Optho Topics List
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
What is the most common type of color blindness?
Red-Green Deficiency
Zeaxanthin, lutein, and meso-zeaxanthin belong to what carotenoid class of pigments?
Xanthophylls
Which carotenoid is found in the center of the retina and helps form the macular pigment of the eye?
Zeaxanthin
Which carotenoid is found in the peripheral regions of the retina and helps form the macular pigment of the eye?
Lutein
Which carotenoid is more effective in antioxidant benefits and absorbs 90% of blue light to protect retina from light induced damage and oxidative stress?
Zeaxanthin
What is myopia?
Nearsightedness; more refraction is needed to focus . CN III triggers ciliary muscle contraction, relaxing tension on suspensory ligament allowing lens to become more rounded
What is Hyperopia?
Farsightedness; light rays are almost parallel requiring less refraction for focus. Ciliary muscle relaxes, stretching suspensory ligament allowing lens to become more rounded at its optimal focal length.
What is presbyopia?
Natural loss of accommodation due to age; inability to focus on objects at a normal reading distance starts at 40
What is Astigmatism?
Refractive error horizontally and vertically
What is the treatment for Neisseria Gonorrhea?
Ceftriaxone 500 mg IM (<150 kg) or 1 gm IM (>150 kg) AND Doxycycline 100 mg PO BIDx 7 days OR Azithromycin 1 gm PO at time of visit AND Bacitracin ophthalmic ointment every 3-4 hours for 10 days 1 tube, no refill
What is the treatment for Neisseria Gonorrhea if pt has allergy to PCN?
Azithromycin 2gm PO AND Ciprofloxacin 500 mg PO once or Gentamicin 240 mg IM
What are the signs and symptoms of Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis?
Watery to mucoid discharge, foreign body sensation, itching (can be profound, burning eyes, no visual symptoms), large “cobblestone” papillae noted on upper tarsal conjunctiva when everted
When should you use a fluorescein stain?
To diagnose corneal abrasions, corneal ulcer, epithelial ulcer, epithelial injury, and dendritic lesions.
What would you see with fluorescein stain of corneal abrasions?
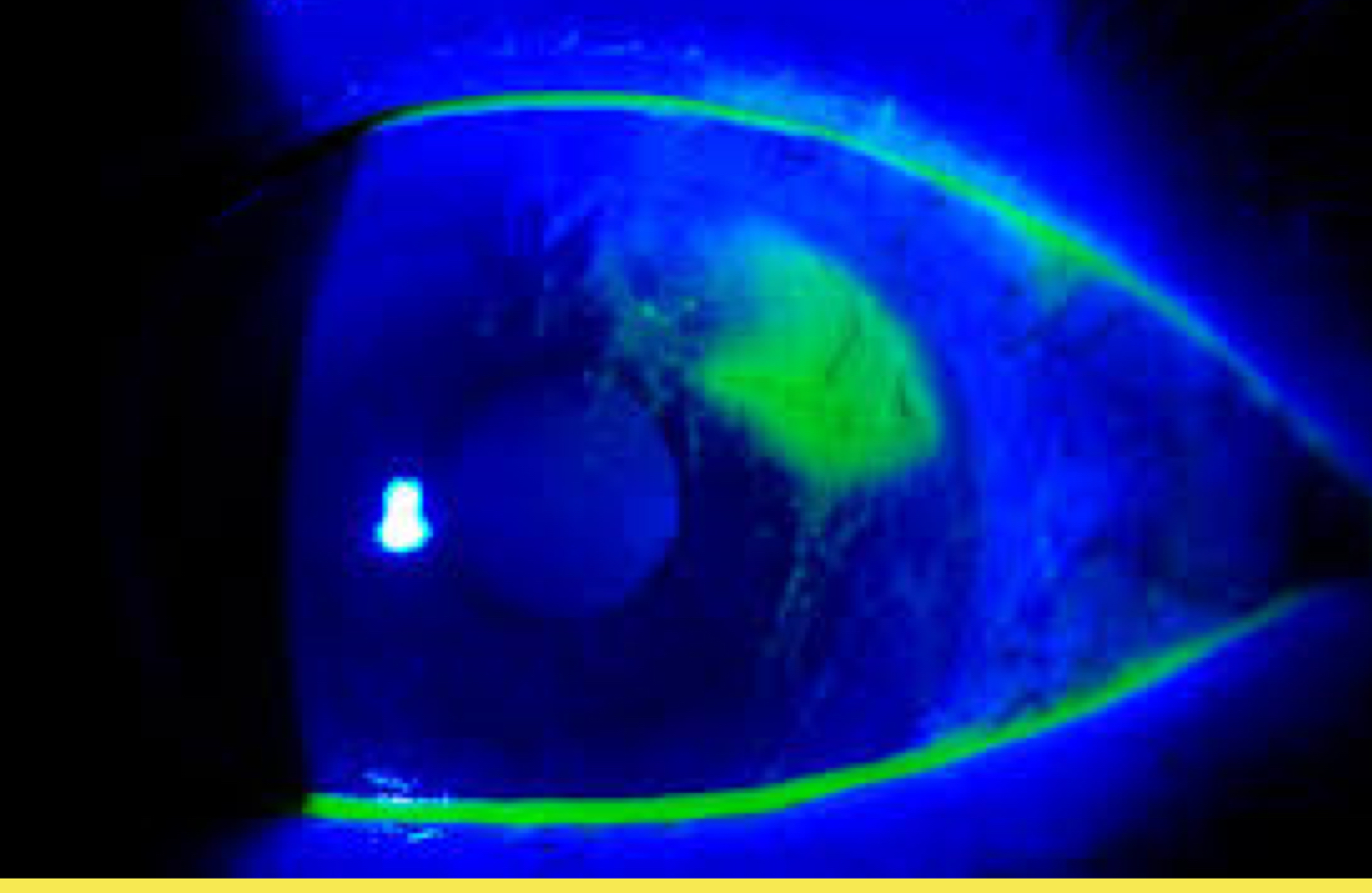
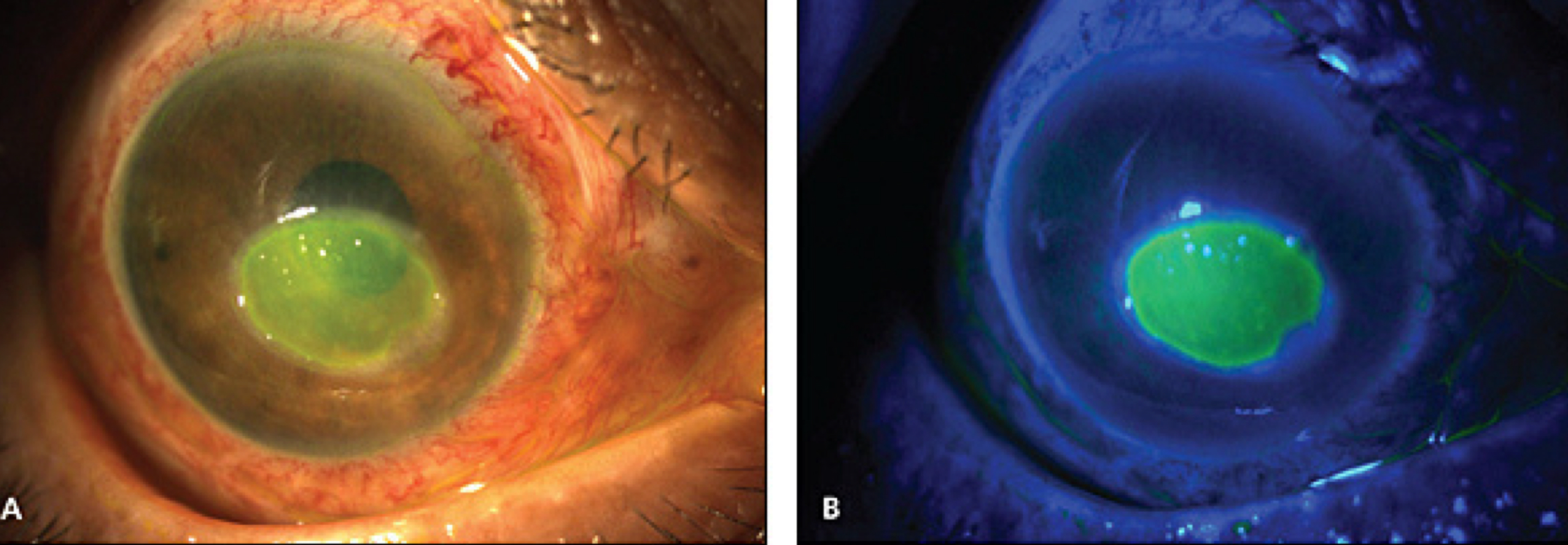
What would you see with fluorescein stain of corneal ulcer?
