Climate Variation and Drought
5.0(3)
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
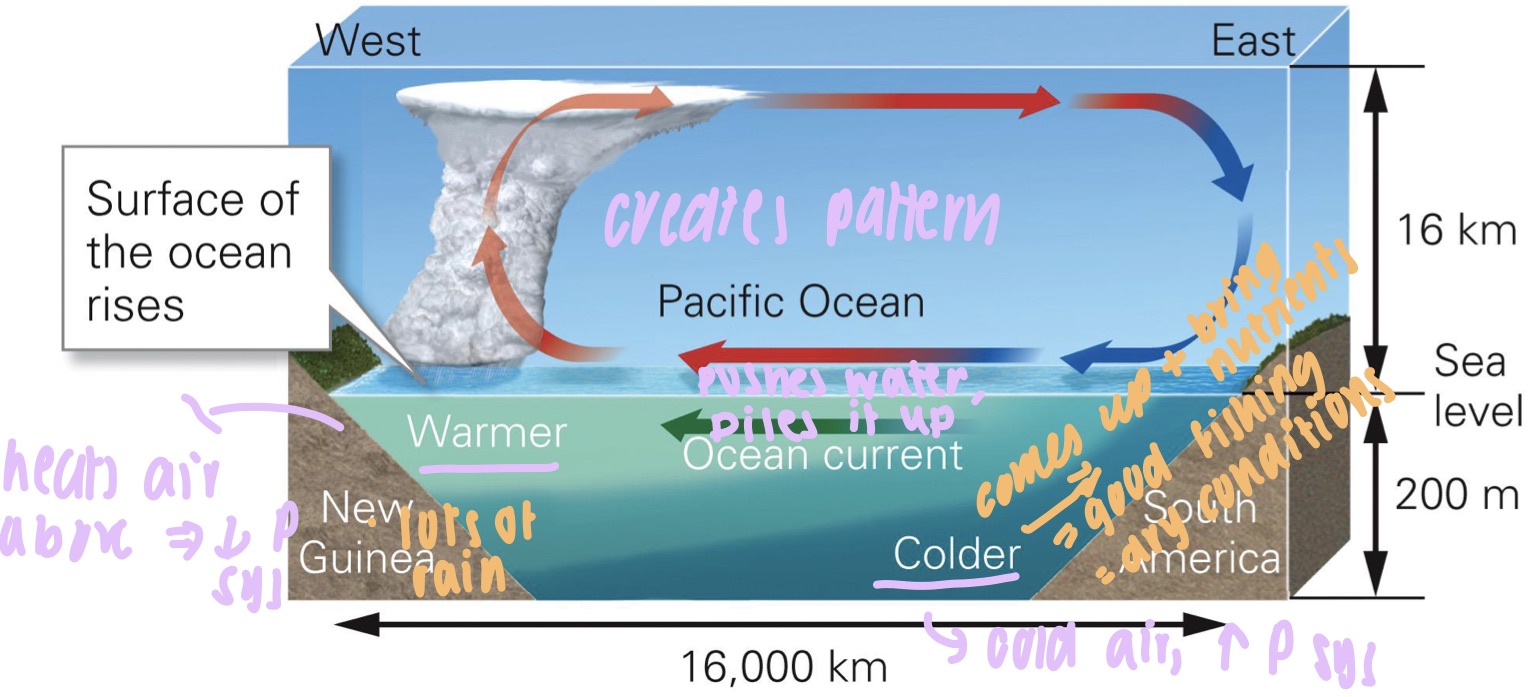
what is the walker circulation?
