Grade 9 Bio - Cellular Respiration + Photosynthesis
1/135
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Energy
The capacity to do work and cause change.
The two kinds of energy are…
kinetic and potential energy
Kinetic energy
The energy of motion
Potential Energy
energy an object possesses due to its position
Chemical Energy
(a type of potential energy) is stored in bonds and available for release in a chemical reaction.
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy in the universe is constant, it cannot be created nor destroyed.
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
Energy conversions increase the entropy (disorder) in the universe.
Any time energy is converted to another form, some of it is ____ as ____.
lost, heat
Exergonic Reactions
Releases energy
Products have ____ energy than reactants in exergonic reactions.
less
Endergonic Reactions
Requires input of energy
Products have ____ energy than reactants in endergonic reactions.
more
Energy Coupling
Energy from exergonic processes drive endergonic processes.
ATP stands for…
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The energy currency of cells. An immediate source of energy that powers most cellular work.
ATP is a modified _________.
nucleotide
Hydrolysis of ATP…
releases energy when third phosphate is broken off
When a phosphate group transferred from ATP to another molecule, it is called…
phosphorylation.
Molecules become _________ when they are phosphorylated.
energized
LEO
Loss of Electrons is Oxidation
GER
Gaining Electrons is Reduction
True of False: In photosynthesis, H2O is oxidized, CO2 is reduced, and electrons gain energy
True
True or false: In cellular respiration, Glucose is reduced, O2 is oxidized, and electrons gain potential energy.
False
What major group of macromolecules provide energy for the cell?
Carbohydrates
Cells in our body break down ________ to make ATP.
glucose
Anaerobic Respiration
Respiration without oxygen, which results in 2 ATP and either alcohol or lactic acid as a byproduct
Cellular Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP
Aerobic Respiration
Respiration with oxygen available as an electron acceptor at the end of the process. This results in a more extensive breakdown of glucose and about 38 ATP.
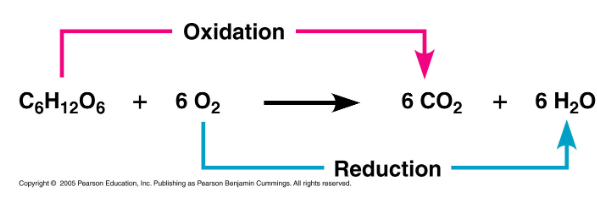
What is this an image of?
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Where does cellular respiration take place?
The mitochondria
Where is the electron transport train?
Inner membrane of the mitochondria
What is another name for the Kreb’s Cycle?
The Citric Acid Cycle
Where does the Kreb’s Cycle happen?
The matrix of the mitochondria.
What is the first cycle of aerobic cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
Glycolysis
Breaks down glucose, a 6-carbon molecule, into two molecules of a 3-carbon compound called pyruvate (pyruvic acid), releases a small amount of ATP.
Where does glycolysis happen?
Cytoplasm
What types of cells do glycolysis?
Every cell
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Completes breakdown of glucose, generates CO2 and small amount of ATP
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Uses electrons from NADH and FADH2 to power the production of ATP molecules
True or False: Glycolysis cannot happen without oxygen.
False
What are the 3 inputs of glycolysis?
1 glucose, 2 ATP (activation energy), and 2 NAD+
What are the 3 outputs of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 4 ATP, and 2 NADH
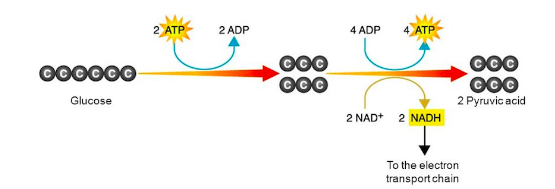
What is this an image of?
Glycolysis
True or False: Fermentation is an anaerobic process.
True
Fermentation
energy-generating process that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
The two types of fermentation are _________ fermentation and ______ ____ fermentation.
alcoholic, lactic acid
In alcoholic fermentation, pyruvic acid is converted to ___ and _______.