Pooling
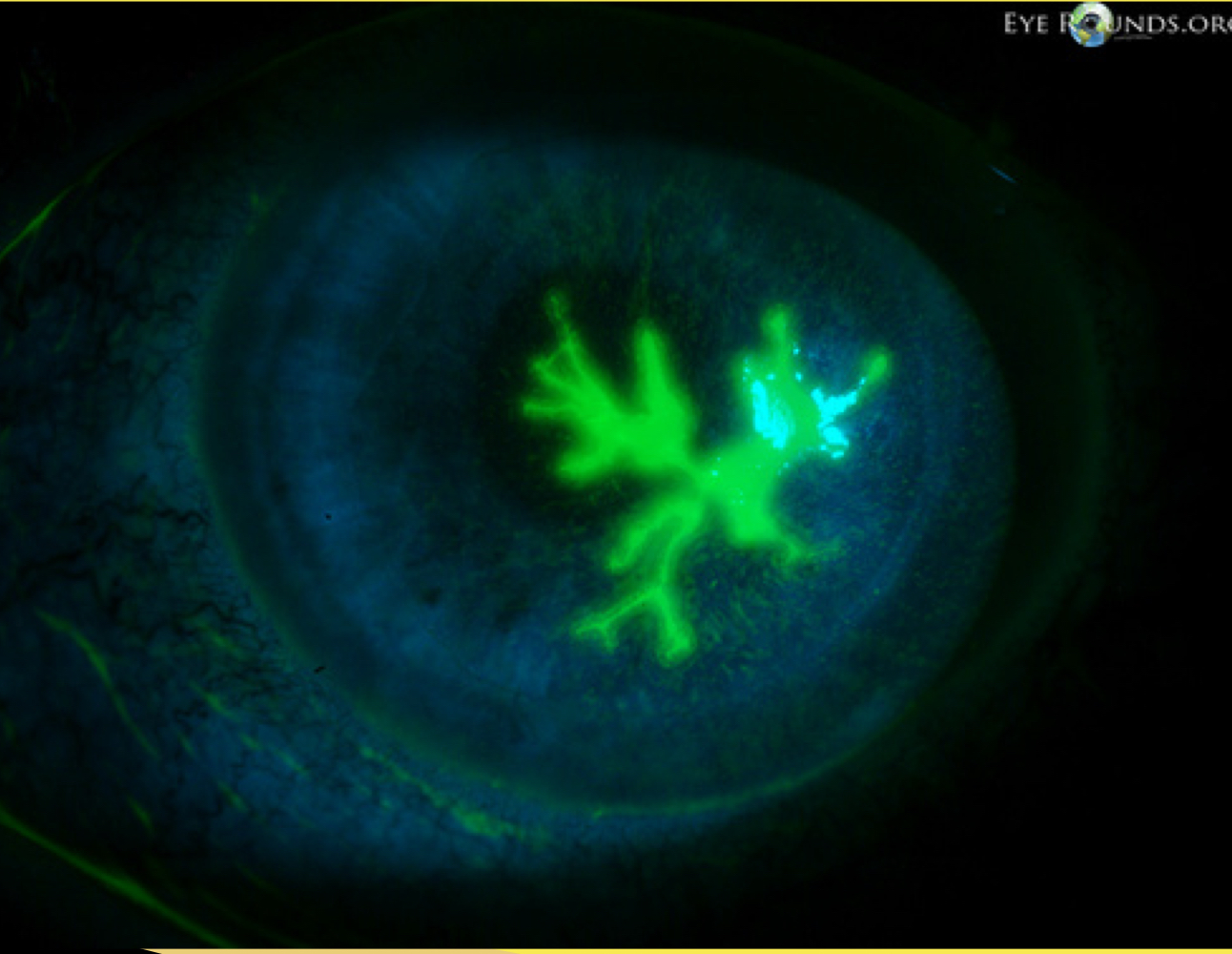
What would you see with fluorescein stain of dendritic lesion?
What is a white pupillary reflection in each eye (more pronounced in right eye) due to bilateral retinoblastoma?
Leukocoria
Which disease shows unilateral proptosis, lid edema, vision loss, and non tender mass?
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Which tumor on a CT shows bony involvement?
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Which tumor on a CT shows intraocular tumor?
Retinoblastoma
What disease is composed of small round neoplastic cells that invade and replace the normal retina? This disease will also have an absence of red- orange pupil reflex on red reflex exam and strabismus.
Retinoblastoma
Which type of conjunctivitis has mucopurulent discharge, FB sensation, no blurring of vision, possible mild discomfort, unilateral or bilateral? (Sudden onset)
Bacterial
What is the first line medication for bacterial conjunctivitis?
Erythromycin Ophthalmic 0.5 % Ointment
What are the common causes of bacterial conjunctivitis?
S. Aureus, S. Pneumoniae, H. Influenzae, M. Catarrhalis
What work up needs to be done for Bacterial Gonorrhoeae conjunctivitis?
STAT gram stain and culture, if positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae report to public health
Which disease has severe pain (burns to the cornea) and severe photophobia and is diagnosed with fluorescein diffuse punctate staining to both cornea?
