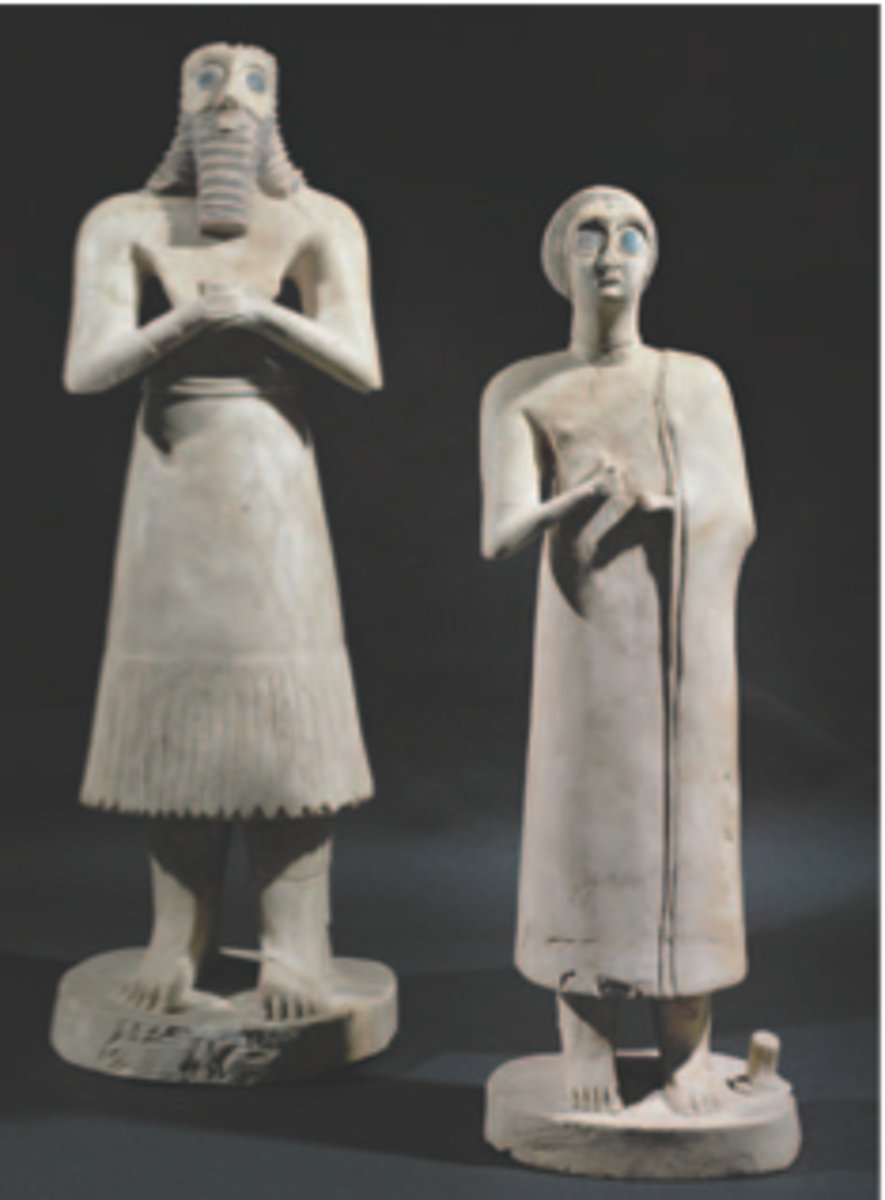
Statues of votive figures
Form:
- bilateral symmetry
- eyes exaggeration (beholding the divine)
-gypsum and black limestone
Content:
-the hands are placed in prayful gesture
- elite male and female figures
Function:
-placed in ziggurat to resemble the people that aren't allowed to be in the ziggurats
Context;
- found in the Square Temple of Eshunna (modern day Tell Asmur, Iraq)
-2700 BCE

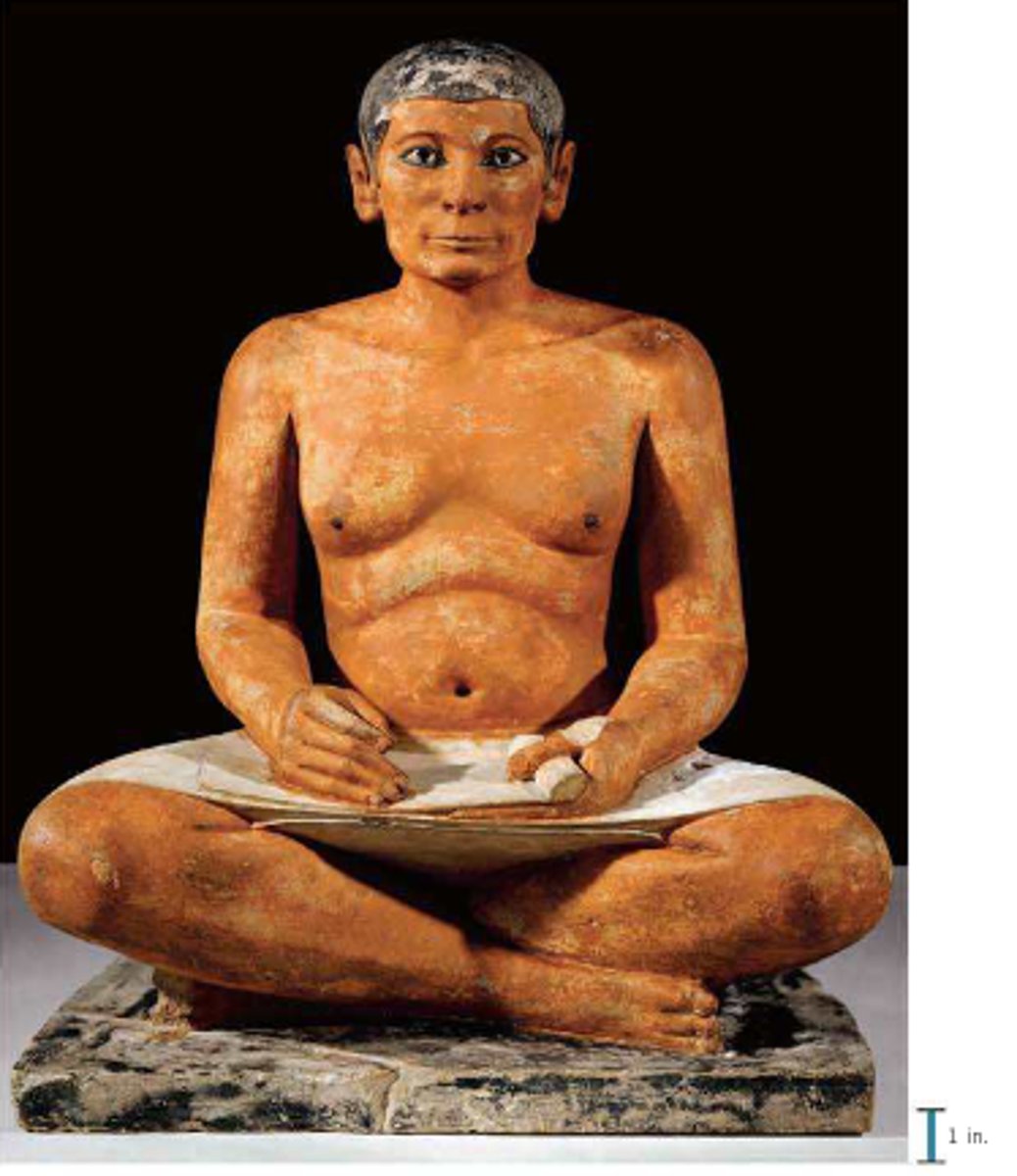
Seated Scribe
Form:
-painted limestone
-crystal limestone eyes
Content:
-royal scribe
-depicted with sagging body (realistic not ideal), thin face
-holding tools to show he is ready to write
Function:
-shows that the scribe is important but not perfect like a pharoah
-made for tomb at Saqqara for the ka
Context:
-Saqqara, Egypt 2500 BCE
-found near tomb (funerary object)

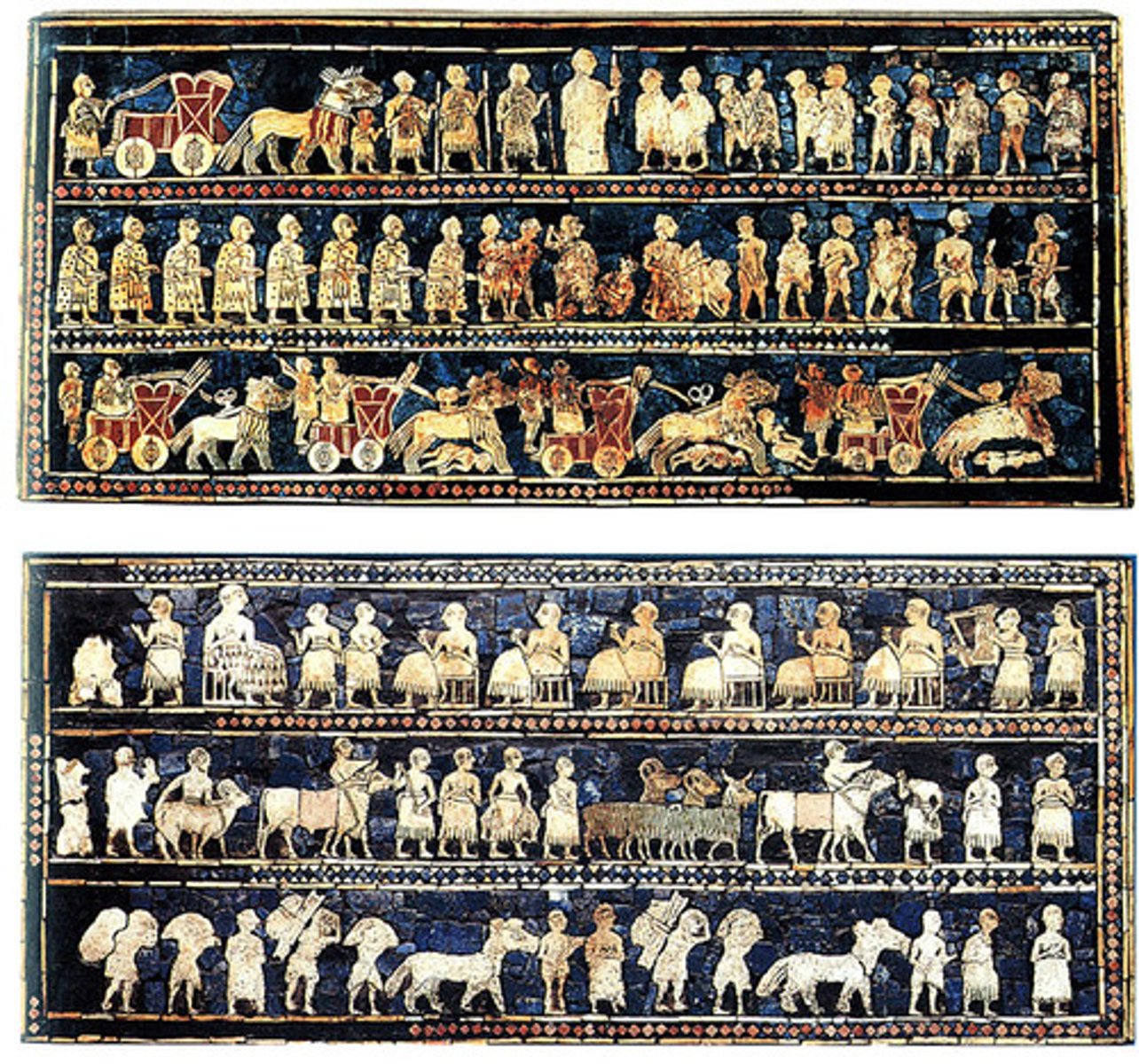
Standard of Ur
Form:
- wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and black limestone
-mosaic
-hierarchic scale to show who was more important in society
-front shoulds, body in profile
Content:
-2 sides: war side and peace side
-war side: shows Sumerian king on larger scale descending from his chariot to inspect captives, lower register shows him riding over dead bodies in his chariot
-peace side: food brought to a banquet, ruler wears a kilt of wool (larger scale)
Function:
- shows the different classes of people
-democratic leadership
Context:
- found in the Royal Tombs at Ur (modern day Iraq)
- 2600-2400 BCE Sumerian

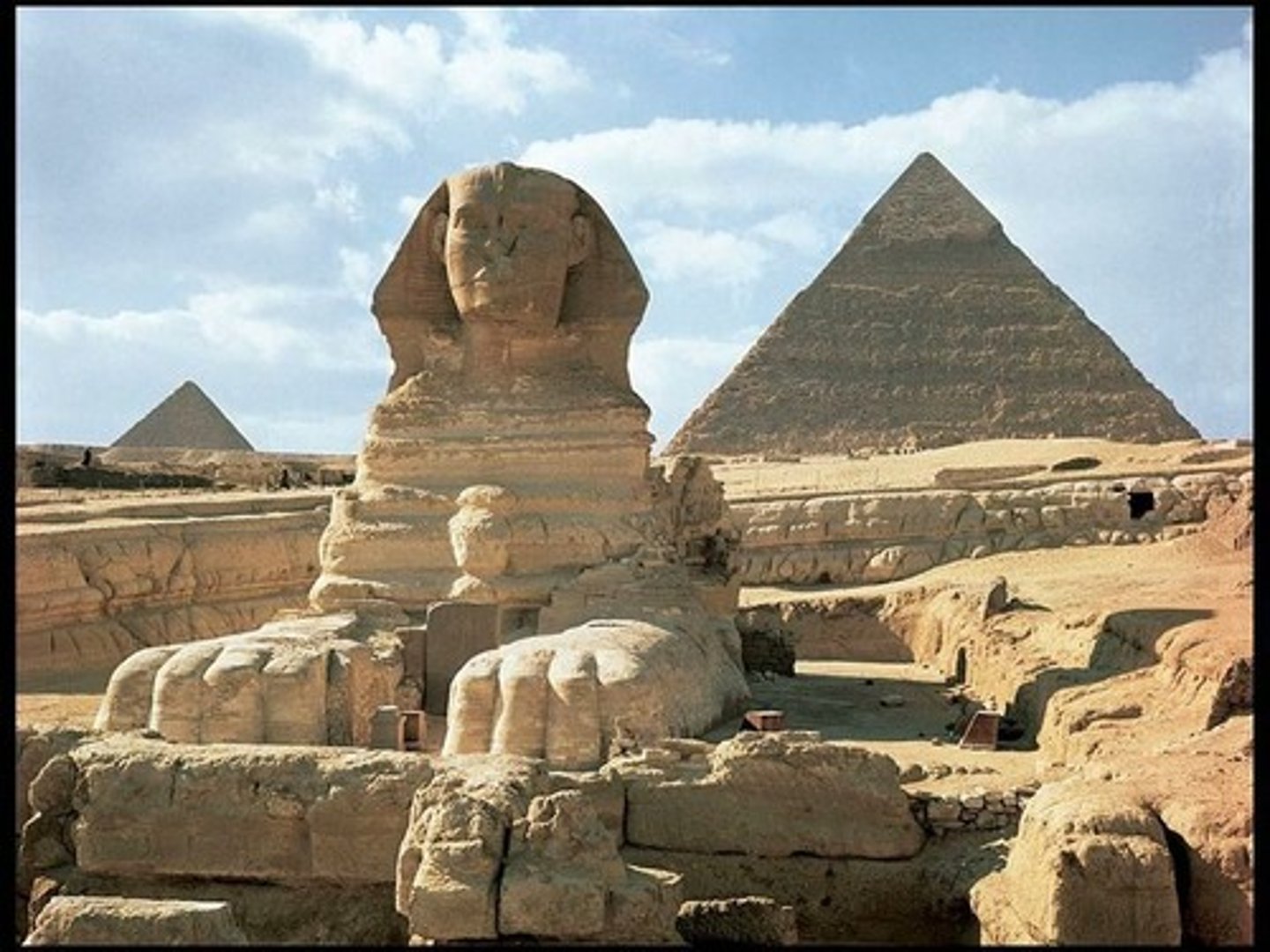
Great Pyramid (Menkaure, Khafre, Khufu) and Great Sphinx
Form:
-square base with 4 sloped sides (represents rays of sun)
-polished limestone
Content:
-pyramids with adjoining funerary complex; get to these through secret passageways
-Great Sphinx: human head with lion head
-descending order on West side of Nile
Function:
-maintain and protect tombs for eternity
-Great Sphinx: protecter the pyramids behind it
Context:
-built by Khufu, Khafre, and Menkuare (each temple name after)
-Khufu temple (oldest and largest)
-Old Kingdom- 2500BCE
-Giza, Egypt

