Chapter 2: Organizational Strategy, Competitive Advantage, and Information Systems IS-300
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Porter’s Competitive Forces Model
Threat of Entry of New competitors: high when entry barriers are low and low when barriers are high
New Bank has high barriers bc of an array of MIS-related services
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: strong if few suppliers exist; weaker when buyers have many options. Supply chain magnifies this
Bargaining Power of Customers/Buyers: strong when customers have choices and low switching costs, and loyalty programs help reduce this power
Threat of Substitute Products or Services: high when many alternatives exist
Rivalry Among Existing Firms within the industry: high with many aggressive rivals; lower when markets are less crowded (product differentiation key to standing out)
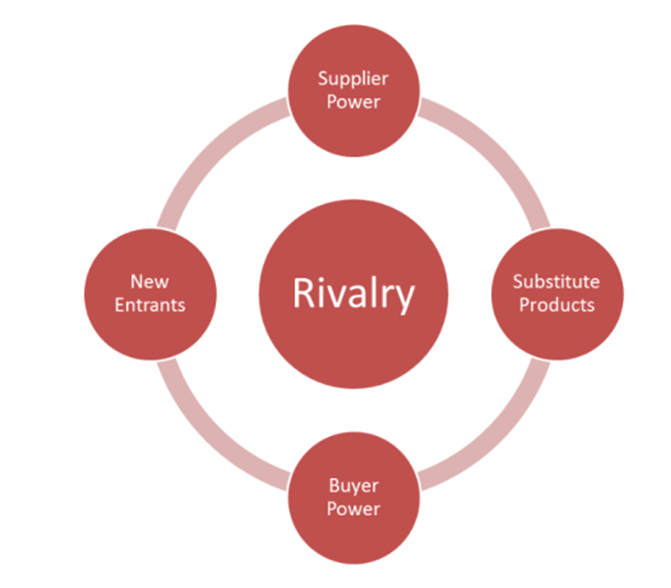
Buyer Power
Ability of buyers to affect the price of an item
switching cost: manipulating costs that make customers reluctant to switch to another product
loyalty program: rewards customers based on the amt of business they do with a particular organization
