KNES260 - Pulmonary cavities
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
How is the thoracic cavity divided ?
2 pulmonary cavities — contain the lungs
1 mediastinum — contains the heart
What’s the difference between the pulmonary artery/vein and bronchial artery/vein?
Pulmonary = involved in gas exchange (from heart to lungs then lungs to heart)
Bronchial = brings blood supply to lung muscles, not involved in gas exchange
Each pulmonary cavity is completely lined by the _____________ (a mesothelial membrane)
Pleural membrane
How many layers make up the pleural membrane (or pleural sac)? What are they?
2 → parietal and visceral pleurae
Where/What is the parietal pleura?
Pleural lining the walls of the pulmonary cavity, adhering to the endothoracic membrane on the inner surface of the thoracic wall, mediastinum, and diaphragm
Where can we find the visceral pleura?
In contact with the lungs → closely covers the lung and adheres to its external surface
We can find the pleural cavity between ____________ and ____________
The parietal pleura and the visceral pleura
What is the pleural cavity?
A potential space (normally exists) between the two layers of pleura
it contains serous pleural fluid which lubricates surfaces for smooth movement during respiration
T/F: the visceral pleura is associated with the walls of the pulmonary cavities
False, it’s the parietal pleura
Name and briefly describe the different parts of the parietal pleura (4)
Cervical pleura → dome-shaped layer of parietal pleura lining the cervical extension of the pleural cavity
Costal pleura → related to the ribs and intercostal spaces, and is separated from the internal surface of the thoracic wall by the endothoracic fascia
Diaphragmatic pleura → covers the diaphragm
Mediastinal pleura → covers the mediastinum
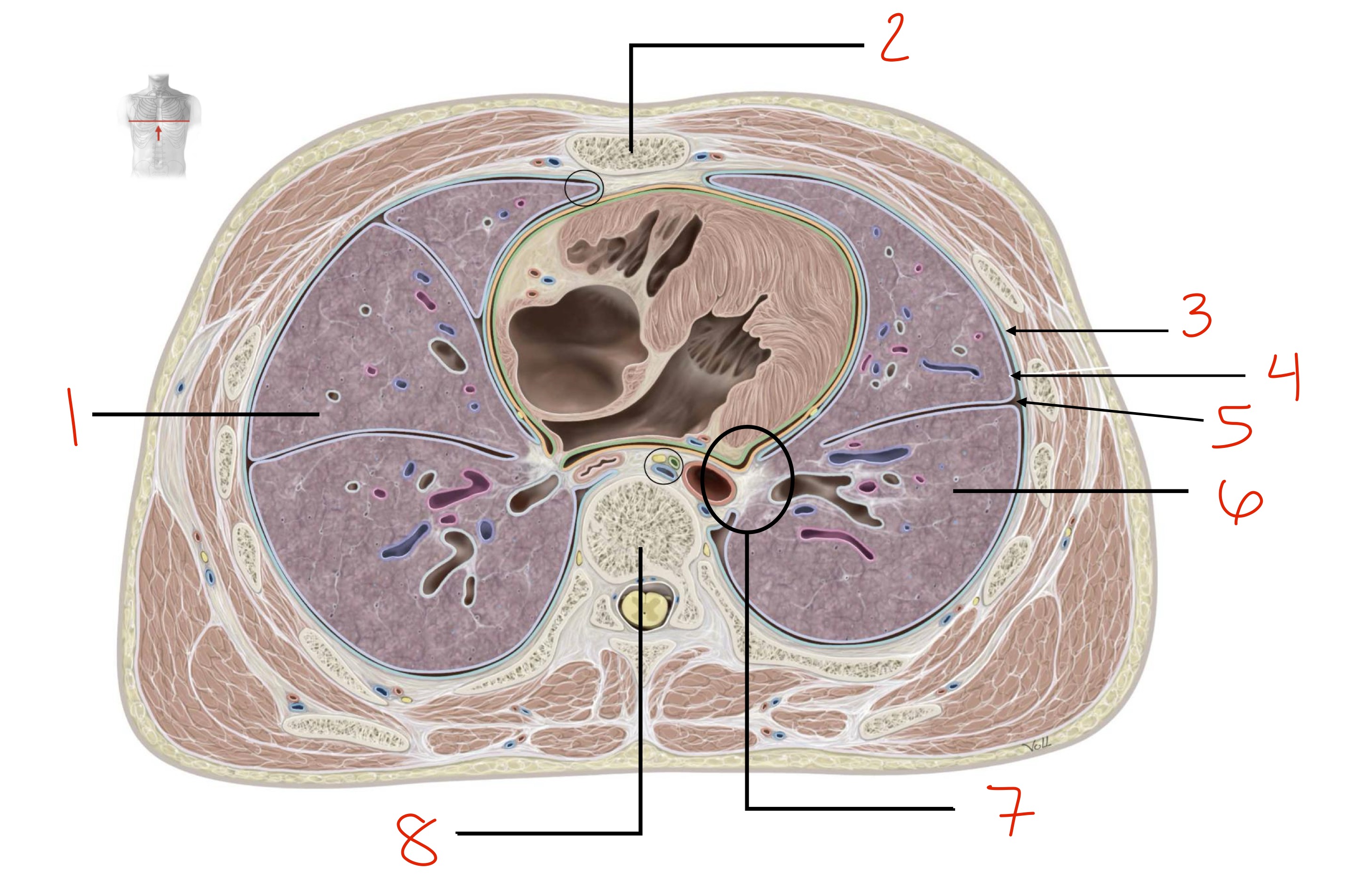
Identify the colored parts (pleura layers or parts)
Orange : visceral pleura
Pink-ish: mediastinal pleura (parietal)
Green: diaphragmatic pleura (parietal)
Blue: costal pleura (parietal)
Yellow: cervical pleura (parietal)
What nerve(s) innervate the costal, diaphragmatic and mediastinal pleurae? Do they bring in/out sensory or motor information?