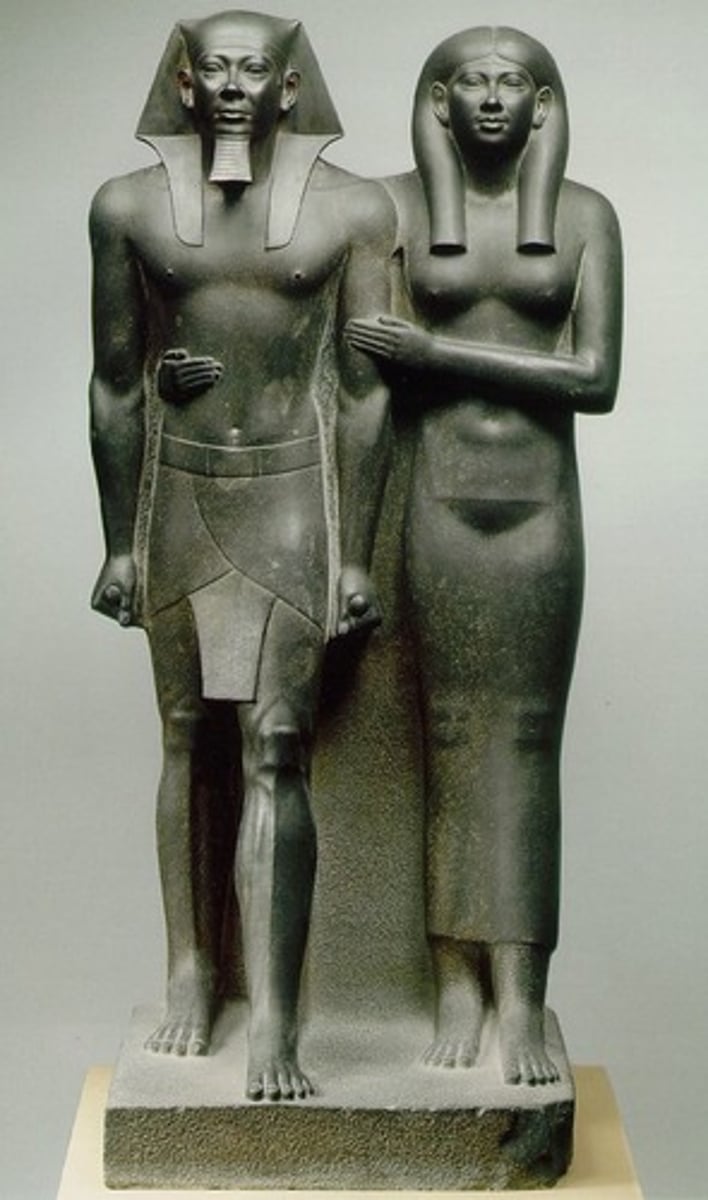
Menkaura and queen
Form:
-greywacke
-under life-size
-symmetrical
-Egyptian style: one foot in front of the other
Content:
-king and queen same height, idealized figures
-pharaoh crown
-wife gives simple affectionate gesture
Function:
-temple sculpture
-symbolize his power and kingship
Context:
-Old Kingdom 2500 BCE

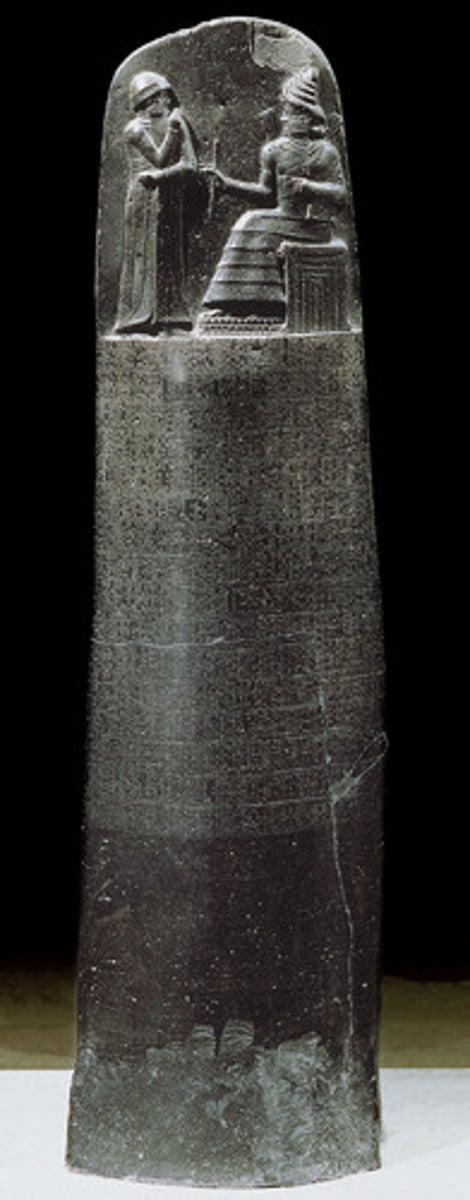
Code of Hammurabi
Form:
-black-stone stele with words carved in it
-basalt
-frontal shoulders, everything else profile
Content:
-divine law code carved in stone
-sun god, Shamash, giving laws to Hammurabi to be king
-god is bigger (hierarchic scale)
Function:
-tells us where the laws came from
-exercises justice and divine authority to carry out the law
Context:
- Babylon (modern day Iran)
-Susian (1760-1750 BCE)

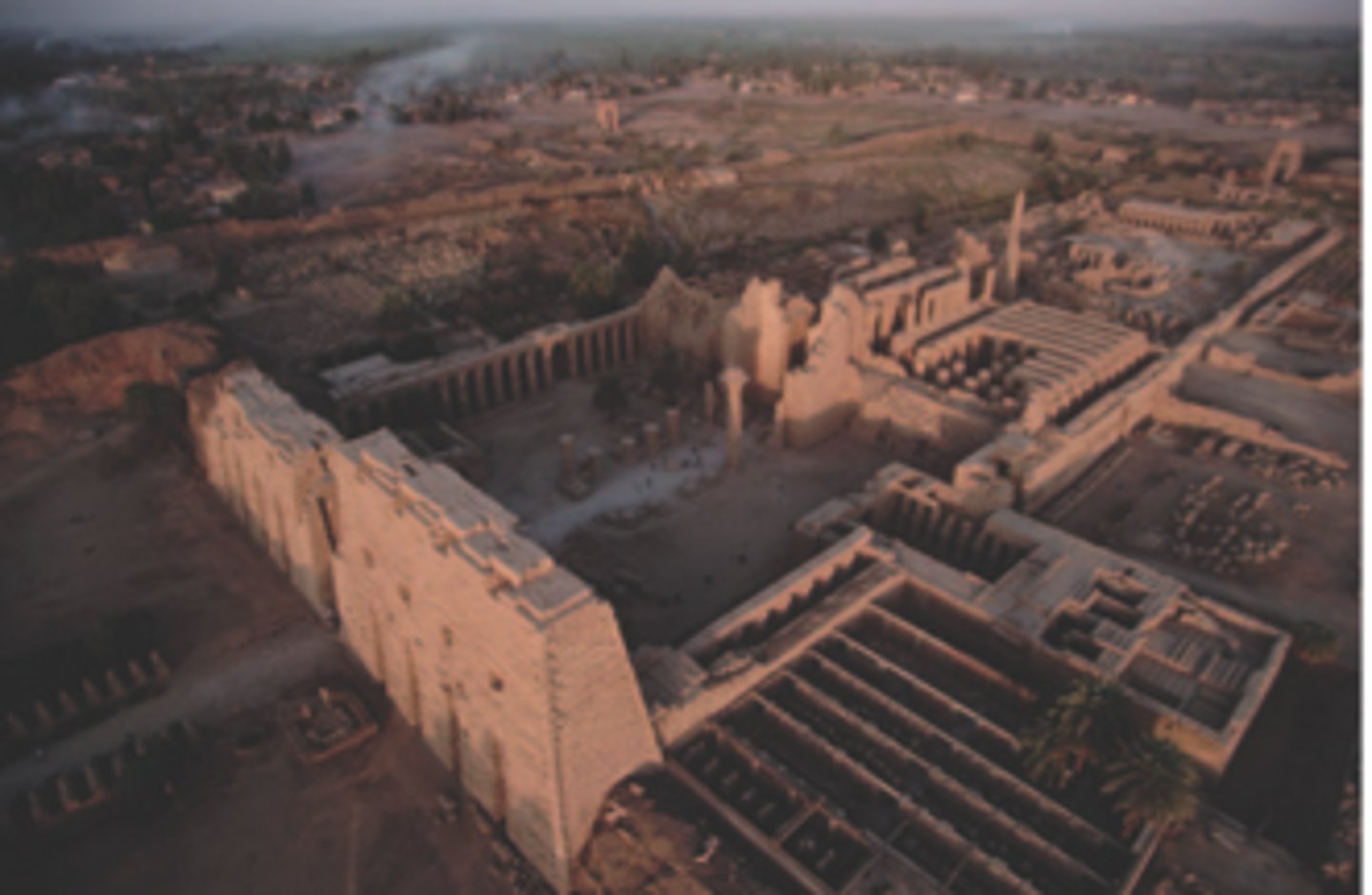
Temple of Amun-Re and Hypostyle Hall
Form:
-cut sandstone and mud brick
-hypostyle hall
-symmetrical plan, axial plan
-open ceilings
-colossal columns with sunken relief
Content:
-134 sandstone columns
-inscriptions/images of kings and gods on walls and columns
-gates (suggesting old world to new world)
Function:
-used for festivities and prayer
-only priests and pharoahs allowed
Context:
-Karnak, near Luxor
-New Kingdom 1250 BCE
-East side of the Nile

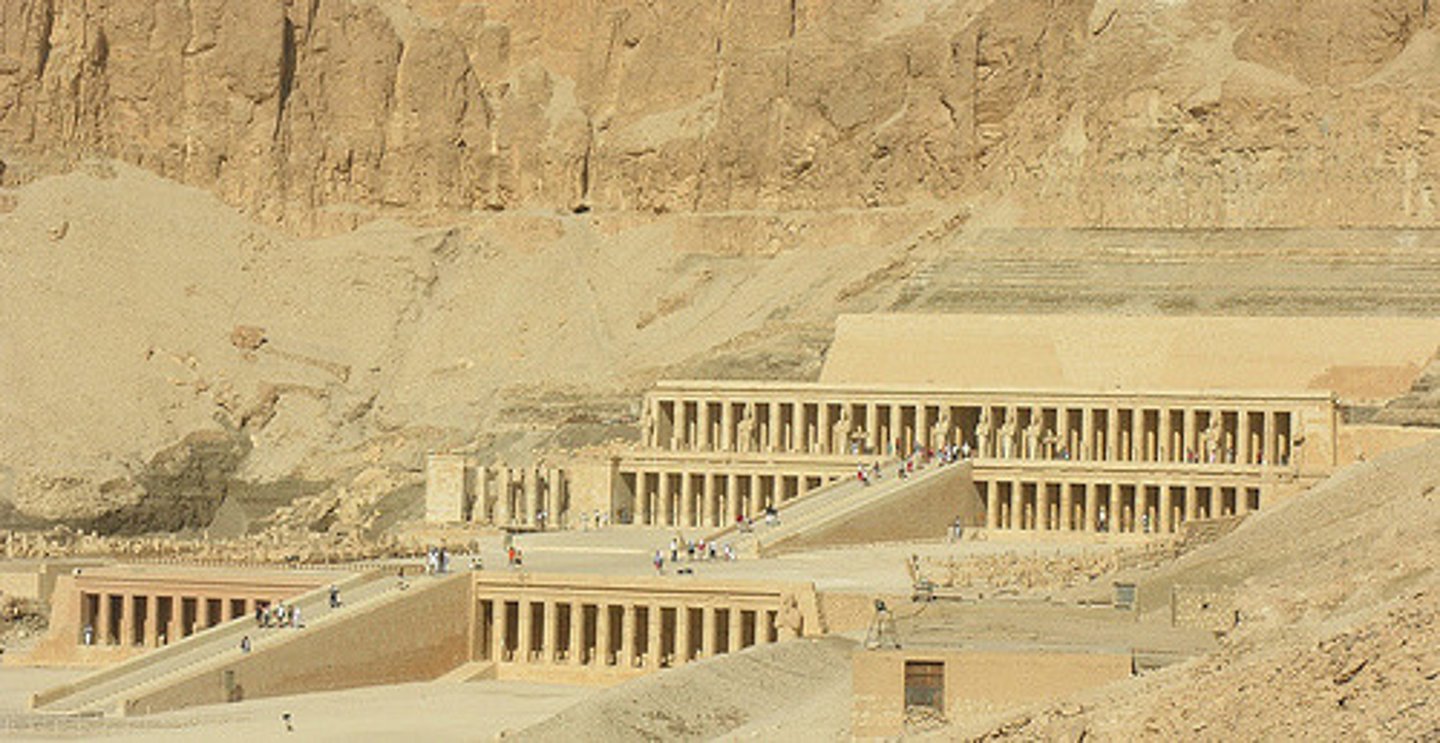
Mortuary Temple of Hatsheput
Form:
-sandstone
-red granite statue
-built into rock cliff
Function:
-mortuary temple for Hatsheput but she wasn't buried there
-statue shows her power in male ways (beard and kneeling is priest-like gesture
Content:
-statue of Hatsheput kneeling: offering plants to Amen, the sun god
-ascent up to temple
-chapels and shrines dedicated to her
-hypostyle hall
Context:
-site specific
-across from Amun temple

