Eye Diseases and Disorders
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
Corneal issue
What eye conditions cause pain?
Retinal issue
What eye conditions cause no pain?
painless temporary loss of vision in one or both eyes (retinal ischemia)
What is amaurosis fugax?
blind spots in the vision
What are scotomas?
moving specs or strands in the vision
What are vitreous floaters?
-disappears with one eye closed
-problem with alignment
Describe binocular blurred vision.
-persists with one eye closed
-problem with cornea or lens
Describe monocular blurred vision.
problem with visual acuity
Define blurry vision.
perception of two images; double vision
-monocular
-binocular
Define diplopia.
-optical problem
-one eye affected
Describe monocular diplopia.
-alignment problem -- a problem with the EOMs (extraocular muscles)
-both eyes affected
Describe binocular diplopia.
-farsightedness
-trouble seeing near
Describe hyperopia.
trouble seeing near due to the aging process
Describe presbyopia.
-nearsightedness
-trouble seeing far
Describe myopia.
blind spots
Describe scotomas.
tears
Describe lacrimation.
sensitivity to light
Describe photophobia.
crossed eyes
Describe strabismus.
-thyroid eye disease
-congenital abnormalities
-orbital infections
-ocular tumors.
Abnormal protrusion or proptosis may be due to what?
hypothyroidism
Lateral sparseness of the eyebrows occurs in ___.
seborrheic dermatitis
Scaliness of underlying skin occurs in ____.
down syndrome
Up slanting palpebral fissures are noted in ___.
-deviate from its normal position
-The eyes will no longer appear conjugate (parallel)
If one of the extraocular muscles are parlyzed, the eye will ___.
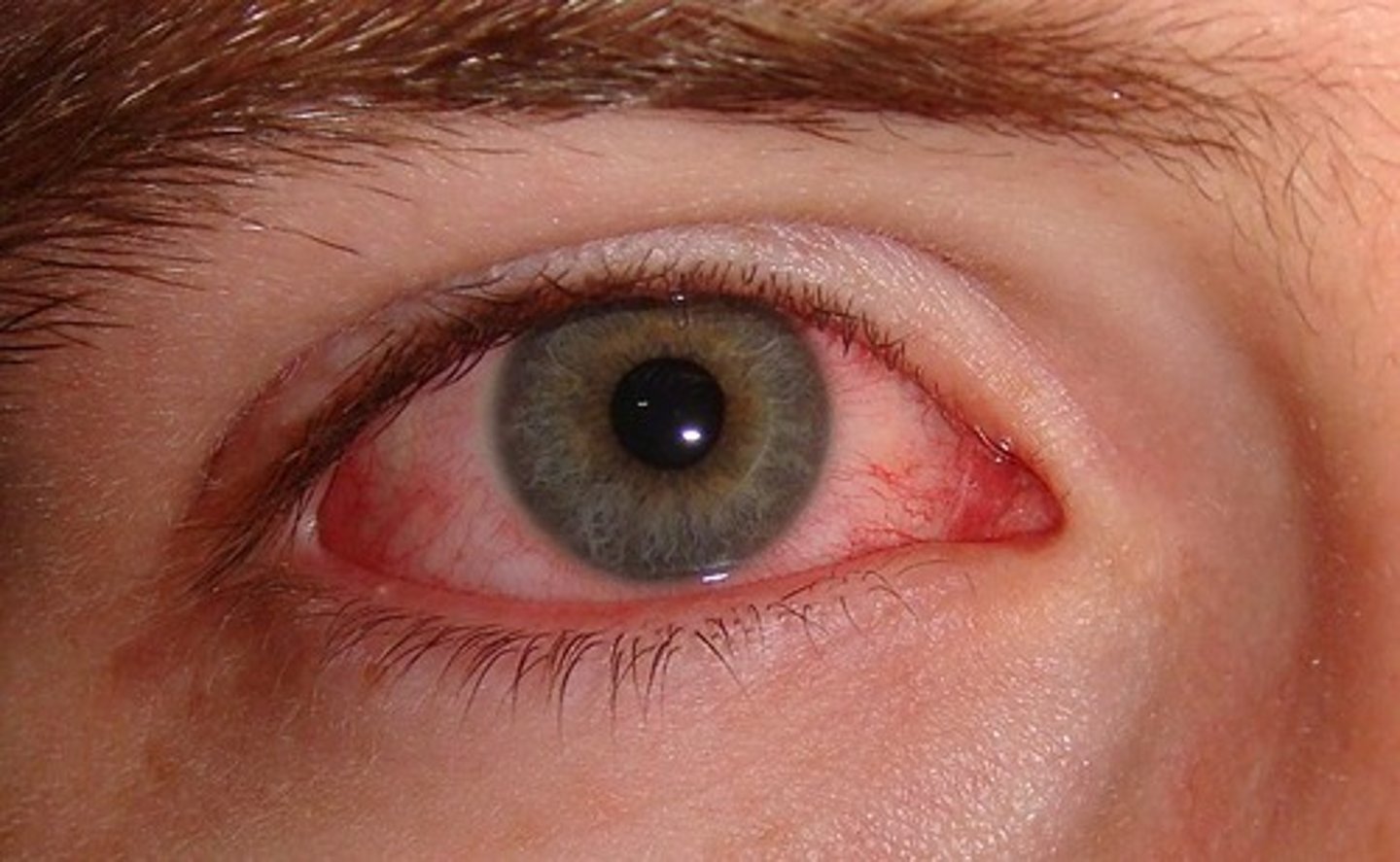
diffuse dilation of conjunctival vessels with redness that tends to be maximal peripherally
Describe the redness of conjunctivitis.
-mild discomfort
-watery, mucoid, purulent
-highly contagious, allergy, irritation
Describe other symptoms of conjunctivitis
-Bacterial, viral, and other infections
-allergies
What is conjunctivitis caused by?
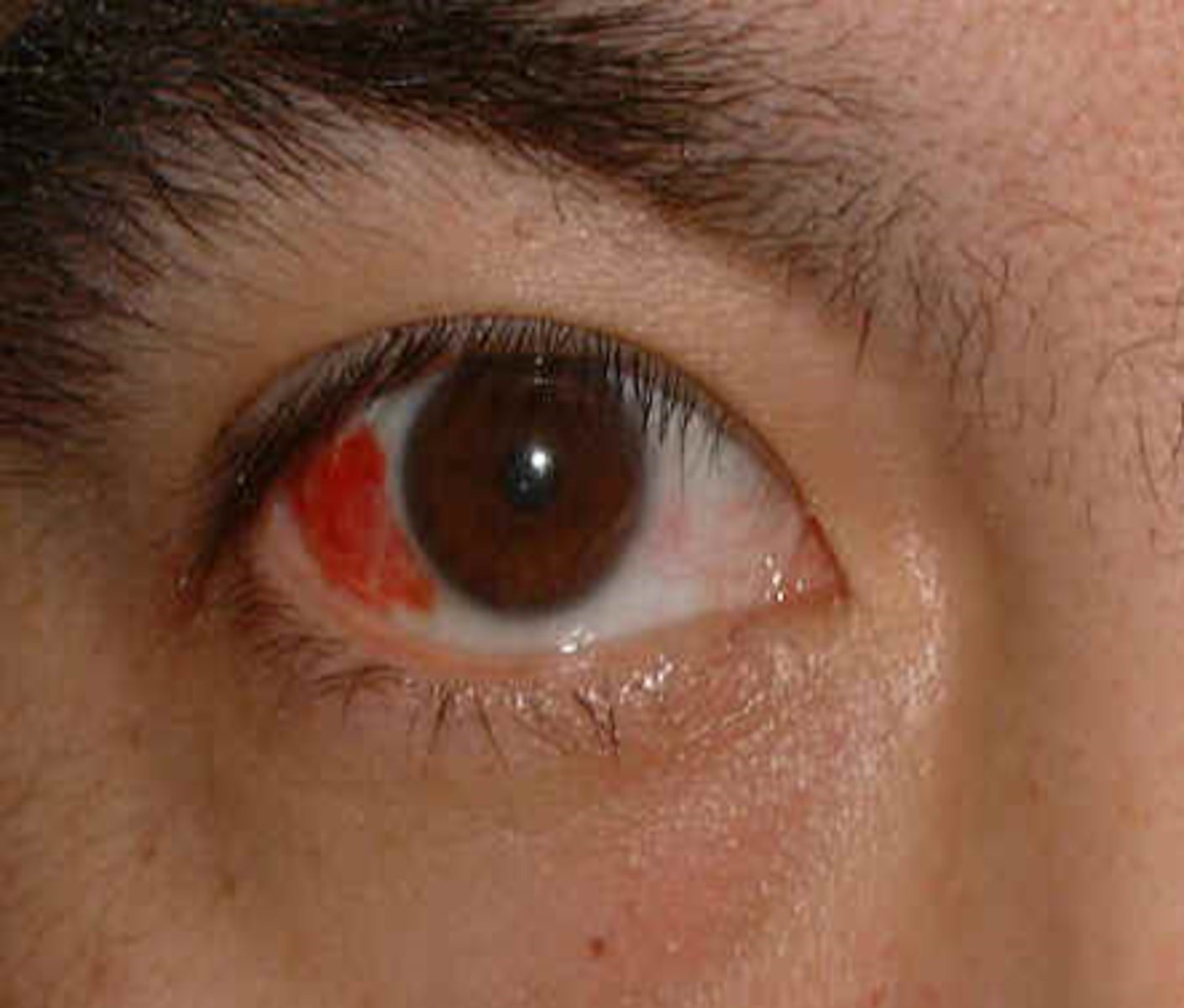
Leakage of blood outside of the vessels, producing a homogenous, sharply demarcated, red area that resolves over 2 weeks
Describe the redness of subconjuctival hemorrhage.
conjunctivitis
-no pain
-no vision changes
Describe other symptoms of subconjuctival hemorrhage.
trauma, bleeding disorders, or increase in venous pressure
What is subconjunctival hemorrhage caused by?
subconjuctival hemorrhage
Ciliary injection: the deeper vessels radiating from the limbus are dilated, creating a reddish violet flush
Describe the redness of corneal injury or infection
-moderate to severe pain
-decreased vision
-watery or purulent
-cased by abrasions
Describe other symptoms of corneal injury or infection
-abrasions
-other injuries
-viral and bacterial infections
What causes corneal injury or infection?