Sensory information for all
Costal pleura : intercostal nerves
Diaphragmatic and mediastinal : phrenic nerves
The visceral pleura is _______ than the parietal pleura, its attached firmly to the ______________, including those within the horizontal and oblique fissures; it is continuous with the ________ pleura at the hilium of the lungs
Thinner, surface of the lung, parietal
What are the functions of the pleural cavity/space?
Contains a small amount of serous/pleural fluid that helps lubricate the pleurae and allows the lungs to move smoothly when breathing
Generates surface tension that provides the cohesion that keeps the lungs surface in contact with the thoracic wall → allows pulmonary cavity to expand during inspiration
Creates a suction between the parietal pleura and visceral pleura
Keeps the two layers stuck to one another but allows the two layers to slide on one another
T/F: lungs do not completely fill the anterior or posterior inferior regions of the pulmonary cavities
True
Name the the two pleural recesses
Costodiaphragmatic recess and costomediastinal recess
Where is the costodiaphragmatic recess? When are they at their biggest and smallest
Inferior to the lungs, between the lungs and the diaphragm
Deepest after forced expiration
Shallowest after forced inspiration
Where are the costomediastinal recesses?
Behind the sternum and rib cartilages
Define thoracocentesis. Where does it take place (anatomical structure)?
A procedure that is performed to remove fluid from the pleural cavity, done for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes
Inserting the needle into the 9th intercostal space → costodiaphragmatic recess (during expiration) to avoid puncturing the lung
Give general characteristics of the lungs and give their primary function
Function = oxygenate blood by bringing inspired air into close contact with the venous blood in the pulmonary capillaries
Also important in removing CO2 and waste products, and regulating blood pH
Lungs are the organs of respiration
They are elastic and spongy
Each lung is contained within the pulmonary cavities, and they lie on either side of the mediastinum
Each lung has 10 functionally independent regions supplied by one segmental/tertiary bronchus; what are those called?
Bronchopulmonary segments
Size-wise, the right lung is ________ and _______ than the left; length and width-wise, it is _______ (why?) and ________ (why?) than the left lung
Larger and heavier, shorter (right dome of diaphragm is higher) and wider (heart bulge more to the left)
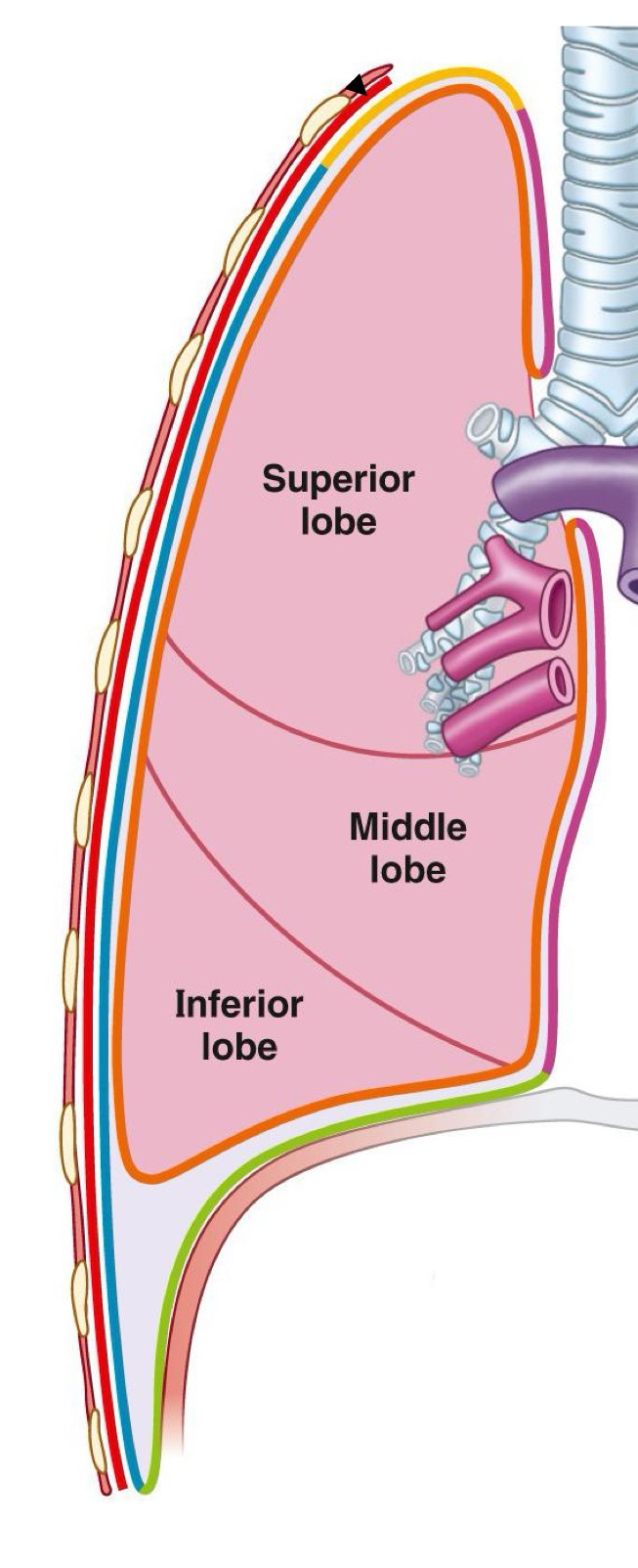
How many lobes and fissures do the right and left lung have?