Akhenaton, Neferiti, and three daughters
Form:
-sunken relief piece, limestone, hieroglyphics
Content:
-couple receiving blessing from Aten (the sun god-rays shown)
-show husband and wife seated with their children
-rays shining upon the family showing their divinity
Function:
-shows intimacy of the family
-conveys realistic fidgetiness of children
-state religious shift in evolving Egyptian art
Context:
-New Kingdom (Amarna) 1350 BCE

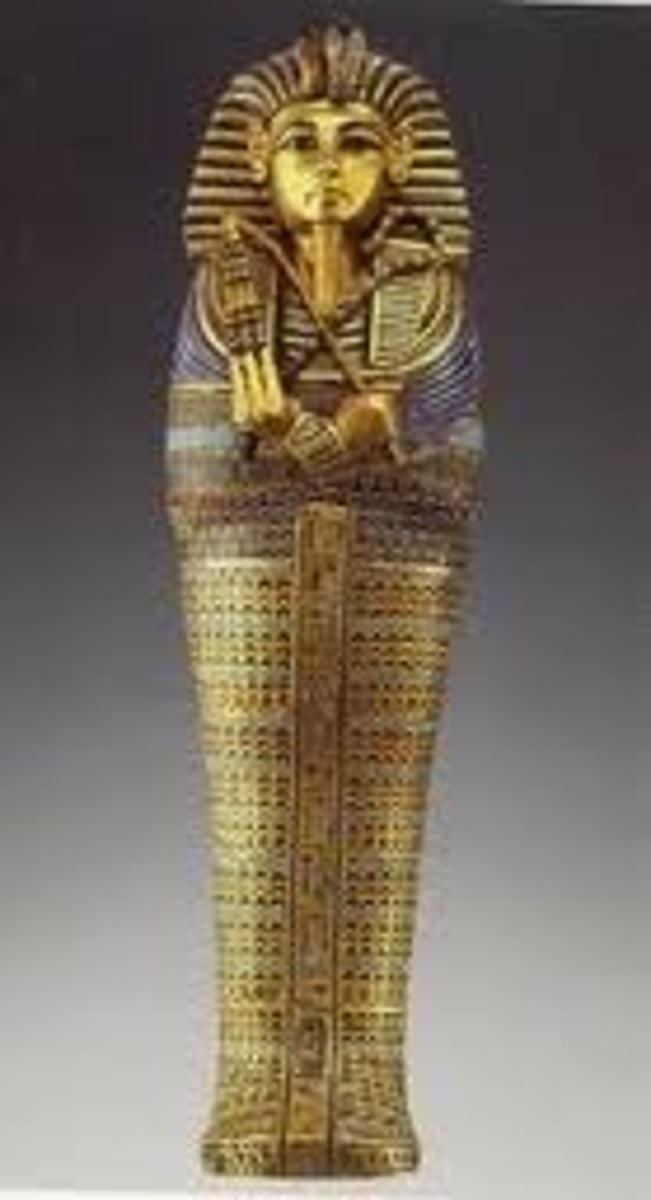
Tutankhamun's tomb (innermost coffin)
Form:
-gold
-inlay with stones and enamel
Content:
-crook and flail- symbols of Osiris
-cobra and vulture coming from headpiece- gods of Upper and Lower Egypt
-Son of Akhenaton
Function:
-sarcophagus (body inside)
-materials used represent the royal wealth (143 objects buried with him)
Context:
- New Kingdom 1325 BCE

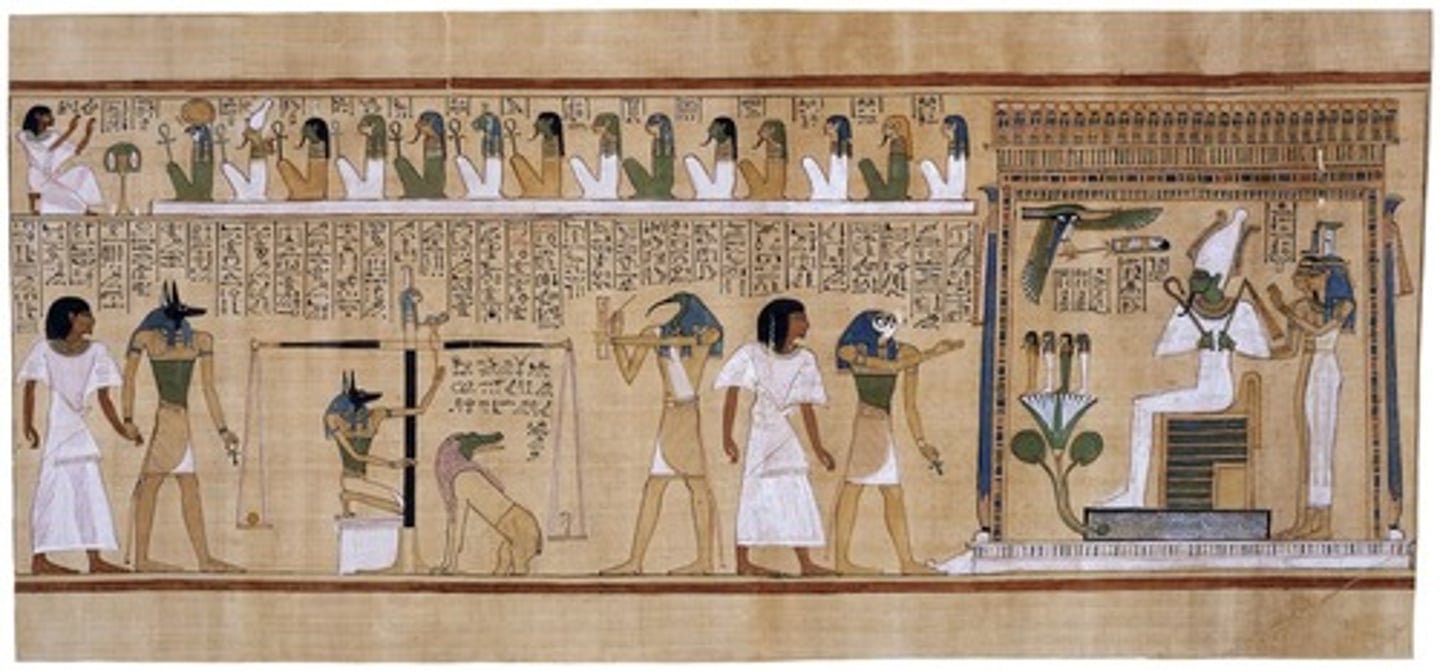
Last Judgement of Hu-Nefer (page from Book of the Dead)
Form:
-painted papyrus scroll
-continuous narrative
Content:
-Hu-Nefer being lead to final judgement
-heart weighed on scale against Osiris (test to see if has a heavy heart)
-sin must weigh less than feather
-Hu-Nefer is accepted into afterlife
Function:
-guide people to the afterlife and make journey from life to death
Context:
-New Kingdom 1275 BCE
-found in Hu-Nefer's tomb
-from the Book of the Dead
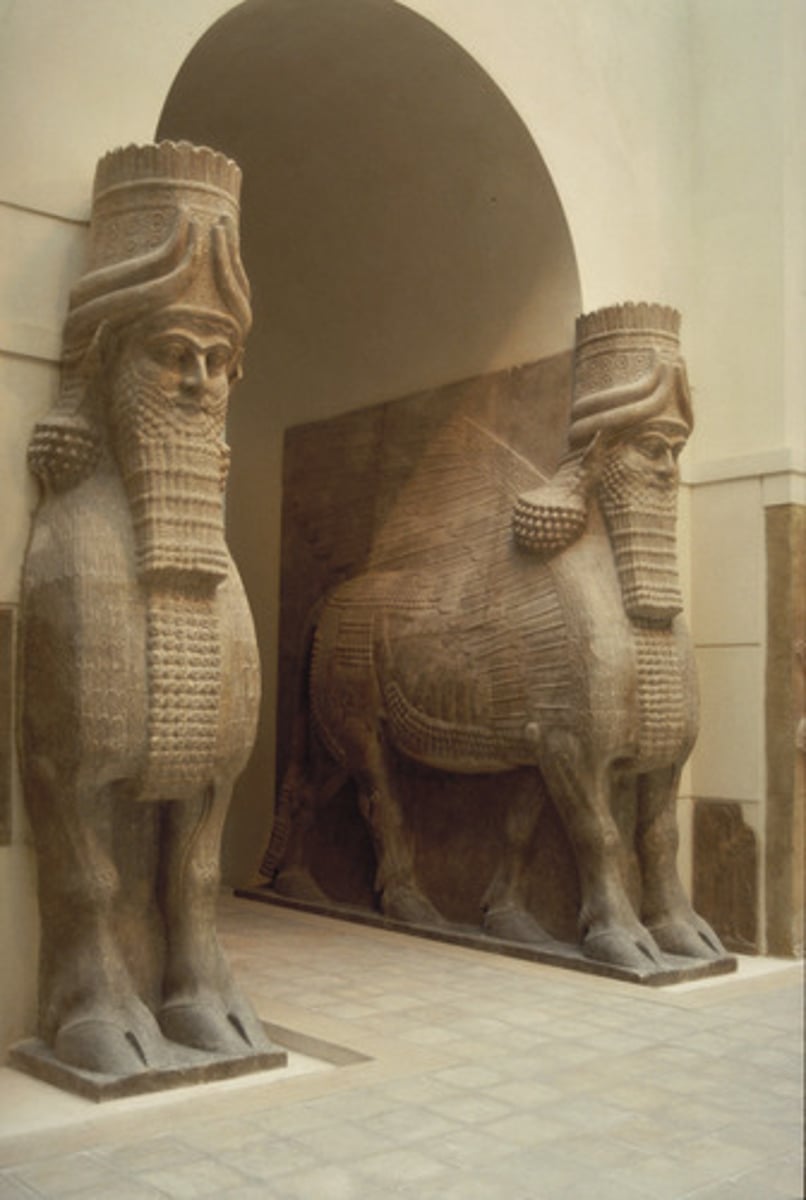
Lamassu
Form:
- alabaster
-limestone
Content:
-god-like figures
-animal body, human head
-5 legs
Function;
-support doorways of Assyrian palaces
-intimidate those who enter
Context:
- from the citadel of Sargon II (modern day Iraq)
- 720-705 BCE
-Sumerian

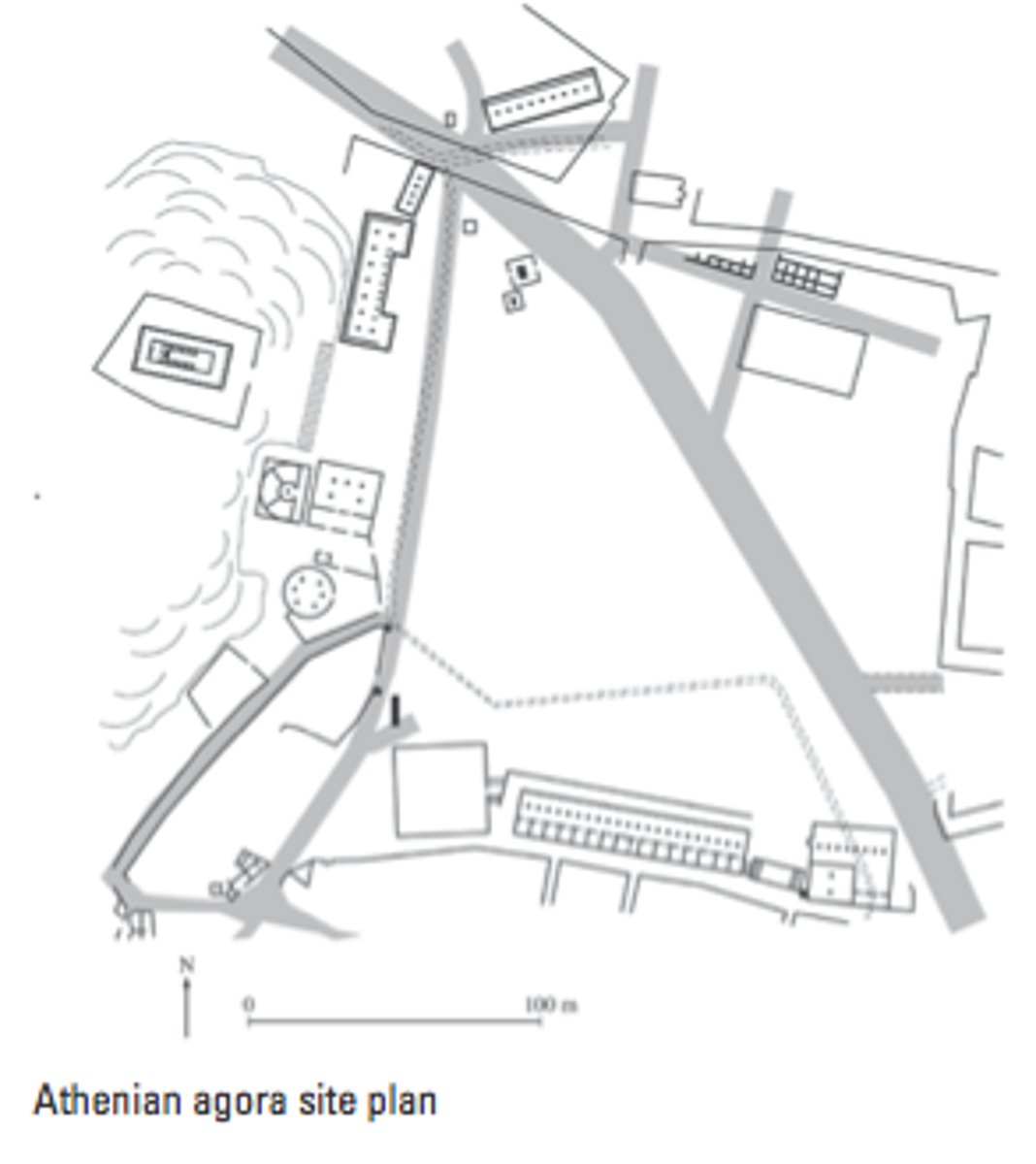
Athenian Agora
Form:
-long buildings (stoa)
-covered places- public markets
-at foot of Acropolis, road that leads up
Function:
-marketplace/meeting area
-temple (pay tribute to Athena)
Content:
-participated with government
-democracy- didn't vote representatives but instead participated directly
Context:
-600-150 BCE
-Athens, Greece
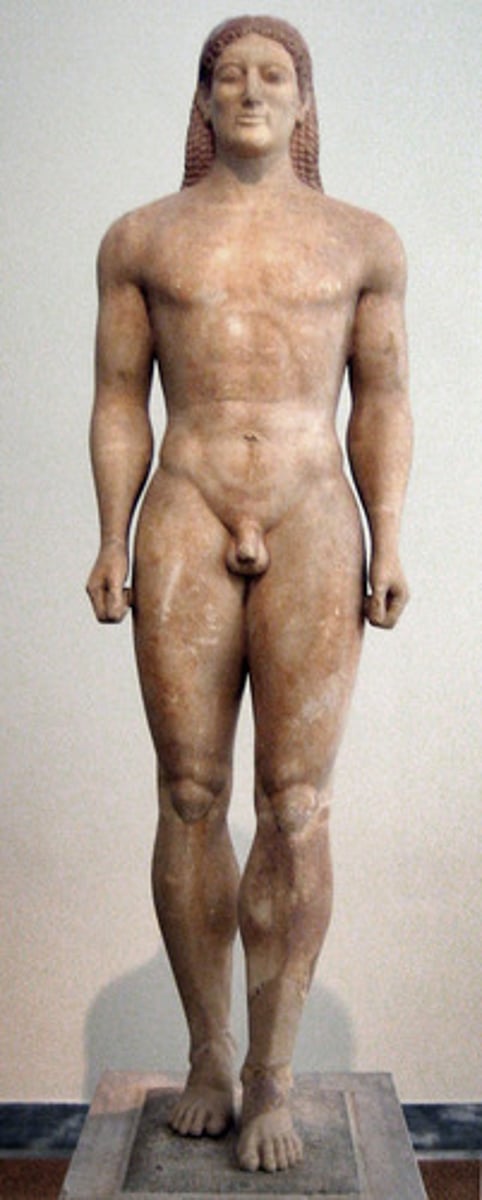
Anavysos Kouros
Form:
-marble with remnant of paint
-archaic smile
-Egyptian inspiration shown through the stance of one foot slightly in front of other
-incaustic paint
Content:
-not a specific civilian depicted (not individualized)
-male nude (warrior)
-observing the human body
Function:
-grave marker
Context:
-530 BCE
-large scaled

