Herpetology Lab Practical 1
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
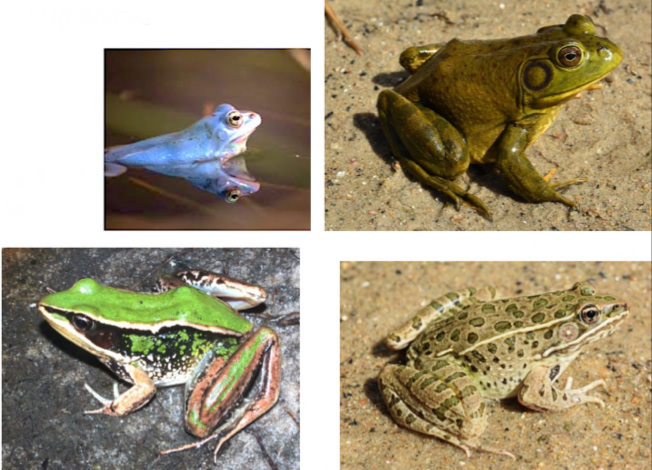

Ranidae - True frogs
CO genus - Lithobates
-extensive toe webbing
-pointed snout
-some species shave dorsolateral folds
-robust, muscular hind limbs for jumping & swimming
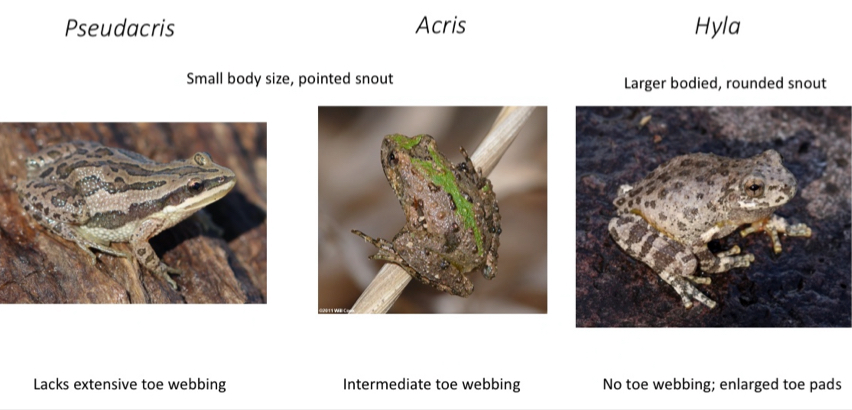

Hylidae - Tree Frogs
CO genus - Pseudacris, Acris, Hyla
-Subdigital toepads
-Extra jointed digits
-Elongate limbs

Microhylidae
CO Genus -Gastrophryne
-Narrow mouth
-Small, round body
-Many species have fold of skin over eyes
-Very small tympanum
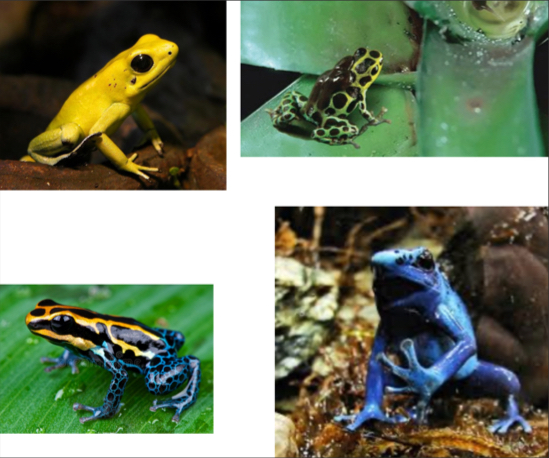

Dendrobatidae - Poison frogs
-Small body size
-Enlarged toe tips
-Diverse aposematic coloration
-Smooth skin
-No webbing
-Proportionally long forelimbs

Pipidae - Aquatic tongueless frogs
-Narrow, flattened skulls
-Many species have claws
-Full webbing on hind feet
-Extremely long fore foot digits for feeding
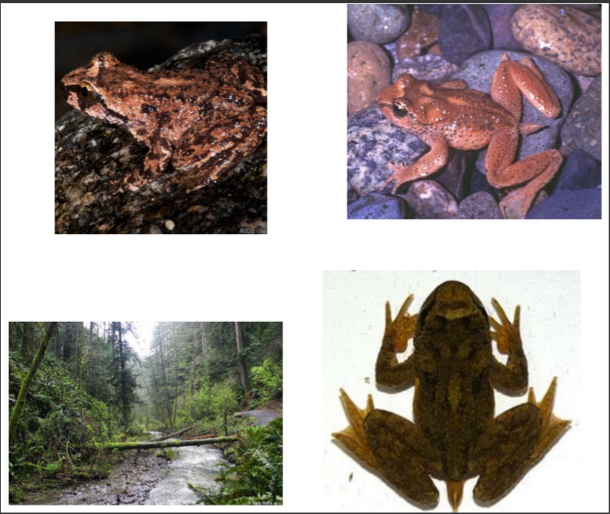

Ascaphidae - Tailed frogs
-Earless frogs
-Males have a tail
-Do not vocalize
-No tympanum
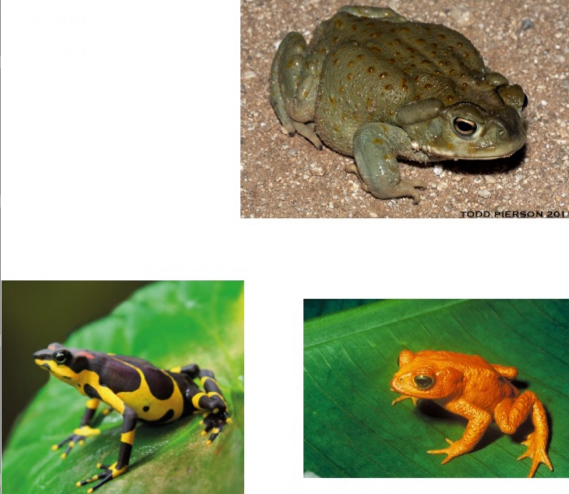

Bufonidae - True toads
CO genus - Anaxyrus
-blunt head, rounded mouth
-paratoid glands
-many species have cranial crests
-most have dry & warty skin
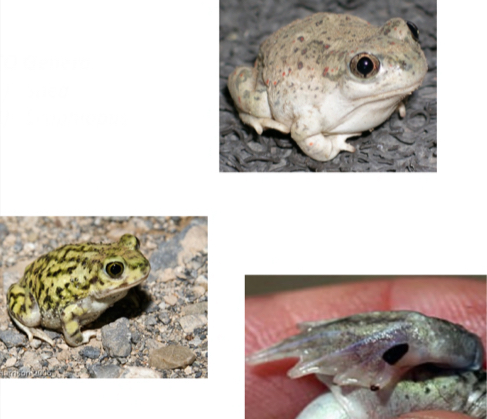

Scaphiopodidae - Spade foot toads
CO Genus - Spea, Scaphiopus
- Keratin-based spade on hindfoot
-Smooth skin
-Some species have a boss
-Hind foot webbing
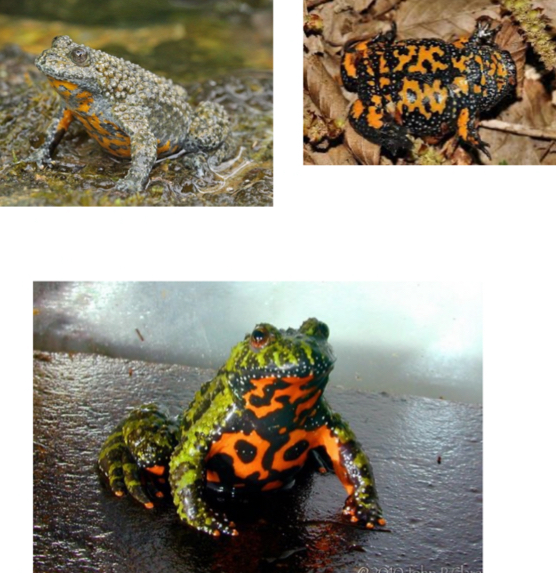

