CE227 Final Exams - ACES Academics Committee '24-'25
1/633
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
634 Terms
What are markers in railroad engineering?
Objects indicating the position, direction, and conditions of specific items to railway staff, considering train operation speed and rolling stock performance.
What is the purpose of the construction gauge in railroad engineering?
To ensure the safety of rolling stock and passengers by preventing any structure from being introduced within the construction gauge.
How is the cant of a track defined?
The shortest distance between the inner side surfaces of two rail heads of a track.
What factors determine the width of the formation level in railroad construction?
The width is determined to ensure the safety of passengers and workers, considering the pitching motion of traveling rolling stock and track structure.
What is a transition curve in railroad engineering?
A curve provided between a straight line and a circular curve or between two circular curves, based on structure, degree of cant, and traveling speed.
How is the center-to-center distance of adjacent tracks determined?
By adding a margin to the width of rolling stock, considering pitching motion to ensure safety, and widening this distance at curves.
What considerations are taken into account when determining the grade of a track?
Power performance, braking performance, speed of operation of rolling stock, and the standard steepest grade for main lines.
What is the purpose of a vertical curve in track design?
To prevent derailing of rolling stock and to avoid unpleasant feelings for passengers when the grade changes.
What are the three main power facilities in railroad engineering?
Contact lines, substations, and lighting facilities.
What measures are included in disaster prevention devices for railroads?
Devices to prevent entry of unwanted persons and falling objects onto tracks, and evacuation devices to guide passengers during emergencies.
What safety considerations are required for substations in railroad engineering?
Substations must ensure safety and security, meet specified load capacities, withstand overloading, and have a power control center.
How should substations be designed in relation to power supply?
They should be designed so that other substations can provide the necessary power for train operation even if one substation fails.
What is the significance of the construction gauge in relation to rolling stock?
It ensures that no structures interfere with the safe operation of rolling stock and the safety of passengers.
What is the role of disaster prevention devices in railroad safety?
To avoid accidents by preventing unauthorized access to tracks and protecting facilities from damage.
What is the importance of the width of the formation level?
It ensures the safety of passengers and workers by accommodating the pitching motion of rolling stock.
What should be considered when introducing a grade on a main line?
The grade should be as gentle as possible to accommodate the rolling motion of rolling stock.
What is the purpose of evacuation devices in railroad systems?
To safely guide passengers during accidents or emergencies.
What is the relationship between track grade and rolling stock performance?
The grade must be determined based on the power and braking performance of rolling stock.
What is the function of a power control center in substations?
To manage and control the power supply for train operations.
What should be done to ensure the safety of buildings near railroad tracks?
Buildings must be constructed to not compromise the safety of rolling stock and passengers.
What factors influence the design of transition curves?
The structure, degree of cant, and traveling speed of rolling stock.
What is the purpose of installing safety devices along the tracks?
To prevent accidents and ensure the safety of passengers and railway facilities.
What is the purpose of lighting facilities in stations and tunnels?
To facilitate the boarding/alighting of passengers and to guide them to safety in case of emergency.
What specifications are important for station facilities?
Specifications such as effective track length, platform length/width, and ensuring smooth train operation with consideration for passenger safety.
What are the key phases in the transportation development process?
1. Nationwide Systems Planning 2. Transportation Programming Phase 3. Project Evaluation 4. Preliminary Development Phase 5. Detail Design Phase.
What is included in the preliminary development phase of project development?
Finalization of various design elements and development of construction plans, including many intermediate reviews prior to final plan submission.
What types of studies are conducted during the transportation development process?
Traffic request/validation, traffic signal warrant analysis, airway-highway clearance study, alignment and grade review, structure type study, and more.
What are highway plans and specifications?
Sets of documents that provide instructions and conditions under which highways and bridges are built.
What does the engineering (route) survey stage involve?
Locating the center line, determining elevations, plotting profiles and cross sections, computing earthwork volumes, and laying out structures.
What are standard specifications in highway projects?
Written instructions and conditions that are integral to the contract between the contractor and highway agency, classified as legal documents.
What do special provisions cover in highway projects?
Peculiar items of the project that include additional modifications to standard specifications.
What is the significance of determining drainage areas in highway construction?
It is crucial for the design of ditches and culverts.
What is the role of fences and right-of-way in bank protection?