Right: 3 lobes, 2 fissures
Left: 2 lobes, 1 fissure
Name the lobes and fissures of the right lung
Lobes:
Superior (mostly anterior)
Middle
Inferior (mostly posterior)
Fissures:
Horizontal (btwn superior and middle lobes)
Oblique (btwn inferior and middle/sup lobes)
How is the anterior surface of the right lung?
Slightly curved
What are the three surfaces on the right lung?
Costal, mediastinal, diaphragmatic
Name the lobes, the surfaces and the fissures on the left lung
2 lobes : Superior (mostly anterior) and inferior (mostly posterior) lobes
3 surfaces: costal, mediastinal, diaphragmatic
1 fissure: Oblique fissure btwn the two lobes
There are 2 distinctive structures on the superior lobe of the left lung that are not present on the right lung. What are they?
Lingula → tongue-like extension found om the inferior portion of the superior lobe, which projects over the heart bulge
Cardiac notch → indentation on the surface of the left lung, allowing space for the heart
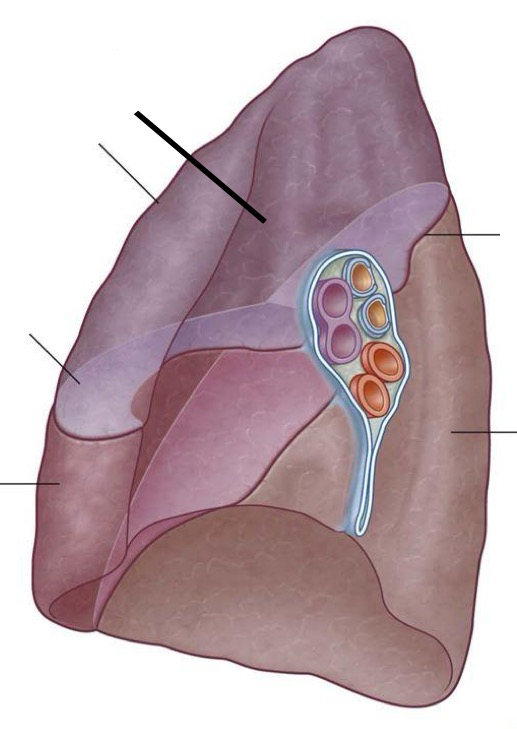
Is this the right or left lung?
Right
Right or left lung?
Right
Right or left lung ?
Left
Right or left lung ?
left

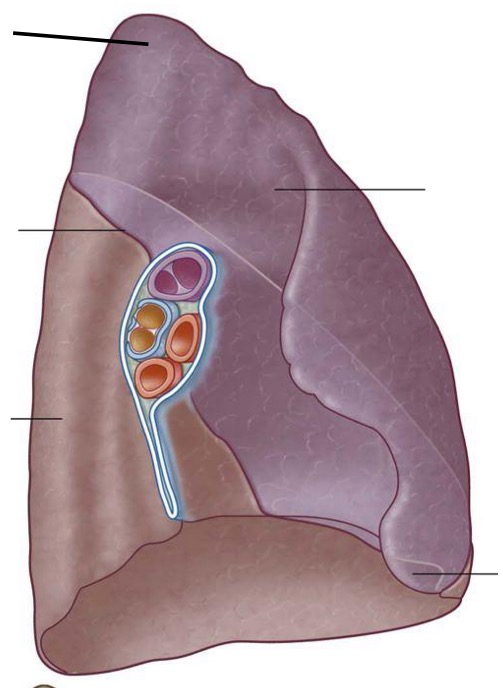
Identify the structures ; is this the right or the left lung? What’s our view?