Peplos Kore from Acropolis
Form:
-archaic smile
-patterned hair
-marble with paint remains
-smaller scale
Content:
-women with arm out (supposed to hold out a oil lamp but hand broken off)
Function:
-in front of temples to "light the way"
-votive figure
Context:
-530 BCE
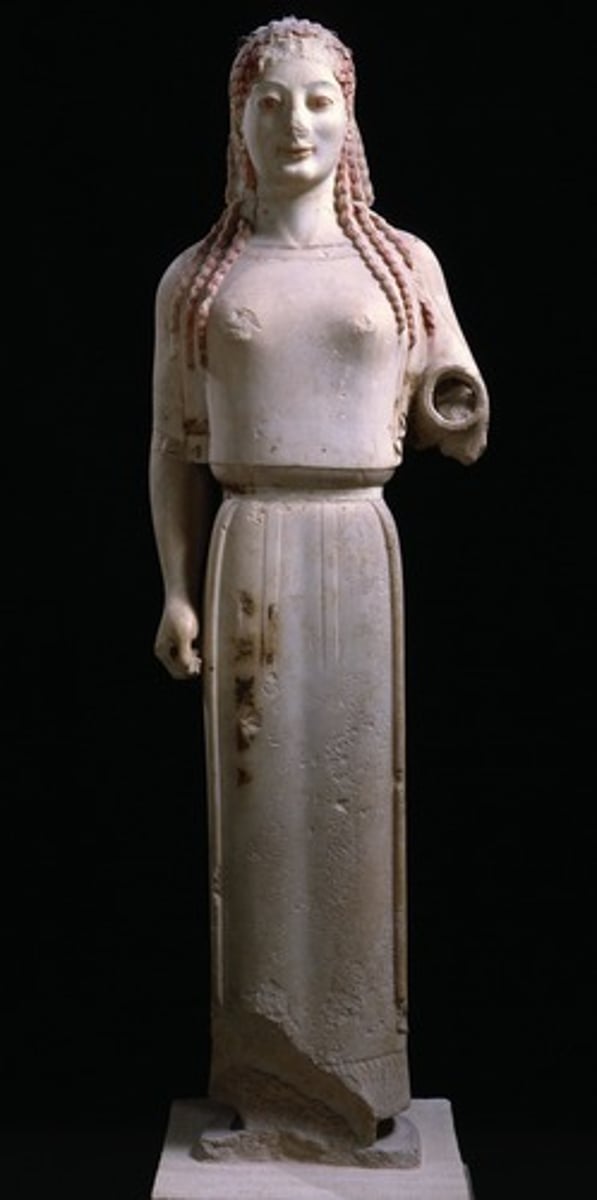

Sarcophagus of the Spouses
Form:
-terra cotta (sign that this is Etruscan)
-lifesize
-archaic smile, patterned hair
-extending arms
Content:
-husband and wife reclining on a couch dining "dining in banquet for eternity"
-four pieces put together
Function:
-funerary container to hold ashes not the body
Context:
-520 BCE Etruscan
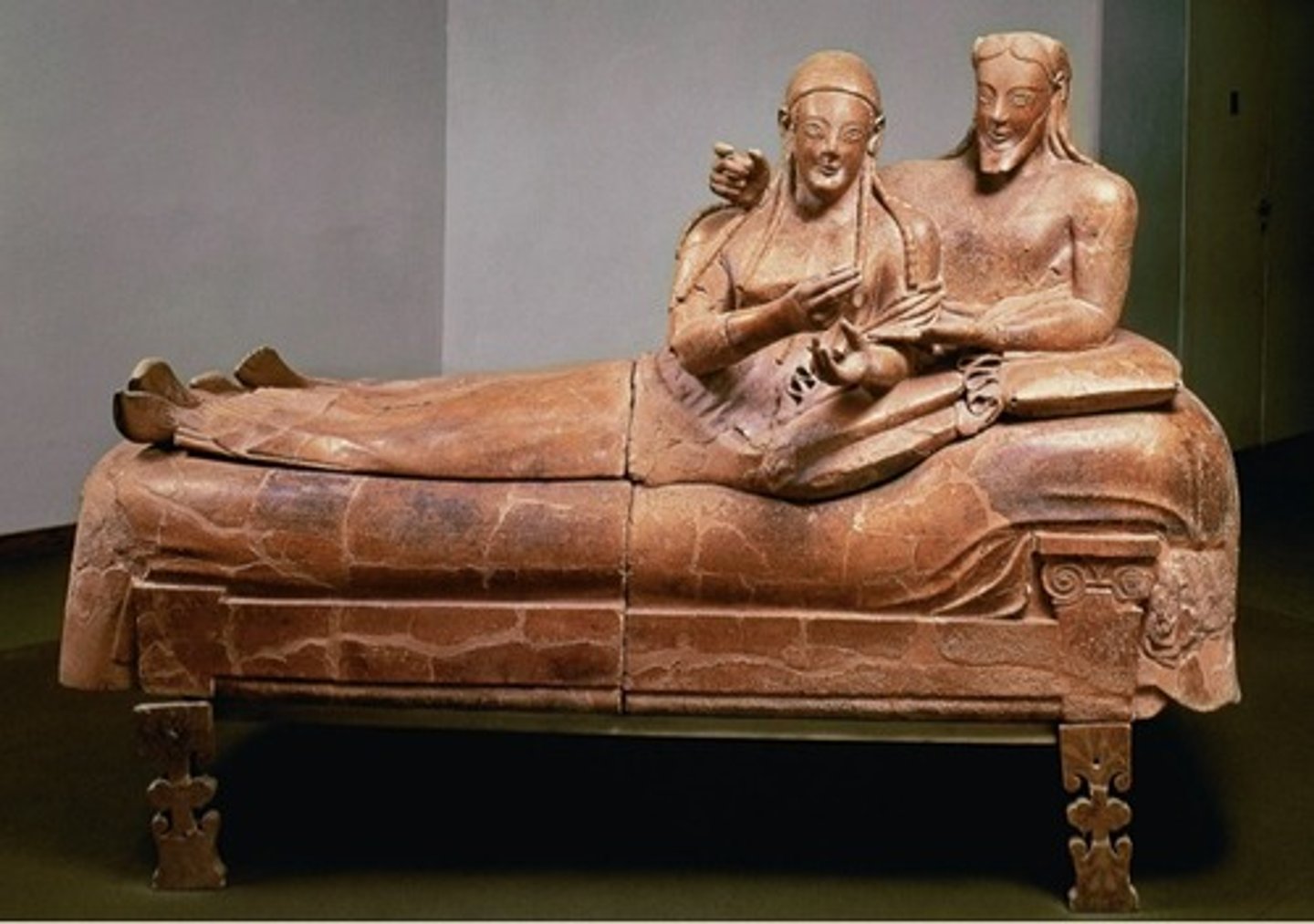

Audience hall (apadana)
Form:
-hypostyle hall
-cut sandstone and mud brick
-built in a hillside with big platform
-72 columns (3 portico made of 12 columns)
Content:
- relief on the side pictures Darius and Xeres
-stairs have central relief of king enthroned with attendants
-reliefs
Function;
-used to hold thousands of people (audience hall), king's receptions
- ascend upwards symbolic
Context:
- Persepolis, Iran; Persian influence
- 520-465 BCE
-built by Darius and Xeres; destroyed by Alexander the Great

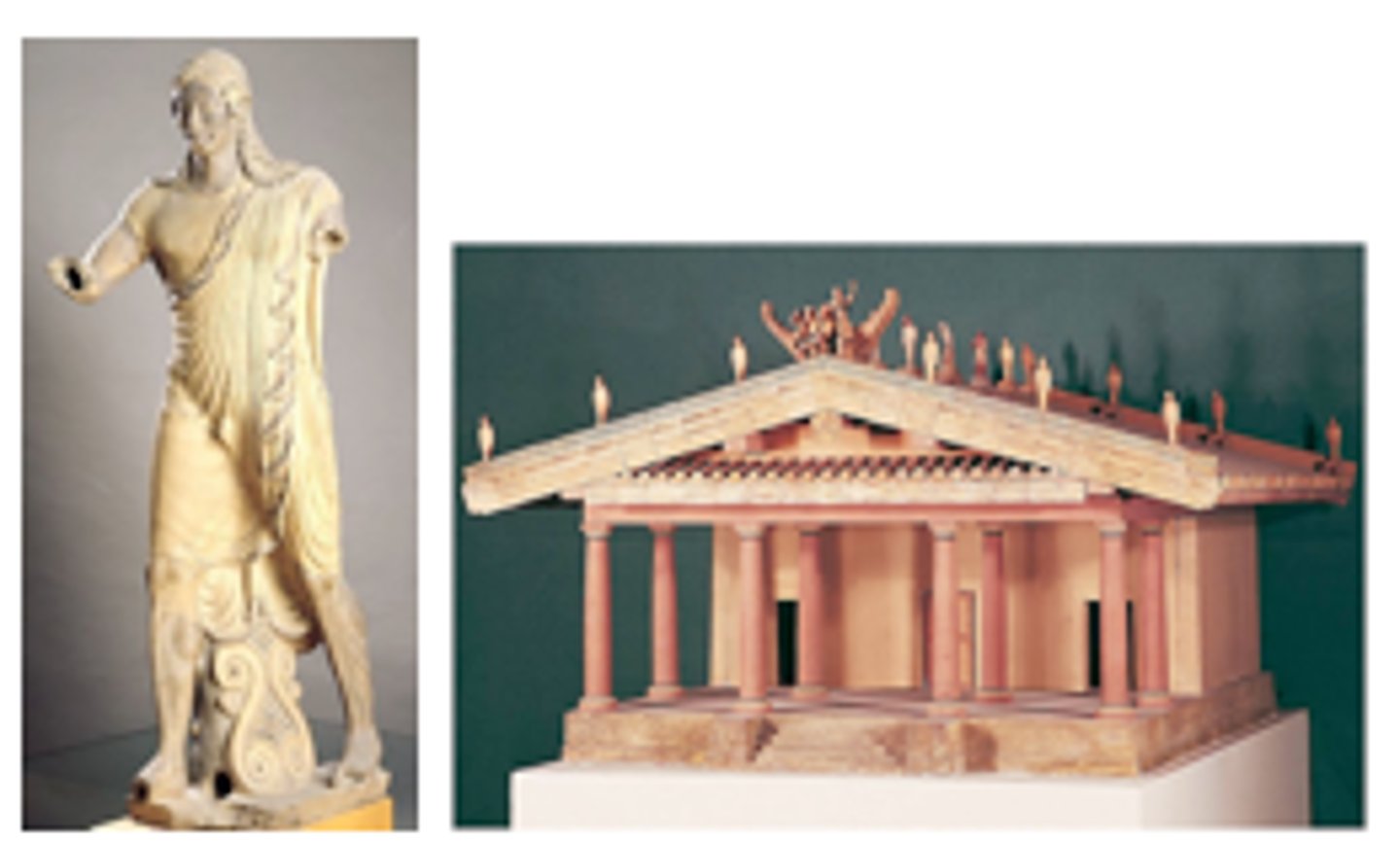
Temple of Minerva and sculpture of Apollo
Form:
-temple: wood, mud brick, tufa (volcanic rock)
-sculpture: terra cotta
-animated and moving sculpture (estruscan)
Content:
-Apollo apart of a narrative of Herakles, acroterion (roof sculpture)
-deep porch, 3 cella (entrance is emphasized)
-archaic Greek smile
Function:
-Estruscan temple made to be a place to worship the Estruscan gods and goddesses
-acroterians probably shows a mythic event
Context:
-Veii (near Rome, Italy)
-Imperial Rome 2nd centry BCE
-sculpture made by Vulca