corneal injury or infection
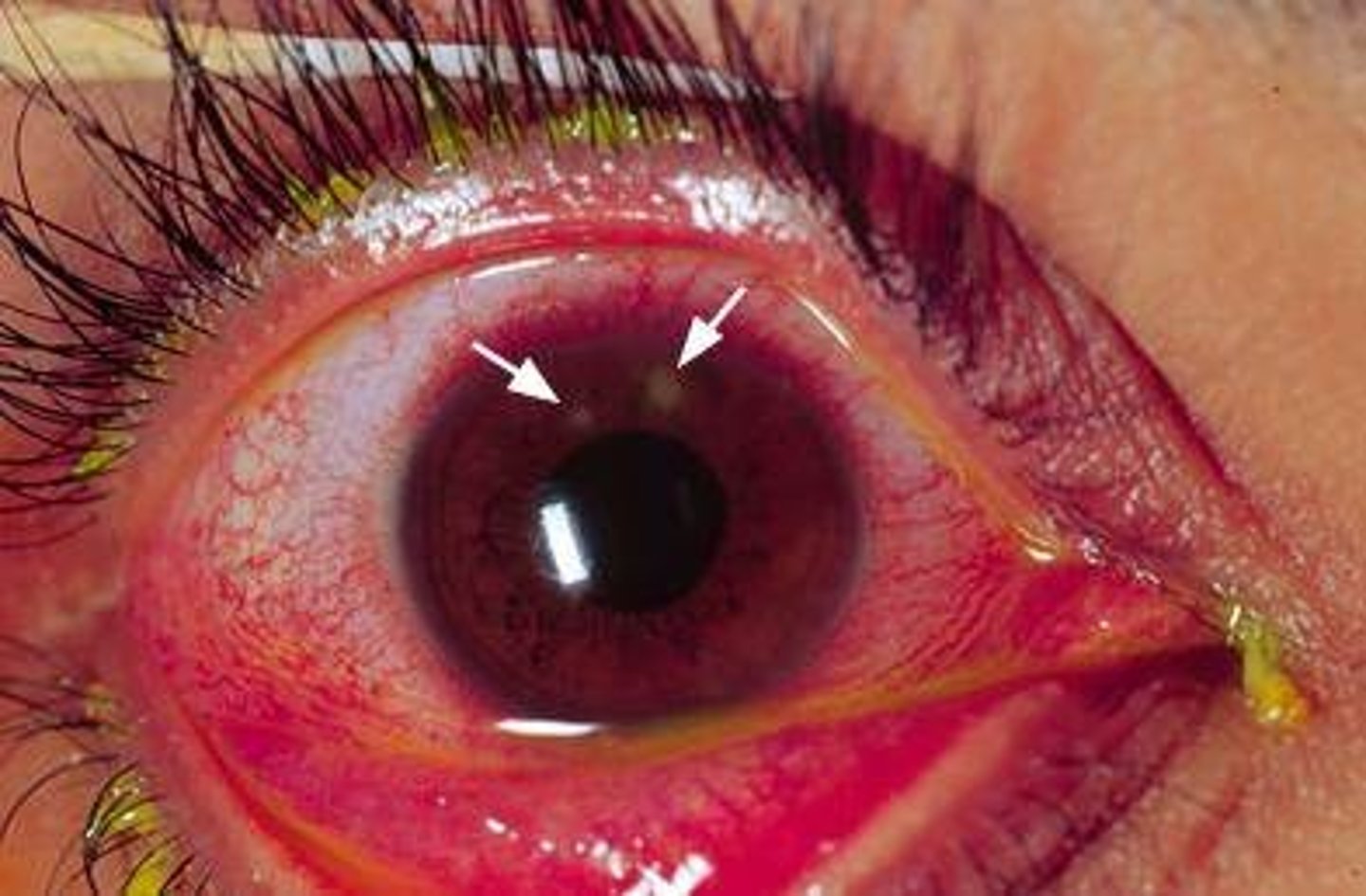
Ciliary injection: the deeper vessels radiating from the limbus are dilated, creating a reddish violet flush
Describe the redness of acute iritis.
-moderate, aching pain
-photophobia
-decreased vision
-small, irregular pupil
Describe the other symptoms of acute iritis.
-systemic infection,
-herpes zoster
-tuberculosis
-autoimmune diseases;
What causes acute iritis?
Acute, dramatic elevation of intraocular pressure if iris blocks exit of aqueous humor from anterior chamber
What is acute angle closure glaucoma?
Ciliary injection: the deeper vessels radiating from the limbus are dilated, creating a reddish violet flush
Describe the redness of acute angle closure glaucoma
-intense ocular pain
-blurred vision
-halos around lights
-possible N/V
Describe the main symptoms of acute angle closure glaucoma.
-diffuse conjunctival injection
-fixed, dilated pupil
-clouding of cornea
Describe the exam findings of acute angle closure glaucoma.
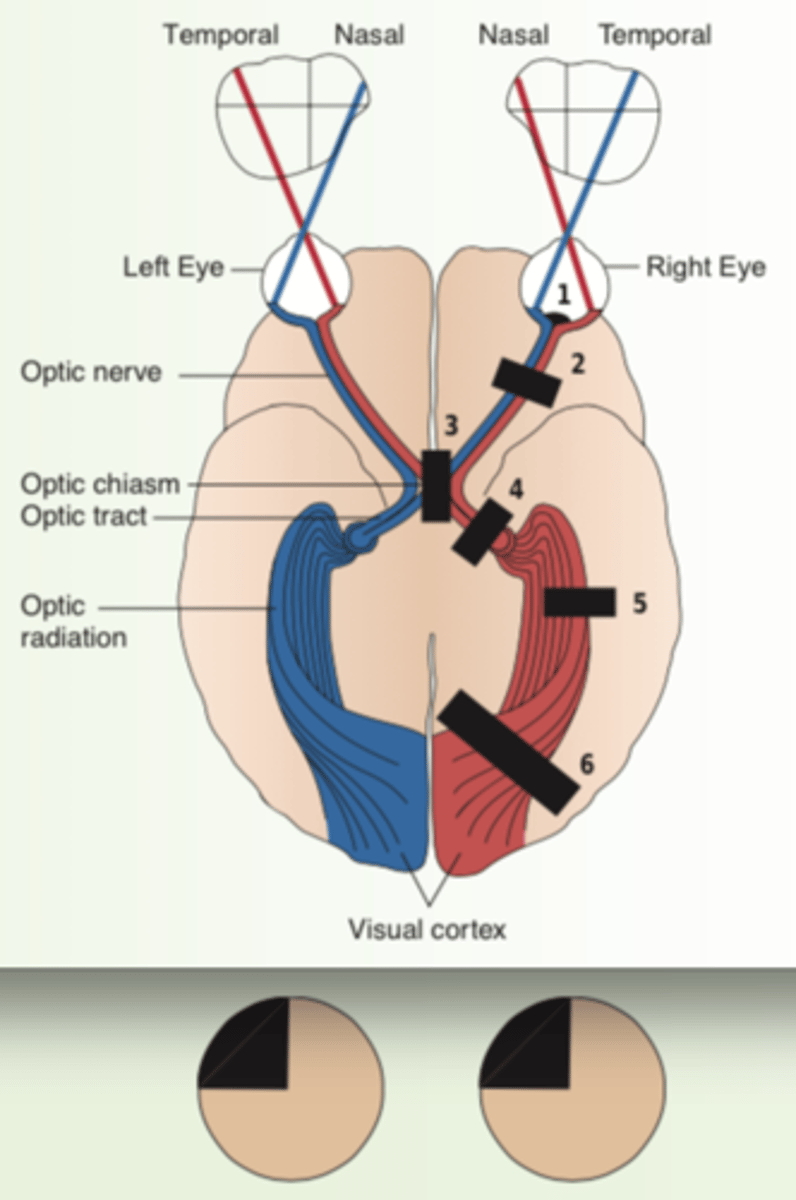
1. Horizontal Defect
2. Blind right eye
3. Bitemporal Hemianopsia
4. Left homonymous heminopsia
5. Homonymous Left Superior Quadrantic Defect
List all the visual field defects.
occlusion of a branch of the central retinal artery or ischemia of optic nerve
What is horizontal defect caused by?
horizontal defect
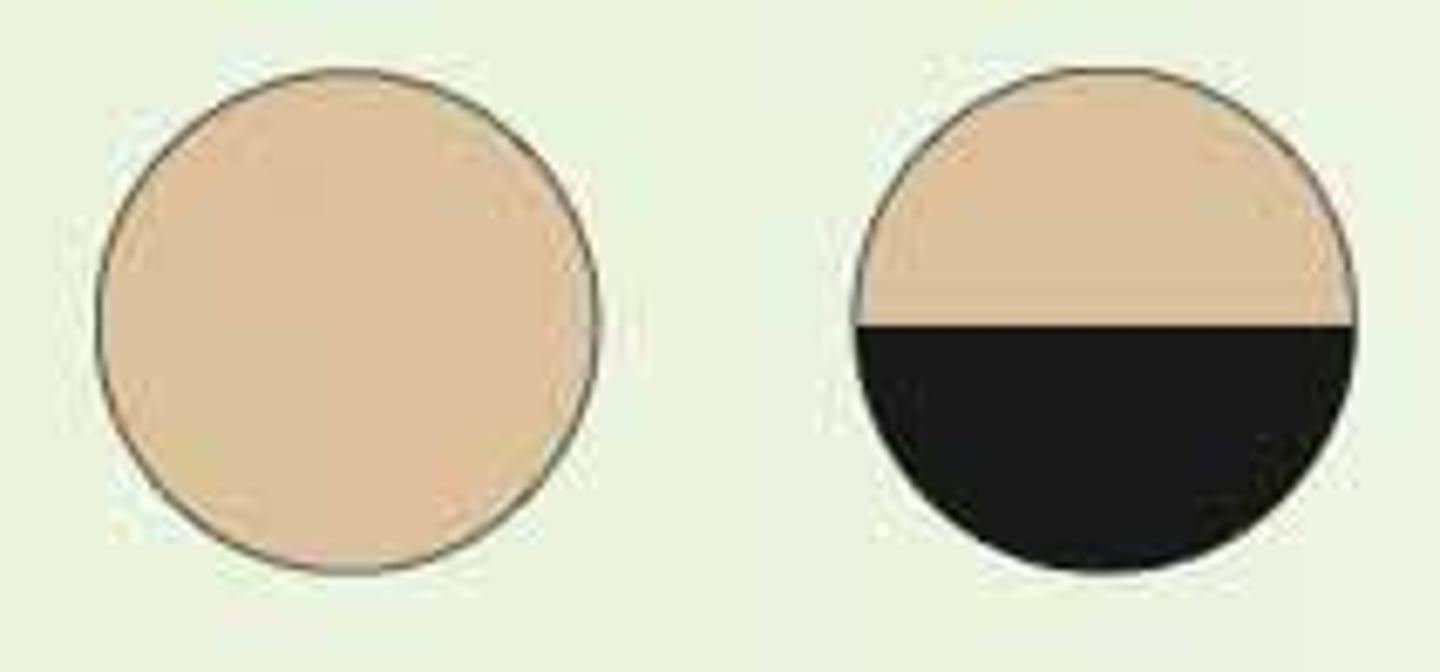
horizontal defect
1
-a lesion of the optic nerve and of the eye itself
What is blind right eye caused by?
unilateral monocular blindness.
What is the result of blind eye?
blind right eye
blind right eye
2
which eye is affected?
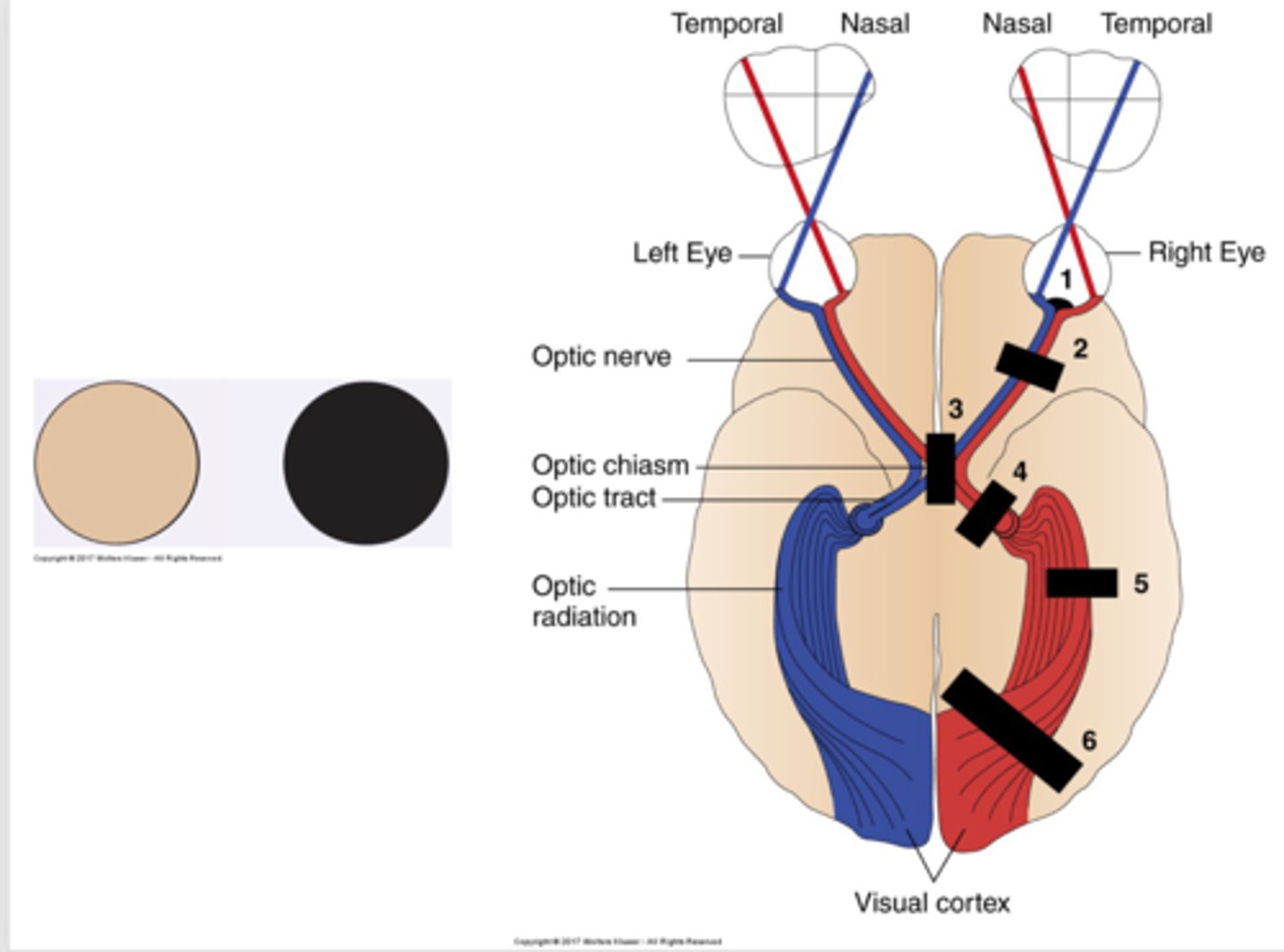
lesion at the optic chiasm
What is bitemoral hemianopsia caused by?