Ultraviolet (UV) Keratitis or actinic keratitis
What is the treatment and management for UV keratitis?
Emergent consult ophthalmologist (both eyes may have to be patched for 24-48 hrs)
What symptoms are seen for acute uveitis ?
Eye pain, marked photophobia, blurred vision, red eye, myosis
What are the treatments for acute uveitis?
Corticosteroids (prednisone), Immunosuppressants (methotrexate), Abx (if- infection related)
What procedures can be done for uveitis?
Vitrectomy (eye surgery removing vitreous fluid from eyeball; can be done to remove cloudy fluid or fluid with debris. vitreous is replaced w/ a clear fluid or gas bubble until body begins producing vitreous again)
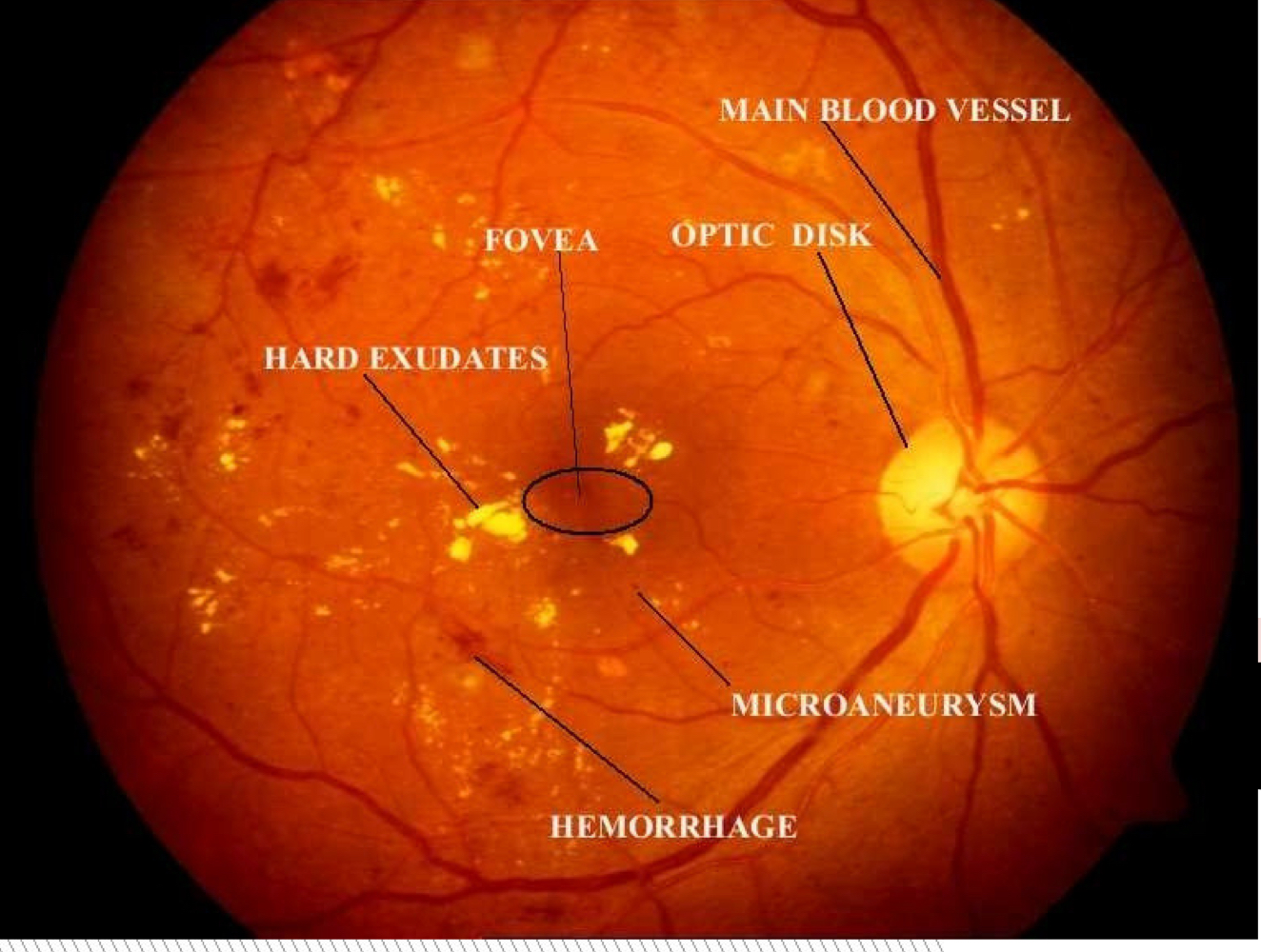
Which type of retinopathy is this?