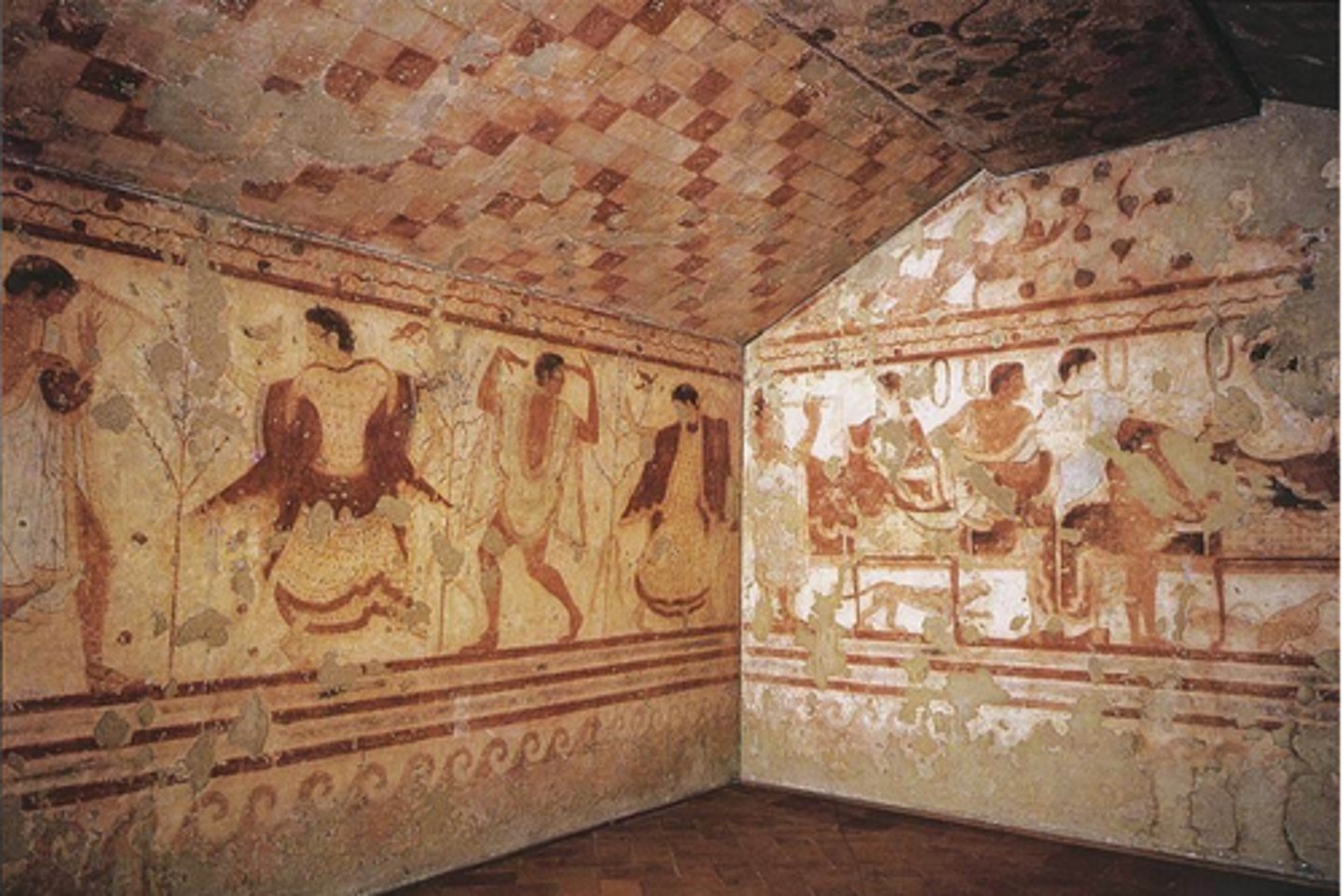
Tomb of the Triclinium
Form:
-tufa and fresco
-wall paintings
-great detailed piers
-color coding to show genders (not race)
Content:
-pictures people casually dining in triclinium (reclined on couches)
-fully furnished
-lively paintings of people dancing and in motion
Function:
-keep record of domestic life
-holds ashes (crematorium) and any other offerings to the dead
Context:
-Tarquinia, Italy
-Estruscan 480-470 BCE

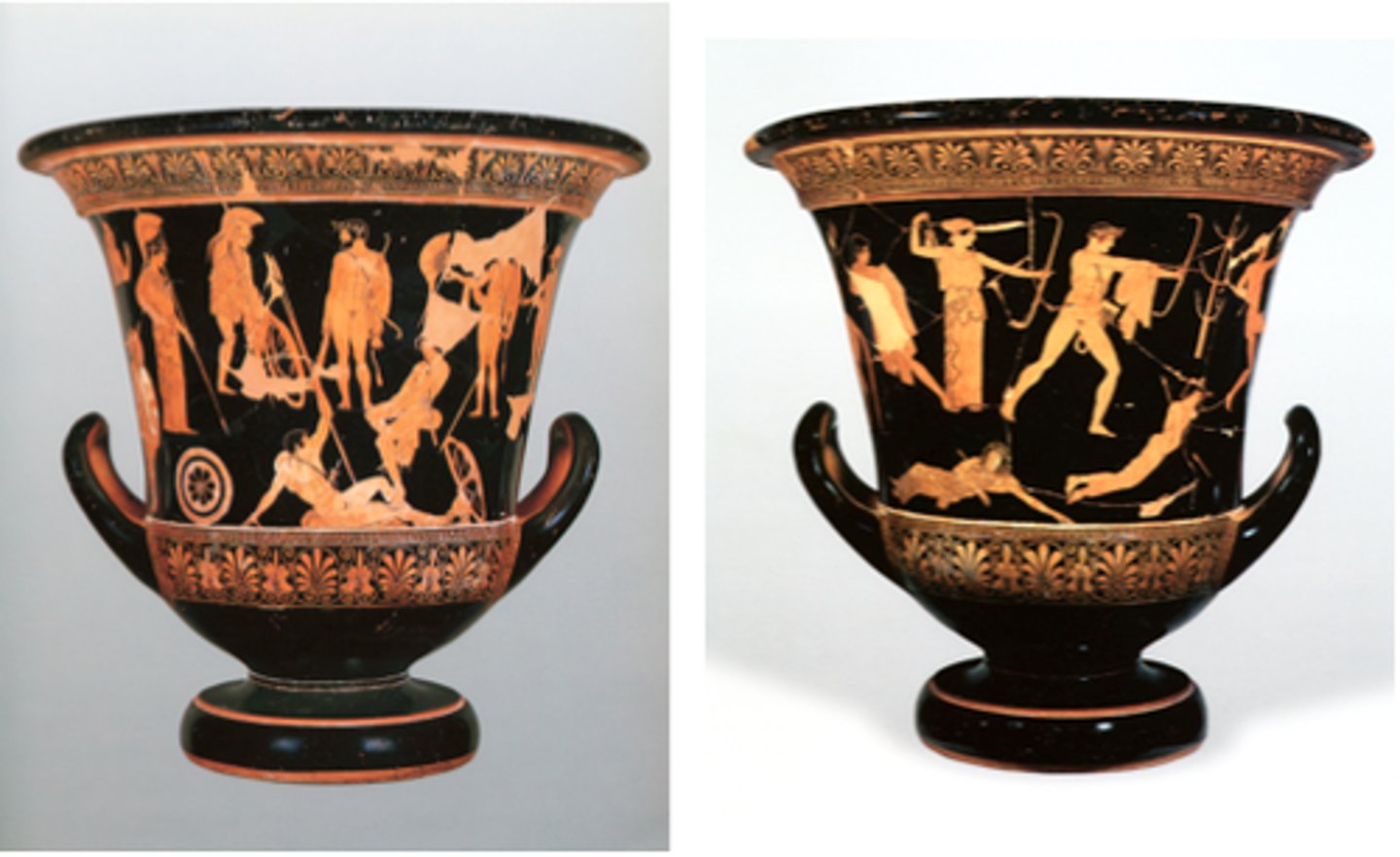
Niobides Krater
Form:
-calyx krater (type of painted pot)
-stiffness in the figures contrast the other relaxed side of the vase
-sense of depth perception
-red figure technique with white highlight
Content:
-one side: mortal woman named Niobe with 12 children would always brag to the goddess Leto that she had more children so Apollo and Artemis (Leto's children) take revenge for their mother by killing all 12 children
-other side: Hercules (identified with club and lions skins) is actually a sculpture (contraposta) and Greek soldiers are offering tribute and prayer to protect them before going into battle
Context:
-460-450 BCE
-not signed

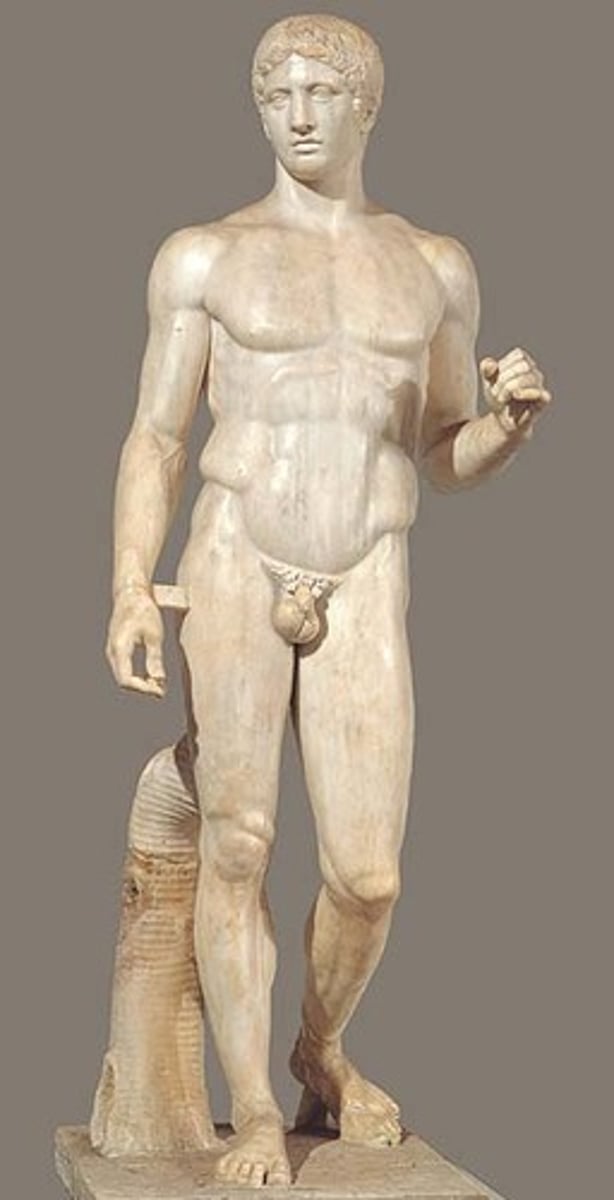
Doryphoros (spear bearer)
Form:
-marble (Roman); bronze (Greek)
-contrapposto: shifted weight
-not meant to portray a specific person but rather specific characteristics of a Greek
Function:
-portray the physical perfection of a human figure
Content:
-everyone is imperfect but brings together different body proportions to make physical
-missing its spear
-athlete and warrior
-gazes off in the distance
Context:
-Artist= Polykleitos of Argos in 450 BCE
-Roman copy of the Greek original

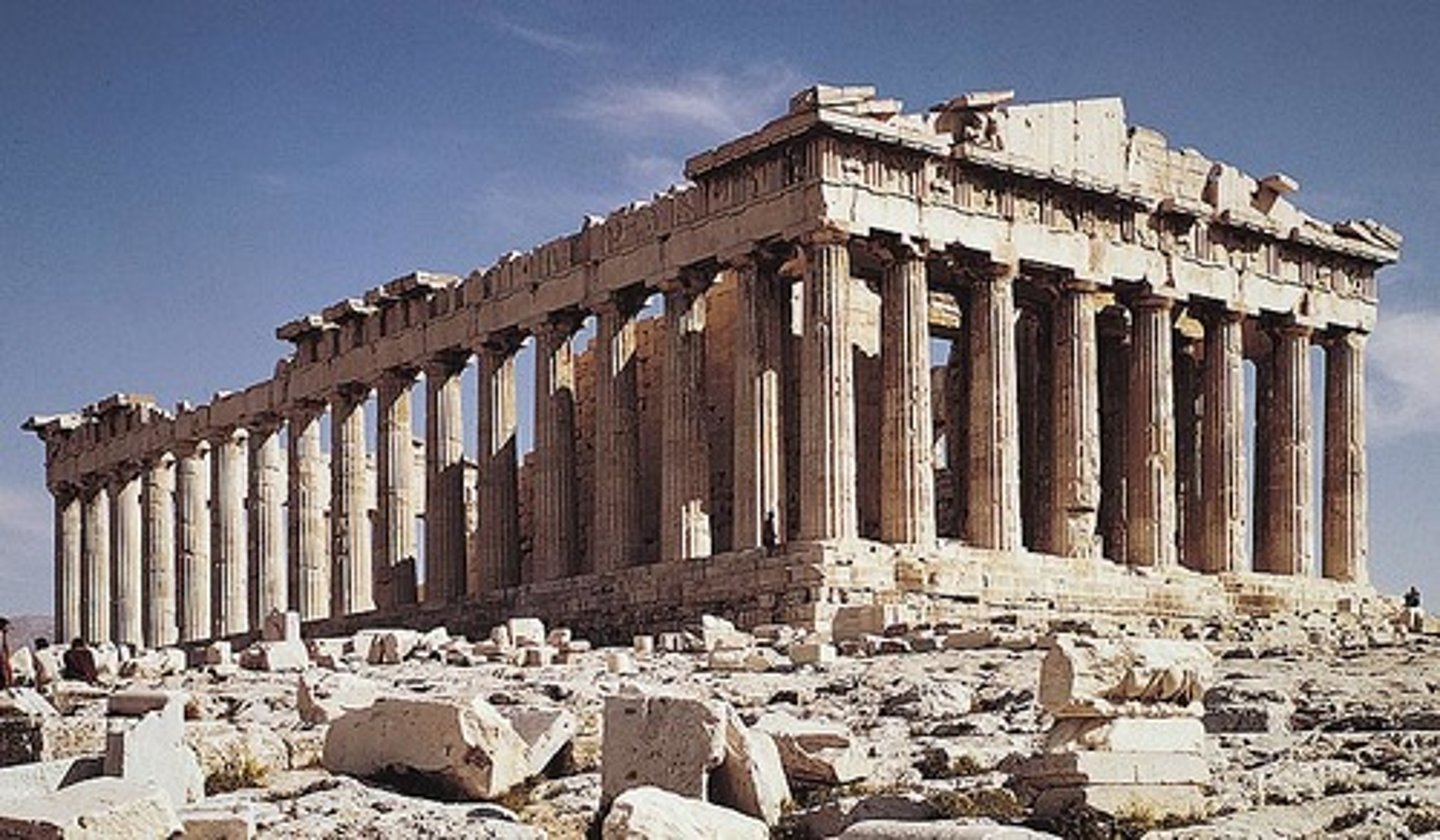
Acropolis
Form:
-marble (wealth)
-winged figure (nike)
-elevated
Content:
-buildings, temples, statues
-Parthenon (constructed under Pericles):
-doric temple
-East Pediment on parthenon: birth of Athena from the head of Zeus (Helios)
-plaque of ergastines: procession held for Athena every 4 years
-Temple of Athena Nike: commemorate Greek victory over the Persians
-Victory Nike adjusting her sandal
Function:
-hold image of goddess Athen (in cella)
-celebrate the female figure
-civic pride (Athena)
-commercial, civic, religious, and social building
Context:
-Athens, Greece 450-410 BCE

