Properties of Water
Cohesion: the tendency of molecules of the same kind to stick together
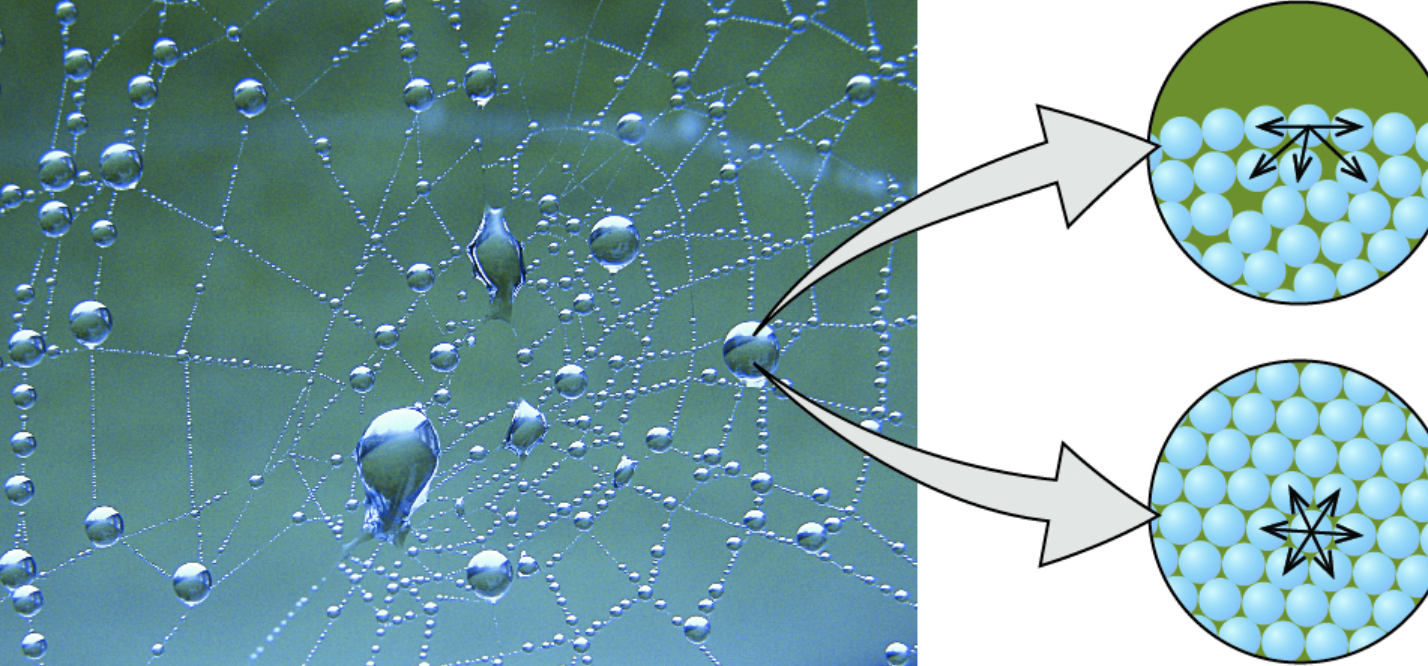
Adhesion: the tendency of two different kinds of molecules to stick together
- Capillary action: the ability to move something up a surface
- Ex: a straw in a glass of water has water slightly higher than the rest: the water rises using adhesion towards the straw, and the rest of the water rises using cohesion
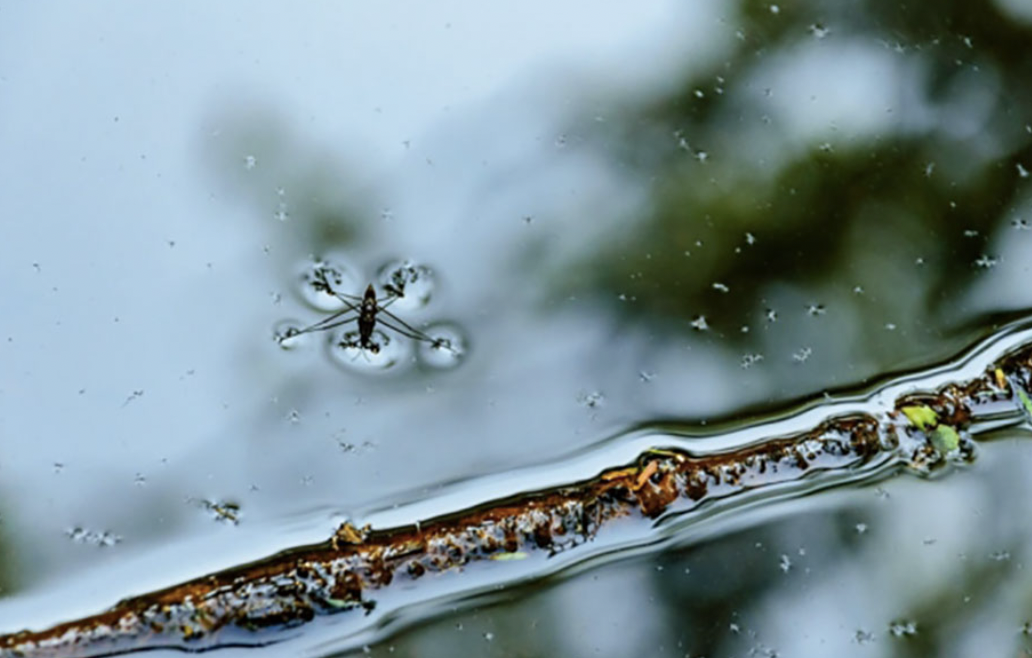
Surface tension: a measure of how difficult it is to break the surface of a liquid
- Hydrogen bonds cause water to stay together


Moderate temperature
- Thermal energy: energy associated with the random movements of atoms and molecules