* an atmos circulation in the equatorial regions of the pacific ocean
* warmer water in the western Pacific → causing pow-p, warmer air
* cooler ocean water in the east pacific → causing high-p, cooler air
* winds blow surface ocean water westward (increase sea lvl). cool deep ocean water wells-up along the west coast of South america bringing deep, nutrient-rich seawater to the surface, allowing fish pop to thrive
* warmer water in the western Pacific → causing pow-p, warmer air
* cooler ocean water in the east pacific → causing high-p, cooler air
* winds blow surface ocean water westward (increase sea lvl). cool deep ocean water wells-up along the west coast of South america bringing deep, nutrient-rich seawater to the surface, allowing fish pop to thrive
2
New cards
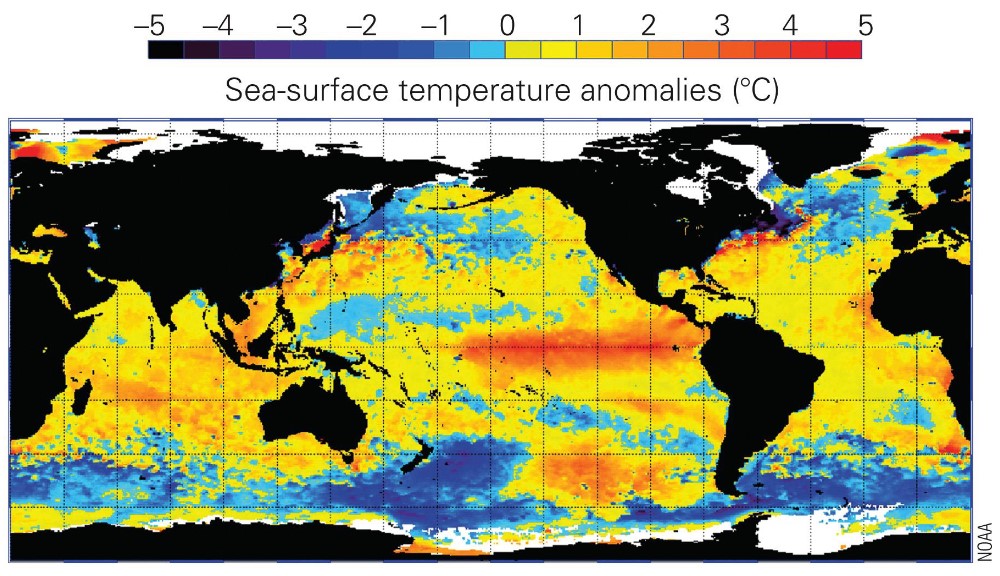
what is la Nina?
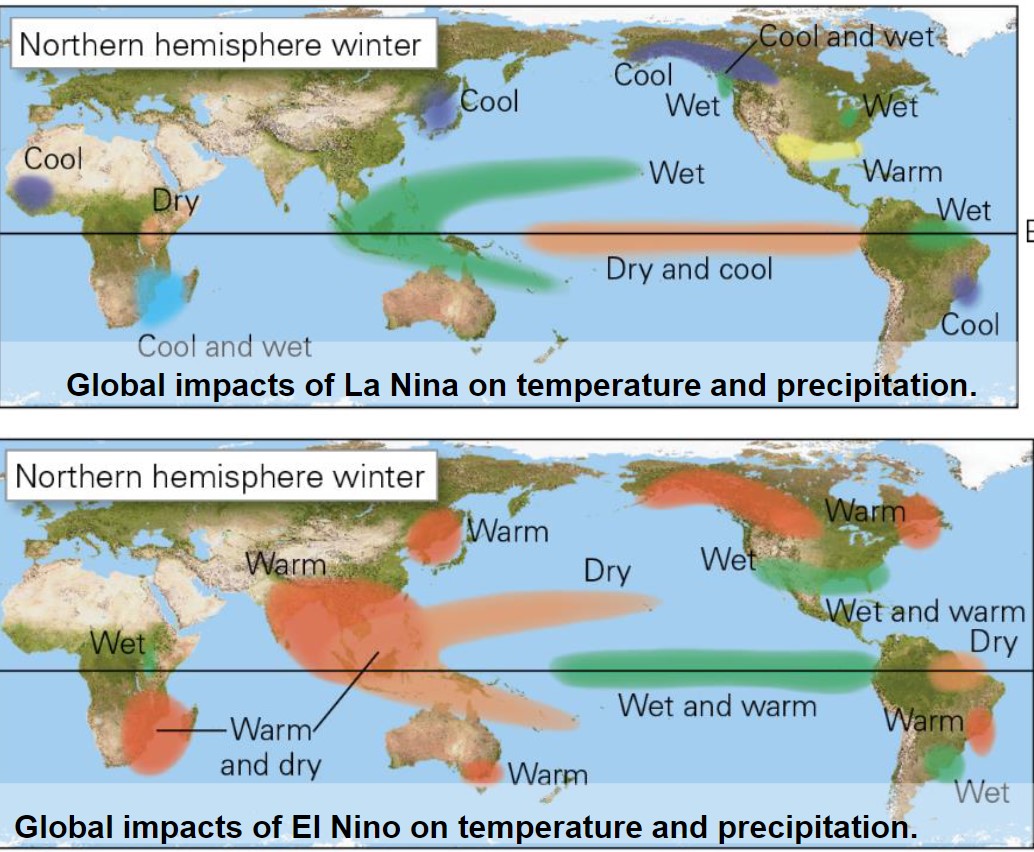
* more amplified ‘normal’ condition leading to direr and cooler conditions in south america and more rainfall in indonesia
3
New cards
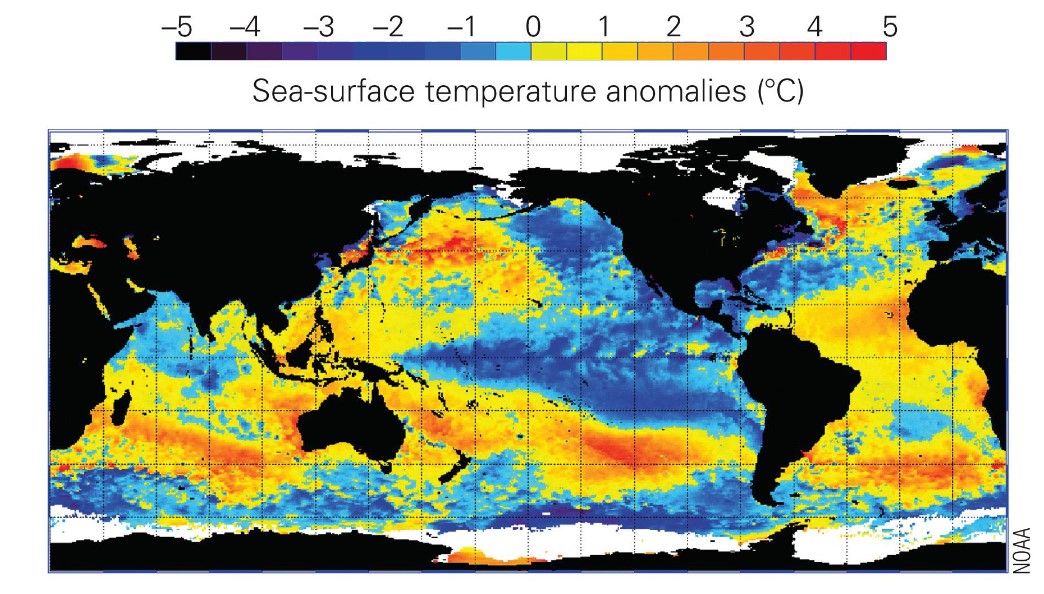
what is el nino?