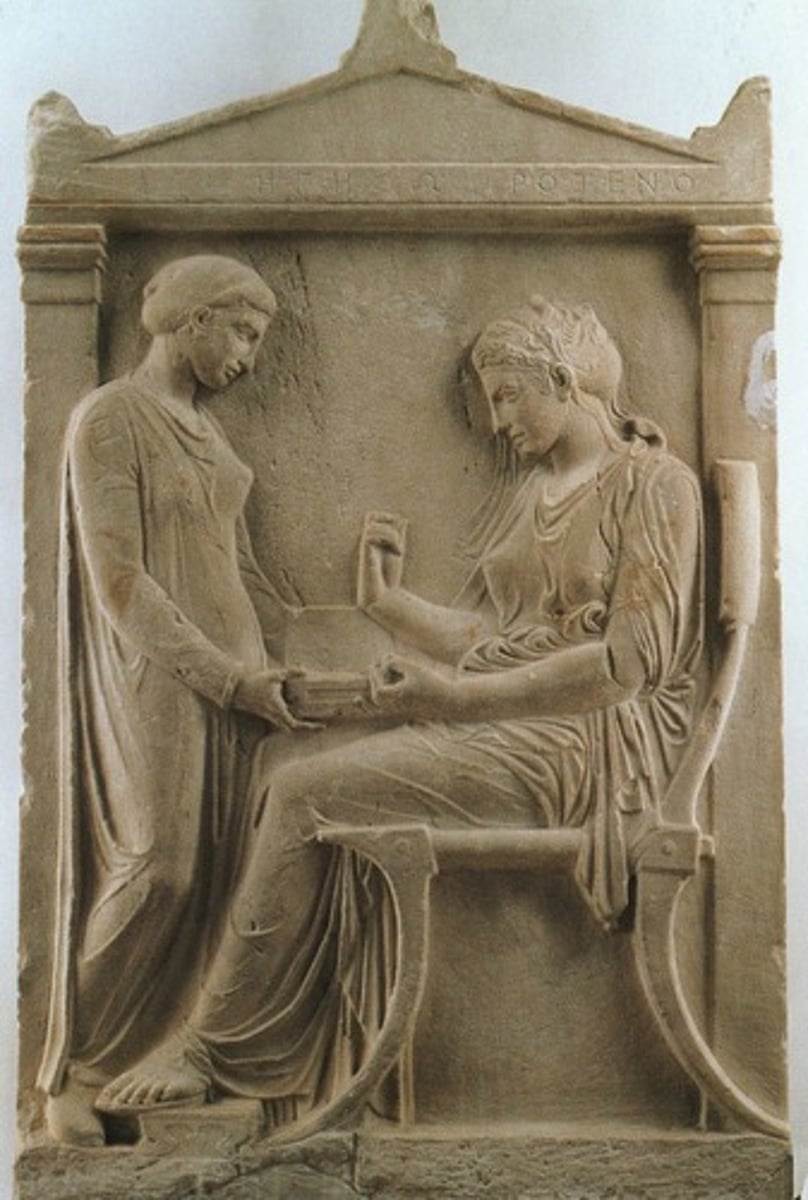
Grave Stele of Hegeso
Form:
-marble with paint
-hierarchic scale
-drape accentuates the body
Function:
-funerary object
-put on graves in Classical period
-commemorates the death of Hegeso
Content:
-genre scene: slave bringing jewelry box to nike figure for her to examine the jewelry
-inscription identifies Hegeso
Context:
-410 BCE
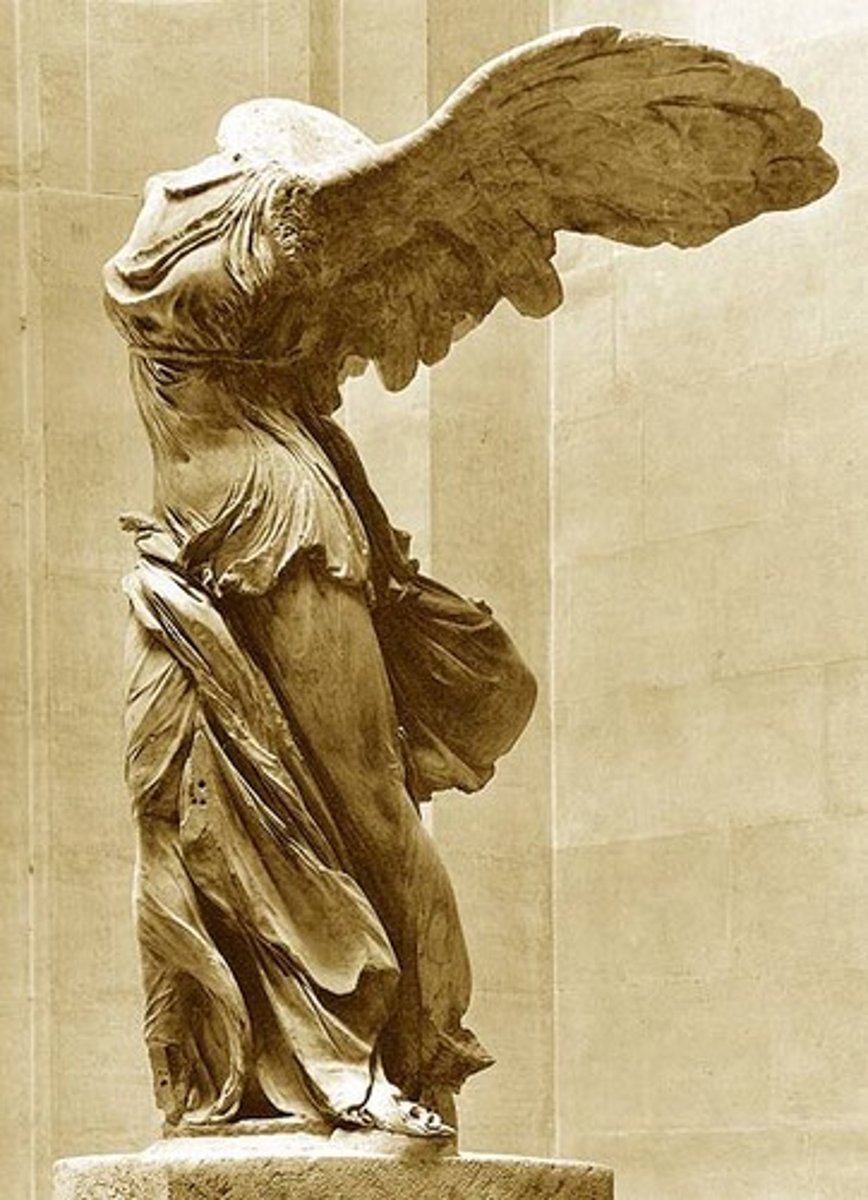
Winged Victory of Samothrace
Form:
-marble
-textures shown
-very dramatic motion, explosive,
-forward movement counteracted by the backward movement of her wings
Content:
-nike lands on front of ship descending from the heavens
-wet drapery look to the sculpture
-twist and contrapposto of the torso
Function:
-war monument
-commemorating a naval victory
-nike is a symbol of victory
Context:
- 190 BCE Hellenistic Greek

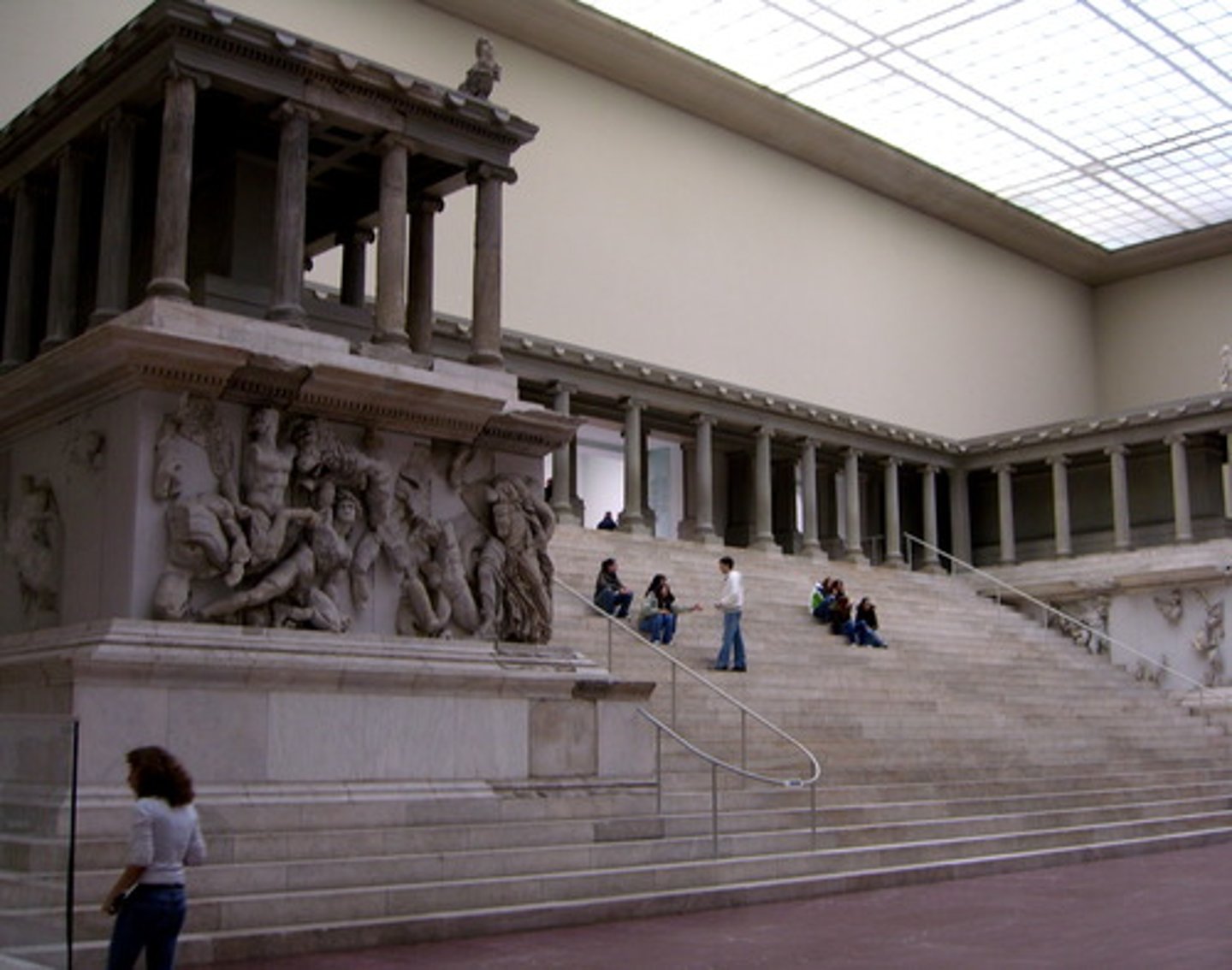
Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon
Form:
-marble frieze
-elevated with steep dramatic staircase
-complex forms with big muscles showing violent energy and detail
-ionic columns
Content:
-frieze wrapping around the monument shows gods overpowering the Titans
-Titans vs. Olympians
-"Athena": gigantomachy, battle between the gods and giants (gods win)
Function:
-war monument (Greek defeat of Gauls)
-break architectural boundaries
-altar dedicated to ZeusContext:
-175 BCE
- Asia Minor, Turkey

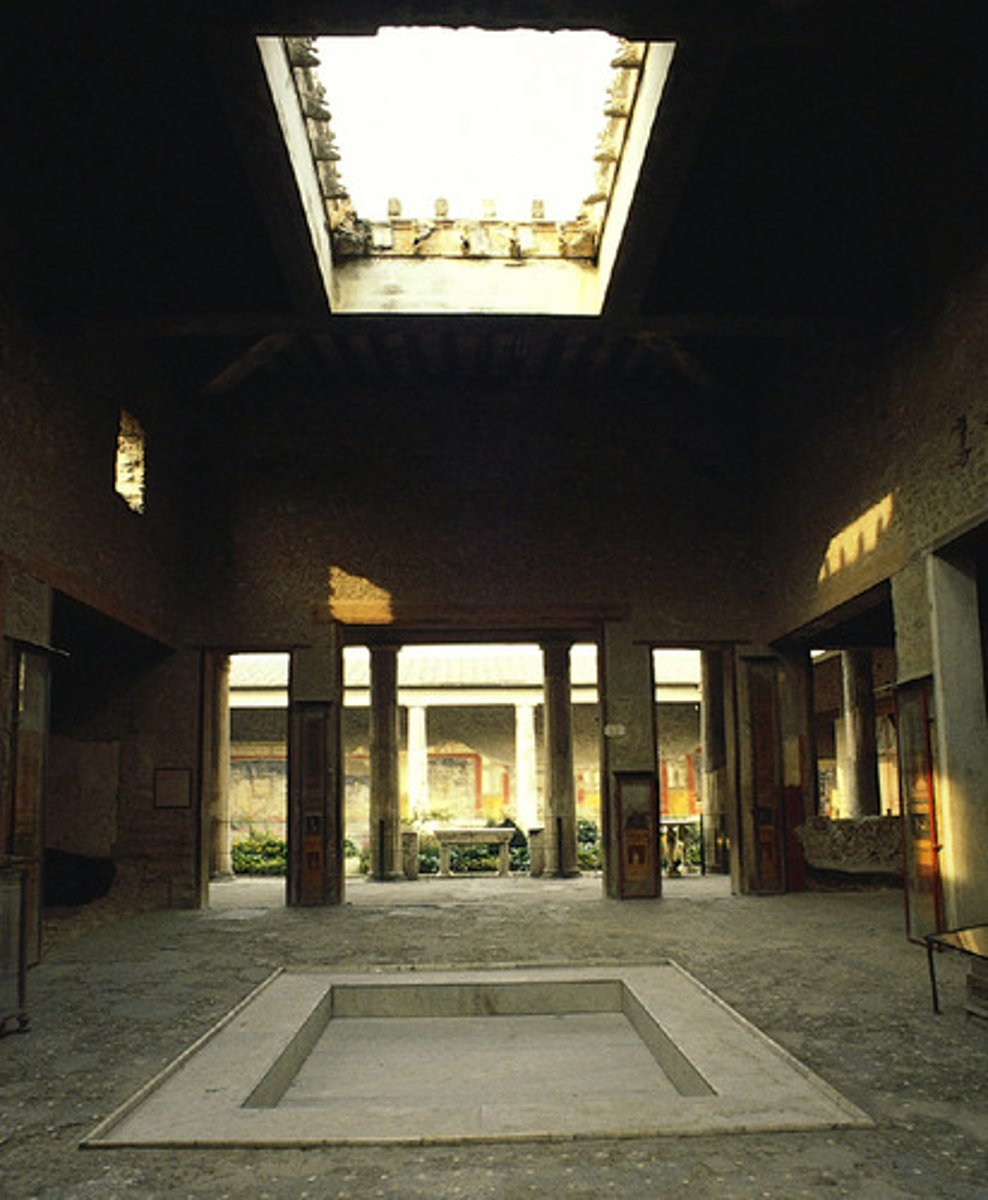
House of the Vettii
Form:
-cut stone and fresco
-axial symmetry
Content:
-atrium (inner courtyard with pool)
-reception area (atrium) has open ceiling
-catch basin to collect rainwater
-peristyle garden in back of house
-living room with frescoes
-frescoes show person's taste and used as conversation pieces for businessmen to discuss
Function;
-represents the wealth of the people who lived there
Context:
-Pompeii, Italy
-Imperial Rome 2nd century BCE rebuilt 62-79 CE
-wealthy family's home set in the middle of markets