Bominatoridae - Fire-bellied toads
-Blunt head, rounded mouth
-Aposematic coloration
-One species is completely lungless - only lungless frog
-Rough skin
-No tympanum
Frogs
Class Amphibia
Order Anura
Salamanders
Class Amphibia
Order Caudata
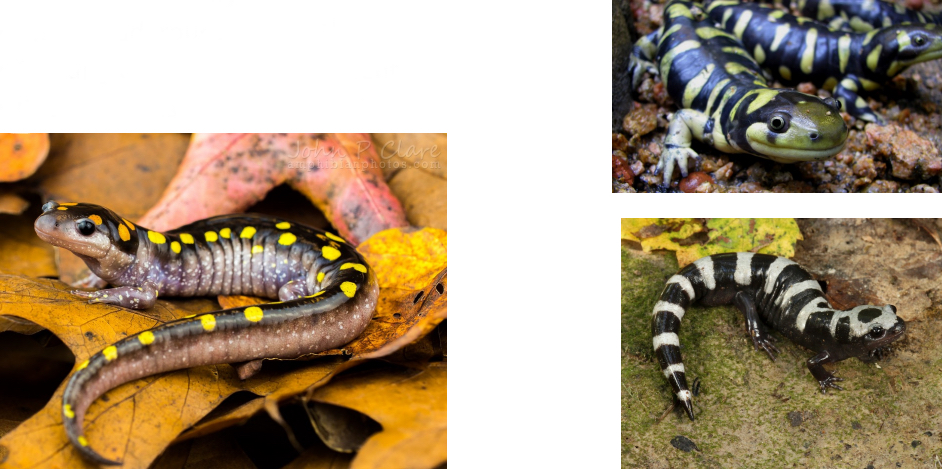

Ambystomatidae
CO Genera - Ambystoma
Biphasic, some paedomorphic
Key traits for family
- Blunt head, rounded mouth
- Costal grooves – very prominent
- Rounded tails

Dicamptodontidae
Biphasic, some paedomorphic
Key traits for family
- Large head, triangular snout
- Huge body size
- Costal grooves – not prominent
- Keeled tail
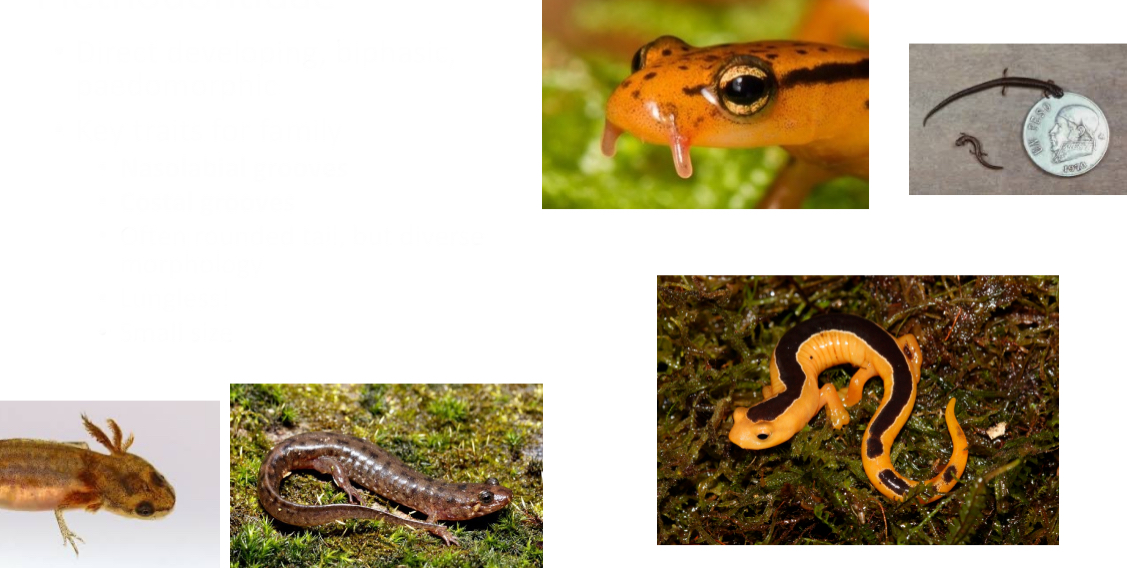

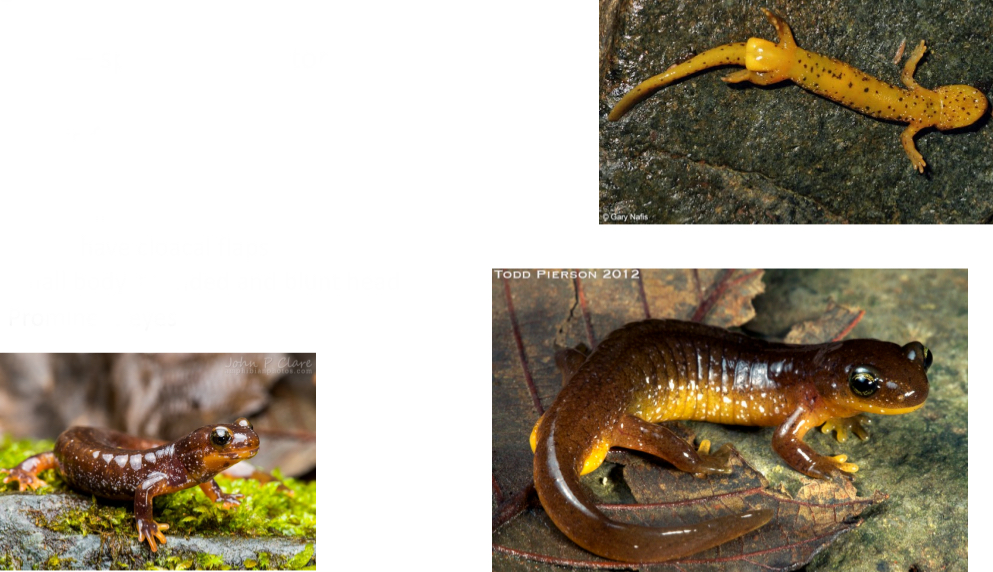
Plethodontidae
Direct developing, biphasic, paedomorphic
Key traits for family
- Nasolabial grooves
- Costal grooves
- Often rounded tail, but diverse morphology
- Lungless!
- Small size
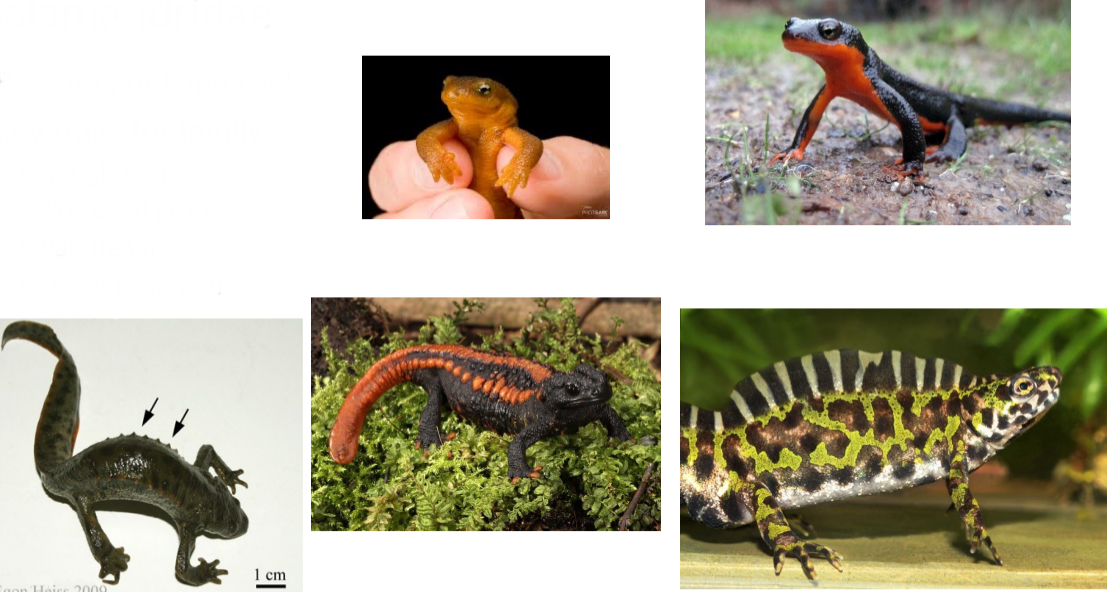