* occurs when surface winds weaken
* tilted sea surface flattens n warm pacific water flows to the eat → water flows back to equilibrium
* water on coast of south america become nutrient poor and impacts fish pop
* droughts occur in australia/indonesia while storms n flooding occur on the coast of the americas
* tilted sea surface flattens n warm pacific water flows to the eat → water flows back to equilibrium
* water on coast of south america become nutrient poor and impacts fish pop
* droughts occur in australia/indonesia while storms n flooding occur on the coast of the americas
4
New cards
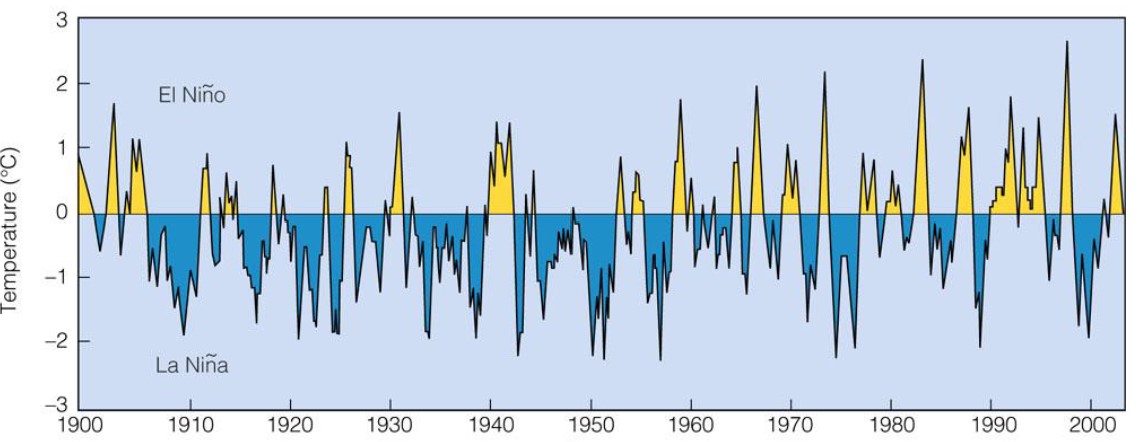
Enso conditions
* ENSO = el nino/southern oscillation
* sea surface temperature anomalies in the mid-pacific ocean for 1900-2003
* el nino has warm temperature anomalies
* sea surface temperature anomalies in the mid-pacific ocean for 1900-2003
* el nino has warm temperature anomalies
5
New cards
global impact el nina/nino
6
New cards
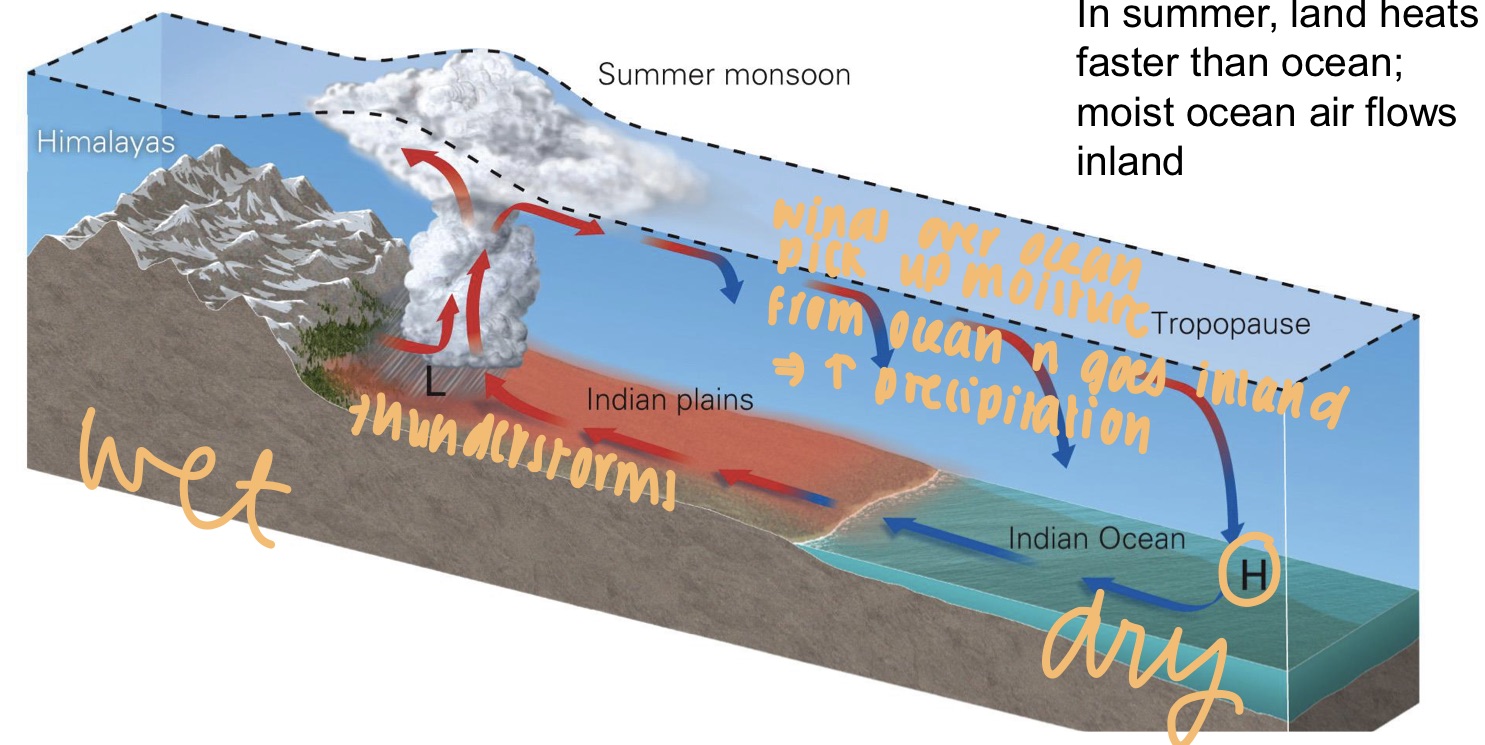
what are monsoon?
* seasonally changing air circulation in the world’s tropical n subtropical regions in which summer winds blow from the ocean toward the land, bringing heavy rain inland
* in summer, land heats faster than ocean; most ocean flows inland
* in winter, winter winds blow from the land toward the ocean, causing drier weather inland
* land cools faster than ocean; air flows toward ocean
* winter n summer r opp
* in summer, land heats faster than ocean; most ocean flows inland
