Bio 1113 Ch. 2- Basic Chemistry terms
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terms and concepts from Chapter 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Atom
Smallest piece of an element that can still retain characteristics of that element.
Mass Number
Protons + Neutrons
How many electrons can the first and second shell of an orbital hold consecutively?
First: 2 electrons
Seconds: 8 electrons
Chemical Bond
An attractive force that holds atoms together and links them into molecules.
Covalent bonds ____ electrons.
share
Ionic bonds _____ electrons.
steal
Electronegativity
The strength with which atoms pull electrons toward themselves.
Polar bonds are created by _____.
Having an electronegativity above 0.4.
Ionic Bond is a ____
bond between a cation and an anion.
Molecular shape is _____?
crucial in determining how biological molecules specifically recognize and respond to one another.
The _____ on the hydrogen atom of one water molecule _____ the _____ on the oxygen of a neighboring water molecule.
slight positive charge; attracts; slight negative charge
The __________ that hold water molecules together give water a collection of _________.
Hydrogen bonds; important unique properties
Hydrophilic
In terms of water as an efficient solvent, these are water loving molecules. Ions and polar molecules stay in solution due to their interactions with water’s partial charges.
Hydrophobic
In terms of water as an efficient solvent, these are water fearing molecules. they are uncharged and non-polar compounds that do not dissolve in water.
Hydrophobic interactions
When Hydrophobic molecules interact with each other, after being forced close to avoid water.
Cohesion
Attraction between like molecules.
Adhesion
Attraction between unlike molecules.
Water is ________ because of __________
cohesive/stays together; hydrogen bonds
Surface Tension
Cohesive forces caused by attraction between molecules at surface of liquid.
Ice is ________ than liquid water.
Less dense (because of the lack of crystal lattices in liquid)
Water resists changing its _________.
temperature (cools and heats very slowly)
Concepts in ‘high specific heat’
vaporization/ evaporation
Concepts in ‘solvent of life’
hydrophilic/hydrophobic/solubility
Reduced density in a solid vs a liquid
solid ice is less dense than liquid water
Water and acid base reactions?
Sometimes water molecules break into two pieces, separating the H atom from the molecule. Since protons (H+) don’t exist by themselves, they associate with another water molecule; dissociation reaction produces hydronium ions (H3O+)
pH scale
Expresses proton concentration (H+) in a solution.
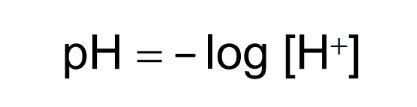
Acids
substances that give up protons during chemical reaction. Have a pH of less than 7.
Bases
substances that acquire protons during chemical reaction. Have a pH of greater than 7.
Does adding Acid to a solution increase or decrease proton concentration of a solution?
Increase
Carbon provides a ______________?
Molecular skeleton
Organic Molecule
Molecule that contains carbon bonded to other elements; linked in a chain or ring.
Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of each other but potentially have different effects.