Salamandridae
Biphasic, or triphasic!
Key traits for family
- Rough skin
- No costal grooves
- Paddle tail
- Danger-mander

Rhyacotritonidae
Biphasic – specialized for torrent streams
Key traits for family
- Costal grooves
- Short tail
- Males have cloacal flaps
- Small body, rounded and blunt head
- Prominent eyes

Hynobiidae
Biphasic, some paedomorphs
Key traits for family
- Costal grooves
- Rounded or slightly keeled tail
- Some are lungless!
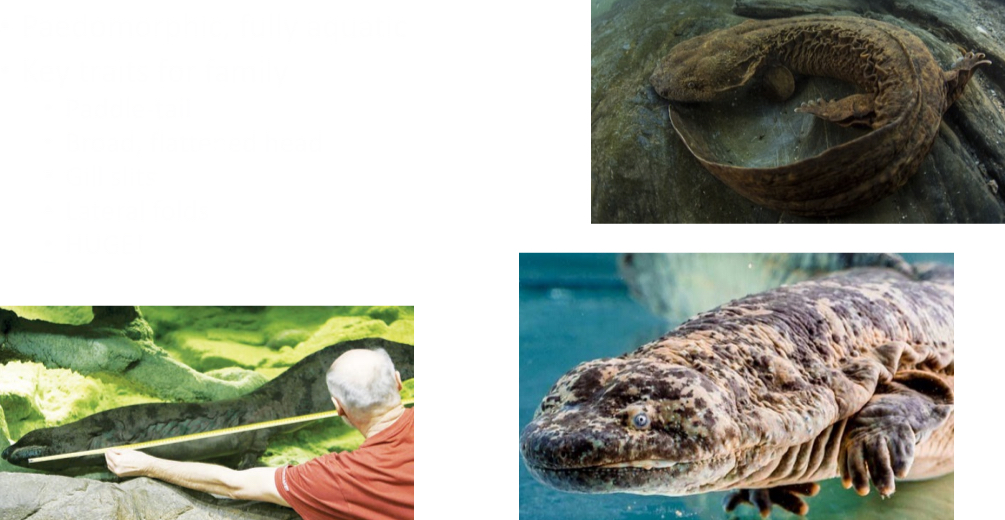

Cryptobranchidae
Paedomorphic, fully aquatic
Key traits for family
- Paddle-tail
- Broad, flattened head
- Gill slits
- Lateral folds
- HUGE!
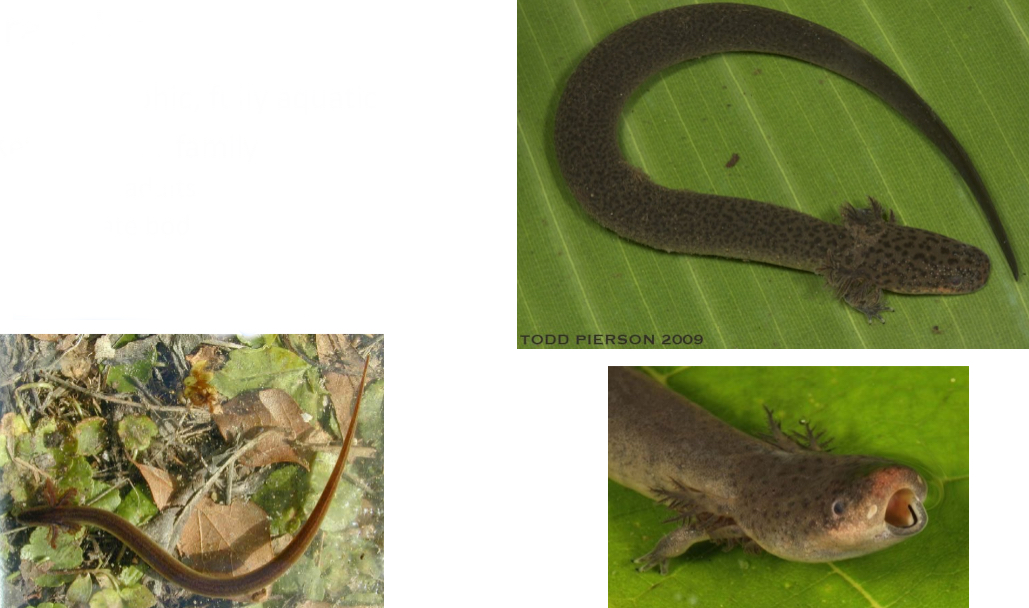

Sirenidae
Paedomorphic, fully aquatic
Key traits for family
- Gills as adults
- Elongate body
- Only has forelimbs = 2 limbs
- Reduced limb size
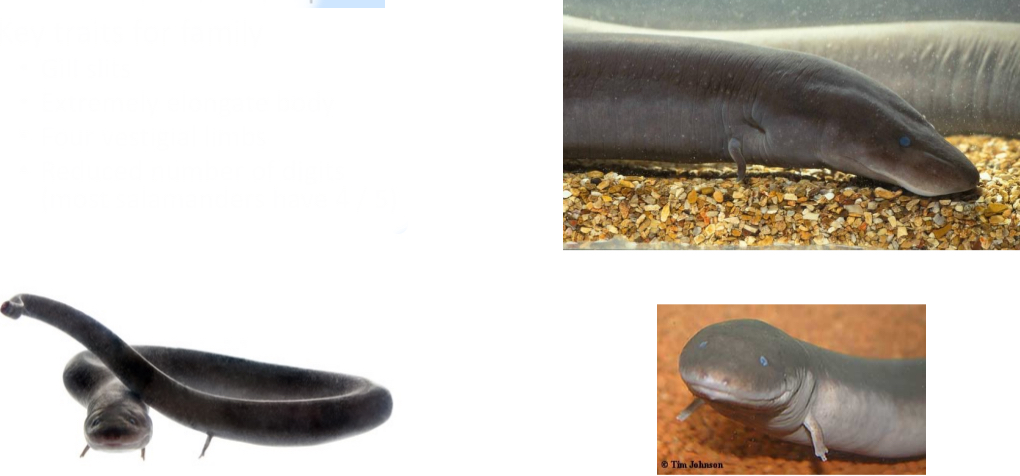