Right lung, medial view
Superior lobe
Horizontal fissure
Middle lobe
Oblique fissure
Inferior lobe

Identify structures 1-3 (hint: lobes) ; which lung is that, what’s the view?
Superior lobe
Middle lobe
Inferior lobe
Right lung, medial view

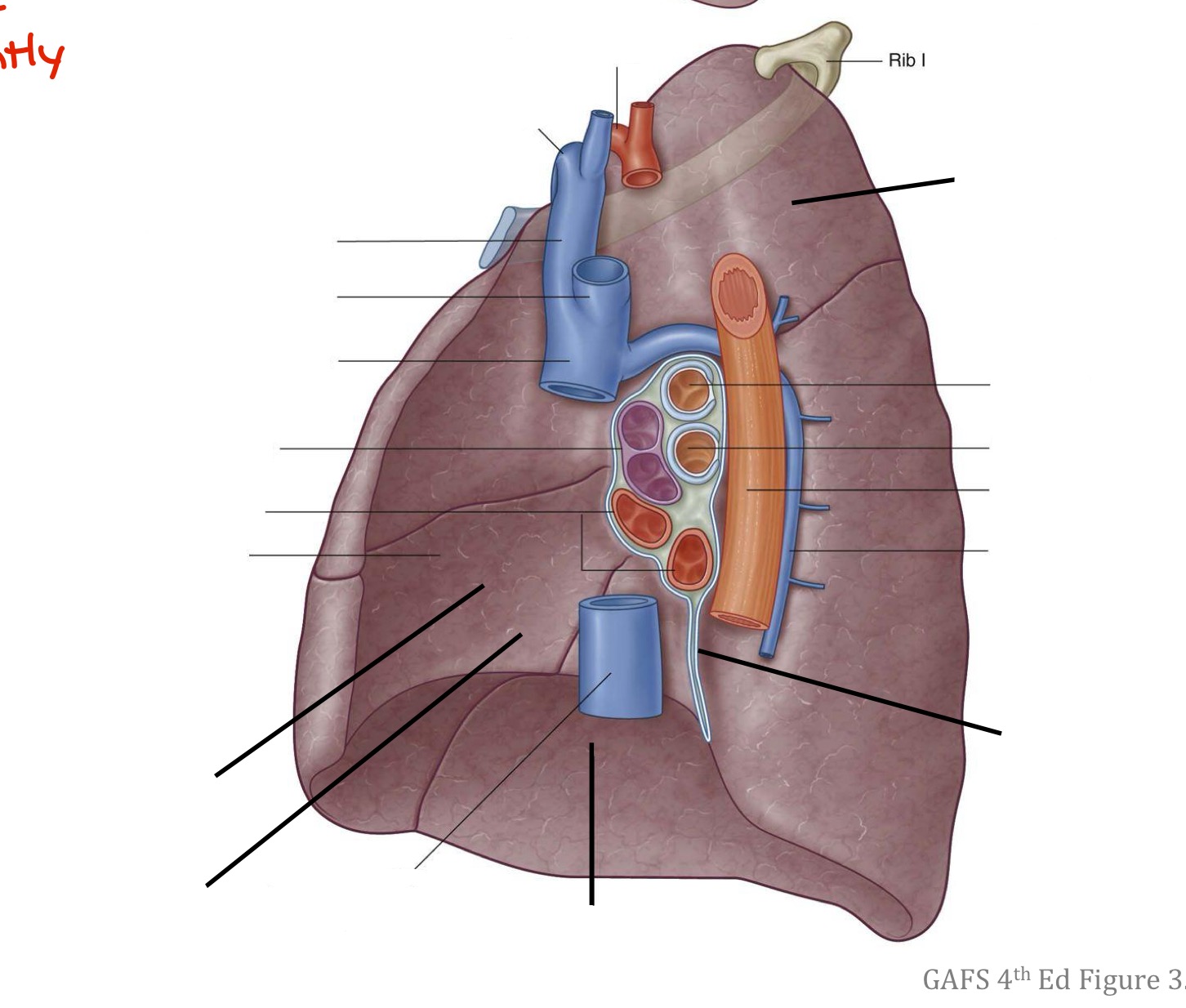
Identify structures A-G
A- Superior vena cava
B- Inferior vena cava
C- Esophagus
D- Azygos vein
E- Pulmonary ligament
F- subclavian vein
G- subclavian artery

Identify surfaces S1 and S2
S1- Diaphragmatic
S2- Mediastinal

Identify what lung this is and the structures numbered
This is the left lung from a medial view
Apex
Oblique fissure
Inferior lobe
Lingula
Superior lobe

Identify
Esophagus
Thoracic aorta
Pulmonary ligament
Cardiac notch
What is the pulmonary ligament?
A double fold of pleural membrane
What important structures can be found on or touching the medial surface of the right lung?