They are devices used for bank protection and to mark boundaries.
What does 'staking out' refer to in engineering surveys?
It refers to marking the required intervals along the center line, usually with stakes called Stations.
What is the purpose of a mass diagram in highway engineering?
To prepare and compute the volumes of earthwork.
What is the importance of smooth transfers in station facilities?
To ensure seamless transitions between railway lines and between railway and other modes of transport.
What is involved in the final roadway check review?
It includes a final check of the roadway, field, and office to ensure compliance with plans.
What is the purpose of a retaining wall justification study?
To assess the need and design of retaining walls in the project.
What does a bridge type, size, and location study entail?
It involves analyzing the appropriate type, size, and location for bridges in the project.
What is the significance of traffic control in highway planning?
Traffic control is essential for ensuring safe and efficient movement of vehicles during construction and operation.
What is the role of sanitary sewer in highway construction?
To manage wastewater and ensure proper sanitation in the vicinity of the highway.
What does the term 'alignment review' refer to in highway engineering?
It refers to the assessment of the horizontal and vertical layout of the highway.
What is the purpose of a drive review in the context of highway projects?
To evaluate access points and driveways in relation to the highway design.
What are the three major structural parts of a roadway?
1. Sub-grade: Reduces traffic stresses to acceptable levels, acts as a working platform, and protects against water. 2. Base Course: High-quality materials like crushed stone or gravel that support the pavement surface. 3. Pavement: The surface layer in direct contact with vehicle wheels, made of asphalt or concrete.
What is the role of the sub-grade in road construction?
The sub-grade is the supporting structure beneath the pavement surface, consisting of properly arranged, graded, compacted, and stabilized earth.
What materials are typically used in the base course of a roadway?
The base course typically consists of crushed stone or gravel, sometimes mixed with asphalt binders.
What is the function of the sub-base layer in a road cross-section?
The sub-base layer, generally made of natural gravel, is provided above the sub-grade to enhance stability and drainage.
What is the purpose of the pavement layer in road construction?
The pavement layer, also known as the wearing course, is the top layer that is in direct contact with vehicle wheels, made of asphalt concrete or Portland cement concrete.
What are the types of base course materials mentioned?
Types of base course materials include bitumen/asphalt, cement, lime, or other binders mixed with aggregate.
What is the significance of AASHTO in road construction?
AASHTO establishes detailed procedures regarding the materials to be used based on soil conditions, type, and behavior.
What is the purpose of asphalt/bituminous treatment in base courses?
Asphalt/bituminous treatment is employed to waterproof and bind granular aggregates, allowing for a thinner overall depth of the pavement.
What is a typical characteristic of untreated gravel road surfaces?
Untreated gravel road surfaces consist of a mixture of soil particles ranging in size from coarse to fine, and must be stable to support the superstructure.
What is the role of guard rails and parapets in road design?
Guard rails and parapets are structures designed to enhance safety by preventing vehicles from leaving the roadway.
What are typical drainage structures included in road design?
Typical drainage structures include pipe culverts, concrete box culverts, drainage inlets and outlets, and manholes.
What is the purpose of curbs and gutter structures in road design?
Curbs and gutter structures are used to manage drainage and define the roadway edge.
What is rip-rap and its function in road construction?
Rip-rap consists of large stones used to protect soil from erosion, often placed along embankments and shorelines.
What is the importance of proper grading and compaction of the sub-grade?
Proper grading and compaction of the sub-grade ensure stability and support for the pavement layers above.
How does the sub-grade protect against water movement?
The sub-grade acts as a drainage layer, intercepting upward movement of water by capillary action.
What is the difference between sub-grade and sub-base?
The sub-grade is the original soil beneath the road, while the sub-base is a layer of granular material placed above the sub-grade.
What are the components of a typical road structure cross-section?
A typical road structure cross-section includes the pavement surface, base course, sub-base, and sub-grade.
