Alcohols CH 10/11
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what are alcohols
organic compounds with hydroxyl group(s) -OH
R-OH
Alcohols with two hydroxyl groups are called
diols or glycols
ex ethane 1,2 diol or ethylene glycol
Physical properties of alcohols
the boiling point increases with increasing molecular weight and decreases with increasing branching
polar
hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole attractions
Solubility properties of alcohols
alcs with 1-3 alkyl groups are miscible
hydroxyl group is HYDROPHILIC
alkyl group is HYDROPHOBIC
alkoxide ion
strong nucleophiles
strong bases
what is the pKa range of an alc
15.5 - 18
why is phenol more acidic than cyclohexanol
more stable, charge delocalized over oxygen and the 3 carbons
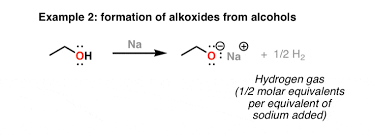
synthesis using sodium/potassium metal
R-O-H +Na → R-O Na+ + hydrogen gas
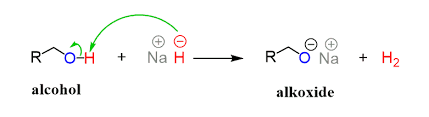
what is used when sodium/potassium metal doesn’t work
sodium hydride
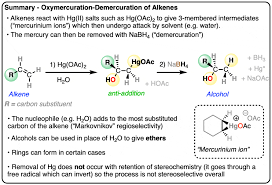
Oxymercuration-demercuration (alkene into alc)
(1) Hg(OAc)2/ H2O
(2) NaBH4
-follows markovnikov's orientation
-H and -OH on products
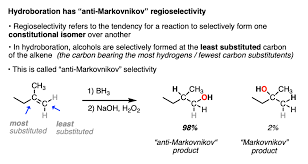
Hydroboration-oxidation (alkene into alc)
REAGENTS:
(1) BH3/ THF
(2) H2O2/ NaOH
-follows anti-markovnikov's orientation
-H and -OH on products
-syn addition
What are Grignard reagents?
R-Mg-X
strong nucleophiles