Diabetic
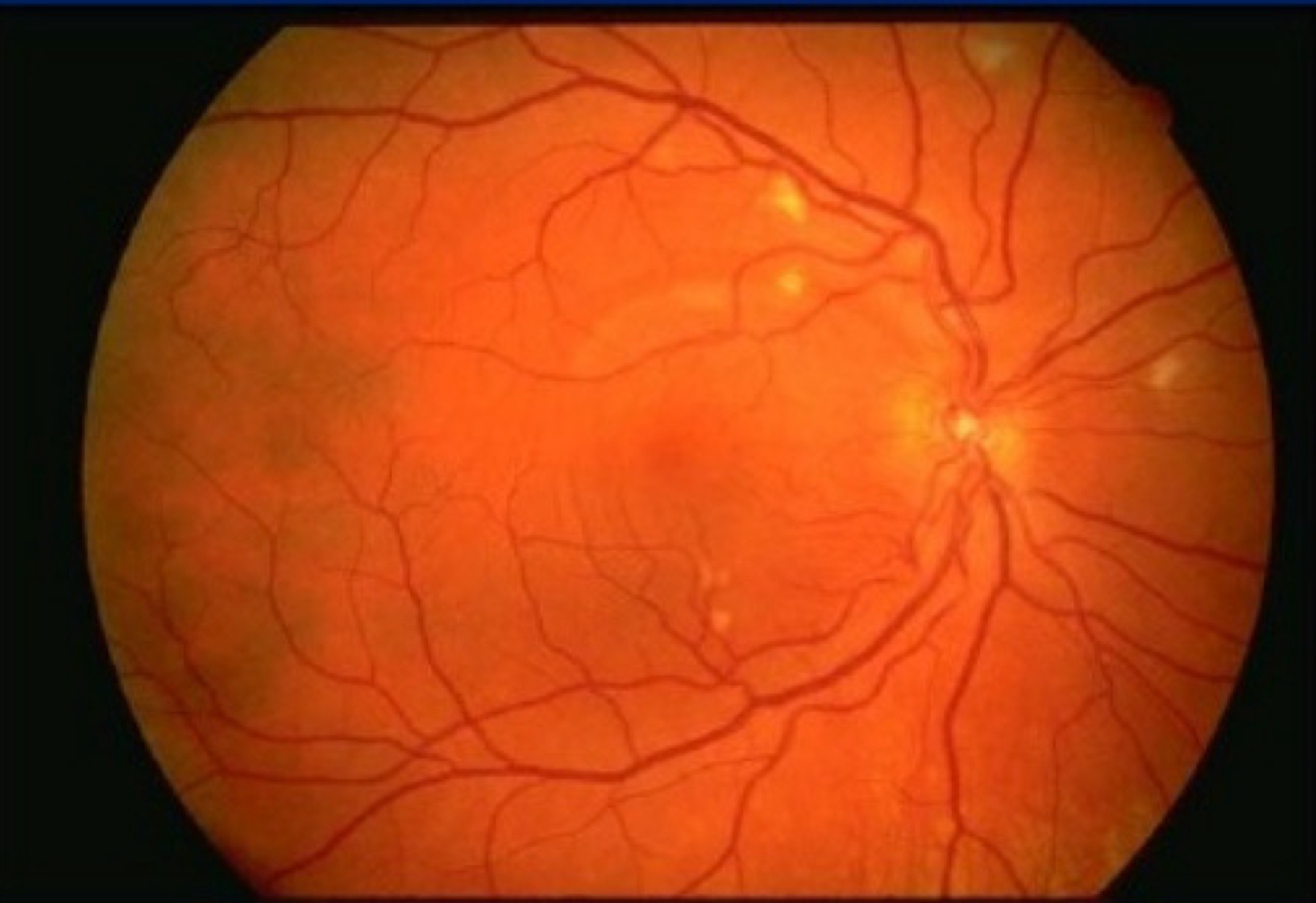
Which type of retinopathy is this?
