1.3 Diversity of Organisms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
organism
any biological system that functions as an individual life form
population
group of organisms of the same species in the same area
communities
populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time
variation
differences between members of a group
discrete variation
traits that can be put into distinct qualitative categories
continuous variation
traits that vary along a quantitative continuum
intraspecies variation
variation within a species
morphological species concept
classified a species as a group of living things recognizably distinct from all others by their shared characteristics (shape + appearance)
biological species concept
classified a species as a population of organisms that are able to freely breed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring
speciation
the splitting of one species into two or more species (usually happens gradually)
hybridization / cross-breeding
forming a cross between two distinct genetic species
biodiversity
the variety of life in all its forms, levels, and combinations
species diveristy
number of different species and abundance of each species that live in a particular location
species richness
the number of different species present in a particular area
species evenness
how close in numbers the different species are
genetic diversity
the variation in the amount of genetic information within and among individuals of a population, a species, an assemblage, or a community
ecosystem diversity
the number of different ecological niches found within an ecosystem
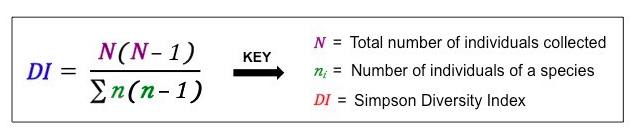
Simpson’s Reciprocal Index
quantifies diversity: the higher the DI, the greater the biodiversity