Amphiumidae
Paedomorphic, fully aquatic
Key traits for family
- Gill slits
- Extremely elongate body
- Four vestigial limbs
- Reduced number of digits (most salamanders have 4 / 5)
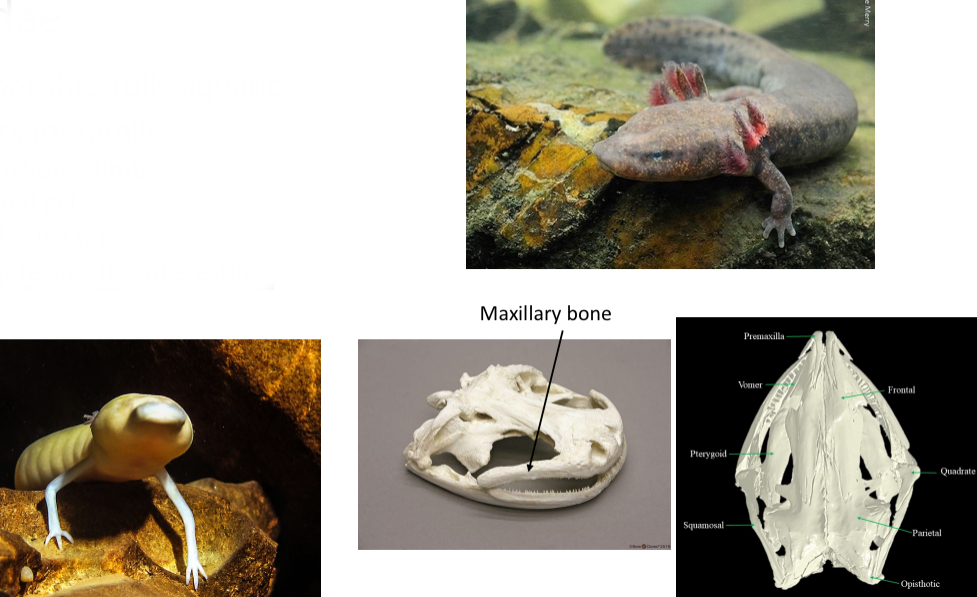

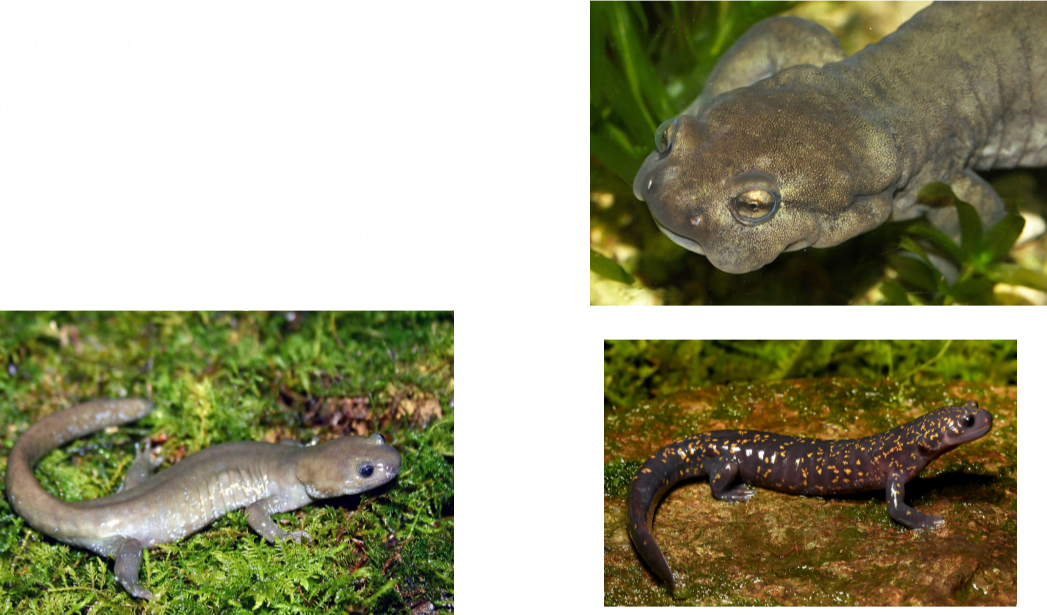
Proteidae
Paedomorphic, fully aquatic
Key traits for family
- Proportional limbs
- External gills
- Paddle-like tail
- Elongate snout - interesting trait
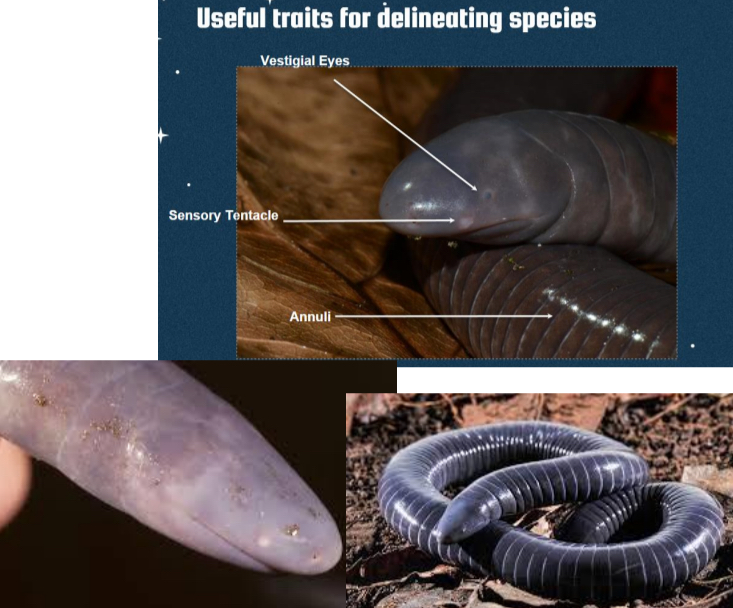

Gymnophiona
- Limbless
- Presence of sensory tentacles
- Annuli
- Eye morphology; vestigial eyes
- Presence/absence of tail
Lizards
Class Reptilia
Order Squamata

CO Families
Teiidae –Whiptails (Aspidoscelis)
Phrynosomatidae – Horned lizards, fence lizards,earless lizards,etc.
Scincidae – Skinks (Plestiodon)
Crotaphytidae – Collard lizards
Family Phrynosomatidae
CO Genera - Holbrookia, Phrynosoma, Sceloporus, Uta, Urosaurus
Morphological diverse family!
Key traits for family
- Labial scales
- Eyelids
- Distinct head