HIV
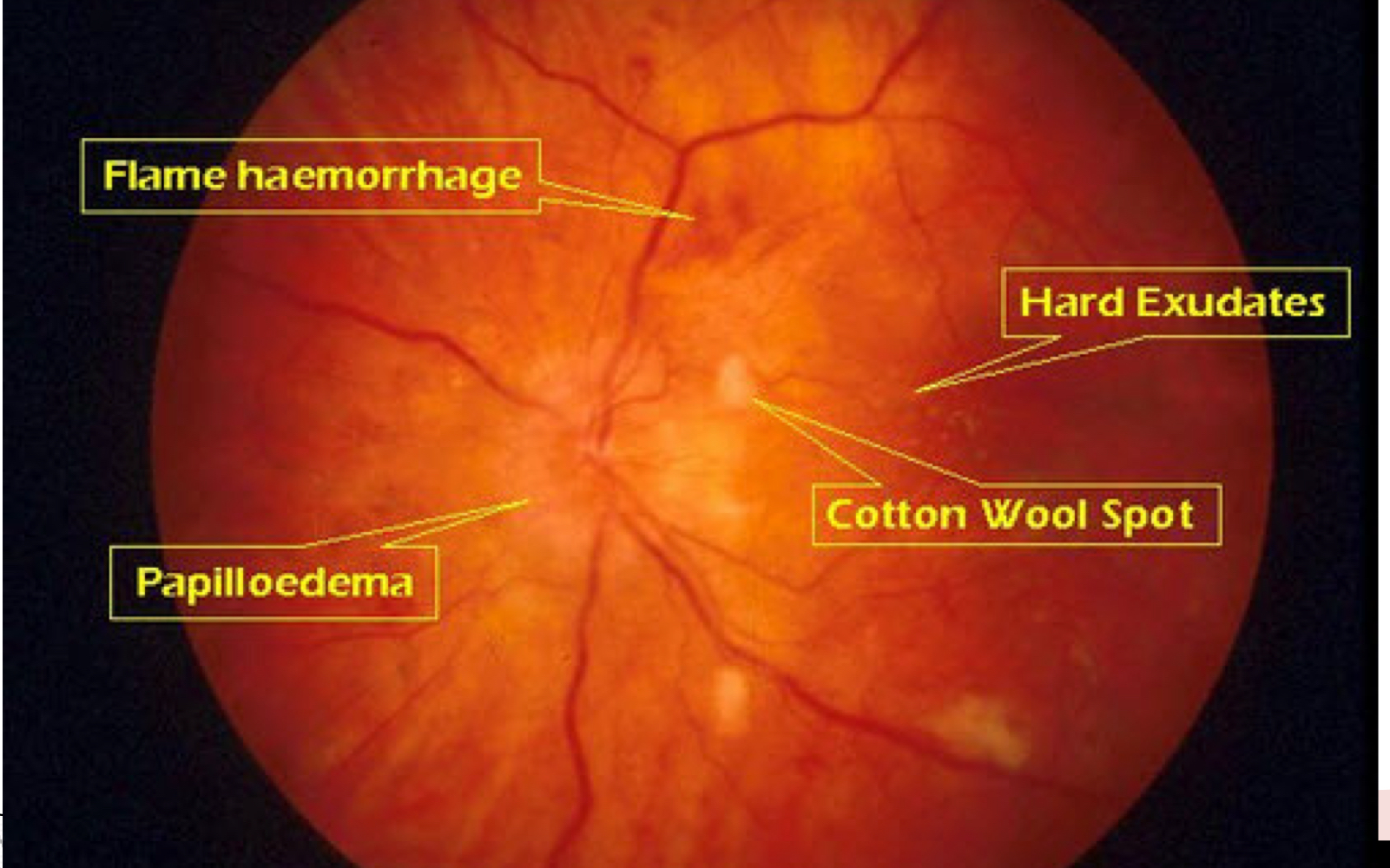
Which type of retinopathy is this?
Hypertension
Which type of conjunctivitis has itching, tearing, redness, clear to white stringy discharge, photophobia, FB sensation, no exposure to COVID?
Allergic
What is the treatment for allergic conjunctivitis?
Mast cell stabilizer- (Cromolyn sodium 4% 1-2 drops 4-6x daily until controlled) cool compress
Which type of conjunctivitis has redness, clear to mucopurulent discharge, FB sensation, photophobia, no blurring of vision, mild discomfort, re- infections are common?
Bacterial, Chlamydia
What is the treatment for bacterial chlamydia conjunctivitis?
Azithromycin 1 gm PO now and bacitracin ophthalmic ointment every 3-4 hrs for 10 days
Which type of conjunctivitis is caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa and has a FB sensation, no blurring of vision, possible mild discomfort?
Conjunctivitis- Contract Lens
Which type of conjunctivitis uses fluorescein stain to diagnose and r/o corneal abrasion or corneal ulcer?
Conjunctivitis- Contact Lens
What is the treatment for Conjunctivitis contact lens?
Ciprofloxacin HCL (Ciloxan) 0.3% ophth solution (1 drop hourly during the day, 1 drop every 2 hrs at night for 2 days, 1 drop every 4 hrs for 5 days)
Which type of conjunctivitis has pain, redness tearing, FB sensation and uses fluorescein stain/ fungal wet mount and culture to diagnose?