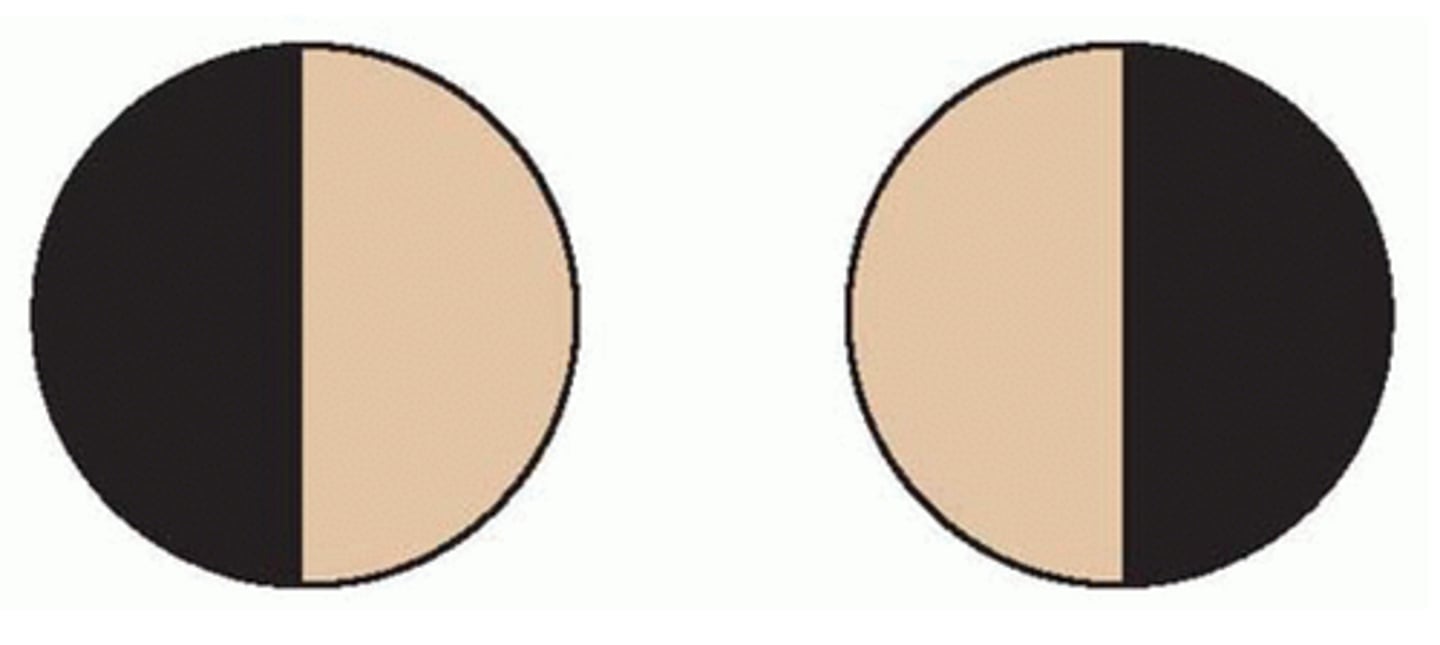
-fibers originate in the nasal half of each retina
-visual loss involves the temporal half of each field.
Describe the effects of bitemporal hemianopsia.
bitemporal hemianopsia.
bitemporal hemianopsia.
3
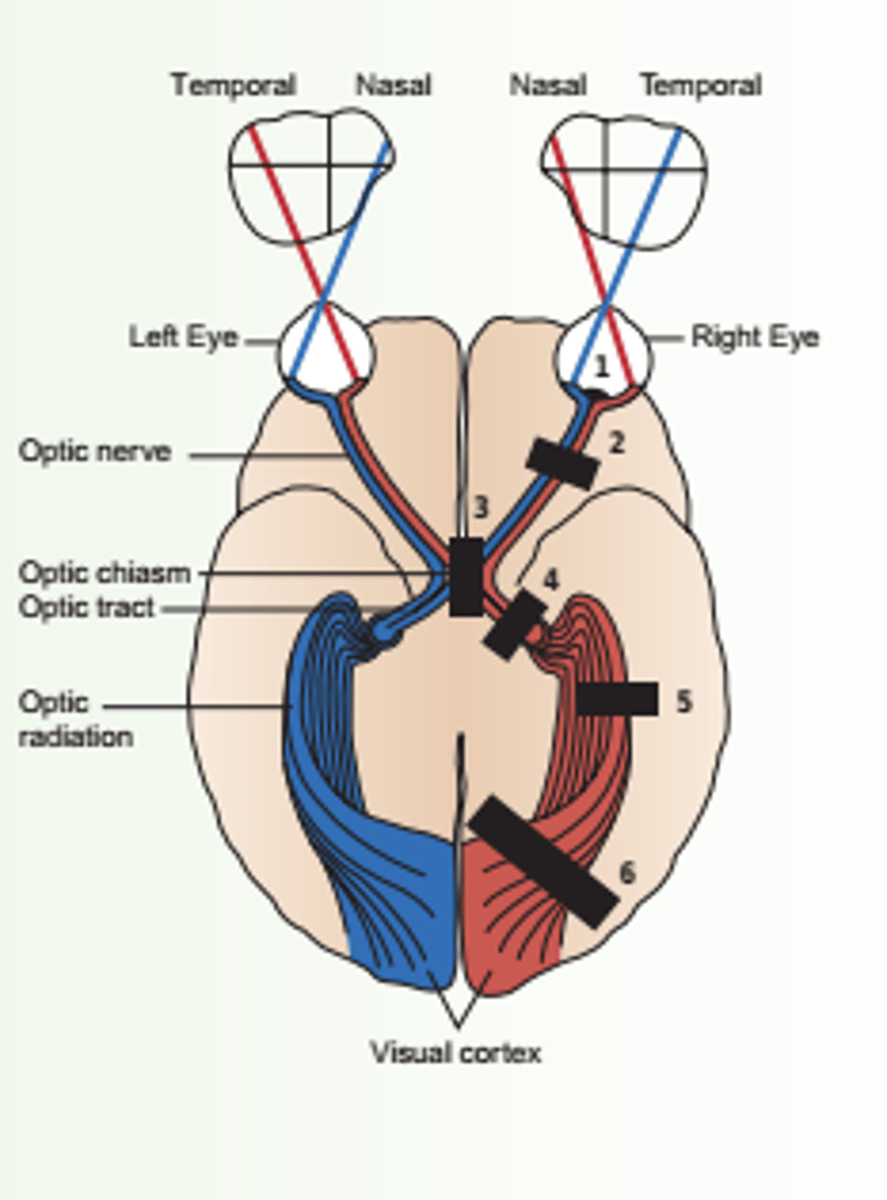
lesion of the optic tract, interrupts fibers originating on the same side of both eyes.
What is homonymous hemianopsia caused by?
-visual loss -- half of each field
Describe the effects of homonymous hemianopsia.
Homonymous Hemianopsia
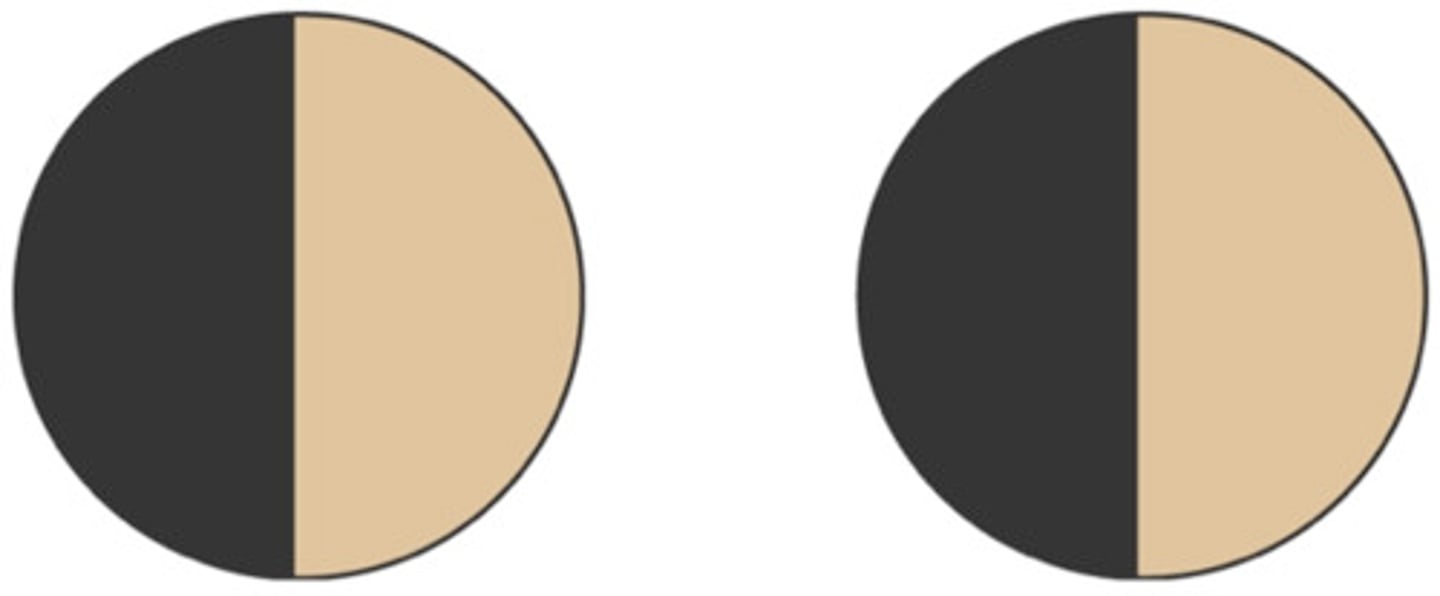

Left Homonymous Hemianopsia
4 or 6
which side of the eye is affected?