CO2, ethanol
____ is oxidized to ____ when pyruvate is reduced to ethanol. This recycles ____ to keep glycolysis working
NADH, NAD+, NAD+
3 foods that use fermentation
Bread, beer, yogurt
Each pyruvate molecule is broken down to form ___ (waste) and a ___ ______ ______ _____, which enters the Krebs Cycle
CO2, two-carbon acetyl group
A lot of electrons are carried by ____ and _____ in the Krebs cycle.
NADH, FADH2
For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, how many ATP molecules are produced?
40 (with a net gain of 38)
How many ATPs are formed through glycolysis?
4 (net gain of 2) ATP
How many ATPs are formed through the Kreb’s Cycle?
2 ATP
How many ATPs are formed through ETC?
34 ATP
How many times does the Kreb’s Cycle happen per glucose molecule?
Twice
FADH2…
carries electrons
NADH…
carries electrons
What happens to the CO2 that is released during the Kreb’s Cycle?
It is breathed out.
How many carbons are in a citric acid molecule?
6
Citric acid is ________, so it _____ __ ________.
unstable, loses an electron
A mitochondria’s inner membrane is a…
phospholipid bilayer (semi-permeable)
Electrons _______ on the proteins.
bounce
The electrons bouncing on proteins pushes what inside?
H+
Chemiosmosis
Going from high to low through ATP synthase, producing ATP.
What is the final acceptor of electrons during ETC?
Oxygen
ETC is also known as…
Oxidative Phosphorylation
What is the goal of fermentation?
Change NADH back into NAD+ to continue glycolysis.
What organelle(s) do(es) cellular respiration?
Mitochondria, cytoplasm
What is the useful product of cellular respiration?
ATP
What is the waste product of cellular respiration?
CO2 and H2O
What two things could happen to pyruvate and under what conditions will they occur?
In aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the citric acid cycle and undergoes oxidative phosphorylation leading to the net production of 32 ATP molecules. In anaerobic conditions, pyruvate converts to lactate through anaerobic glycolysis.
What are the inputs of glycolysis?
2 ATP, 1 glucose, , 2 NAD+
What are the outputs of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, 4 ATP
What are the inputs of the Krebs Cycle?
2 pyruvate, 8 NAD+, 2 ADP, 2 FAD
What are the outputs of the Krebs Cycle?
6CO2, 8 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP
What are the inputs of ETC?
O2, NADH, FADH2, ADP
What are the outputs of ETC?
H2O, NAD+, FAD, 34 ATP
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2+6H2O →(light) →C6H12O6 + O2
Autotrophs
Living things that are able to make their own food without using organic molecules derived from any other living organism
Photoautotrophs
Autotrophs that use the energy of light to produce organic molecules.
Examples of photoautotrophs
plants, algae, protists, some prokaryotes
Chlorophyll
an important light absorbing pigment within chloroplasts, responsible for the green color of plants
Chlorophyll plays a central role in…
converting solar energy to chemical energy
Stomata
Pores in the underside of leaves that can open and close to let materials into and out of the plant
What enters through the stomata?
CO2
What exits the stomata?
O2
Stroma
The dense fluid within the chloroplast.
An envelope of ___ _________ encloses the stroma
two membranes
Thylakoids
interconnected membranous sacs that separate the stroma from the thylakoid space
Grana
Stacks of interconnected thylakoids.
Where do light reactions happen?
Thylakoid membranes
Light energy is converted to
chemical energy and O2
Water is split to provide the __ as well as _________.
O2, electrons
What reduces NADP+ to NADPH?
H+ ions
ATP and NADPH transfer energy from _____ _________ to Calvin Cycle to make sugars
light reactions
What does Photosystem 1 do?
Provides reducing power to reduce NADP to NADPH, which is required for carbon fixation and other synthetic processes
PSII
Where does the Calvin cycle occur?
The stroma of the chloroplast
Carbon Fixation
The process by which plants fix atmospheric carbon to form organic compounds