great to make new C-C bonds
always carried out in DRY solvent
incompatible w/ acidic protons (OH, NH, SH)
R is either alkyl, vinyl, or aryl
X is either I, Br, or Cl
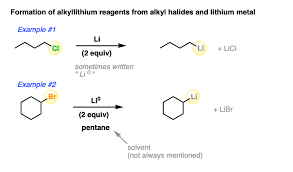
organolithium comps
strong nucleophiles
R-Li
R-X + 2Li --> LiX + R-Li
REAGENTS:
2 Li/ether
thiols “mercaptans”
sulfur analogs of alcohols
R-SH
lower pKa (=10)
thiolates weaker bases than alkoxides
oxidation in ogro is the…
addition of o/o2, addition of x, or the loss of h2
reduction in orgo is the…
loss of o/o2/x or the addition of H- or h2
reagents that stop oxidation of primary alcohols
NaClO (bleach)
PCC
DMP
PDC
how does NaClO and tempo work
oxidizes primary alc into aldehydes at high yields and rates
which arent oxidized under normal circumstances
tertiary alcs, resistant to reagents
other oxidizing reagents
KmnO4
HNO3
CuO
secondary alc are oxidized to….
ketones
primary alcs are oxidized to…. by …..reagents and oxidized to… by ….reagents
aldehydes by mild …. carboxylic acids by strong
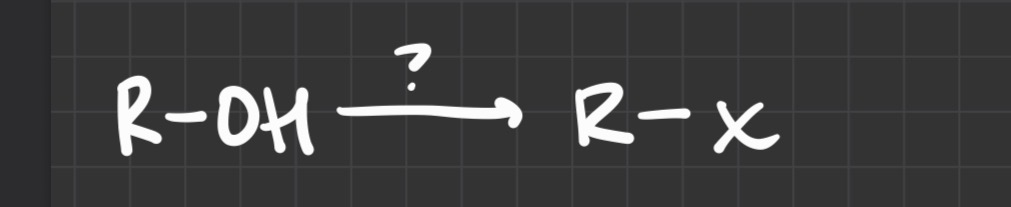
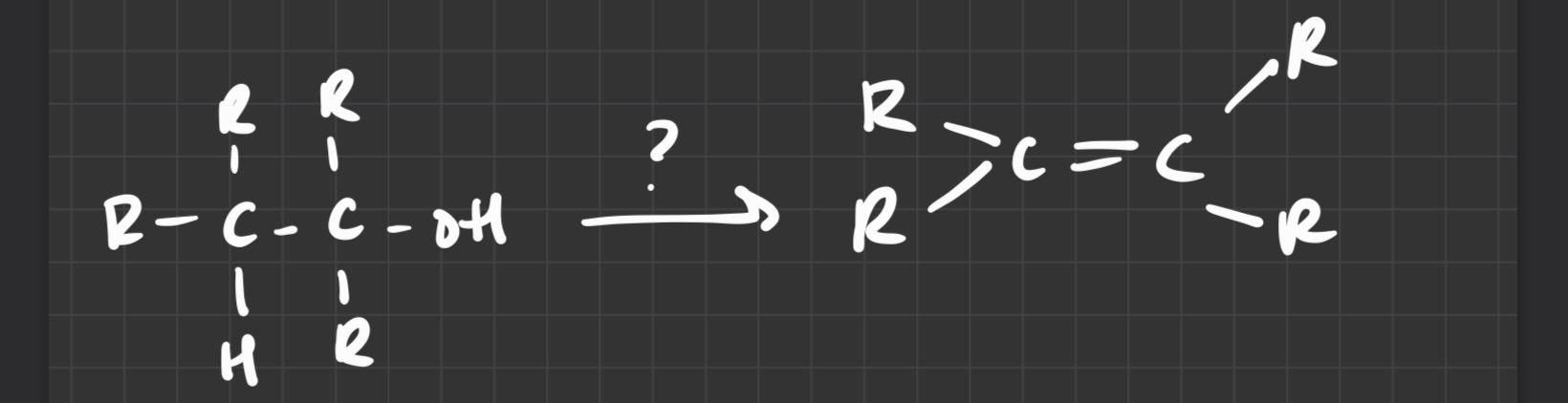
what type of reaction
elimination
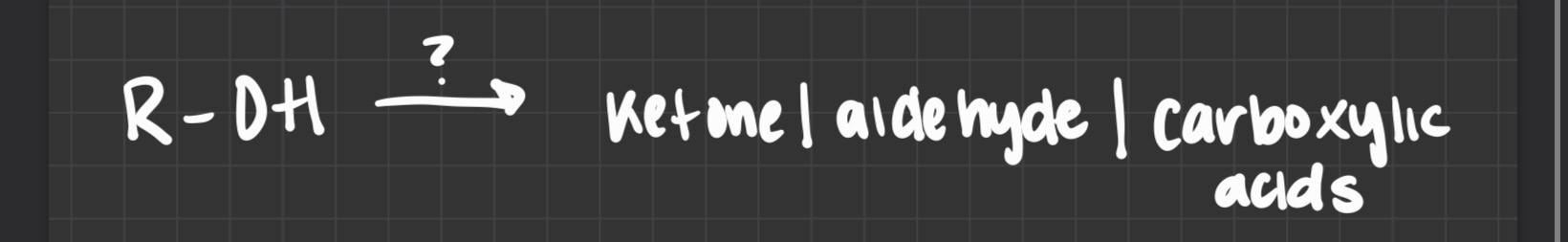
what type of reaction
oxidation

what reagent is used
T3Cl (makes tosylates)

what reagent is used
H+
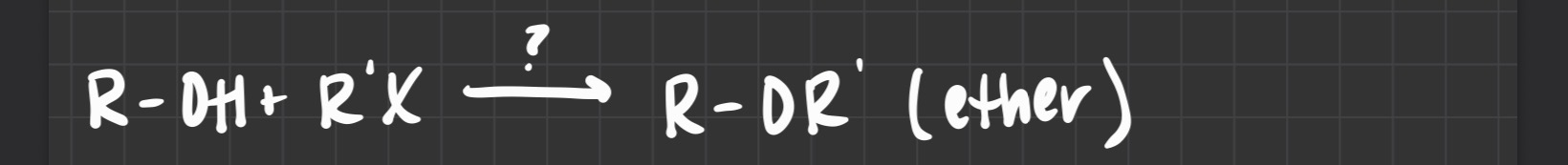
what reagent is used
A base
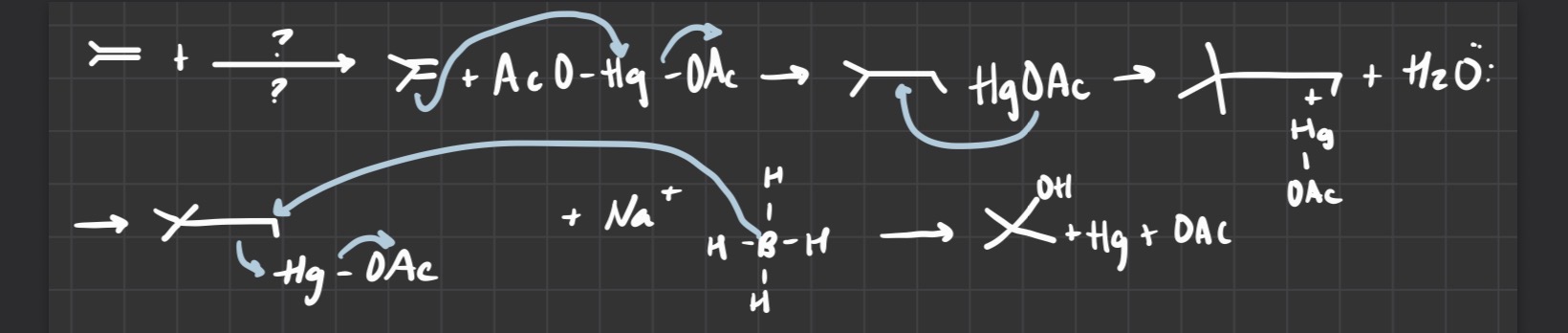
what reagents are used
Hg(OAc)
H2O