Genus: Phrynosoma
CO species (3): P. hernandesi, P. cornutum, P.modestum
Key traits
- Robust body, short limbs / tail, horned scales
- distinct eye lids
- labial scale
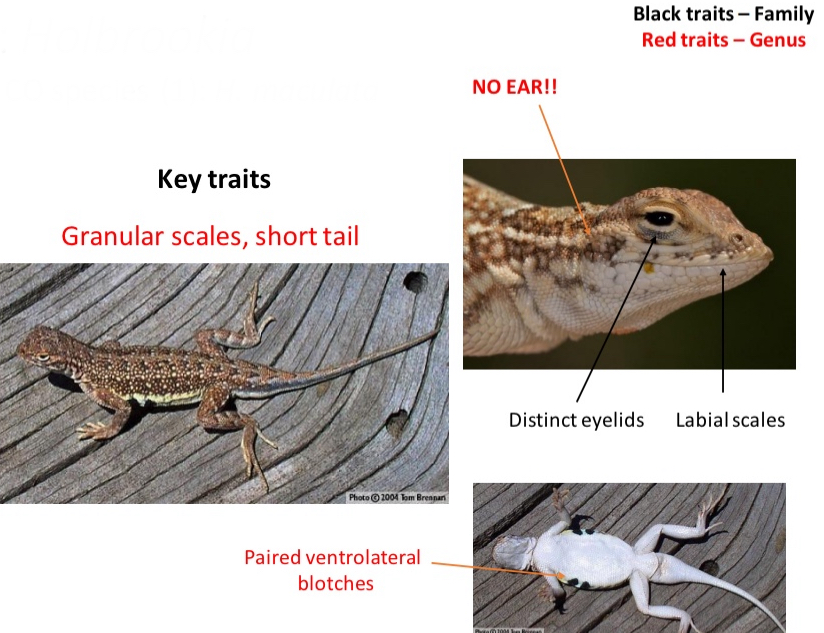
Genus: Holbrookia
CO species (1): H. maculata
Key traits
- Granular scales, short tail, no ears, paired ventrolateral blotches
- distinct eyelids
- labial scales
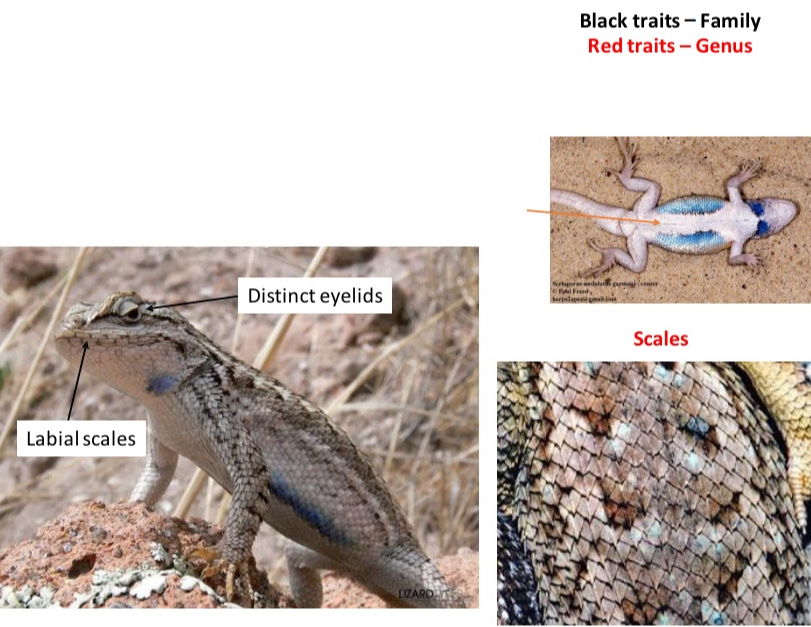
Genus: Sceloporus
CO species (3): S. undulatus, S. magister, S. graciosus
Key traits
- mucronate scales, ventralateral blue blotches
- distinct eyelids
- labial scales
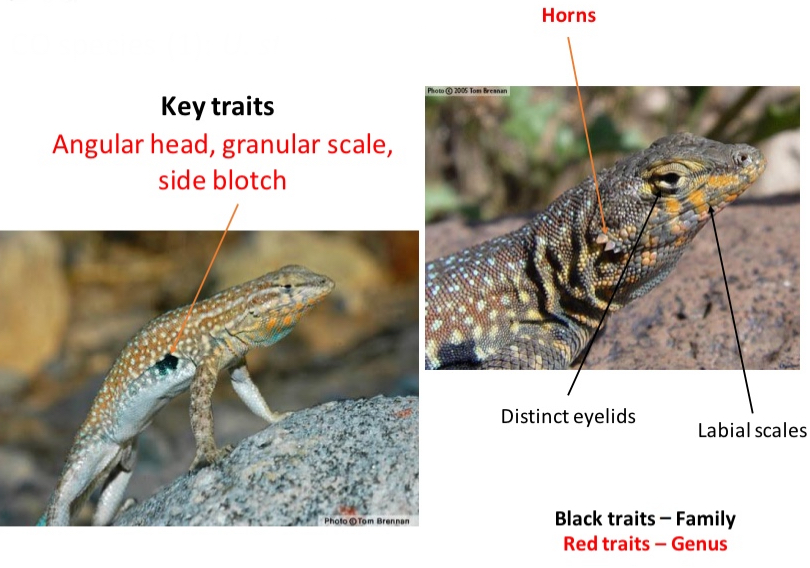
Genus: Uta
CO species (1): U. stansburiana
Key traits
- Angular head, granular scale, side blotch, horn
- distinct eyelids
- labial scales
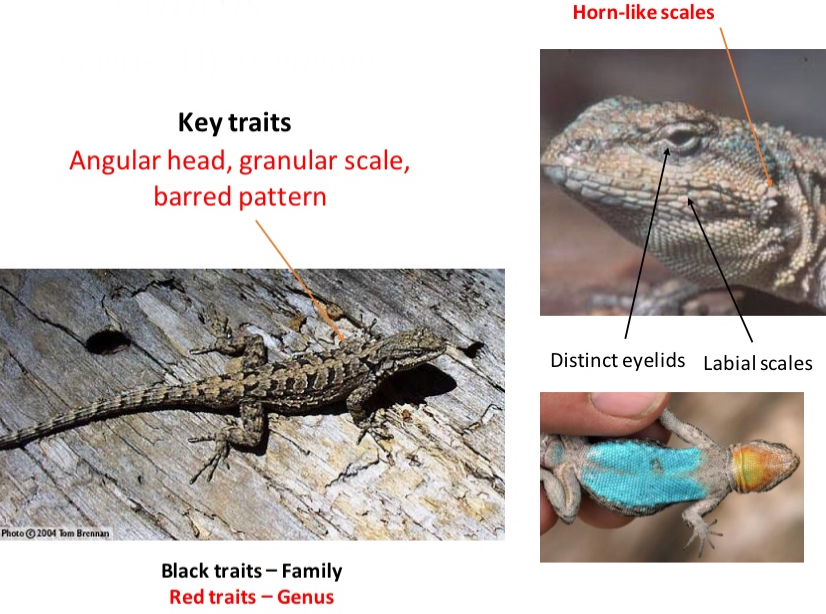
Genus: Urosaurus
CO species (1): U. ornatus
Key traits
- Angular head, granular scale, barred pattern, horn-like scales
- distinct eyelids
- labial scales

Crotaphytidae
Crota – side ; phyte – head
(they have big heads)
CO Genera - Crotaphytus, Gambelia
Key traits for family
- Enlarged musculature on head
- Long tail, muscular legs

Genus: Crotaphytus
CO species (1): C. collaris
Key traits
- collar pattern, robust head, blue/yellow coloration
- Broad head
- long tail
- muscular limbs
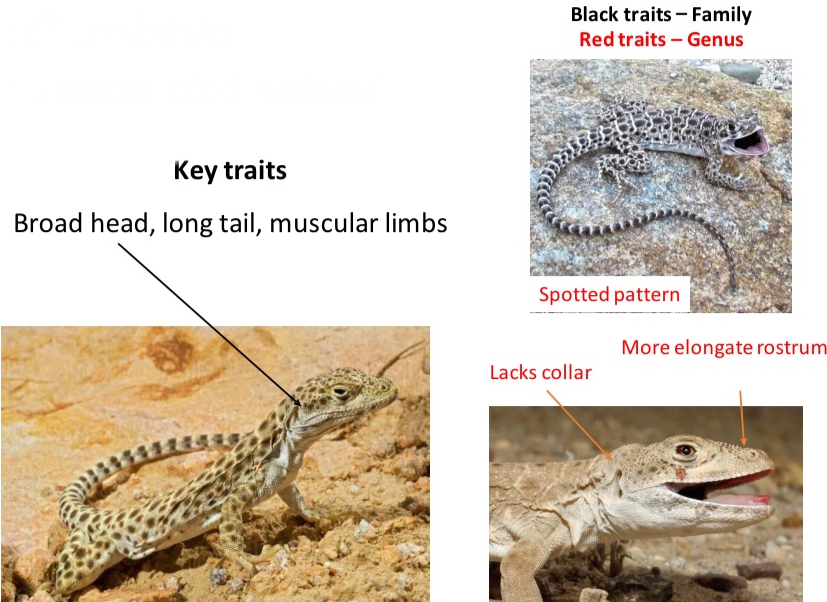
Genus: Gambelia
CO species (1): G. wislizenii
Key traits
- spotted pattern, lacks collar, more elongated rostrum
- Broad head
- long tail
- muscular limbs
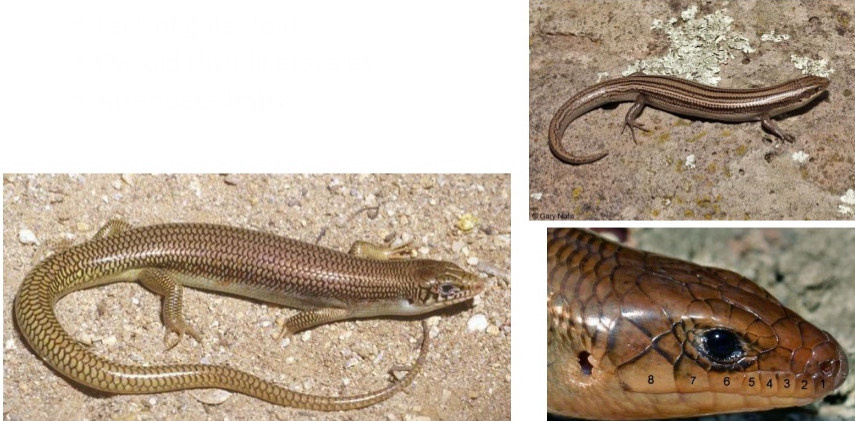