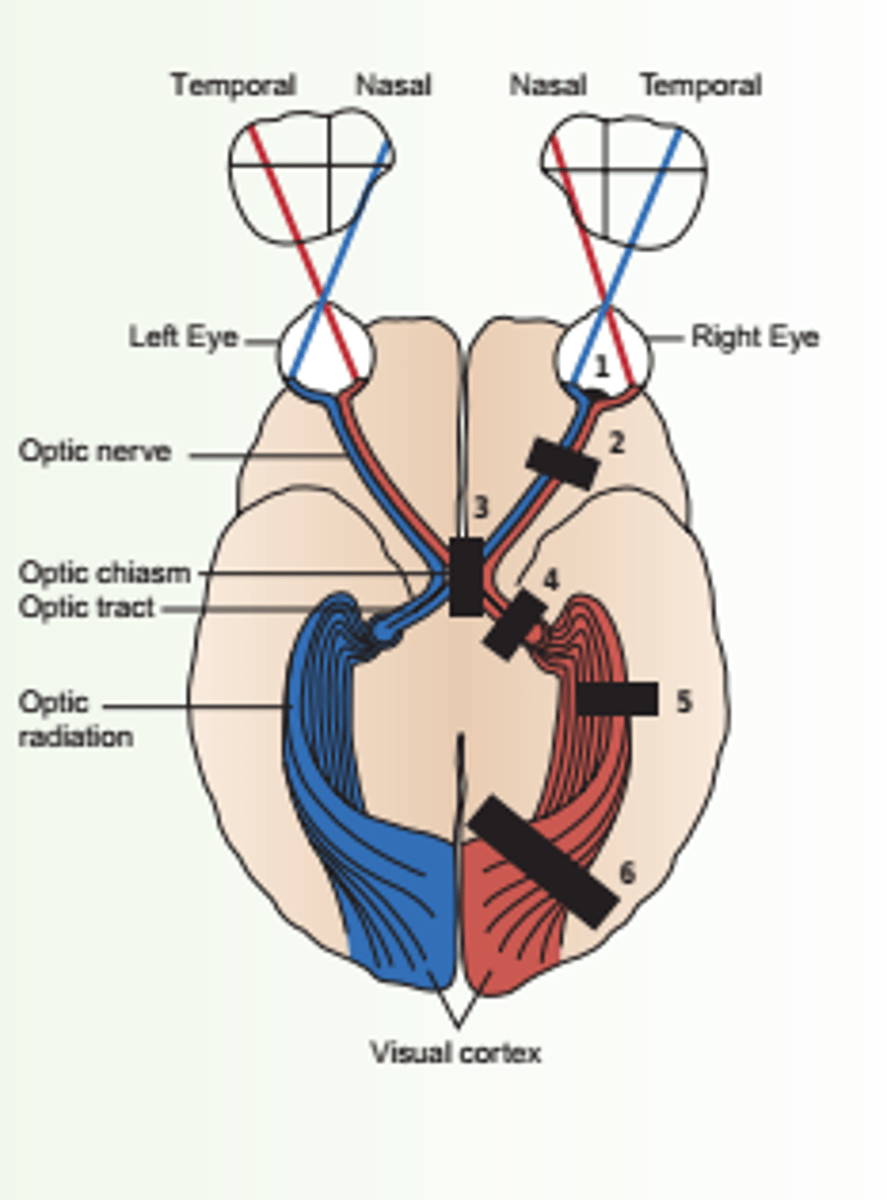
A partial lesion of the optic radiation in the temporal lobe
What is homonymous superior quadrantic defect caused by?
homonymous superior quadrantic defect
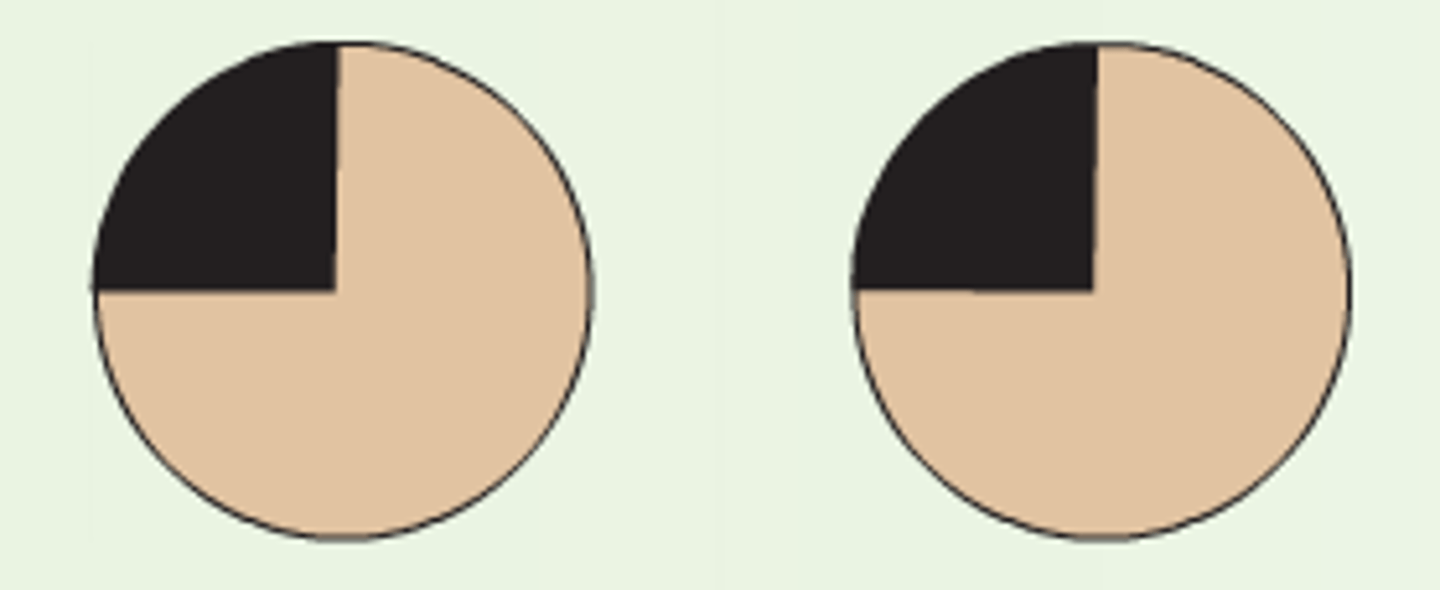
homonymous superior quadrantic defect
5
drooping of the upper lid.
Define ptosis.
-senescence
-myasthenia gravis
-damage to the oculomotor nerve (CN III),
-damage to the sympathetic nerve supply (Horner syndrome).
What can cause ptosis?
ptosis
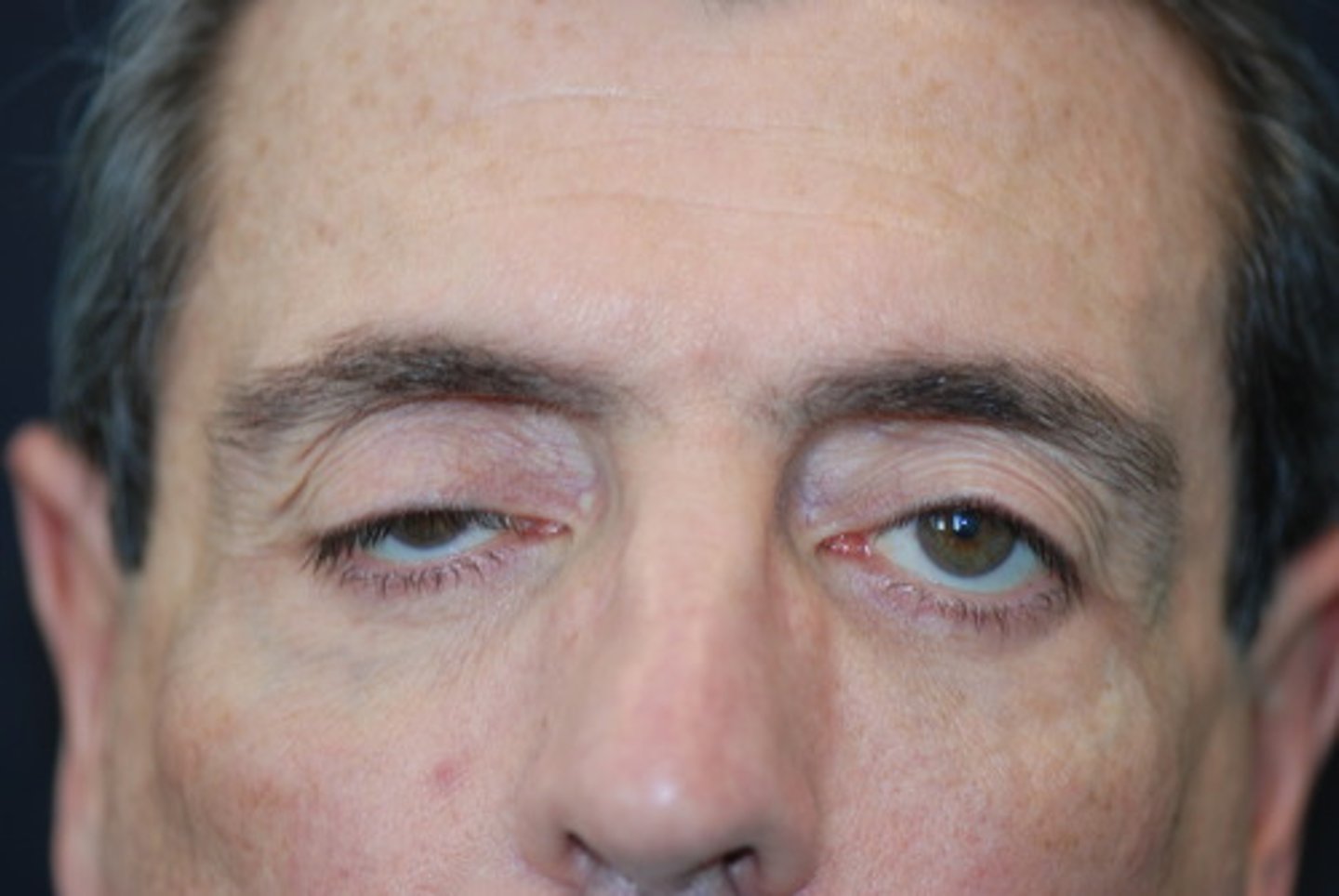
-inward turning of the lid margin
-lower lashes irritate conjunctiva and lower cornea
Define entropion.
entropion
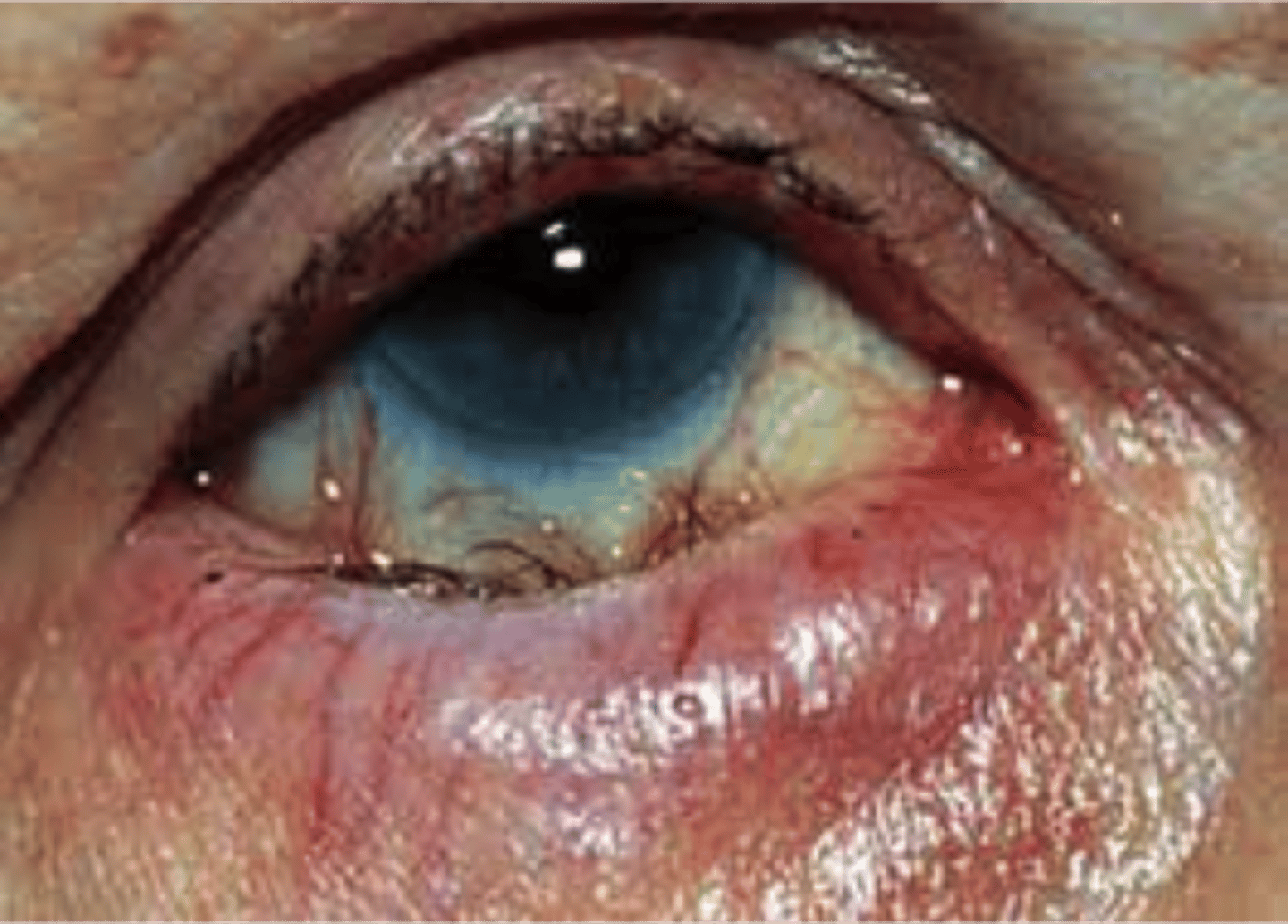
-the lower lid margin turns outward
-exposing the palpebral conjunctiva.