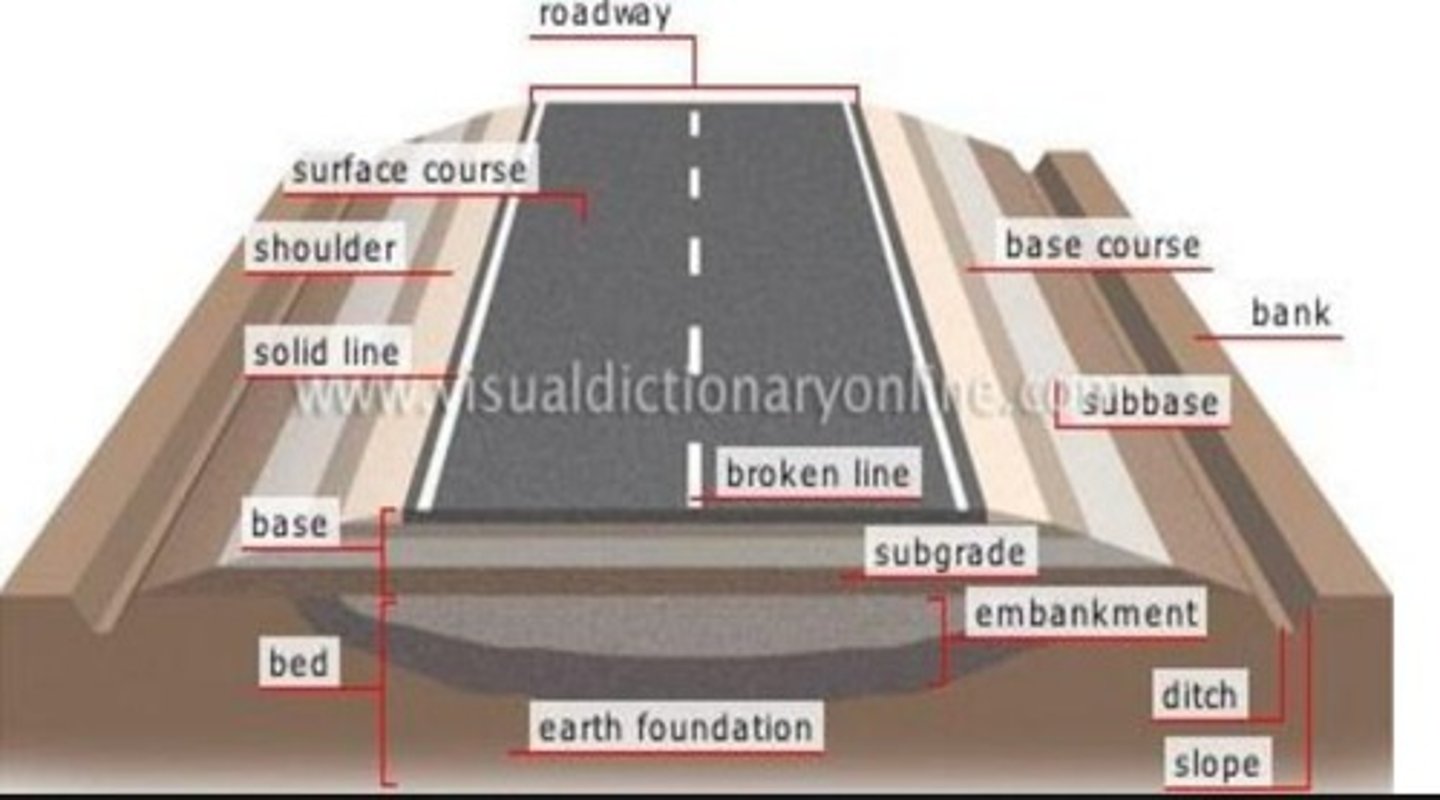
What is the significance of using high-quality materials in the base course?
High-quality materials in the base course are essential to withstand severe loading and ensure the longevity of the pavement.
What is the role of drainage inlet and outlet structures?
Drainage inlet and outlet structures are designed to manage water flow and prevent flooding on roadways.
What are the characteristics of a stable road surface made from untreated soil mixture?
A stable road surface made from untreated soil mixture must support the superstructure and maintain integrity under traffic loads.
What is the impact of water on the sub-grade in road construction?
Water can weaken the sub-grade, leading to potential structural failures if not properly managed.
What is the purpose of sidewalks in road design?
Sidewalks provide a safe space for pedestrians, separating them from vehicular traffic.
What are the key requirements for a satisfactory soil aggregate surface?
It must resist traffic activities, shed rain, be free from large rocks, possess capillarity properties, and maintain moisture.
Why must the road surface shed a large portion of rain?
To prevent water from penetrating the subgrade, which might soften it and loosen surface stability.