Scincidae
Genus: Plestiodon
CO species(2): P. multivirgatus, P. obsoletus
Key traits for family
- Lack of gular fold
- Cycloid (fish-like)scales
- Attenuate limbs
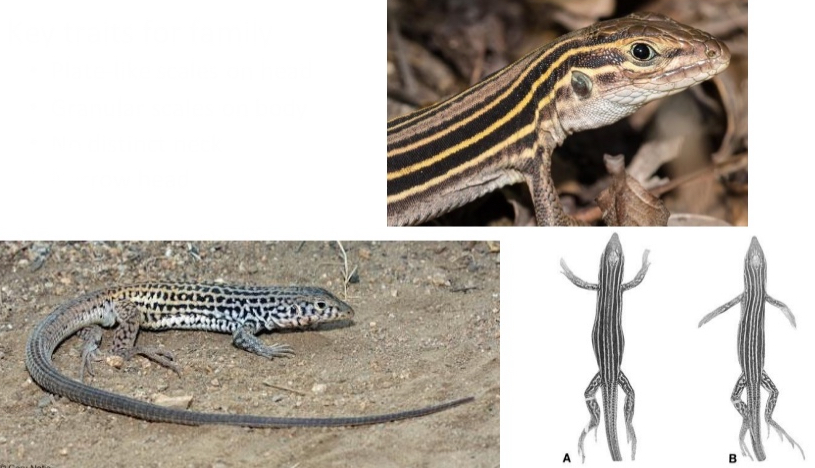

Teiidae
Genus: Aspidoscelis
CO species (5): A. sexlineata,A. tigris, A. tesselata, A. neotesselata, A. velox
Key traits for family
- Plate-like scales on head
- Granular scales on body
- No distinct neck
- Narrow head

Lizard families in the Clade Iguania
Chamaeleonidae – Chameleons‘
Agamidae– Assorted dragons
Iguanidae – Iguanas
Dactyloidae – Anoles
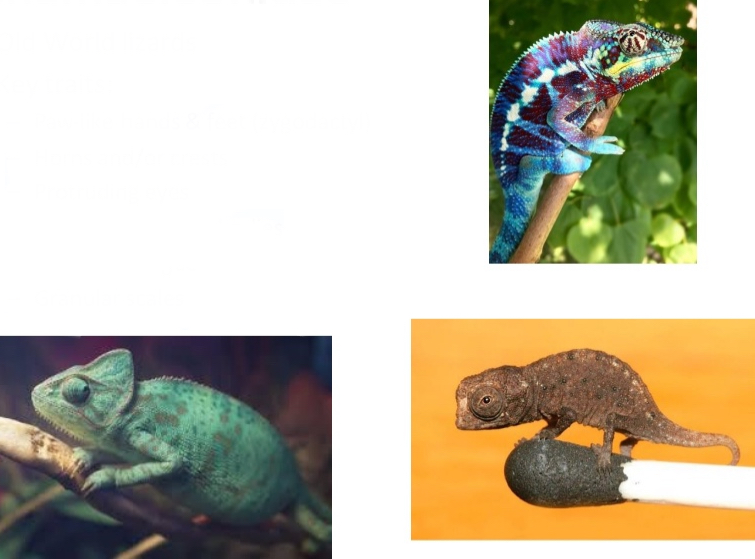

Chamaeleonidae
Old World lizards
Key traits:
– Paw-like hands& feet (zygodactyl)
– Horns and/or crests
– Protruding eyes
– Laterally flattened bodies
– Extensile tongue
– Granularscales
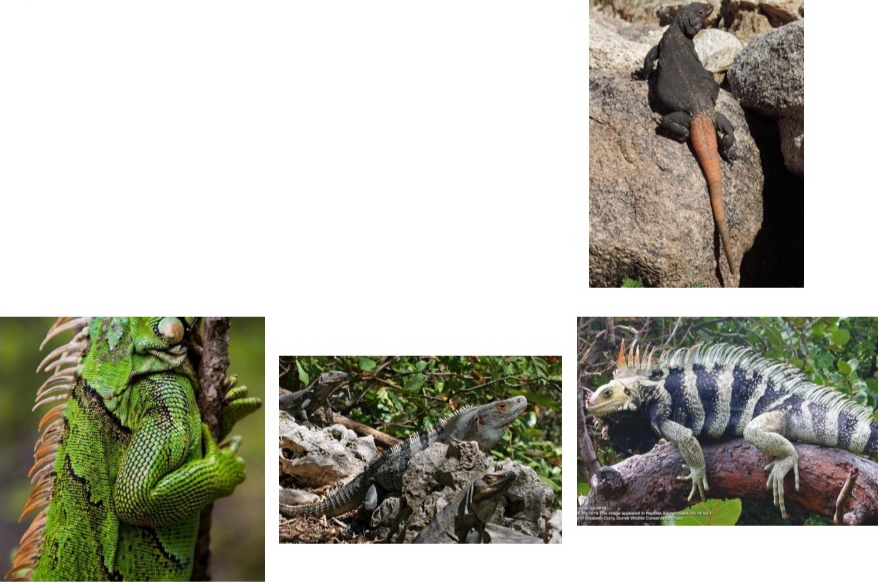

Iguanidae
Key traits:
– Large bodied lizards, often football shaped with robust head
– Can have crest on the back and tail
– Variable scales throughout body
– Can have a dewlap
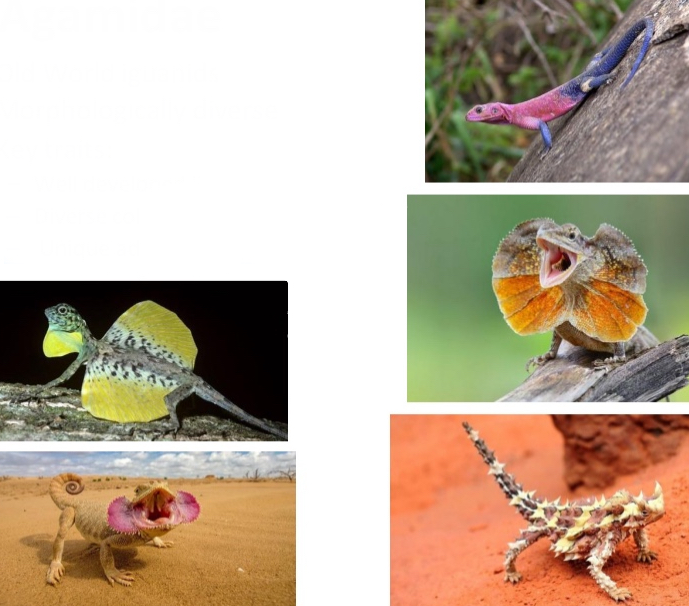