Define ectropin.
ectropin
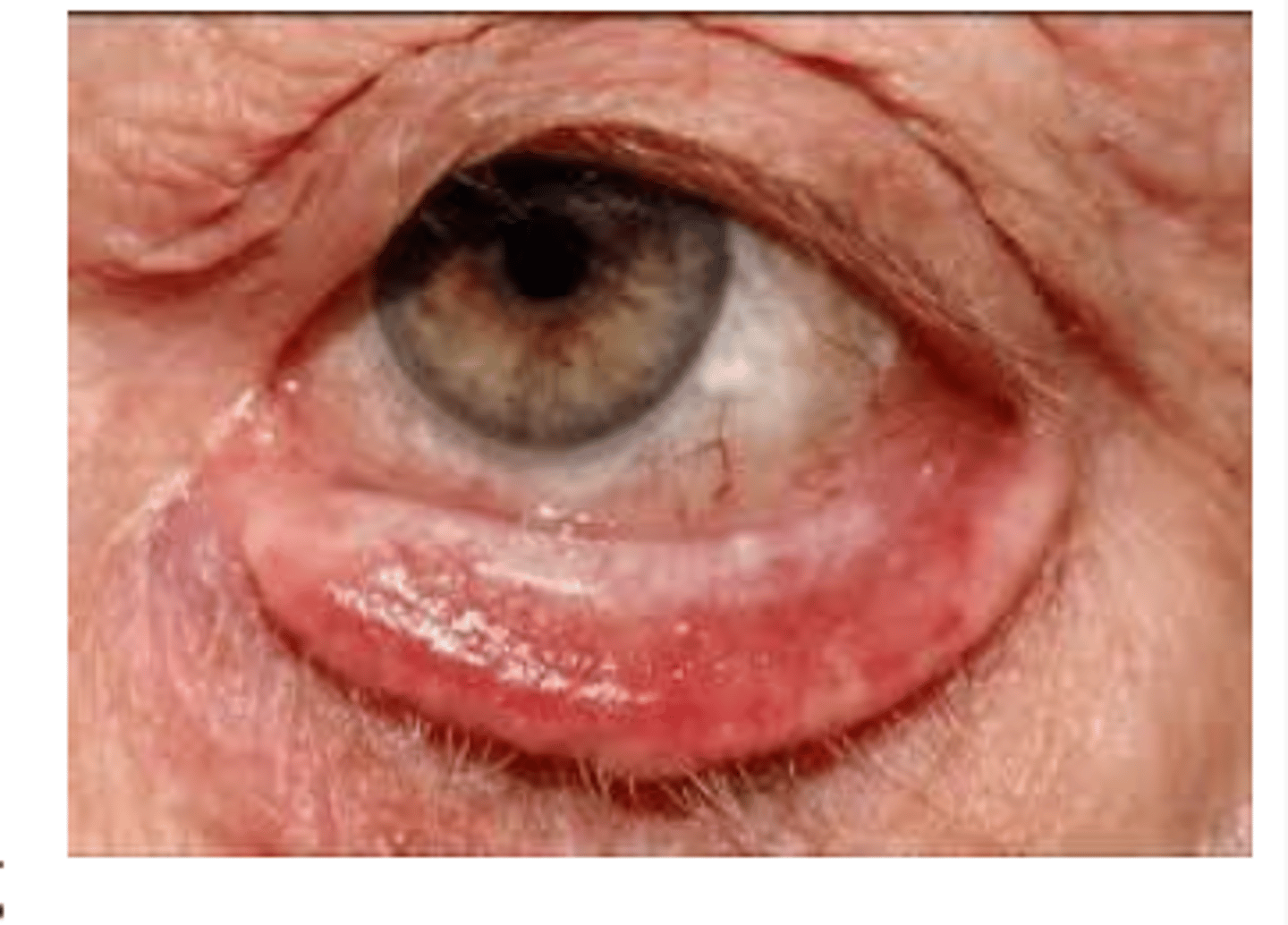
a wide-eyed stare - the rim of sclera between the upper lid and the iris.
Define lid retraction.
lid retraction
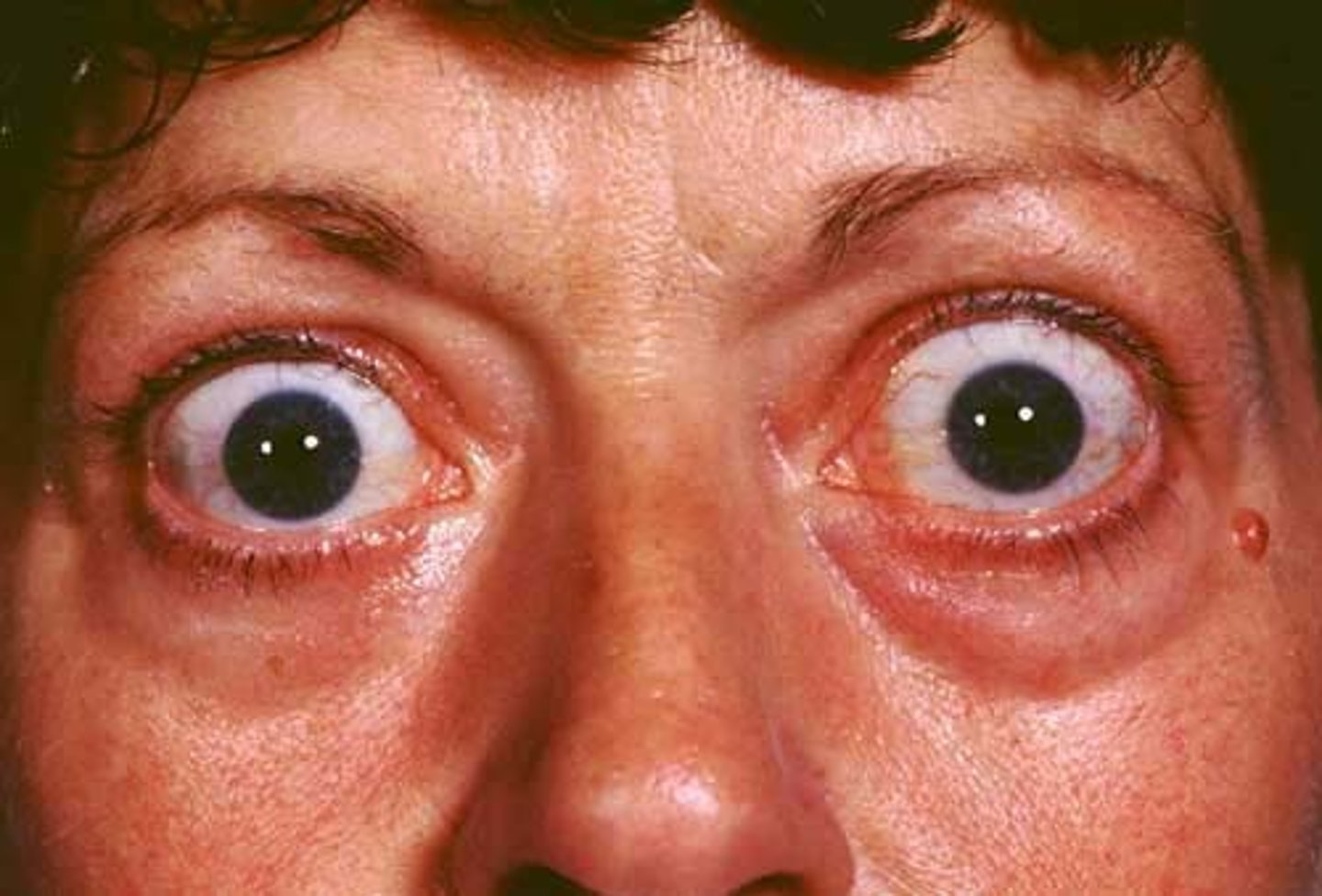
Protrusion of the eyeball
Define exophthalmos.
hyperthyroidism
What causes lid retraction and exophlthalmos?
harmless yellowish triangular nodule in the bulbar conjunctiva on either side of the iris.
Define pinguecula.
Appears frequently with aging
-first on the nasal side
-then on the temporal side.
What is the pattern of pingecula?
pinguecula
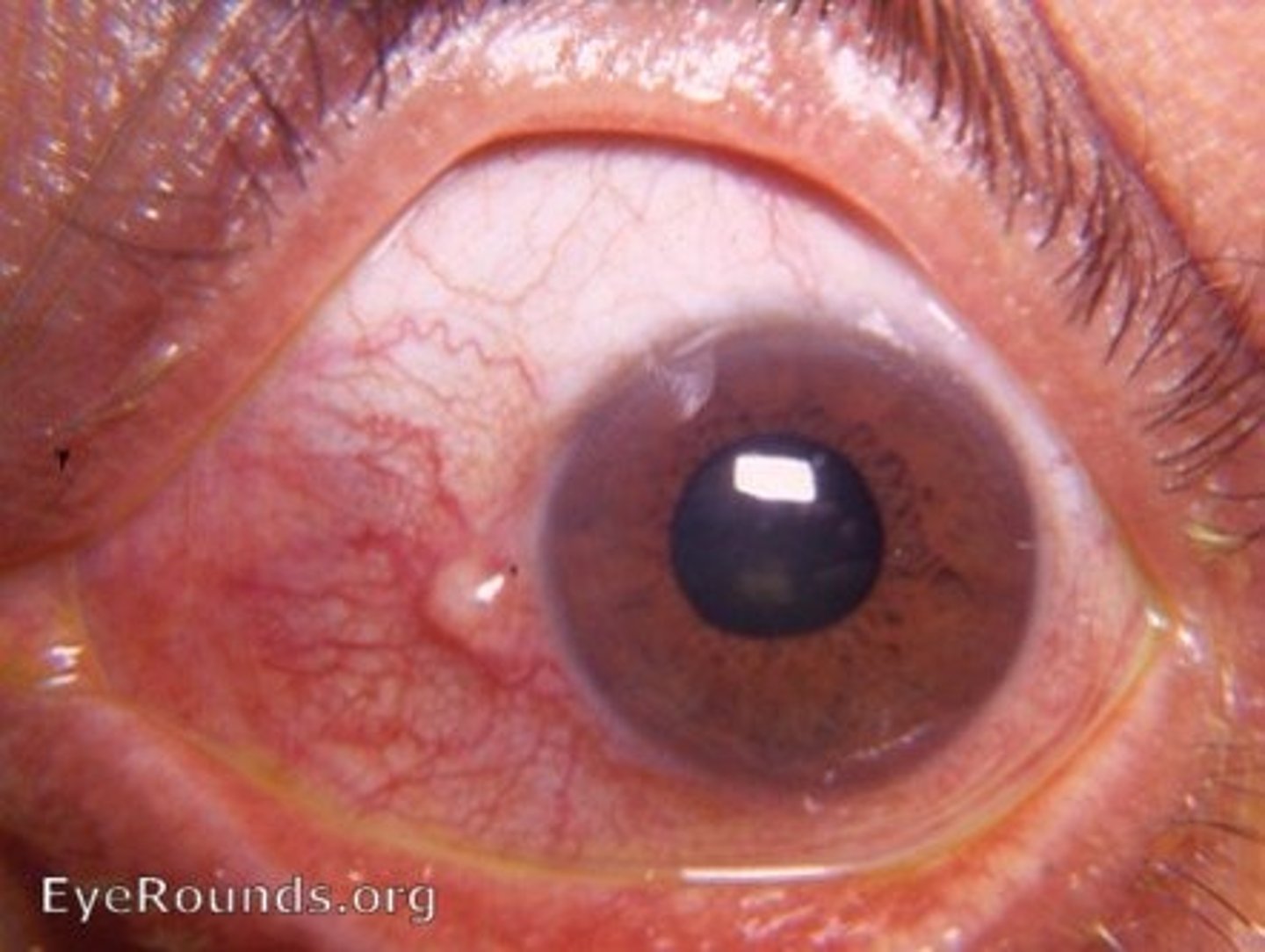
benign, usually painless localized ocular inflammation of the episcleral vessels.