* in winter, winter winds blow from the land toward the ocean, causing drier weather inland
* land cools faster than ocean; air flows toward ocean
* winter n summer r opp
7
New cards
monsoons in south asia
* normally bring 2 months of flooding
* agriculture depends on regular monsoon rain
* economic disaster occurs when monsoon rains fail
* droughts occur if rains do not arrive → no crops = no feeding
* agriculture depends on regular monsoon rain
* economic disaster occurs when monsoon rains fail
* droughts occur if rains do not arrive → no crops = no feeding
8
New cards
what is drought?
* a deficiency of freshwater within a region lasting long enough to harm normal vegetation, crops, livestock, surface n underground water supplies, human health, and human activities
9
New cards
Dust bowl
* decade long drought in the 1930s led to severe drought
* soil has no vegetation, so lifted into clouds
* dust storms carried away topsoil
* soil has no vegetation, so lifted into clouds
* dust storms carried away topsoil
10
New cards
what are the 3 types of drought?
* meteorological drought
* agricultural drought
* hydrological drought
→ they r sequential
* agricultural drought
* hydrological drought
→ they r sequential
11
New cards
what is a meteorological drought?
* precipitation is less than normal for weeks or yrs
12
New cards
what is agricultural drought?
* low soil moisture
* inhibits crop germination or growth
* may be caused by human activity
* inhibits crop germination or growth
* may be caused by human activity
13
New cards
what is hydrological drought?