Agamidae
Old World iguanids
Morphologically diverse
Key traits:
– Well developed limbs
– Diverse color patterns
– Unique adaptations(frills, wings)
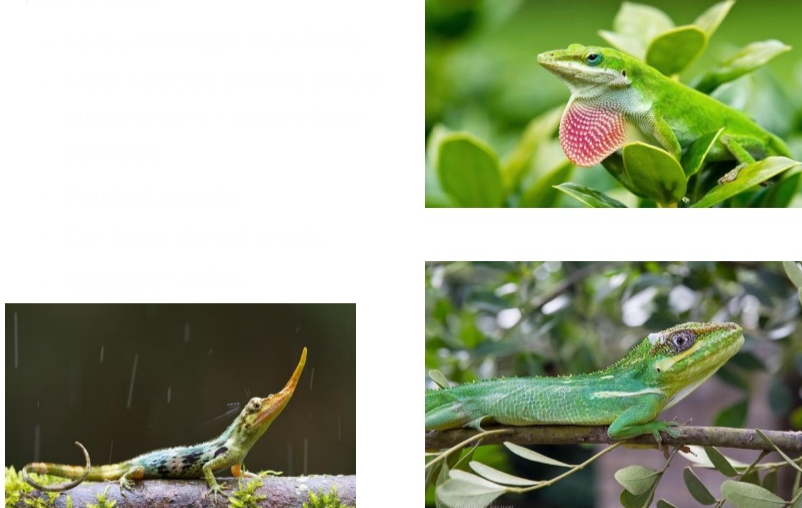

Dactyloidae
Key traits:
– Tails are longer than body
– Most species exhibit sexual dimorphism – males have dewlaps
– Pointed snouts
– Can have dorsal crests
– Granular scales

Lizard families in the Clade Anguimorpha
Varanidae– Monitorlizards, Komodo dragons
Anguidae – Glasslizards, legless lizards
Helodermatidae – Gila monsters
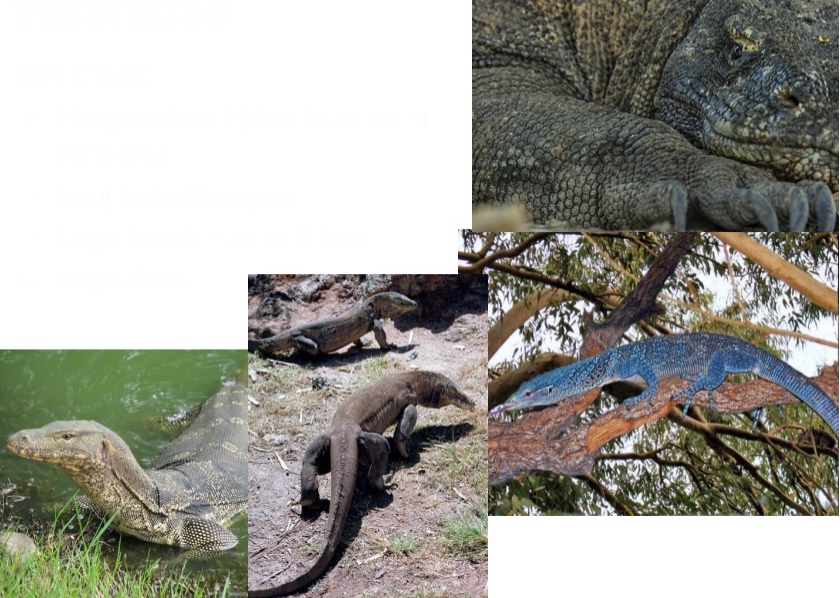

Varanidae
Key traits:
– Elongated neck (due to an extra vertebra)
– Long forked tongues
– Large lizards – up to 9 feet
– Huge claws
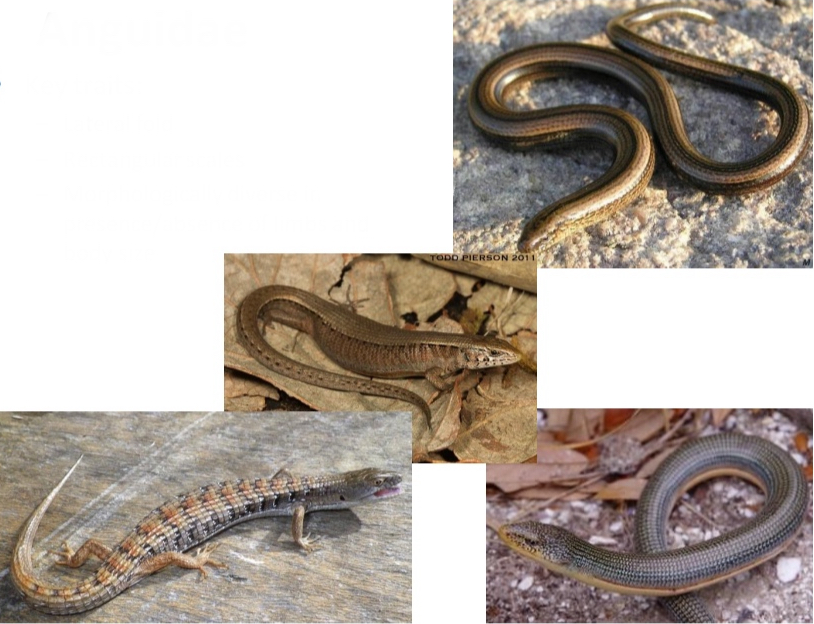

Anguidae
Key traits:
– Lateral fold
– Rectangularscales
– Morphologically diverse in terms of presence/absence of limbs and body size
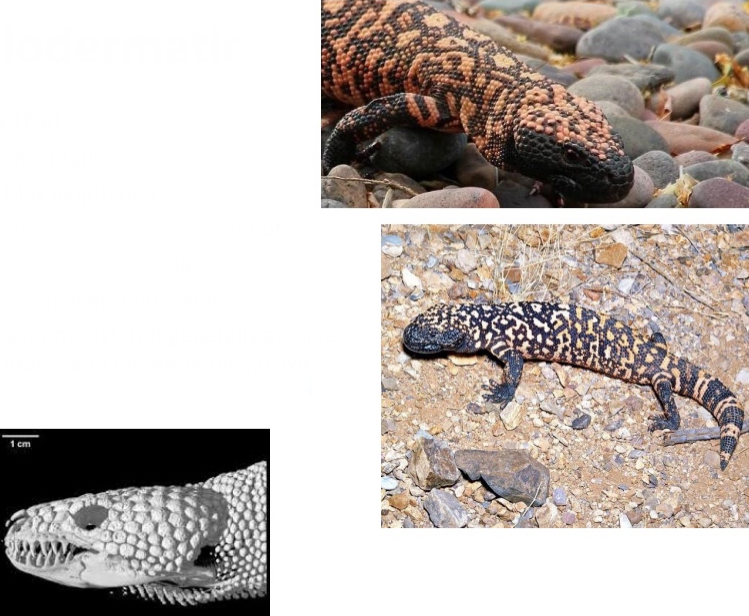

Helodermatidae
Key traits:
– Short tails
– Max length of 3 feet
– Short, broad, rounded snout
– Large granularscales
– Ossified dermalscales
– Venomous!!But generally passive lizards and not excessively toxic
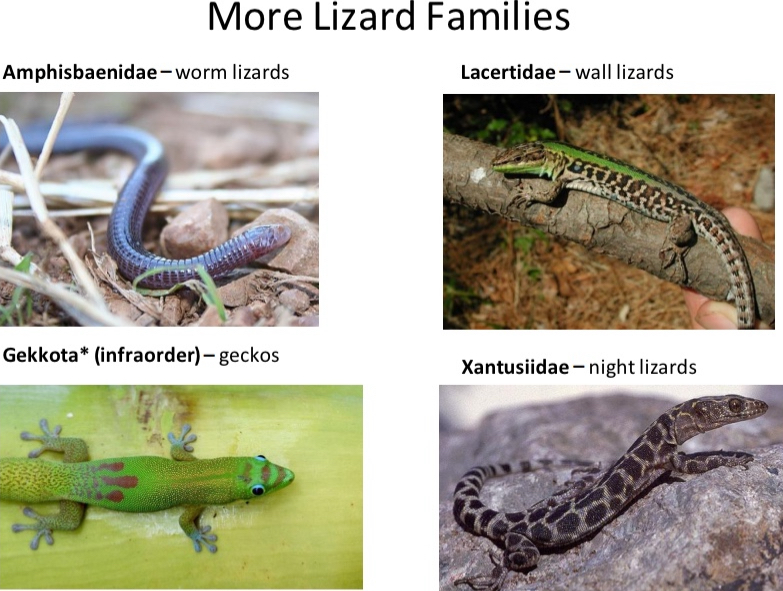

