ACT Math Formulas
1/61
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
A = lw
Area of a rectangle
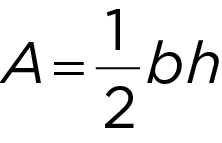
Area of a Triangle
A = πr2
Area of a circle
C = πd or C = 2πr
Circumference of a circle
d = 2r
Diameter and radius of a circle
V = Bh
Volume of rectangular prism
90°
Right angle
180°
straight line
180°
triangle
180°
circle
When a line intersects to parallel lines
2 kinds of angles form: big and small
big angle = big angle
little angle = little angle
big angle + little angle = 180°
a2 + b2 = c2
Pythagorean theorem
sin(θ) =
opposite/hypotenuse
cos(θ)=
adjacent/hypotenuse
tan(θ)=
opposite/adjacent
A = s2
Area of a square
A = bh
Area of a parallelogram
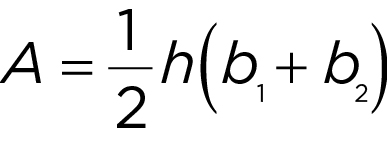
Area of a trapezoid
v = s3
Volume of a cube
v = lwh
volume of a rectangle
v = πr2h
Volume of a cylinder
90°, 45°, 45° triangle
x√2 (hypotenuse), x, x(other 2 sides)
30°, 60°, 90° triangle
2x (hypotenuse), x (near 60°), x√3 (near 30°)
(n-2)180°
Sum of angles in an n-sides polygon
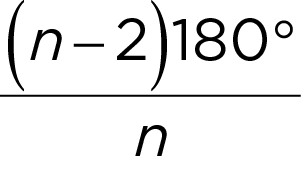
Angle measure of each angle in a regular n -sided polygon
S = 2(lw + lh + wh)
Surface area of a rectangular solid
S = 6s2
Surface area of a cube
Surface area of a right circular cylinder
S = 2πr2 + 2πrh
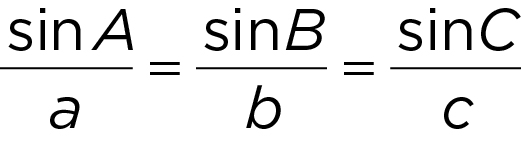
law of sines
S = 4πr2
Surface area of a Sphere
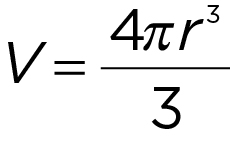
Volume of a sphere

Slope
y = mx + b
Slope-intercept form of a line
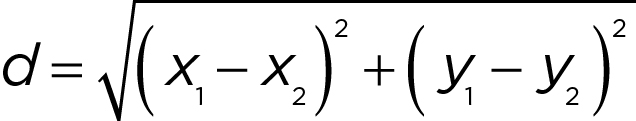
Distance formula
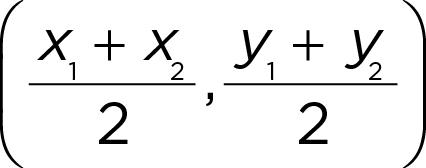
Midpoint formula
Ax + By = C
Standard form
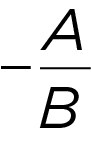
Ax + By = C
Standard form: slope
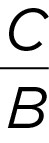
Ax + By = C
Standard form: y-intercept
x2 + y2 = r2
Center of circle at (0,0)
(x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2
Center of a circle at (h,k)
x/a + y/b = 1
Standard equation of an ellipse with center (0,0)
(x - h)2/a + (y - k)2/b = 1
Standard equation of an ellipse with center (h,k)

Quadratic formula
D = b2 - 4ac
Discriminant
D > 0
there will be two distinct, real solutions
D = 0
there will be one distinct real solution
D < 0
there will be no real solutions. Instead, there will be two complex solutions
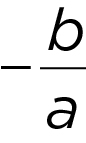
The sum of the roots

The product of the roots
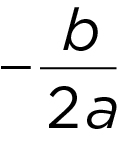
The midpoint of the roots and the
x -coordinate of the vertex
nth term = original term + (n - 1)d [d = constant difference between terms]
Arithmetic sequence
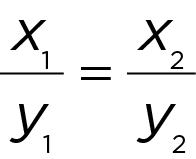
or y = kx [k is a constant]
Direct variation
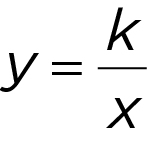
[k is a constant] or x 1 y 1 = x 2 y 2
Inverse variation
nth term = (Original Term)r( n – 1) [r = constant ratio between terms]
Geometric sequence
Total = Group 1 + Group 2 - Both + Neither
Group Formula
Average x Number of things
Average (Arithmetic mean) or Total
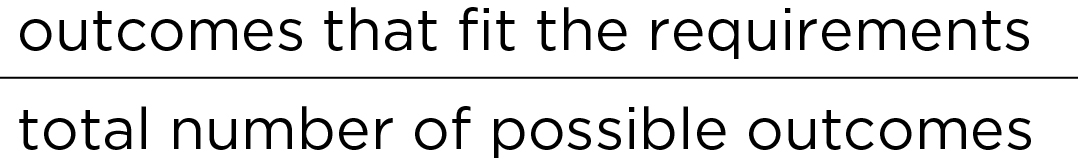
Probability
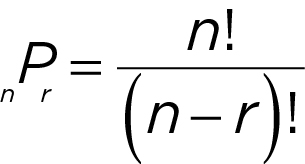
Permutations (the number of ways to arrange or order a group of things)
n P r =
n = number of elements available
r = number of elements chosen

Combinations (the number of ways make different groups out of a group of things)
n C r =
n = number of elements available
r = number of elements chosen
(probability of each occurrence) x (value of that occurrence) then add the sums
Expected vaule