Define episcleritis.
movable over the scleral surface.
In episcleritis, the vessels may appear ___.
episcleritis
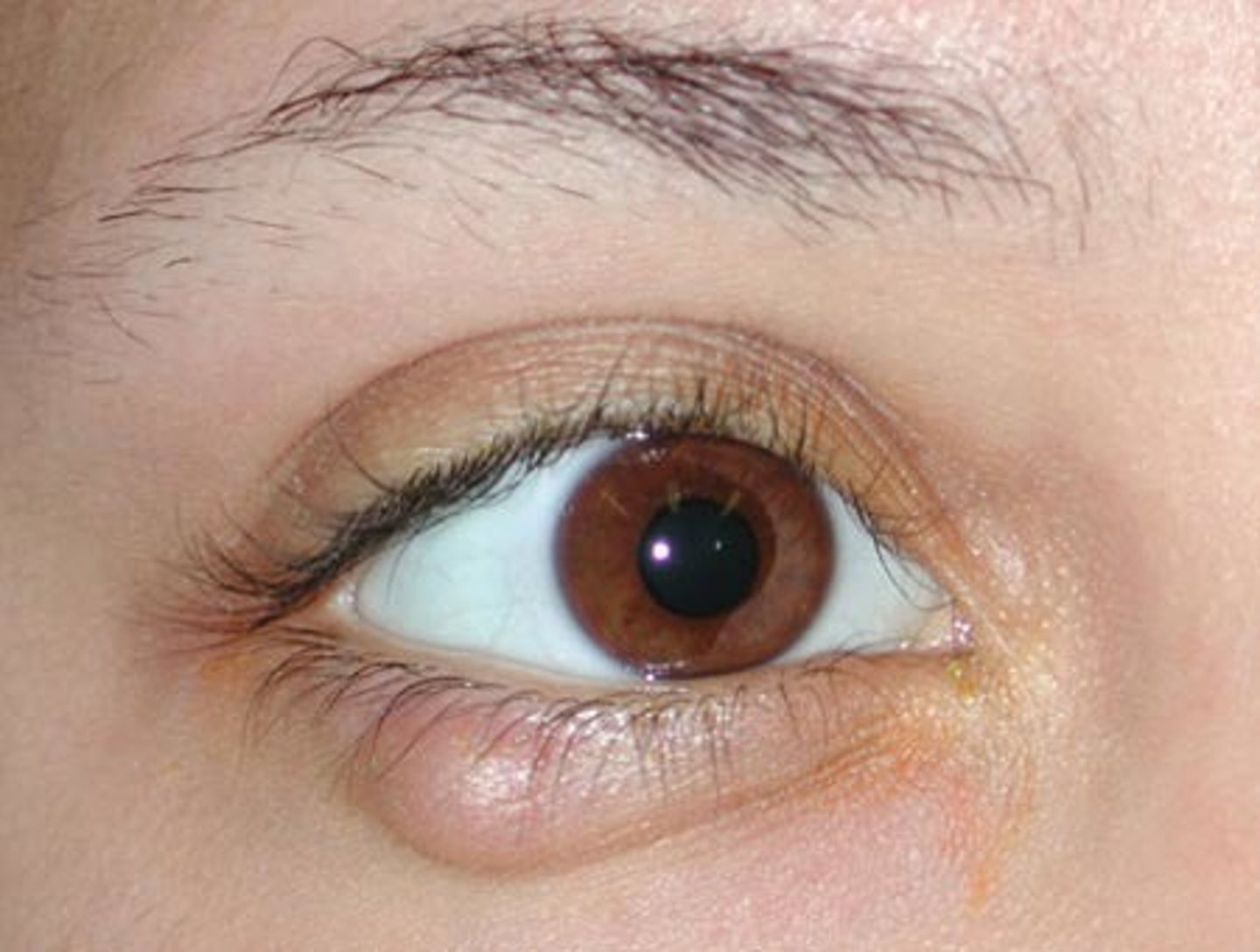
(Stye)
-a painful, tender, red infection at the inner or outer margin of eyelid
Define hordeolum.
a subacute nontender, usually painless nodule caused by a blocked meibomian gland.
Define chalazion.
hordeolum
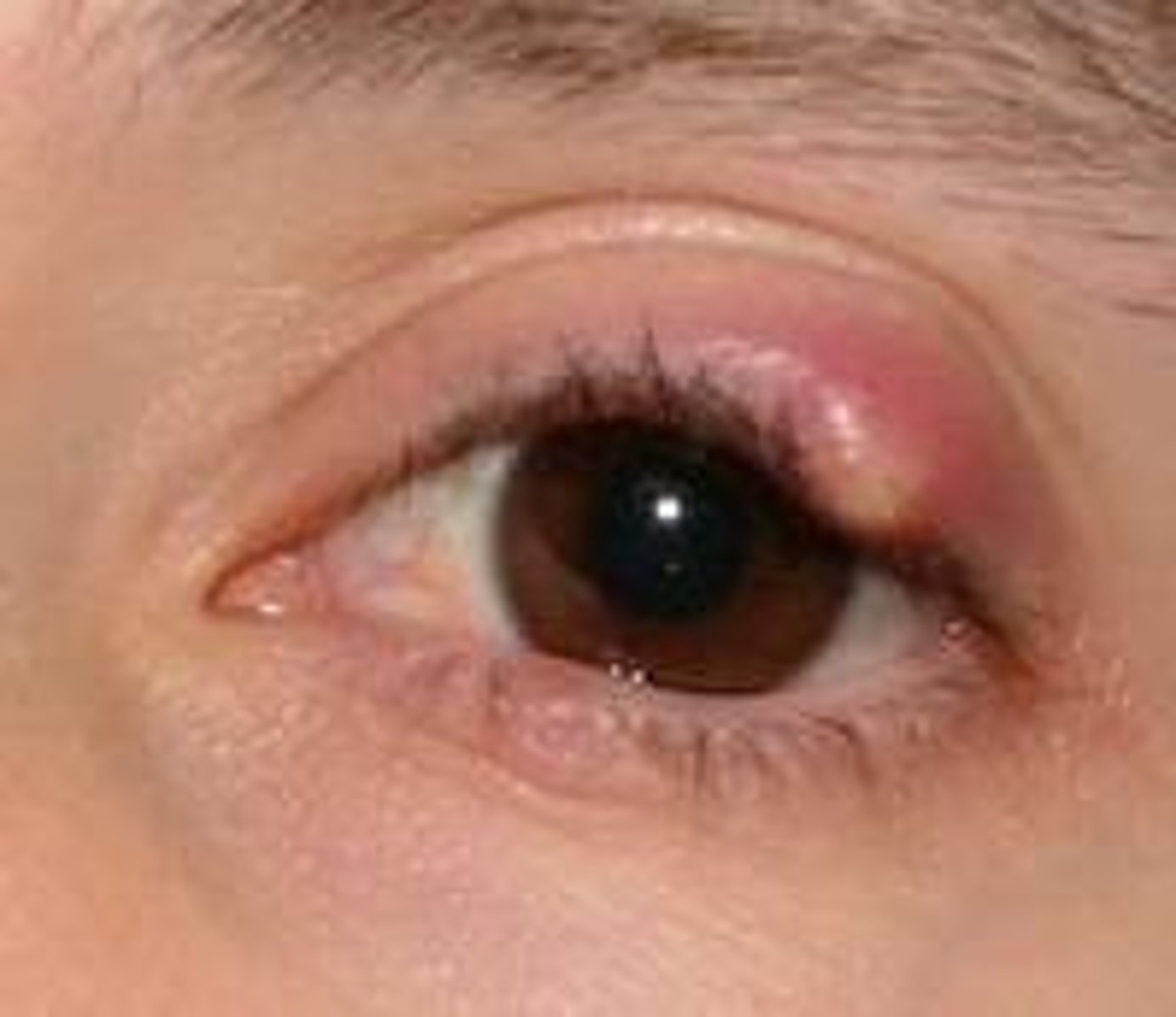
chalazion
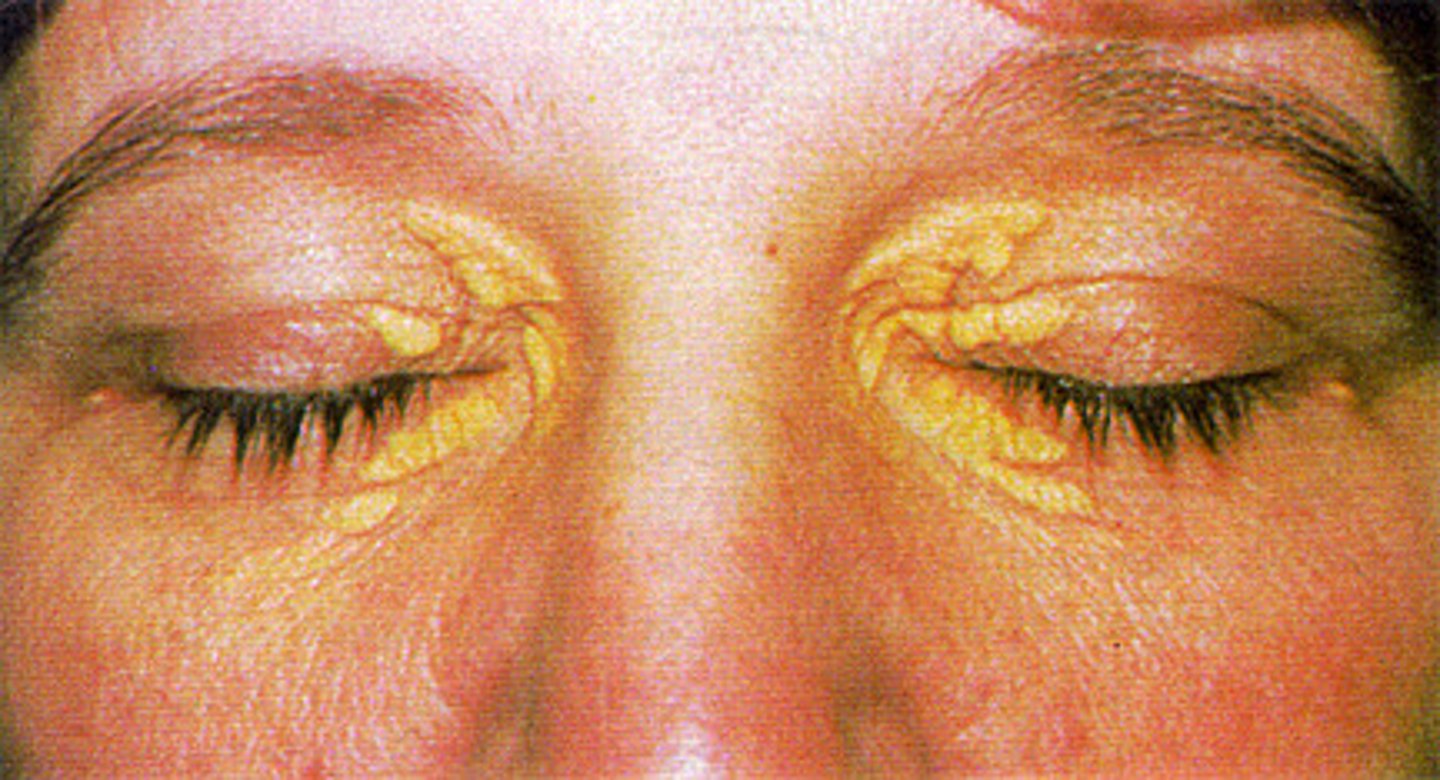
slightly raised, yellowish, well-circumscribed cholesterol-filled plaques that appear along the nasal portions of one or both eyelids.