* insufficient water flows into lakes, streams, or reservoirs
* surface-water lvl drop
* water table drops
* surface-water lvl drop
* water table drops
14
New cards
drought positive feedback
* hot, dry weather increases evaporation, causing ground to dry out
* dry ground contributes to less moisture to air
* plants die, contributes less moisture (evaporation) to air and less shade on the ground
* dry ground contributes to less moisture to air
* plants die, contributes less moisture (evaporation) to air and less shade on the ground

15
New cards
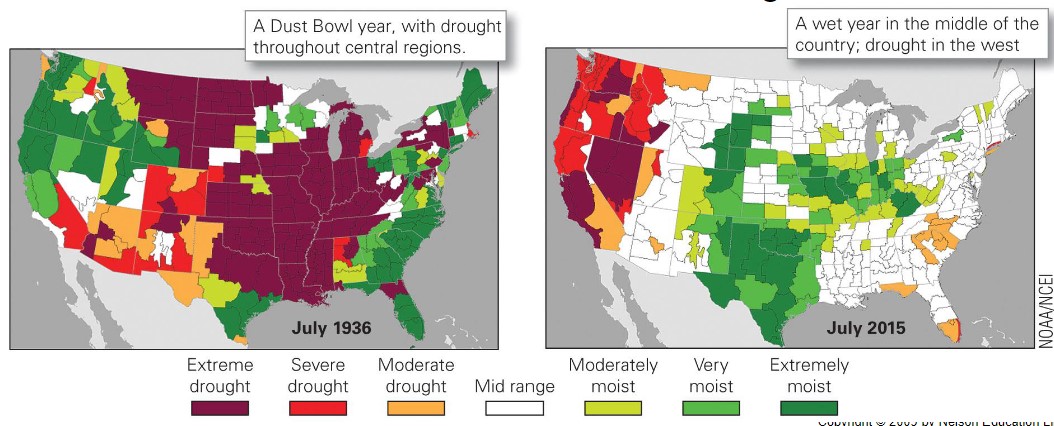
what does the palmer drought index measure?
* moisture deficiency, relative to avg conditions
* compares 2 variables:
* water supply from precipitation n reserves
* water depletion from evaporation, infiltration, n runoff
* allows scientists to visualize cumulative changes over time
* compares 2 variables:
* water supply from precipitation n reserves
* water depletion from evaporation, infiltration, n runoff
* allows scientists to visualize cumulative changes over time
16
New cards
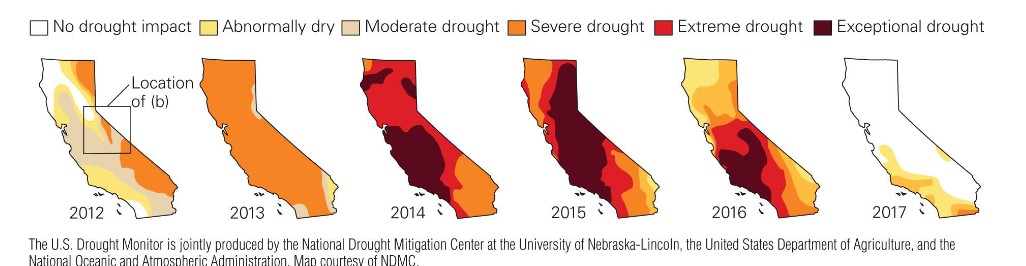
what are droughts in cali caused by?
* insufficient snow in Sierra Nevada created low water supplies
17
New cards
when was cali’s worst drought in 1,200 yrs?
* 2011-2017
* devasted crops
* inconvenienced millions of peep
* killed millions of trees
* reservoirs dropped to all-time low lvls
* devasted crops
* inconvenienced millions of peep
* killed millions of trees
* reservoirs dropped to all-time low lvls
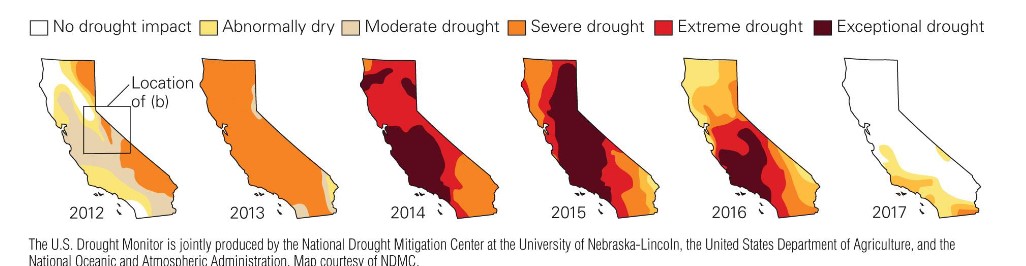
18
New cards
what does monsoonal climate have?