What is the significance of capillarity properties in road construction?
They are necessary to replace moisture lost through surface evaporation, maintaining the desired damp condition to bind particles together.
What should be avoided in the composition of road materials?
An excessive amount of highly expansive clay materials.
What materials are typically used in a treated base course?
Mineral aggregate and additives to enhance strength and moisture resistance.
What is the impact of wet clay on road stability?
Wet clay can swell and unseat coarser materials, weakening the road's stability.
What is a key consideration for gravel roads in terms of funding?
Gravel roads often have limited funding and are frequently overlooked in appropriation priorities.
What type of materials should be utilized for road construction?
Local materials that can be found nearby the project site.
What is the recommended asphalt binder content by weight for a stable mixture?
The content of asphalt binder should range from 4-10%.
What are the AASHTO standard specifications for fine grain asphalt base?
Maximum Liquid Limit of 35, Plastic Index of 4 to 9, and a maximum of 8% passing the No. 200 sieve.
What factors affect the type of asphalt binders for base course?
The mixing procedure (plant or field), the Plastic Index of the mixture, and the percentage of aggregates passing from the No. 200 sieve.
What is the purpose of using Portland cement in soil stabilization?
It was initially practiced after WW1 to stabilize soils and aggregates.
What is the typical percentage of asphalt for stability in mixtures?
The weight of asphalt for stability is typically in the range of 5% to 7%.
What is the typical percentage of asphalt for waterproofing purposes?
For waterproofing, 2% to 3% of the asphalt binder is added.
What happens if emulsion is used in asphalt mixtures?
Enough water must be added to ensure proper mixing.
What is the role of the Marshall or HVEEM Stabilometer procedure?
It is used to measure the stability of asphalt mixtures in the laboratory.
What is the effect of dry weather on clay in road construction?
The moisture film on clay is crucial for maintaining stability and binding particles together.
What are the characteristics of a good sand and asphalt base course?
It should be composed of clean and strong sand to resist displacement under load.
What are the consequences of water penetrating the subgrade?
It may soften the subgrade and compromise surface stability.
What is the importance of using local materials in road construction?
Utilizing local materials can reduce costs and support the local economy.
What is the impact of traffic activities on road materials?
Road materials must be resistant to various traffic activities and abrasive actions.
What is cement stabilization in road construction?
Cement stabilization involves mixing natural materials with Portland cement, compacting at optimum moisture content, and curing to create a strong and stable base.
What are the benefits of cement stabilization regarding moisture and temperature?
Cement stabilization is less susceptible to deformation caused by moisture and temperature changes.
How is the quality of an aggregate cement mixture measured?
The quality is measured by its ability to resist abrasion and disintegration.
What is the role of soil cement in the mixture?
Soil cement is included to allow compaction at near-optimum moisture content.
What types of soils are included in a stabilized cement mixture?
Sandy and gravelly soil with less than 25% silt and clay, sand with fewer fines, and silty and clayey soils.
How does the amount of cement required differ between sandy/gravelly soils and silty/clayey soils?
Sandy and gravelly soils require less cement compared to silty and clayey soils.
What is the most effective routine maintenance for untreated surfaces?
The most effective maintenance is done immediately after rainfall when the surface is soft for the blade to drag.
What is the typical loss of materials due to grading and traffic wear per year?
Losses generally range from 1/2 to 1 inch of thickness per year, varying with traffic volume, rainfall, wind intensity, and maintenance practices.
What equipment is effective for compaction of untreated surfaces?
Compaction is effectively done using pneumatic tired or steel wheeled rollers.
What is the required cross slope for untreated surface gravel roads?
The cross slope must be sufficient to drain water to prevent potholes and softening of the roadway.
What is considered a satisfactory cross slope for road materials that are stable and water tight?
1 inch per slope is satisfactory, although 3/8 inch to 1/2 inch per foot slope is preferred.
What construction method is sometimes adopted in road development?
Stage construction methods, which involve step-by-step improvement of the roadway based on funding and traffic demand.
What are the three sequences of road improvement?
1. Earth Road Surface 2. Untreated Gravel Road 3. Application of Asphalt over the Aggregate Sub-Base Course.
What does Item 200 classify in DPWH standards?
Item 200 classifies the aggregate sub-base course, which includes furnishing, placing, and compacting aggregate on a prepared sub-grade.