Heart → on the lung, there’s the cardiac impression
Inferior vena cava → groove for IVC
Superior vena cava → groove for SVC
Azygos vein
Esophagus → groove for esophagus
What important structures can be found on or touching the medial surface of the left lung?
heart (cardiac impression)
aortic arch (groove for aortic arch)
thoracic aorta (groove for thoracic aorta)
esophagus (groove for esophagus)
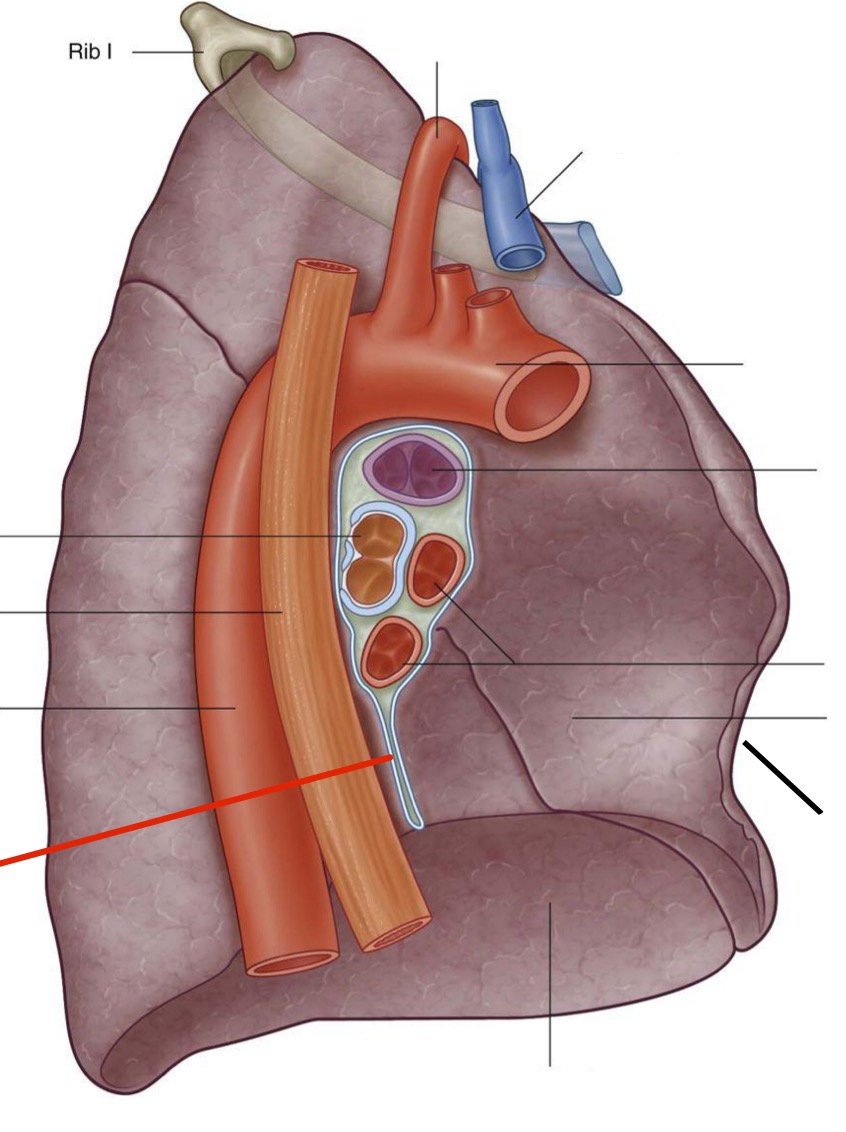
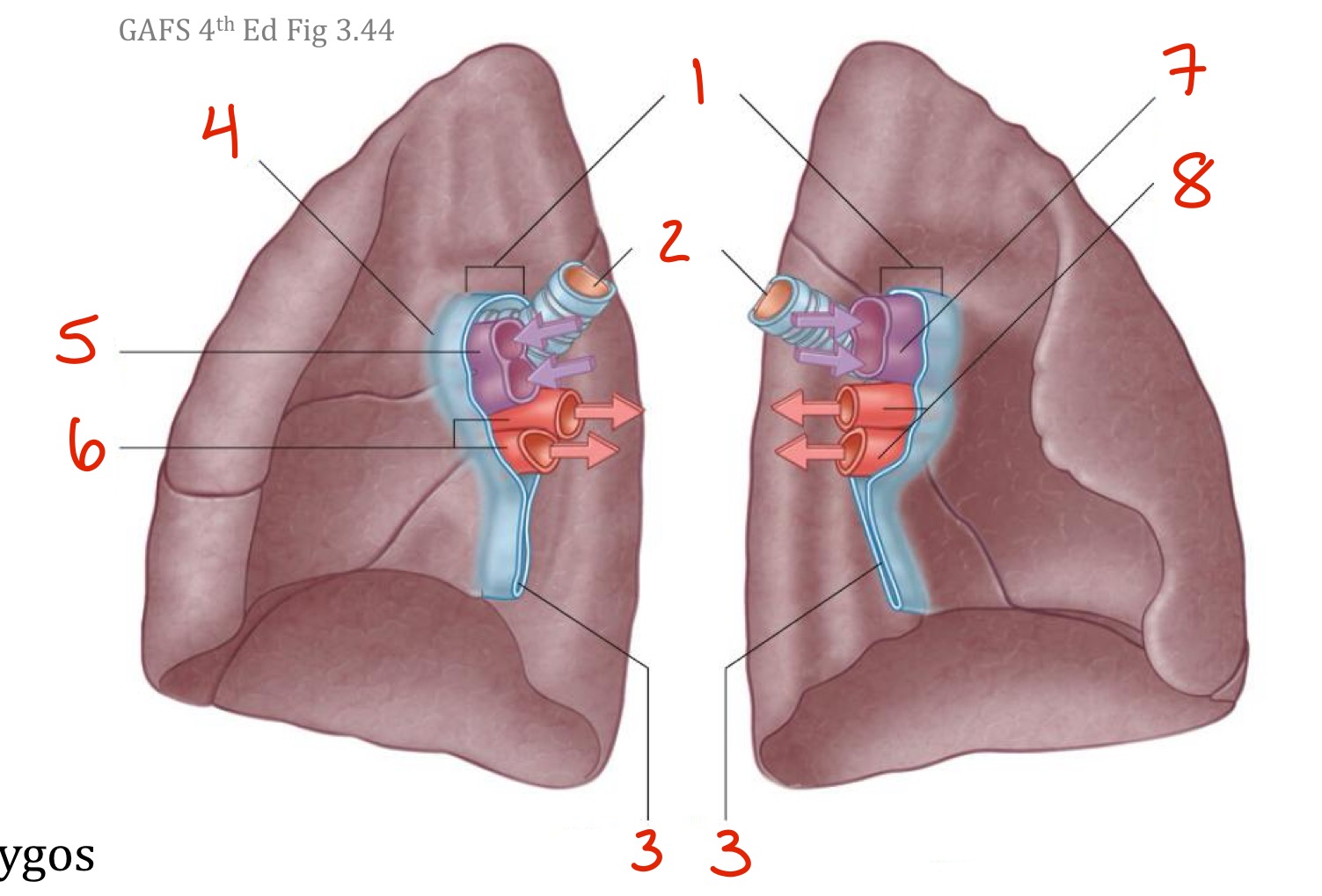
What is the difference between the root of the lung and the hilum of the lung ?
The root of the lung is the collection of structures that connect the lung to the mediastinum; The hilum is the actual “hole” where those structures enter and leave the lung
The (3 most) important structures that make up the root of the lung are…
Bronchi (left and right)
Pulmonary arteries
Pulmonary veins (2 on each side, one inferior, one superior)
The left bronchus divide ______ entering the root; the right bronchus divide ______ entering the root
After, before
Pulmonary arteries are _______ and _______ to the pulmonary veins
Anterior and superior
The vagus nerve passes _______ to the root of the lung. As it passes distal to the becomes vagal trunks: left vagus nerve becomes the ________ vagal trunk (smaller); right vagus nerve becomes the _________ vagal trunk (larger)
Posterior, anterior, posterior
The phrenic nerve passes _______ to the root of the lung
Anterior