Define xanthelasma.
xanthelasma
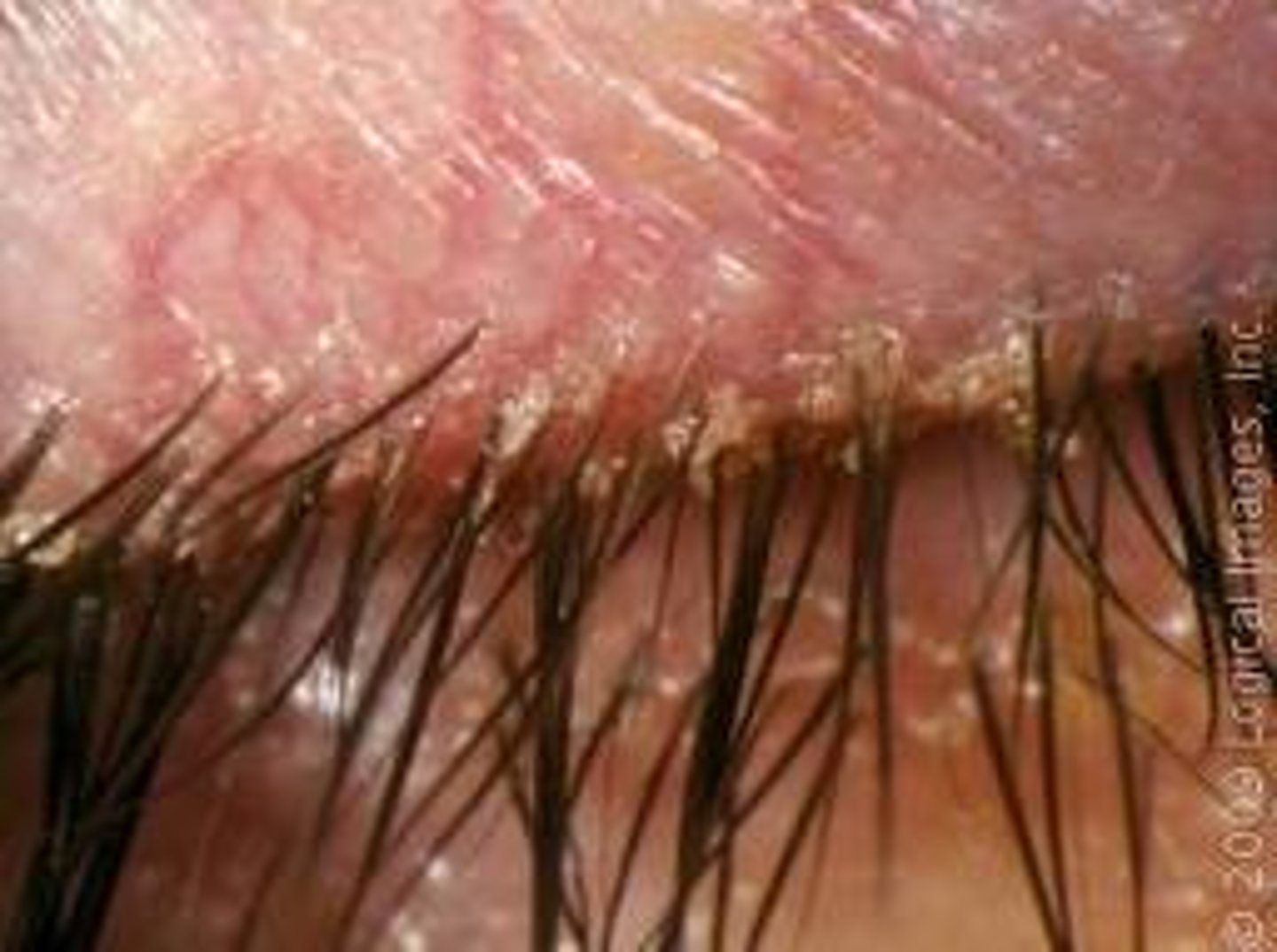
A chronic inflammation of the eyelids at the base of the hair follicles, often from S. aureus.
Define blepharitis.
blepharitis
-corneal arcus
-kayser-fleisher ring
-corneal scar
-pteygium
-cataracts
List the opacities of the cornea and lens.
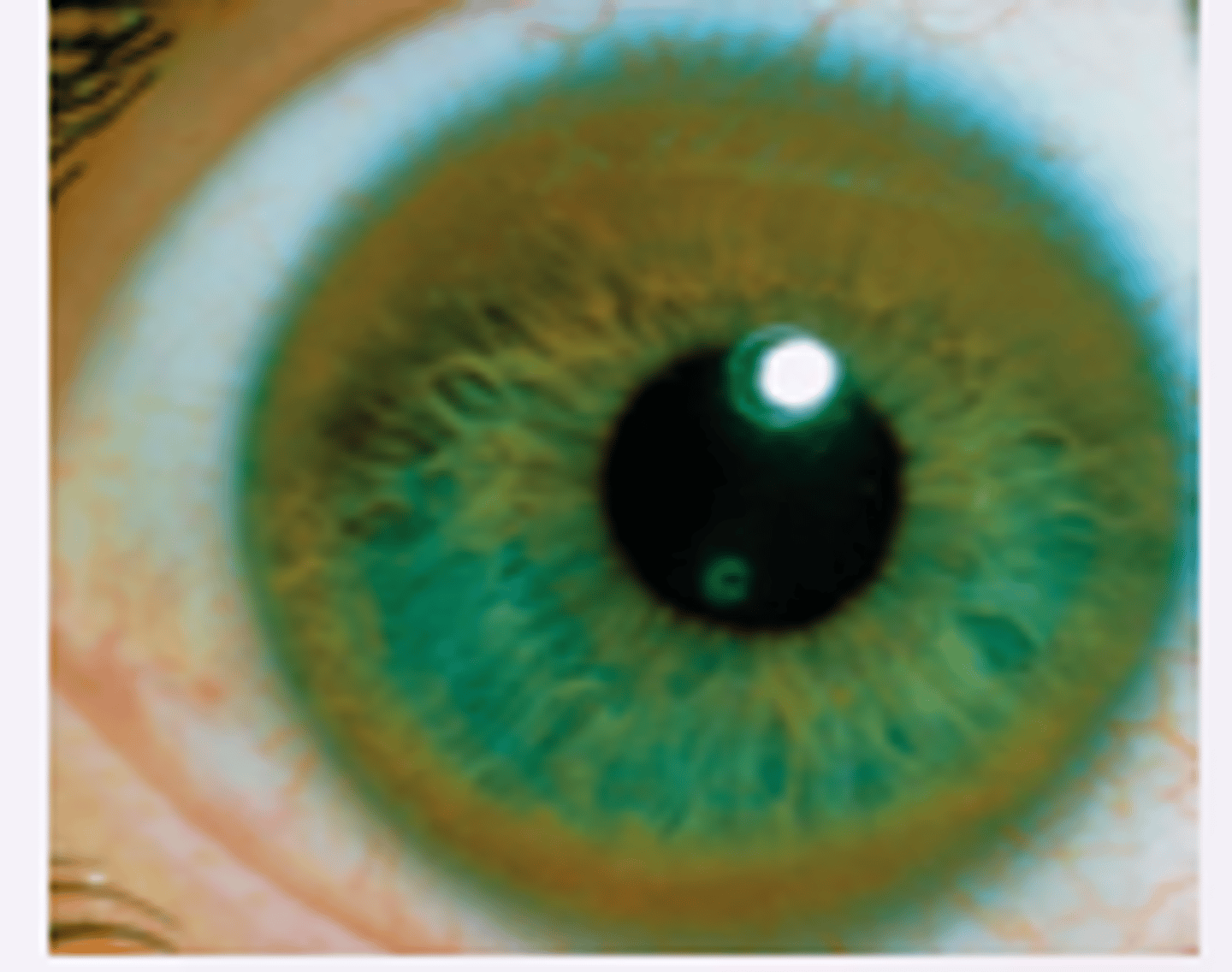
-a thin grayish-white arc or circle not quite at the edge of the cornea.
-usually benign
Describe corneal arcus.
corneal arcus
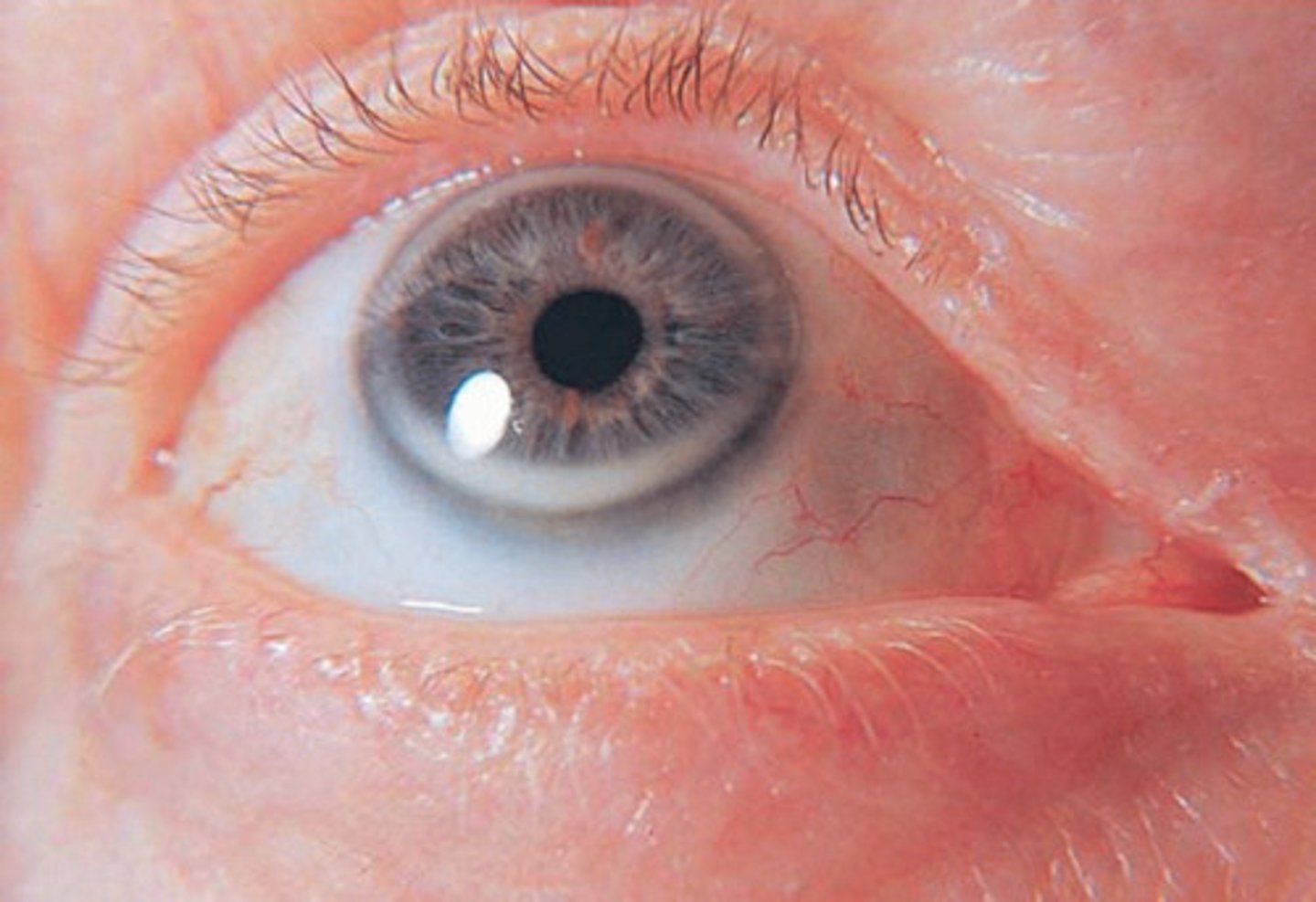
a golden to red brown ring from copper deposition in the periphery of the cornea found in Wilson disease.