* have wet n dry seasons
* heavy rain falls during wet season
* little/no rain falls during dry season
→ risk of famine
* heavy rain falls during wet season
* little/no rain falls during dry season
→ risk of famine
19
New cards
when do droughts occur?
* if rain f n intensity drop
* reservoirs n streams rapidly dry out
* crops n livestocks die as soil dries
* densely pop areas r at high risk of famine
* reservoirs n streams rapidly dry out
* crops n livestocks die as soil dries
* densely pop areas r at high risk of famine
20
New cards
in a monsoonal climate zone, the shift from drought conditions to flood conditions can happen ____________
* rapidly
→ shown by precipitation records from east-central africa and madagascar
→ shown by precipitation records from east-central africa and madagascar
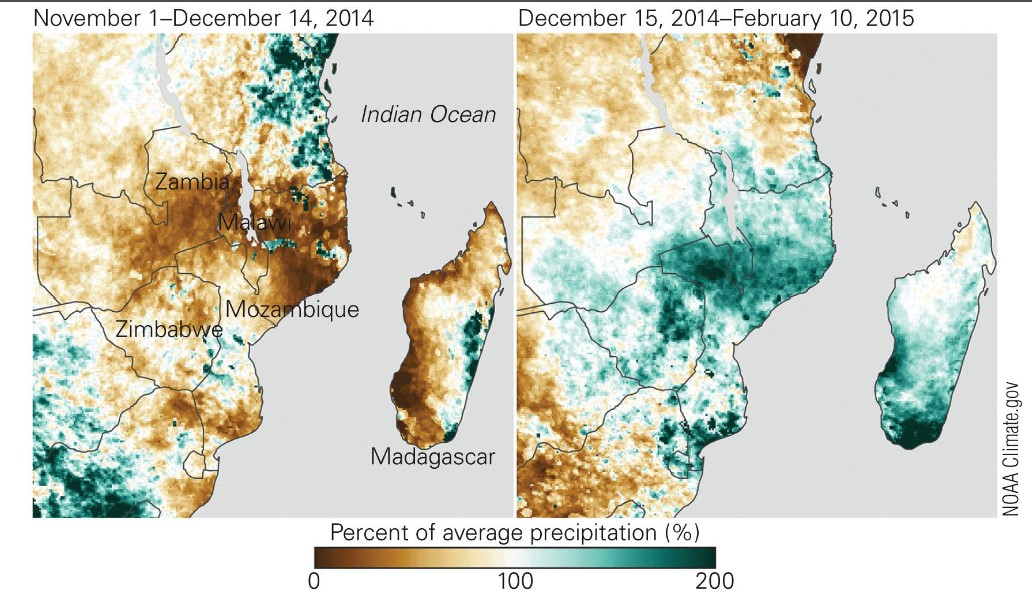
21
New cards
droughts in africa
* poor dev n poverty increases drought risk in africa
* horn of africa has been n a drought since 2011
* 17 million peep face water stress n food insecurity
* 5.5 million peep have access to only contaminated water
* lack of infrastruct n poor security hamper relief efforts
* horn of africa has been n a drought since 2011
* 17 million peep face water stress n food insecurity
* 5.5 million peep have access to only contaminated water
* lack of infrastruct n poor security hamper relief efforts