Conjunctivitis- Fungal
What is the treatment for Conjunctivitis- Fungal?
Natamycin 5% ophth suspension, 1 drop 4-6 x daily for 7 days
What type of conjunctivitis has FB sensation, copious watery discharge, painful and is caused by adenovirus?
Conjunctivitis- Viral (non herpetic)
What is the treatment for conjunctivitis -viral (non herpetic)?
None- self limiting
Which conjunctivitis has eye redness, ocular irritation, eye soreness, FB sensation, tearing, mucoid discharge, eyelid swelling, congestion, chemosis? (was in contact with someone who has COVID)
Viral- COVID
Which type of conjunctivitis has pain, visual blurring, watery discharge, injection near limbus, red eye, FB sensation, photophobia and is diagnosed with fluorescein stain w/ dendrites?
Viral- herpetic
What is the treatment for conjunctivitis viral (herpetic)?
Trifluridine 1% ophthalmic solution (Viroptic) 1 drop every 2 hrs while awake up to max 9 drops for 2 days then 1 drop every 4 hrs for 7 days (possible systemic treatment for HSV)
What disease has CN V (trigeminal), extremely painful, photophobia, tearing, ocular redness, blurred vision, prodromal fever, malaise, HA, eye pain prior to vesicles, HUTCHINSON SIGN (Lesions on nose)?
Herpetic Zoster Ophthalmicus
Which disease uses Tzanck smear or PCR or direct fluorescent antibody testing to diagnose?
Herpetic Zoster Ophthalmicus
What is the treatment for Herpetic Zosrter Ophthalmicus?
IV Acyclovir (zovirax) 10 mg/kg/dose every 8 hrs for 7 days (renal adjustment) OR valacyclovir 1 g PO TID x7 days [Famciclovir 500 mg PO TID x7 days outpt no IV renal dose adjustment]
Retinopathy (CMV)
CD4, yellow- white patches
Retinopathy Diabetic
DM pt w/ retinal changes, leading cause of blindness
What are symptoms of nonproliferative retinopathy diabetic?
Microanuerysms, intraretinal hemorrhages, cotton wool spots, hard exudates (yellow appearance), retinal edema
What are symptoms of proliferative retinopathy diabetic?
Neovascularization, vitreous hemorrhage, possible retinal detachment
Retinopathy HIV
Positive HIV test, cotton wool spots,
Retinopathy hypertension
AV nicking, flame, hemorrhage, copper wire, silver wire, papilledema, cotton wool spots, hard exudates; risk factors (HTN, pheochromocytoma, preeclampsia)
Non-proliferative sickle retinopathy
Fundoscopic sea fan, salmon patches or black sunburst
What are symptoms and diagnostic studies for glaucoma chronic open angle (Primary open angle glaucoma)?
Elevated IOP, progressive loss of VF, pathologic cupping of optic disc (>.5); IOP > 22
What is a complication for chronic open angle glaucoma?
Blindness
What is the treatment for chronic open angle glaucoma?
Timolol 0.25% ophthalmic solution; avoid beta blockers in pts w/ asthma, COPD, 2nd and 3rd degree AV block
What are symptoms and diagnostic studies of acute closed angle glaucoma?
Sudden onset of severe pain, steamy cornea, fixed mid-dilated pupil, blurred vision, redness, halos around lights, HA, N/V, shallow anterior chamber; IOP >22 (40-70)
What are complications of acute closed angle glaucoma?
Cataract, decreased Visual acuity, repeat episodes
What is the treatment for acute closed angle glaucoma?
1 drop each 1 min apart:
Timolol 0.5%
Apraclonidine 1%
Pilocarpine 2%
Possible IV acetazolamide 500 mg ; avoid decongestants, motion sickness, antidepressants, anticholinergics
*Referral emergent to ophthalmology w/in 1 hr of pt presentation- immediate surgery
What is glaucoma caused by?
Obstruction to the drainage of aqueous humor
What are the risk factors of retinal detachment?
>50 yrs, recent cataract sx, blunt or penetrating trauma
what are the symptoms and diagnostic studies of retinal detachment?
Rapid loss of vision in one eye, “curtain” spread across visual fields, no pain or redness, central vision intact until macula becomes detached; ophthalmoscopy (vitreous looks like grey cloud)
What are complications of retinal detachment?
Vision loss
What is the treatment for retinal detachment?
Emergent consult to ophthalmology, if central vision is affected (Transport w/ head position so that gravity causes retina to fall back)
What bacteria is associated with Dacryocystitis?
Staphylococcus aureus
What bacteria is associated with Anterior and Posterior Blepharitis?
Staphylococcus aureus
What bacteria is associated with Hordeolum?