Describe kayser-flesicher ring.
kayser-flesicher ring
-A superficial grayish-white opacity in the cornea
-due to old injury or inflammation
Describe corneal scars.
corneal scar
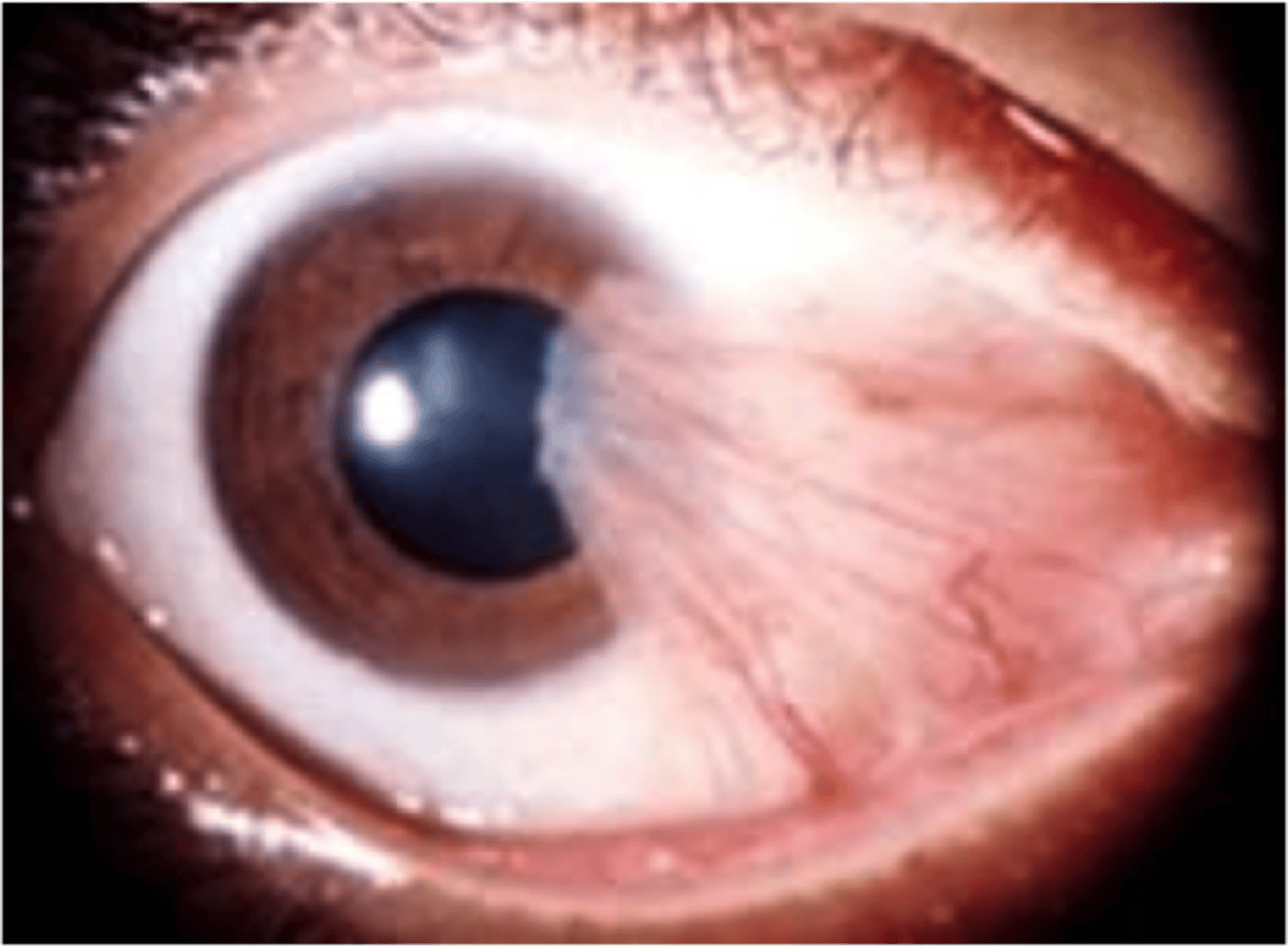
-triangular thickening of the bulbar conjunctiva that grows slowly across the outer surface of the cornea, usually from the nasal side.
-redness and iritation
-may interefere with vision
Describe pterygium.
pterygium
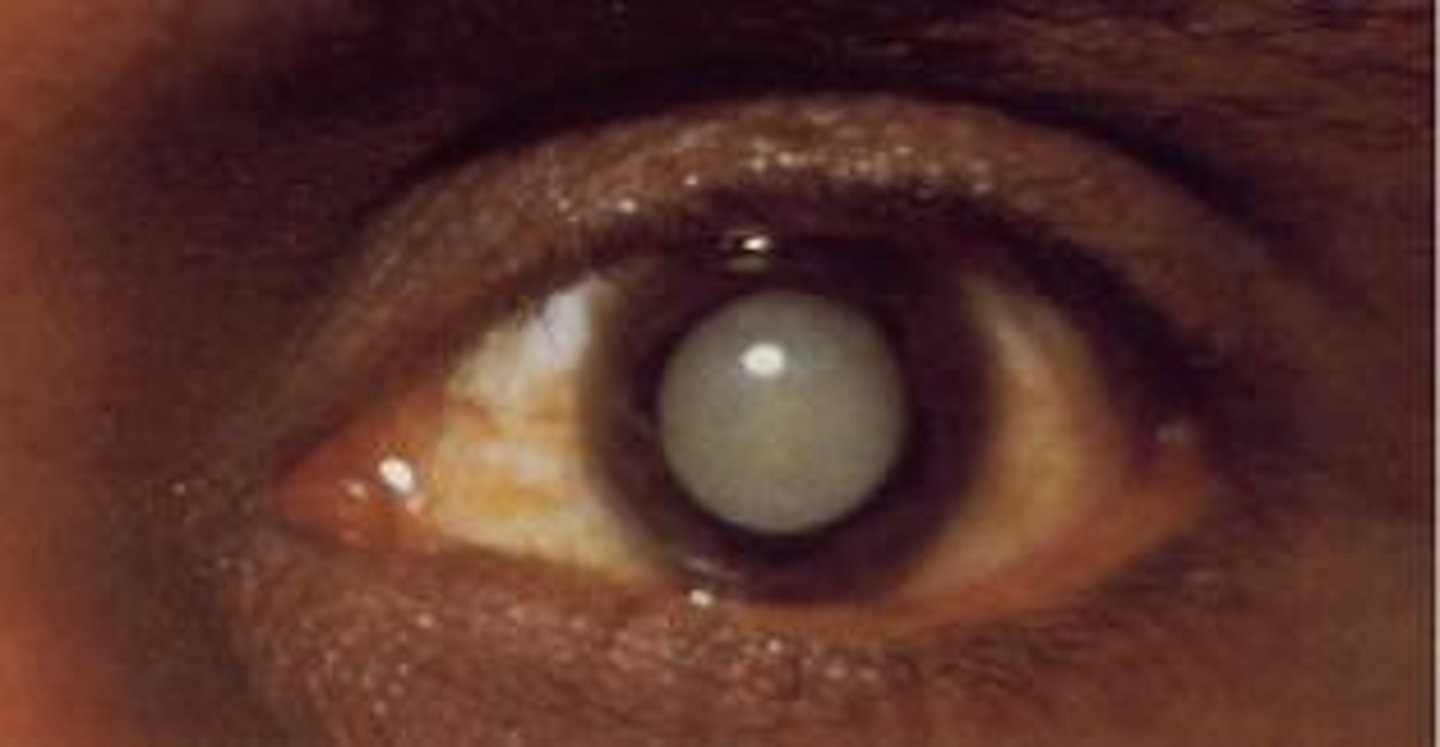
-Opacity of the lenses = most commonly from denaturation of lens protein caused by aging
-generalized bilateral blurred vision
-cloudiness of the lens
Describe cataracts.
age
UV light
trauma
steroids
diabetes
cigarette smoking
family history
What are the risk factors for cataracts?
cataracts
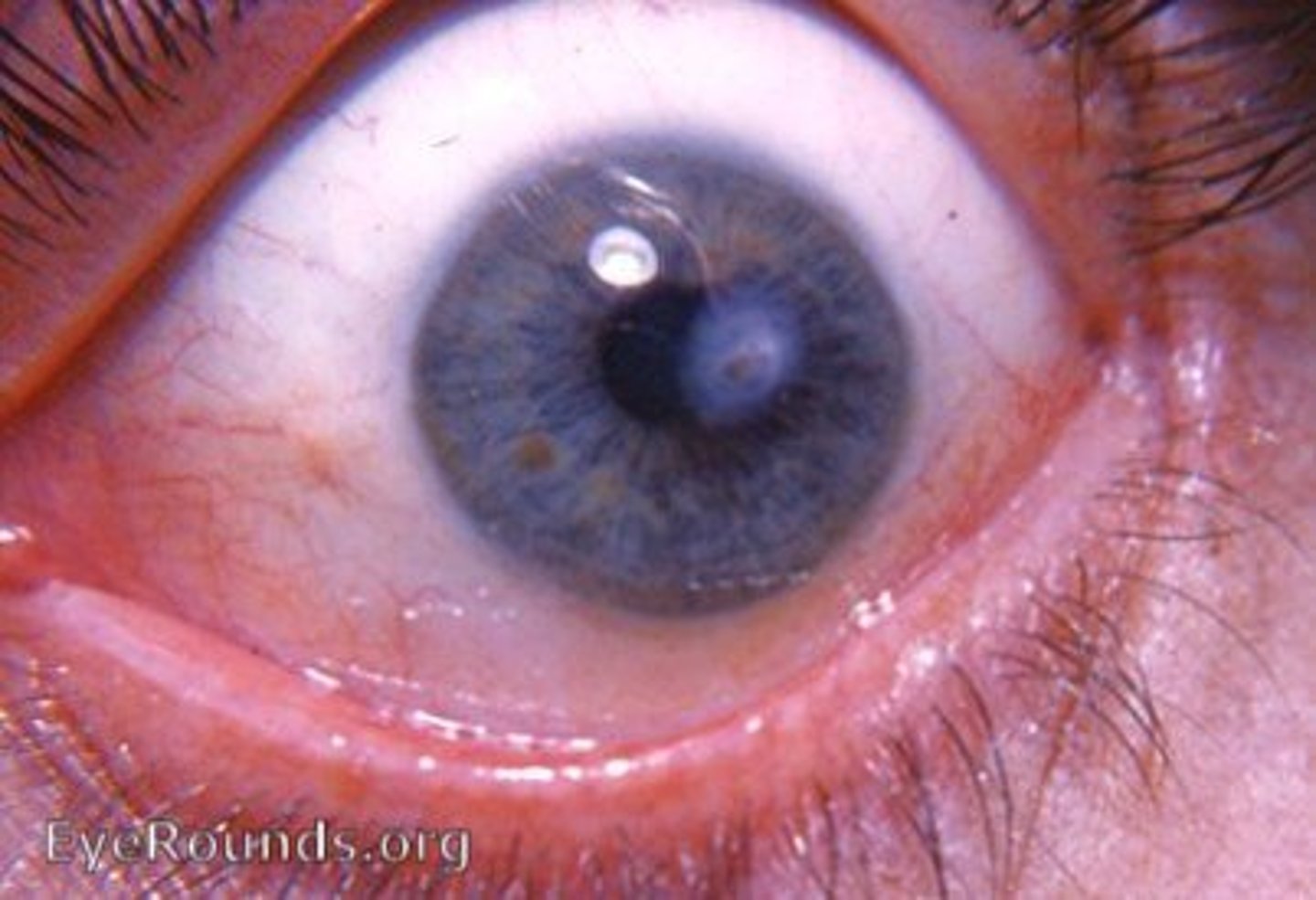
-unequal pupils (anisocoria)
-tonic pupil (adie pupil)
-oculomotor nerve (CN 3) damage
-horner syndrome
-argyll robertson pupill
List the unilateral and bilateral pupillary abnormalities.
-parasympathetic
-sympathetic
Constriction and near effort are mediated by ____.
Dilation is mediated by ____.