- Heat: transfer of thermal energy from hot → cold
- Temperature: measure of intensity of moving atoms
- A lot of heat needed to be absorbed for water to change temperature
- High heat capacity
- Raising temperatures → bonds must break to vibrate faster, despite high surface tension
- Lowering temperatures → bonds must break to evaporate, despite high surface tension
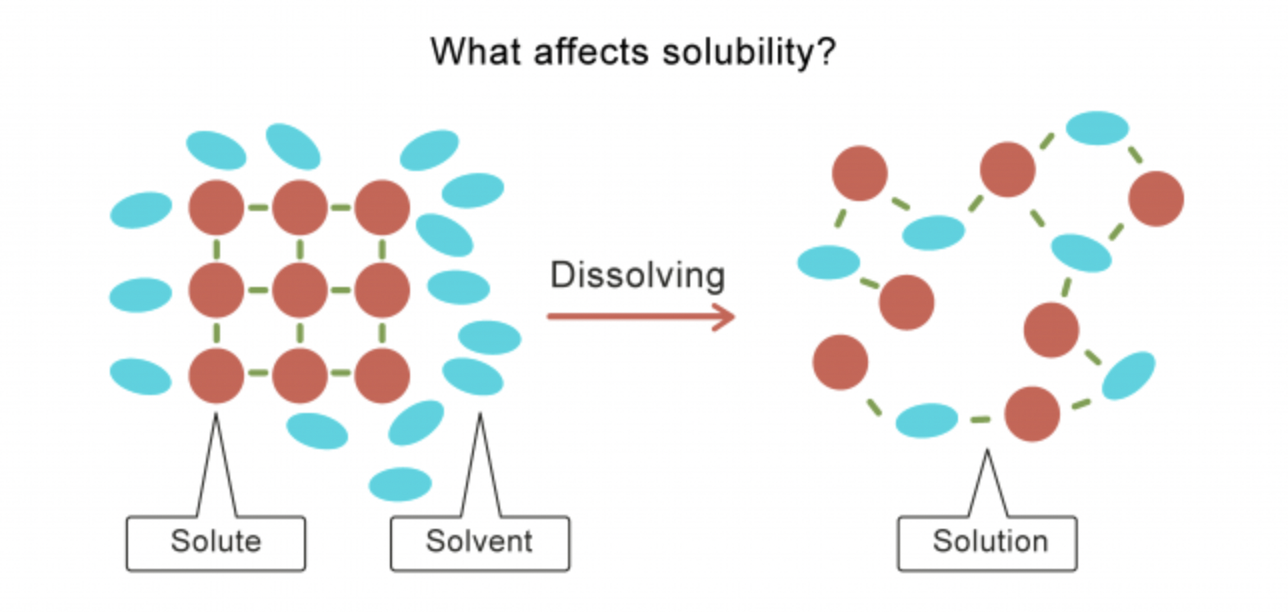
Major solvent
- Solvent: dissolving agent
- Solute: dissolved substance
- Solution: solvent + solution
- Aqueous solution: solution where the solvent is water
- Charge of the water molecules breaks about other molecules, causing them to dissolve