Insulin and diabetes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
how can blood glucose levels be measured
enzymatically from a drop of blood with glucose oxidase, H2O2 is detected colorimetrically
glucose + O2 → glucose-δ-lactone + H2O2
longer term average inferred measuring haemoglobin glycation
reaction of glucose with primary amines in Hb, rate of glycation is proportional to [glucose]
how does increase in blood glucose lead to secretion of insulin
insulin is secreted when intra-cellular ATP levels rise in pancreatic B-cells, sign of overflow of its energy status
more glucose, more respiration, more ATP produced
ATP:ADP ratio increases and promotes influx of Ca2+ into cell which induces synthesis and release of insulin
how is insulin made
as a precursor
pro-insulin is cleaved in 2 places to give A and B chain
insulin has 2 intermolecular disulphide bonds between the chains and 1 intramolecular disulphide bond on the A chain
how is insulin stored
intracellular granules as crystals formed from hexamers
hexamer surrounds 2 Zn2+ ions and loses these ions when it breaks down into a dimer, then monomer
insulin receptor (IR)
a2-B2 tetramer with long extracellular domain to bind insulin and intracellular TK domain
insulin binds a-subunits and structure of IR changes to bring TK domains together
B-subunits autophosphorylate 3 tyrosines which transduces signal into cell by turning on receptor’s catalytic activtiy
activated receptor phosphorylates multiple intracellular proteins which alters their activity and leads to biological response
autophosphorylation of 3 tyrosines
they are in a loop, and when phosphorylated, the loop moves and the active site is open to bind substrates
how does insulin increase glucose uptake into cells
in absence of insulin, GLUT4 glucose transporters are in cytoplasmic vesicles
binding of insulin to IR leads to phosphorylation of IRS, causing several phosphorylation cascades and leading to rapid fusion of vesicles with cell membrane, GLUT4 is in the membrane to facilitate glucose uptake
when insulin levels decrease and IRs are unoccupied, GLUT4 are recycled back into vesicles
how does insulin signalling lead to glycogen synthesis
insulin binds IR, IRS is phosphorylated by IR, causes several phosphorylation cascades including
phosphorylation (activation) of glycogen synthase phosphatase
this dephosphorylates glycogen synthase (activating it) which synthesises glycogen
type 1 diabetes mellitus
autoimmune, usually arising in childhood
body destroys insulin/cells that make it
destruction of pancreatic islet B-cells by T cells leads to insulin deficiency
type 2 diabetes mellitus
characterised by high blood and urine glucose levels that are resistant to insulin
tissues do not respond to circulating insulin
unable to push plasma glucose into storage or metabolise into fat even with high insulin
pancreas keeps pumping out insulin, leading to other issues
fat disposed in adipose tissue, muscle, liver, pancreas, heart etc
pathological outcomes of lack of insulin signalling
high blood/urine glucose levels, lack of glucose uptake causes cellular starvation
cells breakdown fats to generate energy and produce ketone byproducts
ketones build up and make blood acidic
ketoacidosis is accompanied by water and ion loss and thick blood - diabetic coma and life-threatening
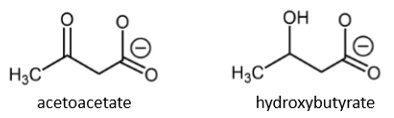
ketone bodies
acetoacetate and hydroxybutyrate
soluble forms of energy to be released into bloodstream
how blood glucose and insulin concentrations change during and between meals
glucose levels spike at meals, closely followed by insulin, neither levels return to 0
injected insulin acts like insulin but levels reach 0 between meals
pathogenic glucose levels are consistently high
fast acting insulins
immediate, shift insulin towards active monomer by disruption of dimer interface
insulin Aspart
insulin LisPro
insulin Aspart
mutation in B28 from Pro to Asp
disrupts dimer by opposed negative charges with 21Glu
no dimer, no hexamer, so more of the active form
insulin LisPro
mutation in B28-29 from Pro28-Lys29 to Lys28-Pro29
long acting insulins
avoid cellular hypoglycaemia (glucose starvation) overnight
add fatty acid to end of B chain at Lys29 (myristoylated Lys29)
increases pI to reduce solubility/diffusion
adding residues with high pKas slow diffusion
semi-synthesis of insulin
from pig insulin
cleave Ala30 from pig insulin by specific proteolysis
add specific peptide using trypsin in organic solvent, protect Lys NH2 and add Thr or another residue using solid state synthesis
deprotection