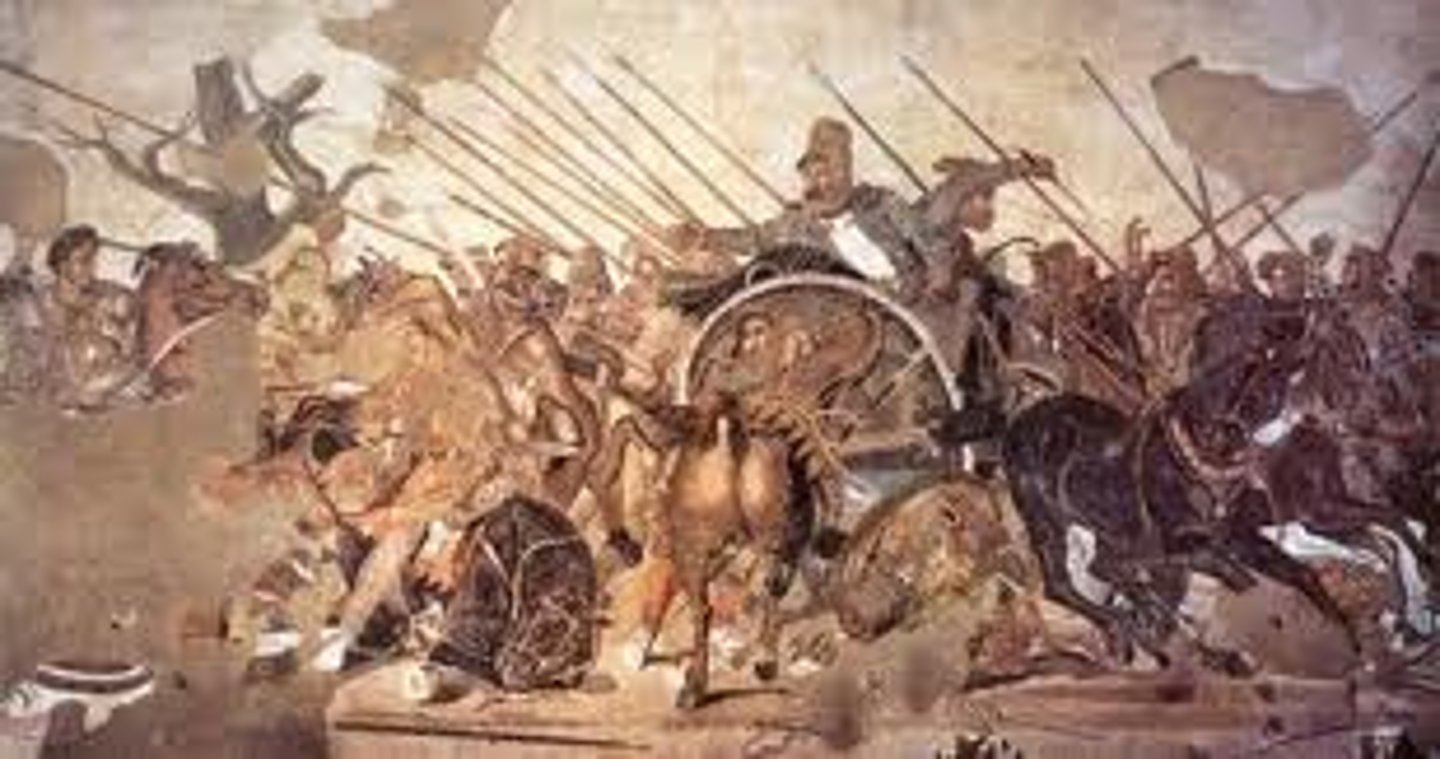
Alexander Mosaic
Form:
-mosaic copy of a Greek wall painting
-tessarae: individual pieces of a mosaic
-spacial illusionism
-interweaving of figures
Content:
-Alexander the Great confront Darius III at Battle of Isos
-dead tree signifies the death and sadness
Function:
-floor mosaic showing dramatic representation of a historical event
-last major defeat of the Persians
Context:
-Roman Republic
-House of Faun, Pompeii 100 BCE

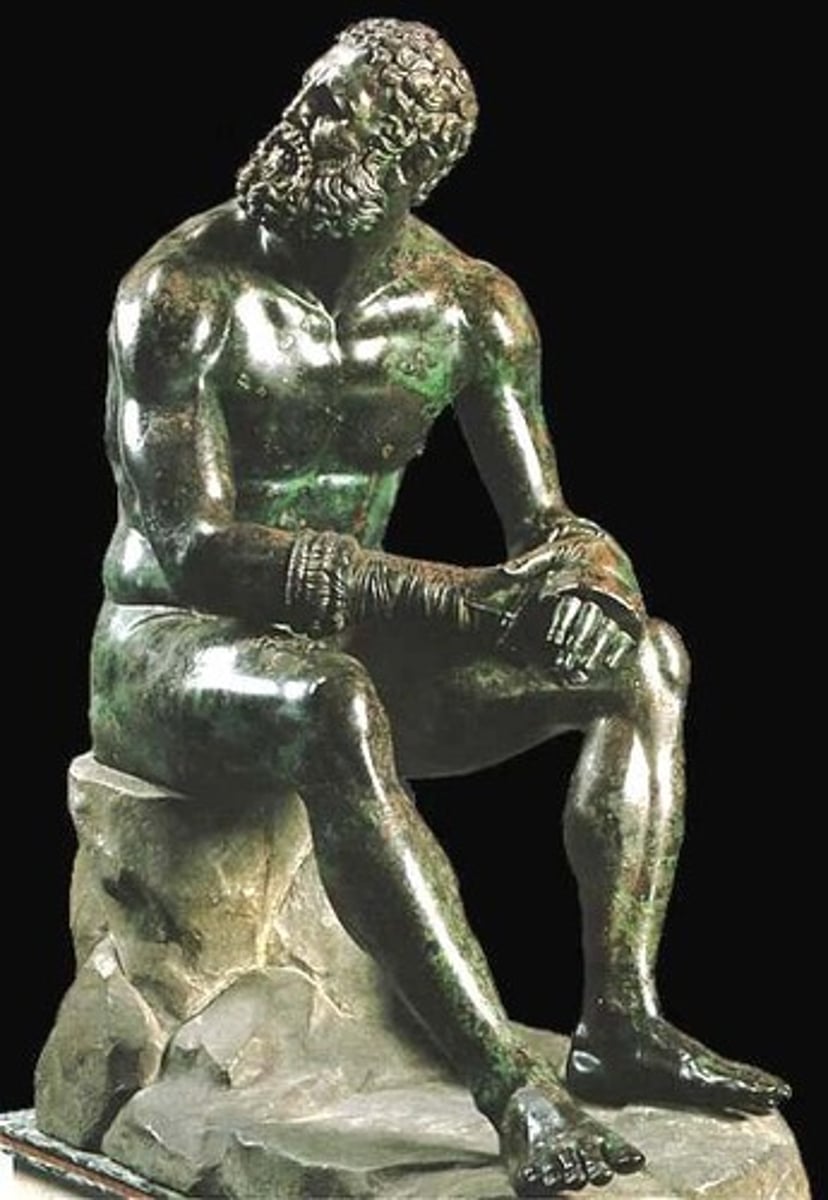
Seated Boxer
Form:
-bronze
-realistic- shows the exhaustion of a real athlete
Content:
-boxer seated naked with only his boxing gloves
-copper shows blood
-cuts and bruises
Function:
-show a boxer after a fight
Context:
-Greek 100 BCE
-Hellenistic

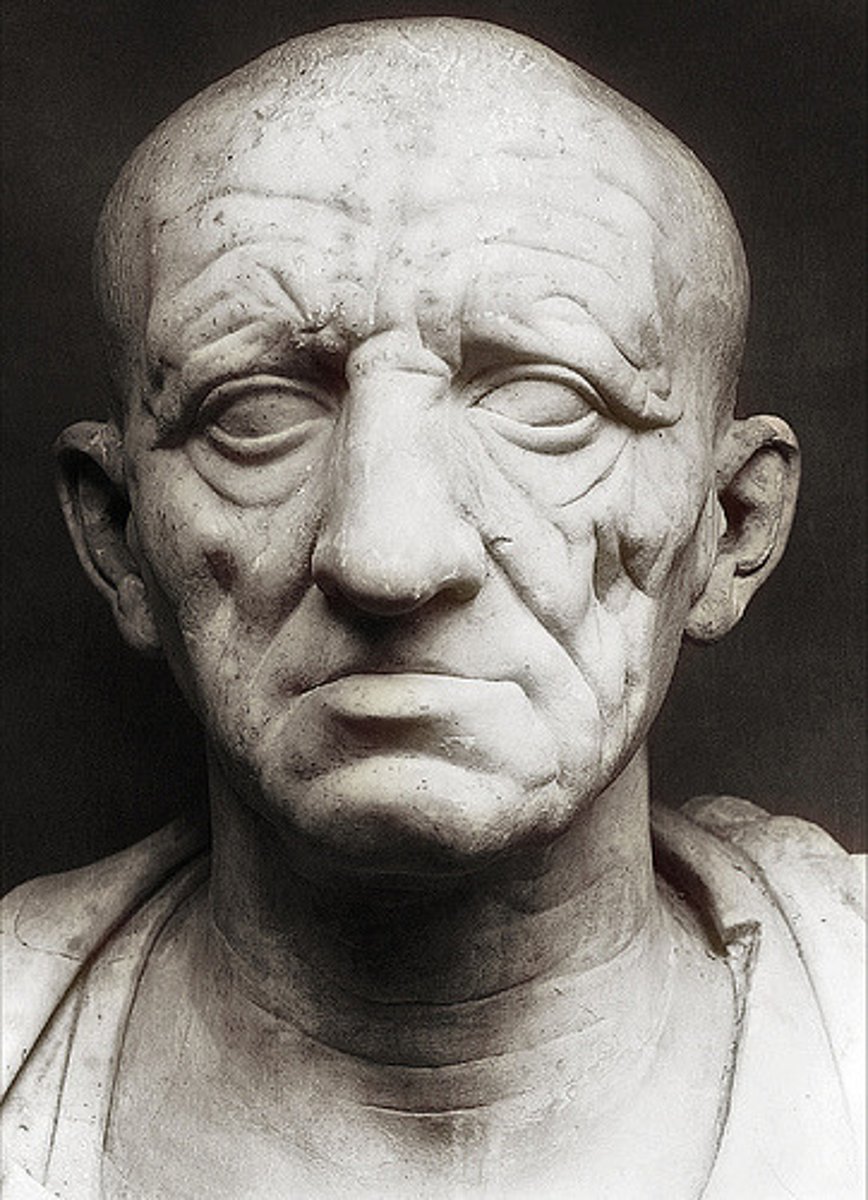
Head of a Roman partician
Form:
-marble
-deep wrinkles, hooked nose, defined cheek bones
Content:
-realistic portrayal of a Roman patrician
-show sense of civic virtue: wisdom, seriousness, public service
Function:
-kept in shrines of Roman houses
-mask of values and virtues of Republican men in Rome
Context:
-Republican Roman 75-50 BCE
-influence of Greek Hellenistic art

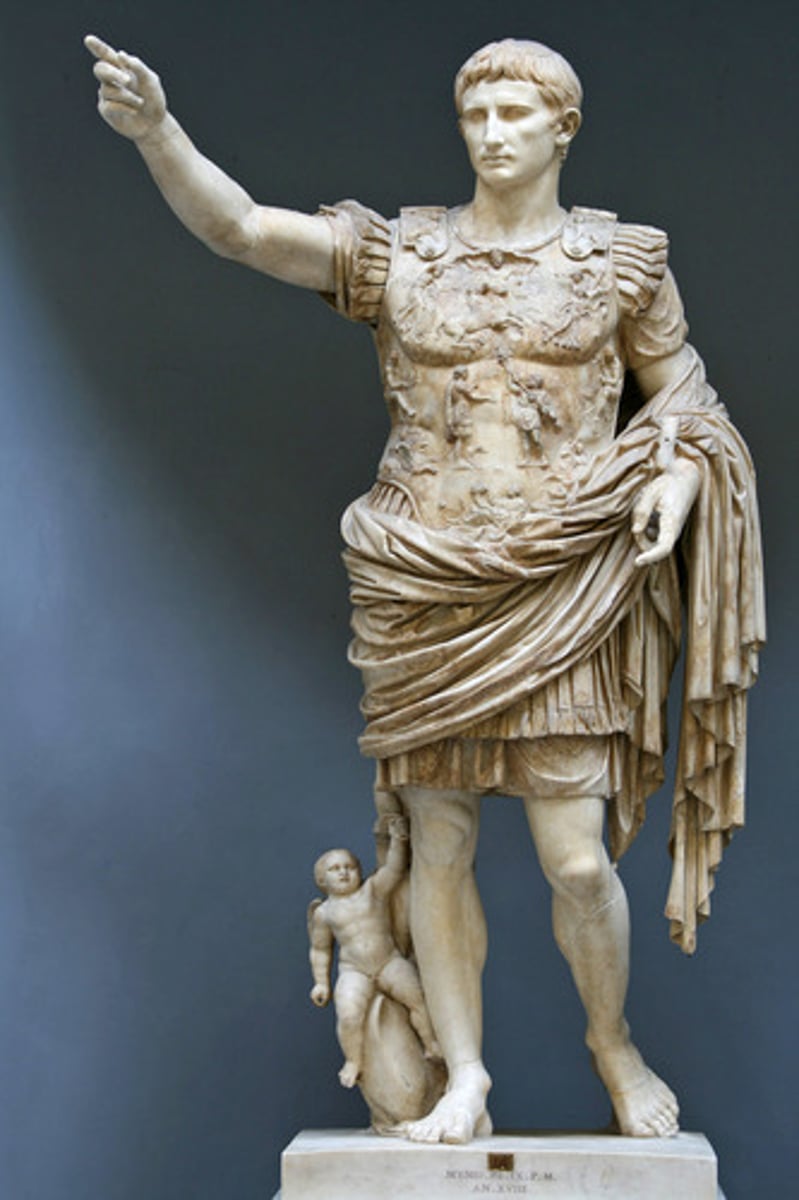
Augustus of Prima Porta
Form:
-marble, over life-size
-elevated to be more god-like
-contrapposto
Content:
-Augustus barefoot
-cupid riding dolphin (shows divinity
-breastplate is about the Pax Romana: the power of empire is due to the military
Function:
-shows Augustus as a god because he thought he was (barefoot and cupid riding dolphin signs of this)
-shows him as civic ruler (judge's robe) and warrior (breastplate)
Context:
-Imperial Rome (early empire) 1st century CE