Identify. Make sure to mention right or left when relevant
Roots of lungs
Bronchi
Pulmonary ligament
Hilum of lung
R pulmonary artery
R pulmonary veins
L pulmonary artery
L pulmonary veins
T/F: the hilum stabilizes the position of the inferior lobe (of the lungs)
True
What’s the difference between the pulmonary and bronchial circulations?
Pulmonary: blood circulation between heart and lungs, involved in gas exchange — low pressure
Bronchial: blood supply to the airways and lung tissue and else, NOT involved in gas exchange— high pressure
The pulmonary arteries move __________ blood, while the pulmonary veins move ___________ blood
Deoxygenated, oxygenated
T/F: the bronchial veins drain most of the blood supplied to the lungs
False, they drain only parts of it; majority drained by the pulmonary veins
Define and give characteristics of a pulmonary embolism
It is the obstruction of a pulmonary artery by a blood clot (embolus)
Forms when a blood clot, fat globule, or air bubble travels in the blood from a leg VEIN → passes through the right side of the heart to a lung (though a pulmonary artery)
Result: partial or complete obstruction of blood flow to the lung → acute respiratory distress → right side of the heart may become acutely dilated (can’t drain though one of the pulmonary arteries)
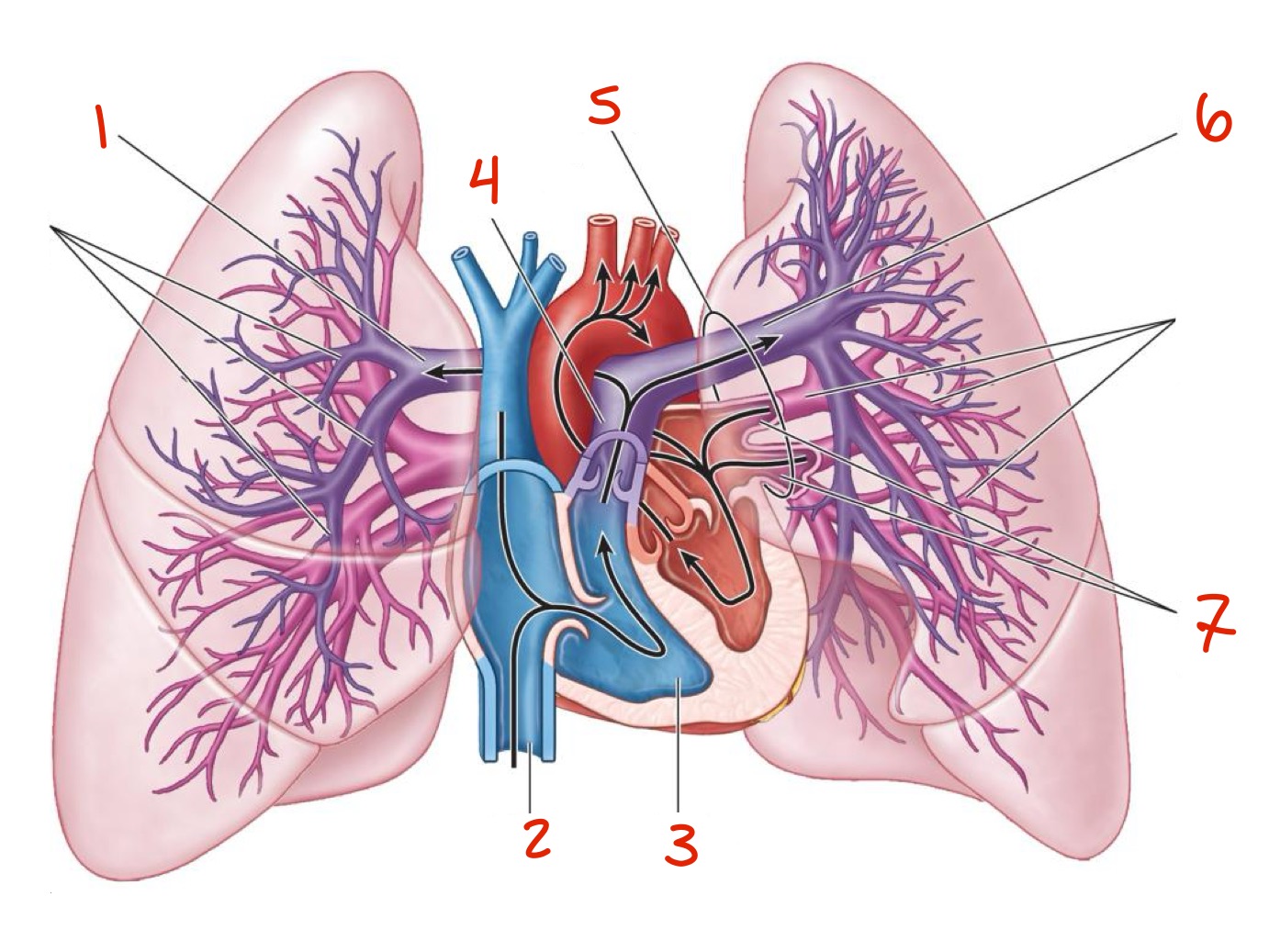
Identify
Right pulmonary artery
Inferior vena cava IVC
Right ventricle
Pulmonary trunk
Hilum of the lung
Left pulmonary artery