Supplier Power
The suppliers’ ability to influence the prices they charge for supplies
Supply Chain—consists of all parties involved in the procurement or a product or raw material
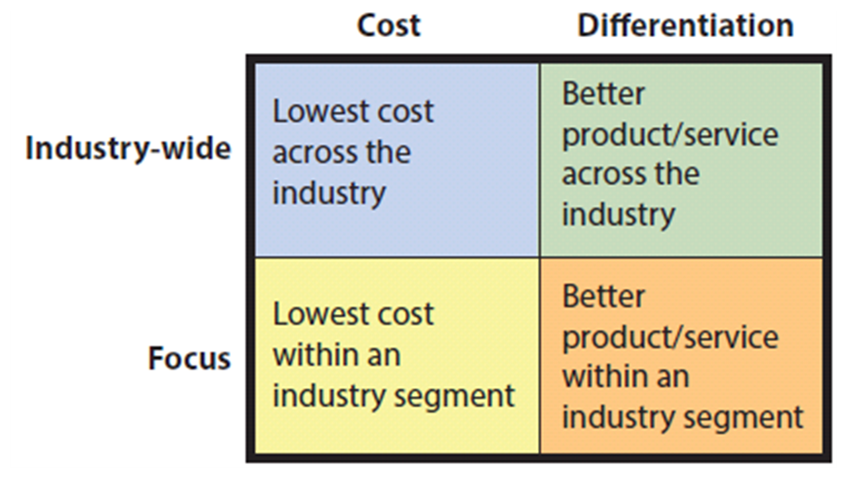
competitive strategy
a statement identifying a business’s approach to compete, its goals, and the plans and policies required to attain those goals
Strategies for Competitive Advantage
cost leadership: compete on price efficiency
differentiation: unique products/services
innovation: new products, features, or ways of doing business
operational effectiveness: perform activities better than rivals
customer-orientation: build loyalty through personalized services
Porter’s Four Competitive Strategies
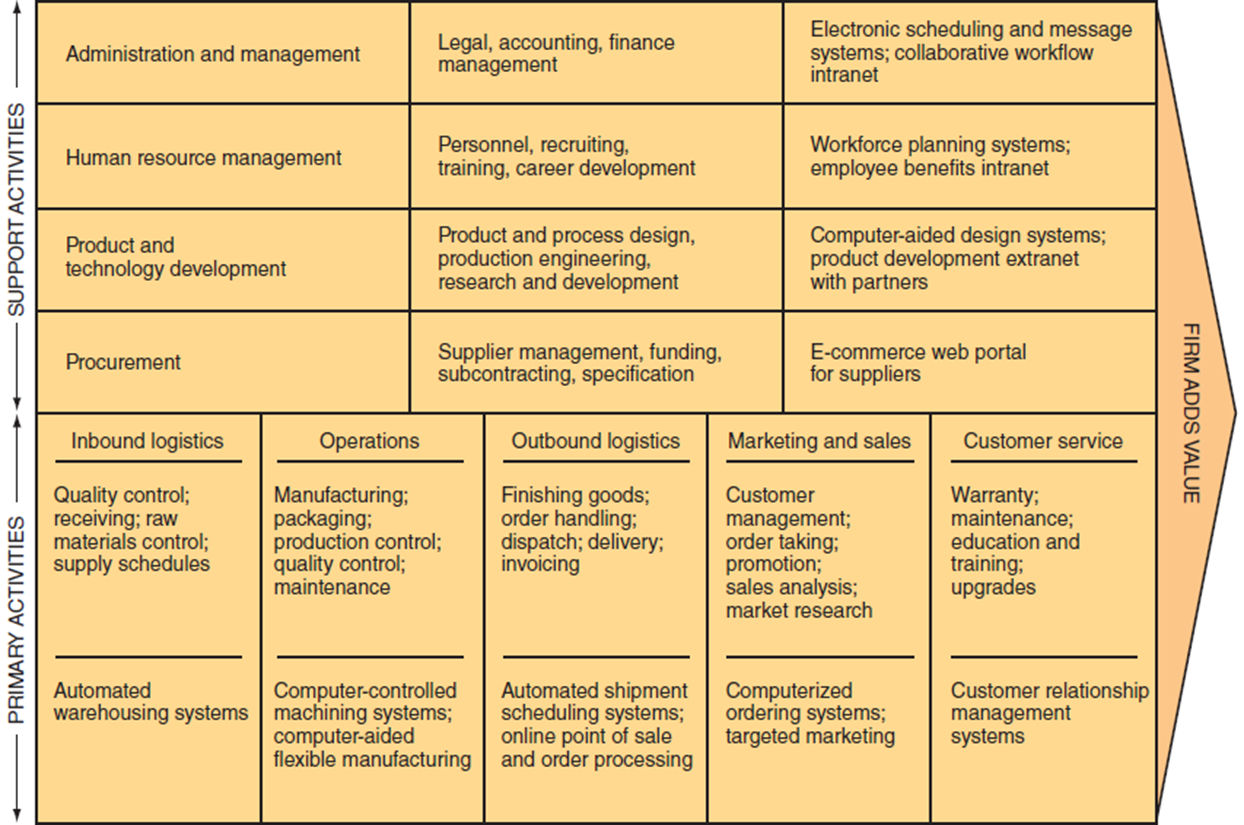
Porter’s Value Chain Model
definition: a sequence of activities transforming inputs into outputs of value
primary activities: production/distribution: inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing & sales, customer service
support activities: support primary activities such as infrastructure, HR, tech development, procurement