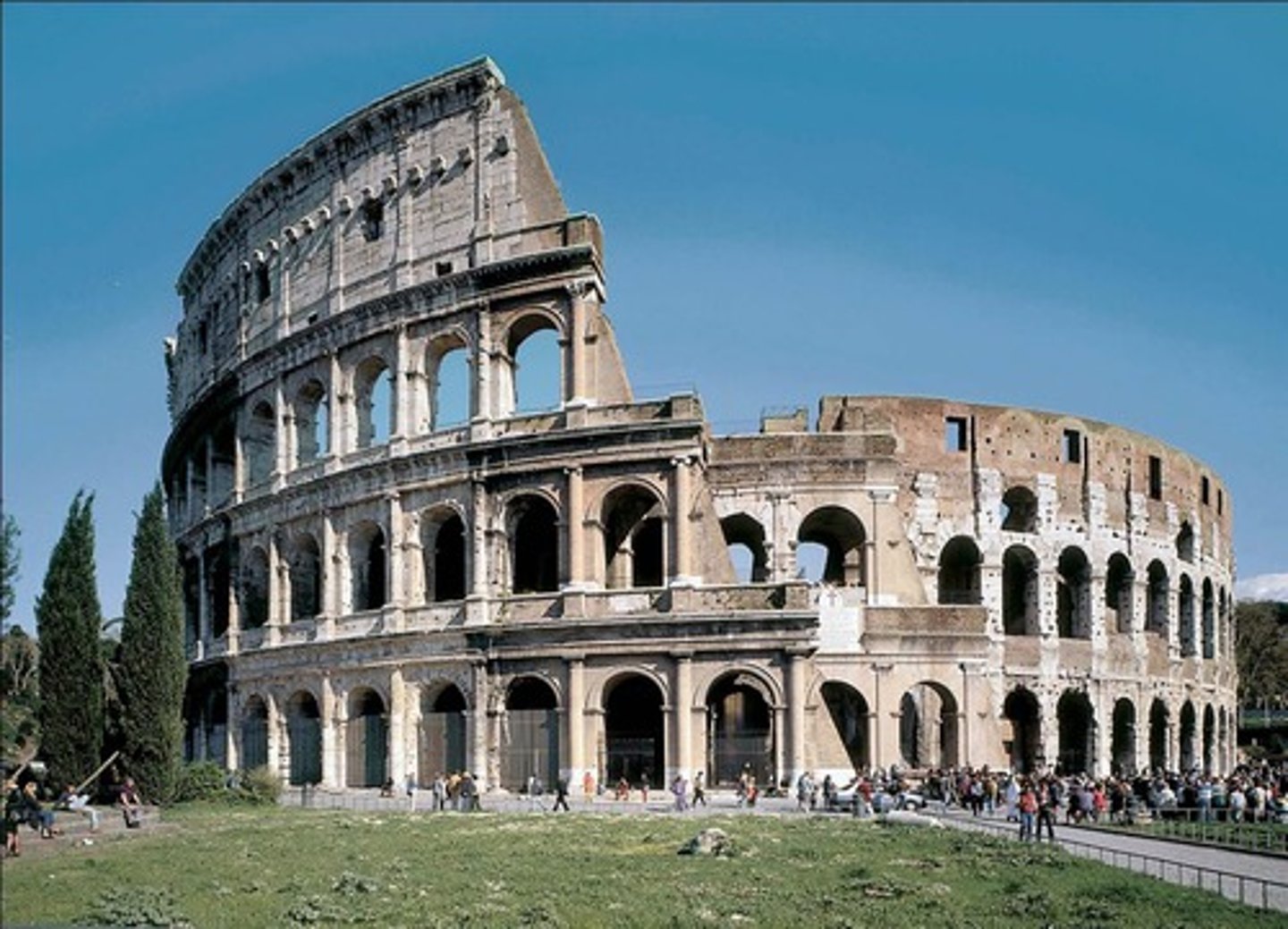
Colosseum
Form:
- stone + concrete
-Corinthian, Doric, and ionic columns
-outside mostly intact
-barrel vaults, thick walls, groin vaults, arches
Content:
-2 theaters
-downward force of arches
-bronze shield on top, 4 layers
-76 entrances
Function:
-entertainment for the public
-usually dangerous like gladiator fights or animal hunts
Context:
- Rome, Italy 70-80 BCE
- Imperial Rome

Forum of Trajan
Form:
-column: marble, low relief
-brick and concrete architecture
-scroll-like frieze on column- continuous narrative
-groin vaulting/barrel vaults in market
Content:
-forum: basilica in back with equestrian figure in the center and two libraries
-marble column of trajan: ashes of trajans put in bottom, crowded composition, story of defeat of the Dacians
-market of trajan: multilevel mall with 150 shops
Function:
-column: monuments celebrates the victory in the Dacian war
-forum: marketplace
Context:
- Rome, Italy 106-112 CE column 113 CE
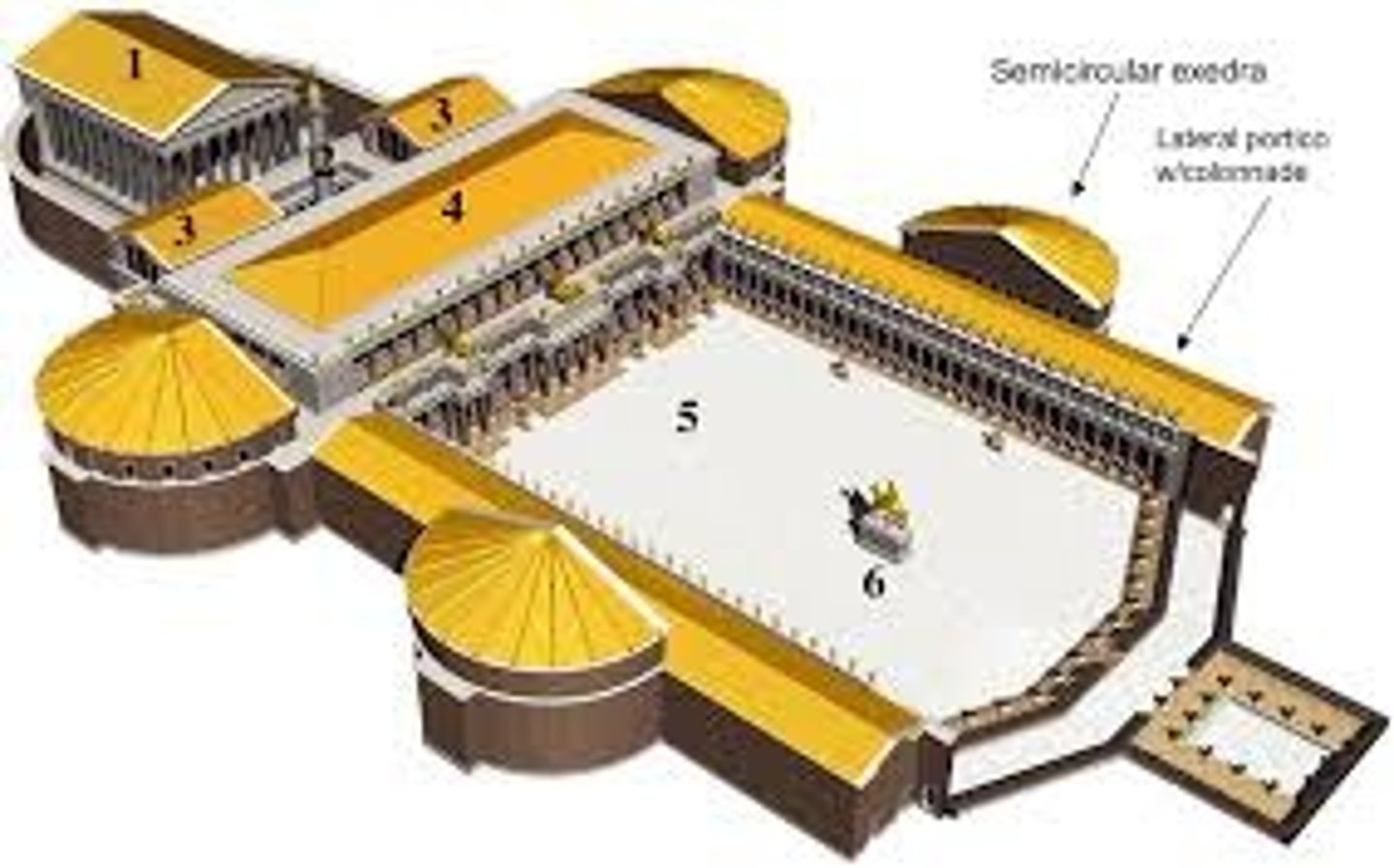
Pantheon
Form:
-marble
-coffers: indentations in the ceilings
-15' thick walls
Content:
-big portico in the front with a rotunda in back that has a dome with an oculus
-sculptures of gods in niches
Function:
-houses all 7 planetary gods
-famous burial space
-coffers create illusion of heaven
Context:
-imperial Rome 118-125 CE

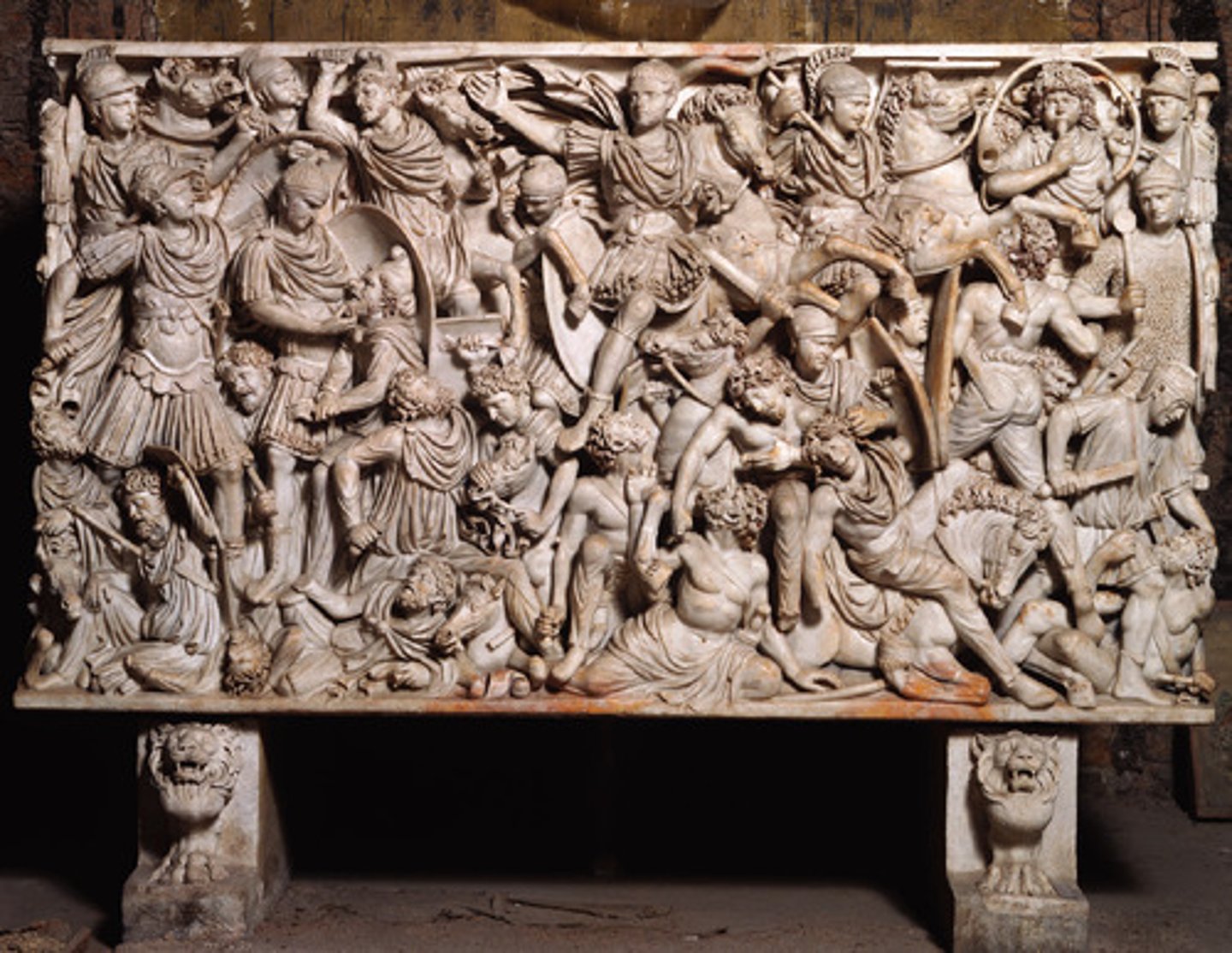
Ludovisi Battle Sacrophagus
Form:
-marble
-high relief
Content:
-figures piled on top of each other, crowded surface
-Romans shown as the good guys (ideal/noble)
-Romans trampling over defeated barbarians
- enemies very caricatured with great detail
Function:
-tomb
Context:
-late imperial empire; 250 CE