Left pulmonary veins
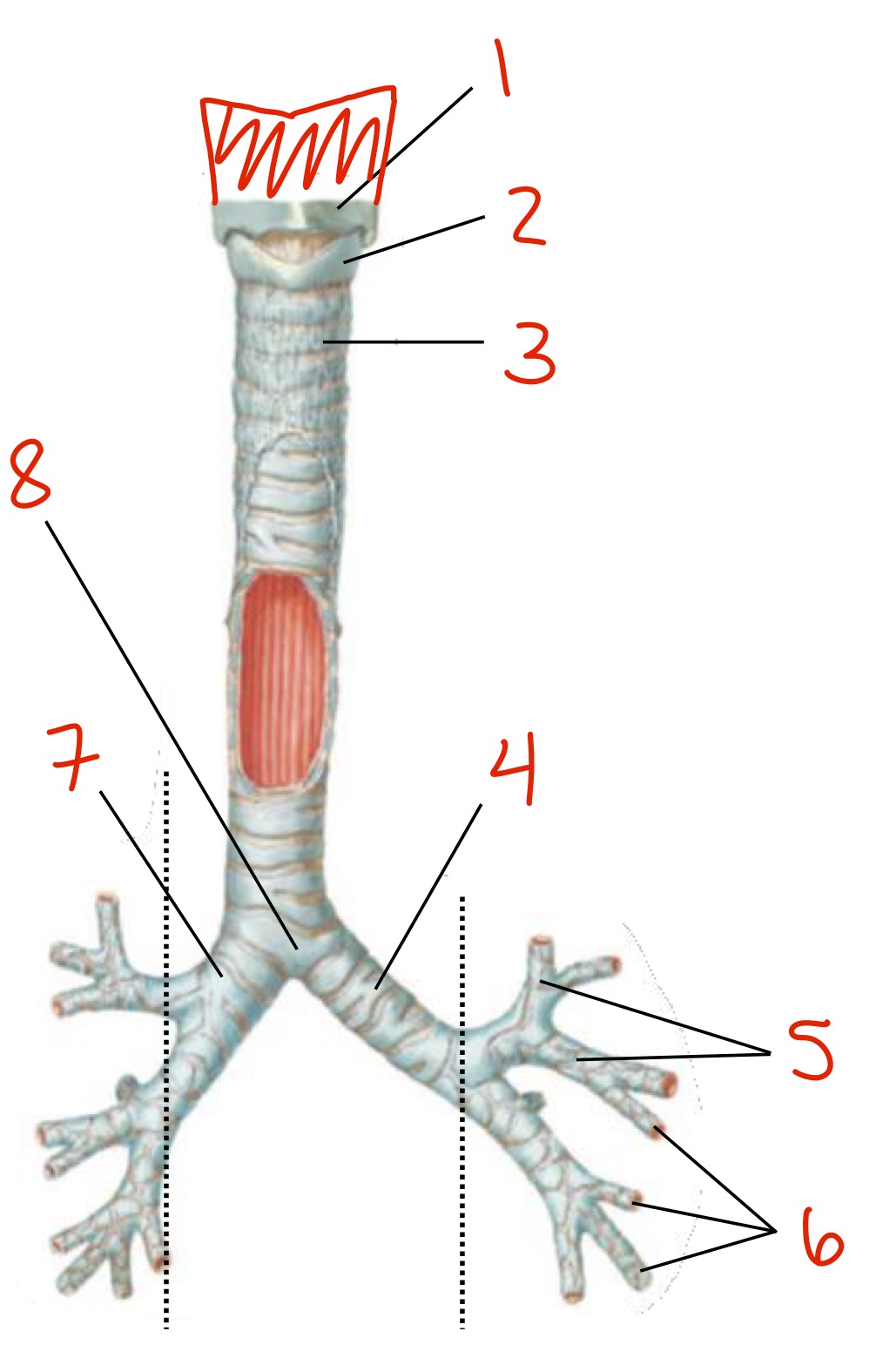
Identify
Thyroid cartilage
Circoid cartilage
Tracheal cartilage
Left primary (or mainstem) bronchus
Secondary (or lobar) bronchi
Tertiary (or segmental) bronchi
Right primary (mainstem) bronchus
Carina
From superior to inferior, name the 3 cartilages from the mouth to the bronchi
Thyroid → circoid → tracheal
Are the following cartilages complete or incomplete rings? What does it mean?
Thyroid
Circoid
Tracheal
Thyroid is incomplete (makes a U-shape, not connected posteriorly)
Circoid is complete (O-shaped)
Tracheal is incomplete
“Adam’s apple” is a piece of _________ cartilage that we see on the neck
Thyroid
The trachea divides into two ____________; each of them further divides into ____________ (how many on left vs right?), which further subdivides into ___________. Those become even smaller __________ and ___________
Primary/Mainstem bronchi (a left and a right), secondary/lobar bronchi (2 left, 3 right), tertiary/segmental bronchi, bronchioles (respiratory and terminal), alveoli
What is Carina?
The ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi (can see from the inside of the trachea)
T/F: the right primary bronchus is wider, shorter, and courses more vertically than the left main bronchus
True!
Referring to the last question, what’s the functional consequence?
Mistakenly swallowed or inspired objects/things are more likely to go down the right side and so, more likely to get a clogged right lung
The trachea is a …
Conducting airway
The tracheal cartilage is a(n) __________ ring lined with _______ membrane, and with a smooth muscle (__________) forming the _________ border of the trachea
Incomplete, mucous, trachealis, posterior
What are the main functions of the mucosa present in the respiratory tract (remember the trachea is lined by a mucous membrane)?
Provides humidity, warming, or cooling to the inhaled gases
Serves as a mucociliary escalator
What is a mucociliary escalator?
It describes one of the role of the mucosal layer in the trachea: ciliated epithelial cells transport mucus, with any captured foreign particles (such as viruses or bacteria), in an upstream direction toward the upper airway (to be expelled out of the airways) → keeps those foreign particles away from the alveoli and blood
How different is the trachea in kids compared to adults ?
Their trachea is funnel-shaped, and relatively smaller in diameter and shorter in length
more prone to significant airflow obstruction (can enter more easily since its funnel shaped, then gets clogged in smaller airways)
The alveoli, or alveolar sacs, serve as the location for what?
Gas exchange → blood-air barrier
where CO2 and O2 exchange between our blood and our lungs
Happens across the surface of the alveoli and pulmonary capillaries
T/F: Terminal bronchioles facilitate the exchange of air at the alveoli
False, it’s the respiratory bronchioles