Business process
definition: an ongoing collection of related activities that create a product or service of value to the organization, its business partners, and/or its customers
three elements of the business process
inputs: materials, services, and information that flow and are transformed as a result of a process
resources: the people and material that perform process activities
outputs: the products or a service created by the process
metrics to assessing process
Efficiency: doing things well (low cost, low speed, low resources)
Effectiveness: doing things that matter (higher quality output)
IS three areas of business processes
executing the process
capturing and storing process data
monitoring process performance
Cross-Functional Processes
span multiple departments
No single functional area is responsible
steps executed in a coordinated, collaborative way
Procurement & fulfillment cross-functional processes
Improving process through better collaboration
tools like Microsoft HoloLens enable real-time teamwork across functions
Types of Process Models: Process Maps
Step-by-step flow (ordering e-tickets online)
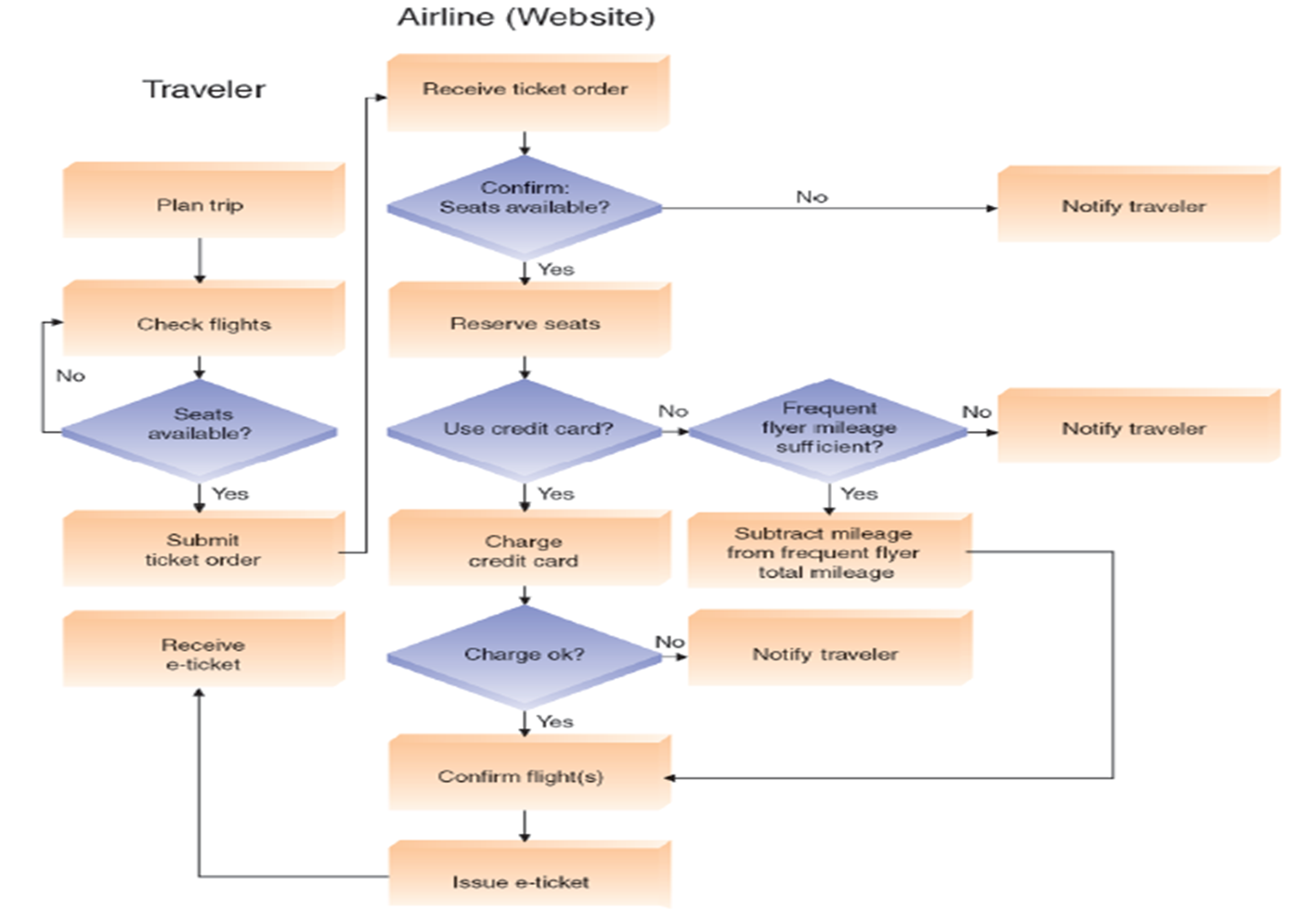
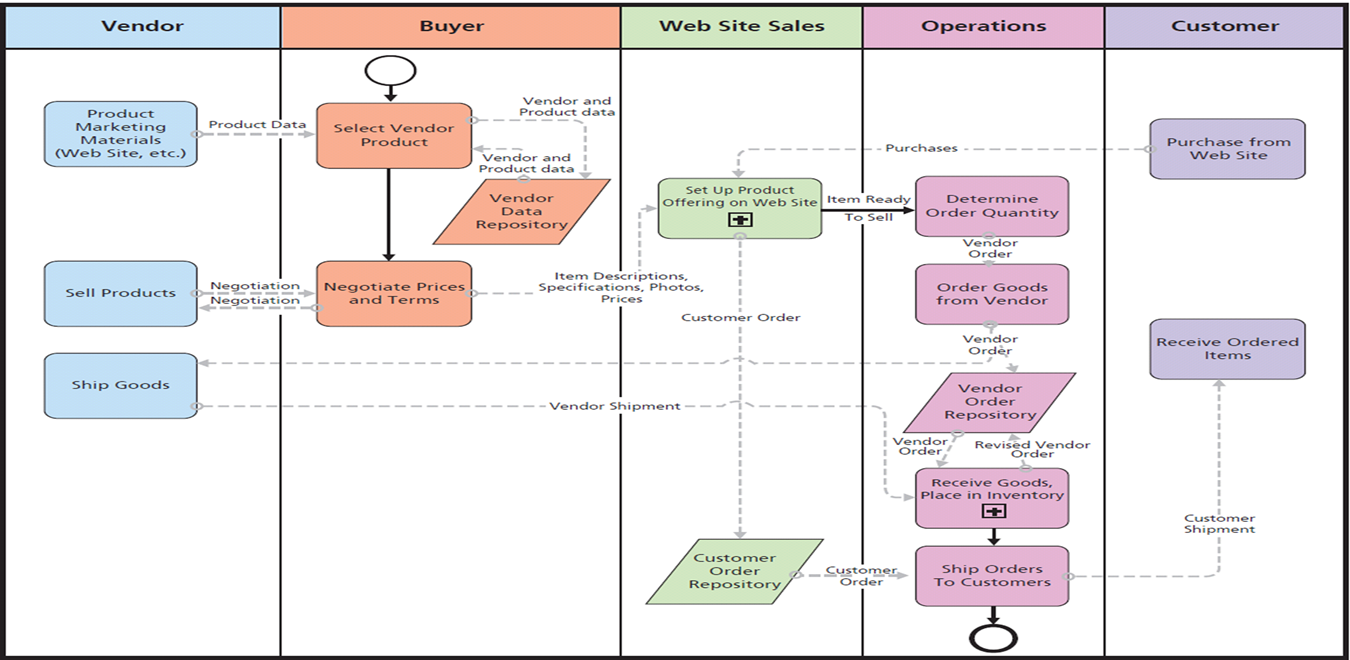
Types of Process Models: Swim Lane
similar to a flowchart in that it maps out a process, decisions, and loops; however, a swim lane map places events and actions in "lanes" to delineate a person/group responsible, or a specific sub-process.
A swim lane map has three elements: time, people (or job functions), and tasks/processes. It may also show what data you need.
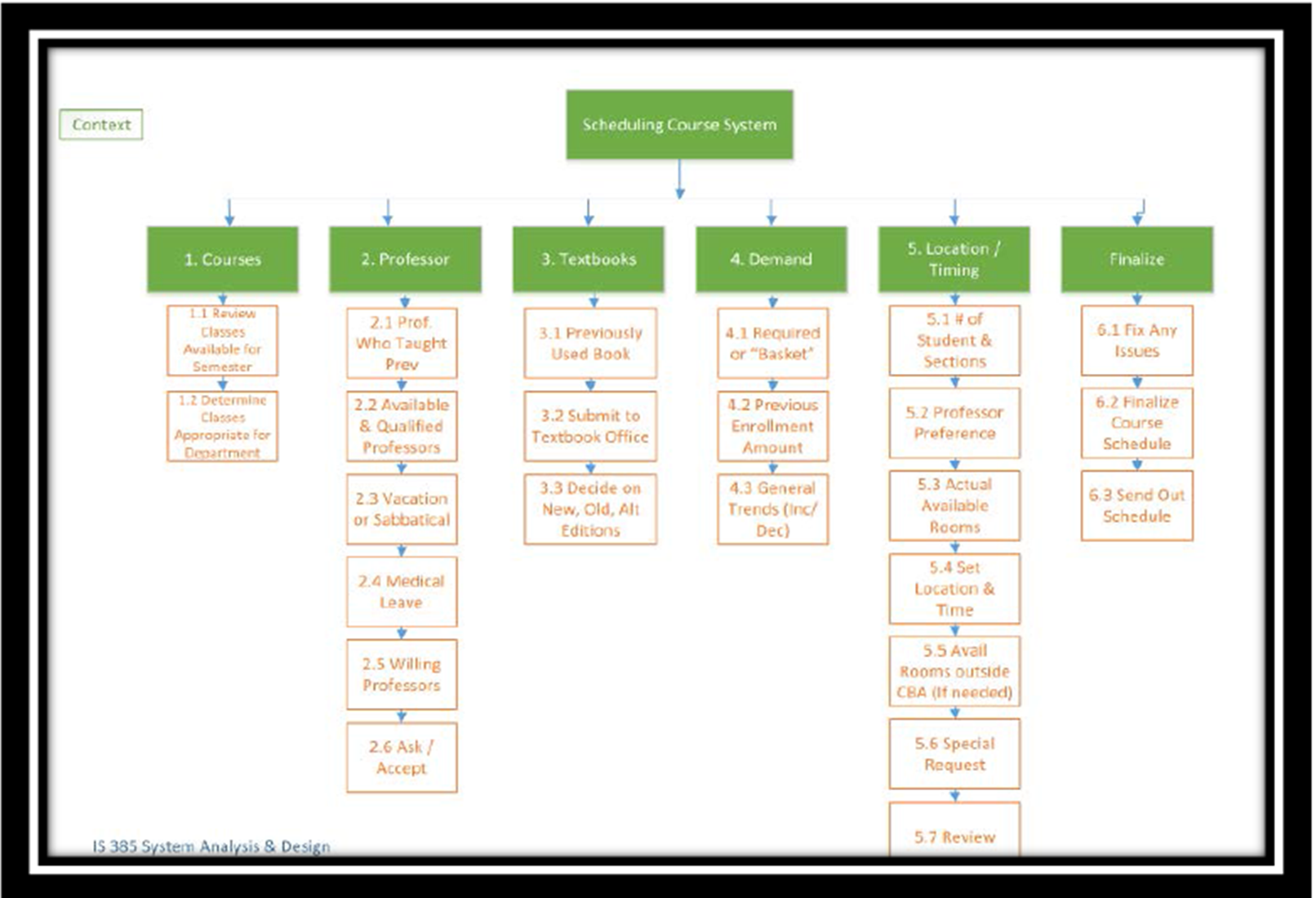
Types of Process Models: Process Decomposition Diagram
shows pure process, break down high-level process into sub-processes
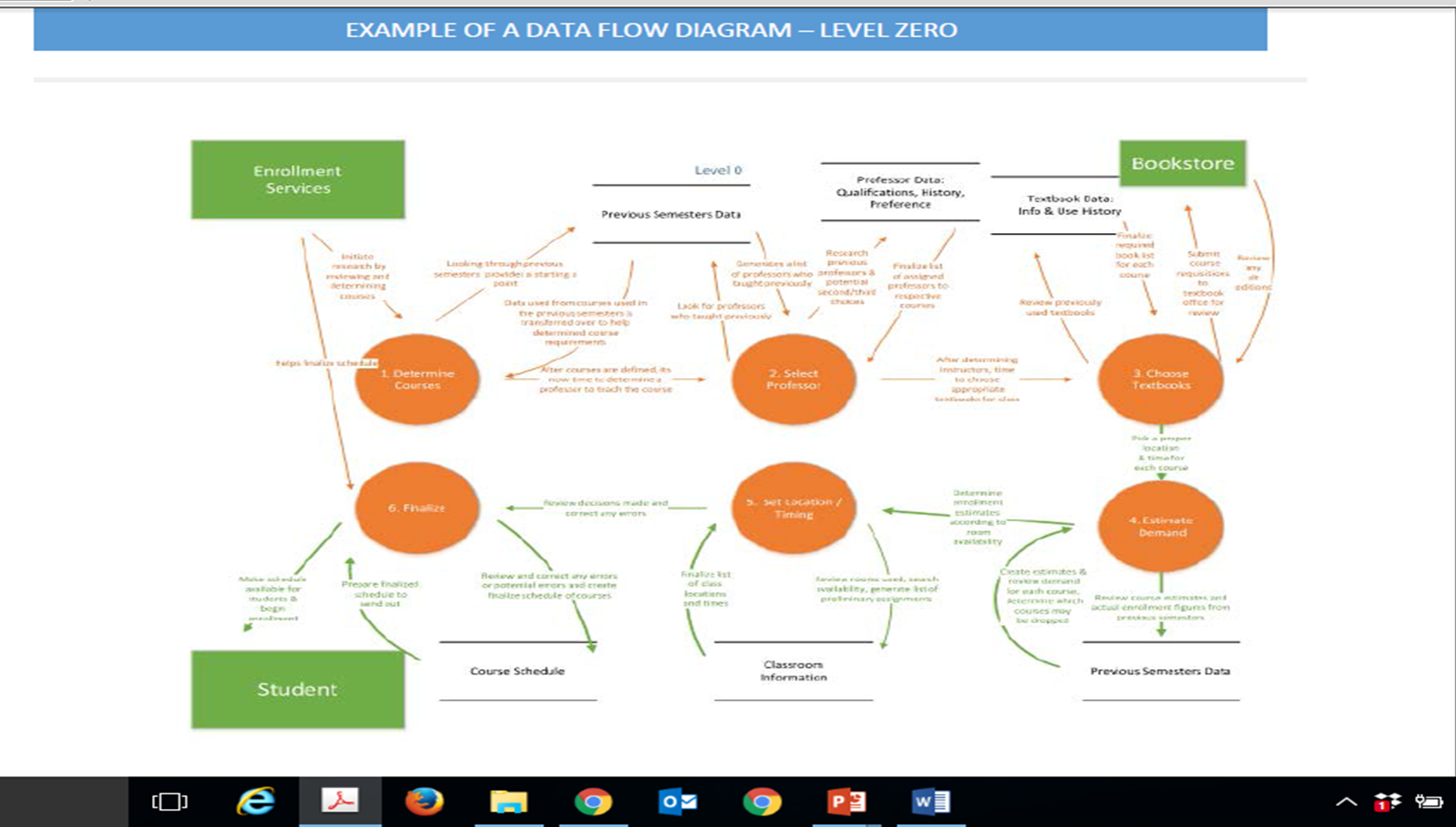
Types of Process Models: Data Flow Diagram
uses the decomposition diagram and adds what entities are out of your system and data
shows process in sequence and the necessary inputs/outputs of the process
Measures of Excellence in Executing Business Process
customer satisfaction
cost reduction
cycle and fulfillment time reduction
quality
differentiation
productivity
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
radical redesign; “clean slate” approach
