cells
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
prokaryote
more simple
no nucleus
no membrane bound organelles
ex. bacteria
eukaryote
more complex
has nucleus
has membrane bound organelles
ex. plants, animals, fungi, protists
what do eukaryotes/prokaryotes have in common?
cell membrane bound
have cytoplasm, DNA, ribsomes
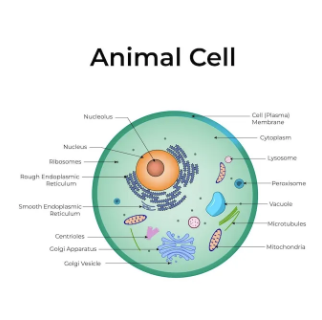
animal cell
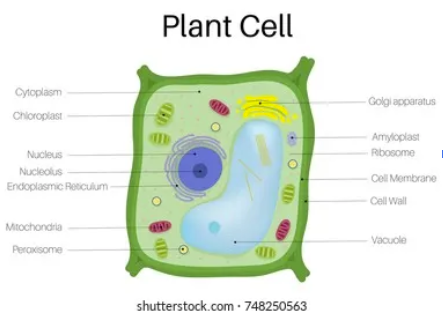
plant cell
what is cell theory?
all organisms are composed of one or more cells
the cell is the basic unit of structure + organization in organims
all cells come from preexisting cells
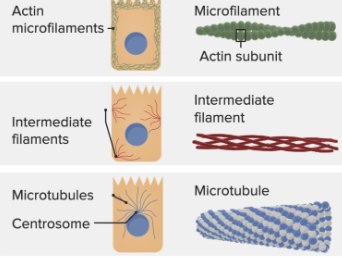
cytoskeleton
provides structure/support to the cell; network of fibers, involved in cell movement
prokaryote and eukaryote
both in plant/animal cells
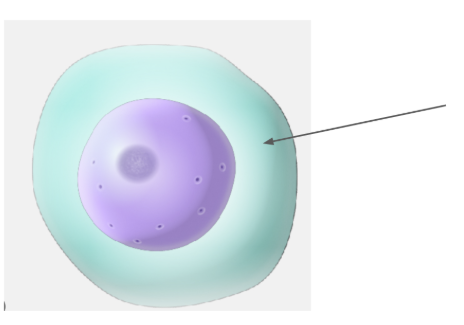
cytoplasm
transports process like metabolism
golgi apparatus
modifies, sorts + packages proteins and lipids for delivery
vacuole
used for storage within the cells, larger in plant cells; used for nutrients, waste, etc
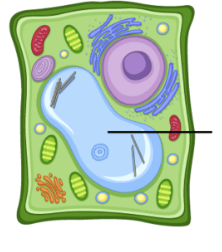
chloroplast
site of photosynthesis in plant cells; converts light energy to chemical energy; food storage

nucleus
control center of the cell, contains the majority of genetic material

flagella
whip-like structure that aids in movement of certain cells (locomotion) and allows them to swim through lipid environments
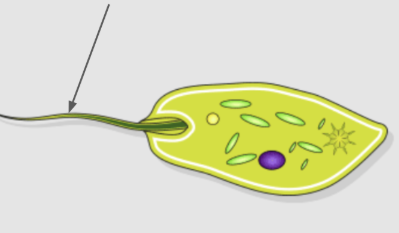
pseudopod
temporary foot-like extensions of the cytoplasm used by some protozoa for movement and feeding
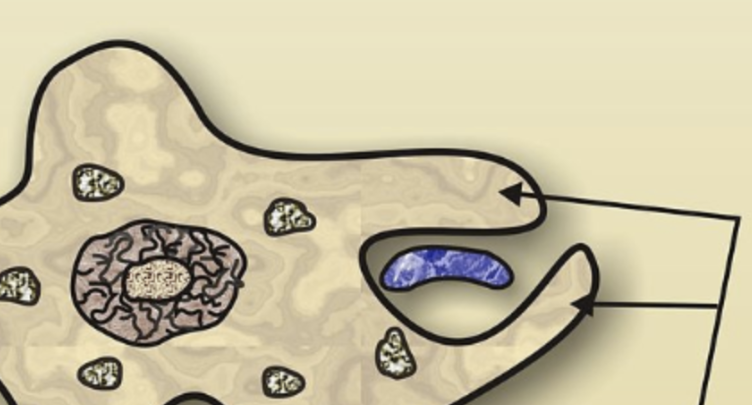
cell membrane
selective barrier that regulates what enters/exits the cell
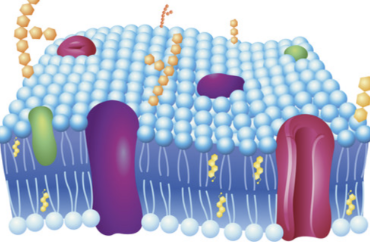
cell wall
provides structural support + protection to plant cells; maintains shape + prevents excessive water loss