Staphylococcus aureus
What bacteria are associated with anterior periorbital cellulitis or preseptal cellulitis ?
Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae
What bacteria are associated with posterior orbital cellulitis?
S. pneumoniae, H. Influenzae, M. Catarrhalis, S. aureus
What bacteria is associated with Argyll Robertson?
Treponema pallidum, neurosyphilis
For what diseases would you use Fluorescein stain
Conjunctivitis (Contact lenses), Conjunctivitis (Fungal), Conjunctivitis (Viral- herpetic), Corneal Trauma/Abrasion, Corneal Trauma/Ulcer, Ultraviolet Keratitis,
For what diseases would you need an emergent consult to ophthalmology?
Conjunctivitis (Viral-COVID), Conjunctivitis (Viral-herpetic), Infection Keratitis, Corneal Trauma/Ulcer, Ultraviolet Keratitis, Dacryocystitis (possible sx), Cataract Traumatic, Posterior orbital cellulitis, retinal detachment, retinopathy cytomegalovirus and hypertension and sickle cell, chemical injury, globe rupture, Acute Uveitis, Central retinal vein occlusion , Vascular disorder vitreous hemorrhage, Transient amaurosis fugax (ocular TIA), Vision loss secondary to scleritis
For what diseases would you admit to the hospital?
Herpetic Zoster Ophthalmicus, Optic neuritis, Oculomotor palsies (3rd N), Posterior orbital cellulitis, blowout fracture, hyphema, central retinal artery occlusion
For what disease would you order an MRI?
Nystagmus (r/o mass), Oculomotor palsies (3rd/4th/6th n- r.o lesion)
What other imaging (besides MRI), would you order for Oculomotor palsies (3rd n)?
Contrast enhanced MRI w/ MRA or CTA to r/o aneurysm, Non contrast CT then LP to r/o meningitis
For what diseases would you order a CT of orbits and sinus?
Anterior periorbital cellulitis
For what disease would you order a CT?
Posterior oribital cellulitis (contrast enhanced), Rhabdomyosarcoma, Blowout fracture (immediate to r/o ruptured eye)
For what disease would you order an optical coherence topography and fluorescein aniography?
Wet Age Related Macular Degeneration, Acute Uveitis
For what disease is there a referral for urgent consult?
Retinopathy (HIV), subconjunctival hemorrhage,
For what disease would you order ocular ultrasonography, MRI of brain and orbits, CT?
Retinoblastoma
What is the treatment for Anterior periorbital cellulitis?
Augmentin 875 mg PO BID for 5-7 days OR Augmentin 875 mg PO BID 5-7 days, Bactrim DS PO BID OR Clindamycin 300 mg PO TID
What are symptoms of anterior periorbital cellulitis?
Infection of anterior portion of eyelid, redness, pain, eyelid swelling
What is the treatment for Posterior orbital cellulitis?
IV Vancomycin AND IV Ceftriaxone OR IV Ciprofloxacin
What are the symptoms of posterior orbital cellulitis?
Proptosis, swelling, pain w/ eye movement, redness, edema, diplopia, vision loss
Xanthelasmas
Hyperlipidemia and yellow lesions on lids
Pterygium
UV exposure/ sunny climates, triangular wedge crosses cornea
Pinguecula
Yellow bump on conjunctiva; deposit of fat, protein, or calcium
Hordeolum
Blocks meibomian sebaceous glands; most common is external
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
CN 5 affected, early signs (fever, malaise, HA, eye pain), Hutchinson’s signs
When would you use Erythromycin (EryPed) 0.5% ophthalmic ointment?
Bacterial conjunctivitis, Corneal abrasion, Anterior/posterior blepharitis, Hordeolum, Foreign body
When would you use Cromolyn (Opticrom) 4% ophthalmic solution?
Allergic conjunctivitis, Vernal keratoconjunctivitis
When would you use Ciprofloxacin (Ciloxan) 0.3% ophthalmic solution?
Bacterial gonorrhea conjunctivitis (IF PCN allergy), Contact lens conjunctivitis, Posterior orbital cellulitis (septal)
When would you use Natamycin (Natacyn) 5% ophthalmic suspension?
Fungal Conjunctivitis
Which eye conditions have sudden vision loss?
Transient amaurosis fugax, acute closed angle glaucoma, vitreous hemorrhage, CRVO, CRAO, retinal detachment, Wet ARMD, Traumatic cataracts
Which eye conditions have progressive vision loss?
Chronic open angle glaucoma, Dry ARMD, Optic neuritis, nontraumatic cataracts
Which eye conditions can have sudden or progressive vision loss?
Rhabdomyosarcoma and papilledema