high risk, costly, top-down, time-consuming, high failure rate but transformative
BPR: Taco Bell Example
example: taco bell - restructured kitchen-to-dining ratio, eliminated 3 management levels, shifted to centralized cooking.
reengineered its marketing to become value-driven
Result: sales increase $500 million to $3 billion 10 years later, restaurants grew from 1,500 restaurants to 3,600 from 1983-1993, profit growth 31% per yr over same period
Business Process Improvement (BPI)
5 basic phases of successful BPI: define, measure, analyze, improve, control
incremental, continuous improvement
focuses on reducing variation in process outputs by identifying the underlying cause of the variation
low-risk, low-cost, less time than BPR, bottom-up, quantifiable results
Toyota BPI Example
ex: Toyota—process improvement through lean manufacturing (waste reduction & efficiency) (JIT, Kaizen, Jidoka, Standardized Work)
•Just-In-Time (JIT) Production: Minimizes inventory costs and reduces waste
•Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Encourages all employees to suggest and implement improvements
•Jidoka (Automation with a Human Touch): Combines automation with human oversight to ensure quality
•Standardized Work: Establishes best practices for each process to maintain consistency
These principles have allowed
Business Process Management (BPM)
continuous cycle of BPI with IT support
Includes: process modeling, business activity monitoring (BAM), and Business Process Management Suites (BPMS)
Trend: Social BPM—collaboration through social media tools
National Geographic Reengineering
Problem: images not properly resizing, download times were long, marketing was hindered due to platform mismatches, and needed to restructure web development
approach: used third-party commerce and open source software, and restructured web development
results: increase 232%, 65% in mobile page views, streamlined content, improved communications
geo-engineering
to combat climate change. this refers to a set of emerging technologies that could manipulate the environment and partially offset the impacts of climate change
business pressures and responses
pressures: market, technology, and societal pressures
organizational responses: strategic use of IT, process innovation, and organizational flexibility