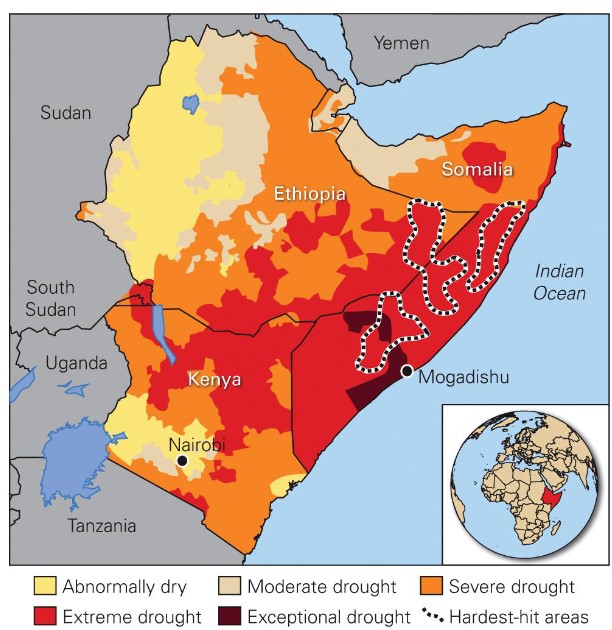
22
New cards
drought effect on lake chad
* hydrological drought has led to the progressive shrinkage of lake chad, central africa
* formerly the world's 6th largest lake
* lake chad has decreased by 90% due to climate change, pop growth n irrigation
* formerly the world's 6th largest lake
* lake chad has decreased by 90% due to climate change, pop growth n irrigation
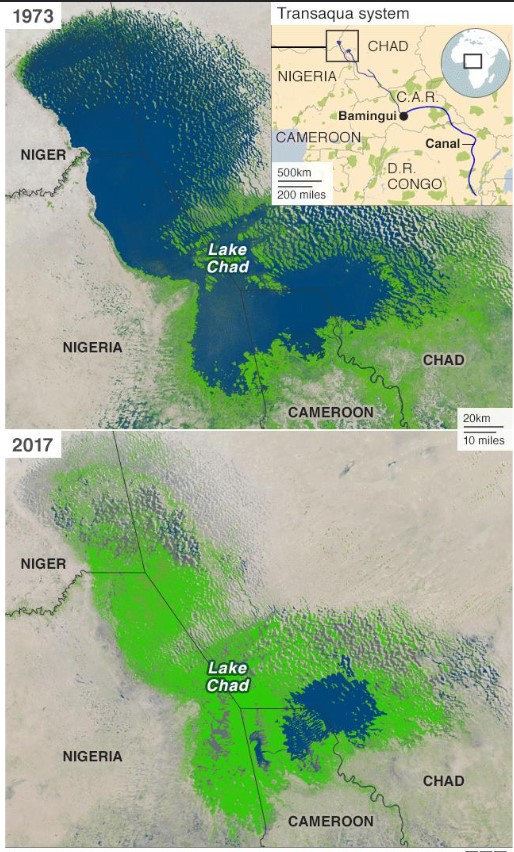
23
New cards
video
* el nino effect
* lack of rain + sever drought
* cow death (livestock in general)
* poor government intervention
* food security at risk
* people starving to death
* lack of rain + sever drought
* cow death (livestock in general)
* poor government intervention
* food security at risk
* people starving to death
24
New cards
what are the impacts of drought?
* severe natural hazard in many areas of the world often accompanied by famine n starvation
* often called a ‘creeping’ phenomena until conditions have deteriorated
* costs r more difficult to assess than other hazards
* China, 1928: 3 million deaths
* NE Africa, 1983:150,000 deaths
* Somalia, 2017–2018: Food shortages for 6 \n million
* often called a ‘creeping’ phenomena until conditions have deteriorated
* costs r more difficult to assess than other hazards
* China, 1928: 3 million deaths
* NE Africa, 1983:150,000 deaths
* Somalia, 2017–2018: Food shortages for 6 \n million