nuclear envelope
double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, controls the passage of substances in/out of the nucleus
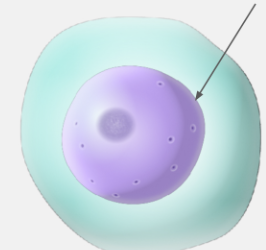
mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell, generates ATP through cell respiration

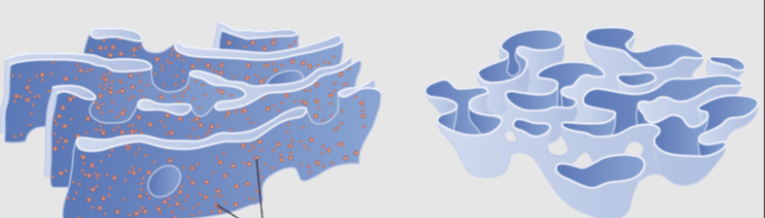
endoplasmic reticulum (ER), rough/smooth
network of membranes that work to transport proteins and lipids internally
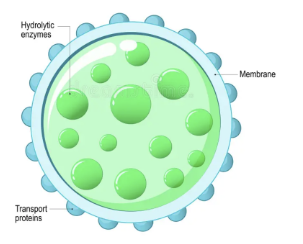
lysosomes
contains digestive enzymes for breakdown of waste + cellular debris
centriole
cylindrical structure involved in cell division; helps organize the mitotic spindle + ensure proper chromosome separation

ribosomes
site of protein synthesis, can be found floating freely in cytoplasm (or attached to ER)

cilium
short hair-like projections that move in a coordinated manner to help propel cells or move fluids along the cell surface
nucleolus
region within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesized and ribosomes are made
vesicle
destroys/absorbs toxic substances
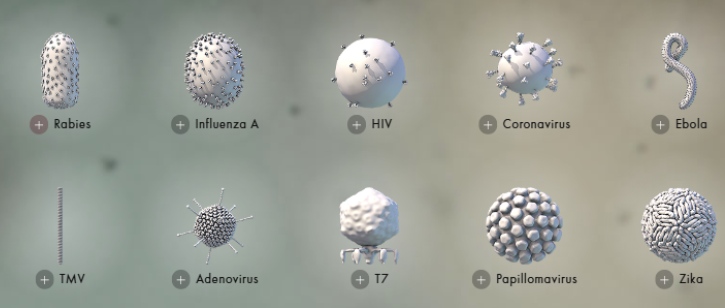
virus shapes
is a virus alive?
a virus is not alive
viruses don’t have cells
can’t reproduce or copy their DNA
uses hosts to create more viruses
binds to receptors on cells
cannot maintain homeostasis
are NOT made up of cells and dont have a metabolism
lytic cycle
shorter cycle, viruses cause cell to burst → cell dies
lysogenic cycle
longer cycle, viruses stay hidden and multiply —> cell survives but more viruses are created