More Lizard Families
Amphisbaenidae – worm lizards
Lacertidae – wall lizards
Gekkota* (infraorder) – geckos
Xantusiidae – night lizards›
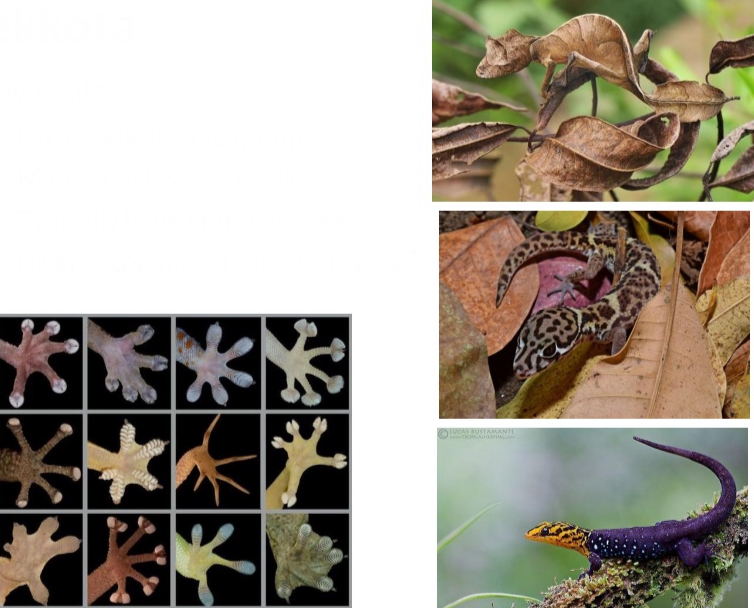

Gekkota
Key traits:
– Extremelydiverse group
– Many specieslack eyelids
– Typically have granular scales
– Diverse toe morphology – toe pads
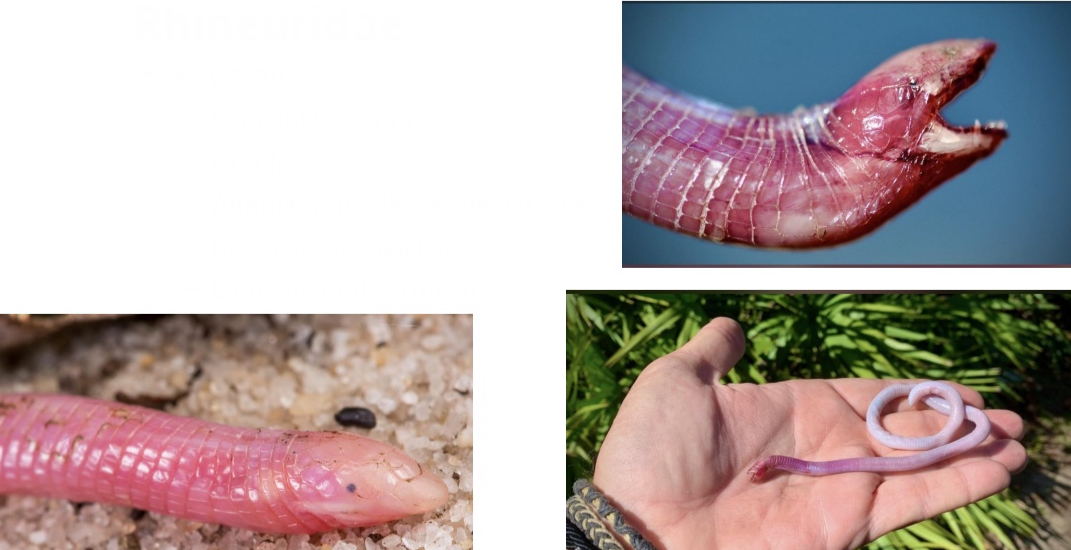

Rhineuridae
Key traits:
– Shovel-like snout
– Limbless
– Annular (ring-like)scale pattern
– Reduced/vestigial eyes
– Elongate body,truncated tail
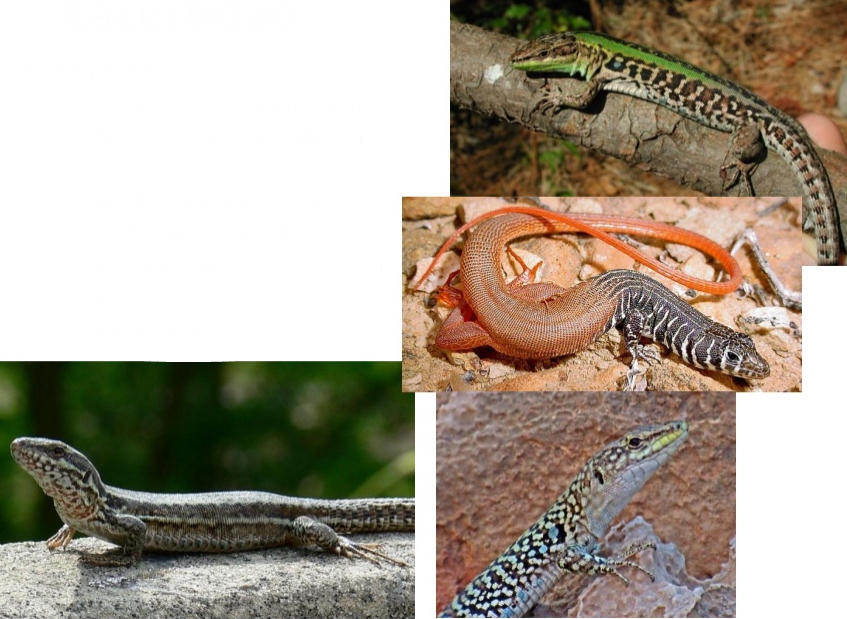

Lacertidae
Key traits:
– Granular scales on most of body, rectangular scales onstomach
– Small lizards with slender bodies and long tails
– Back legs typically largerthan front
– Wide range of colors
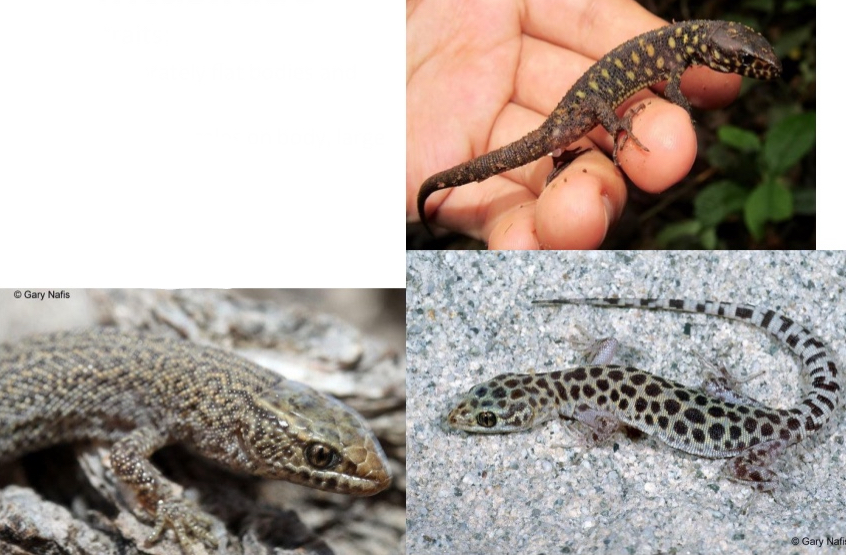

Xantusiidae
Key traits:
– Moderately flat bodies and heads
– Granularscales on body, large plates on head
– No eyelids
– Elliptical pupils
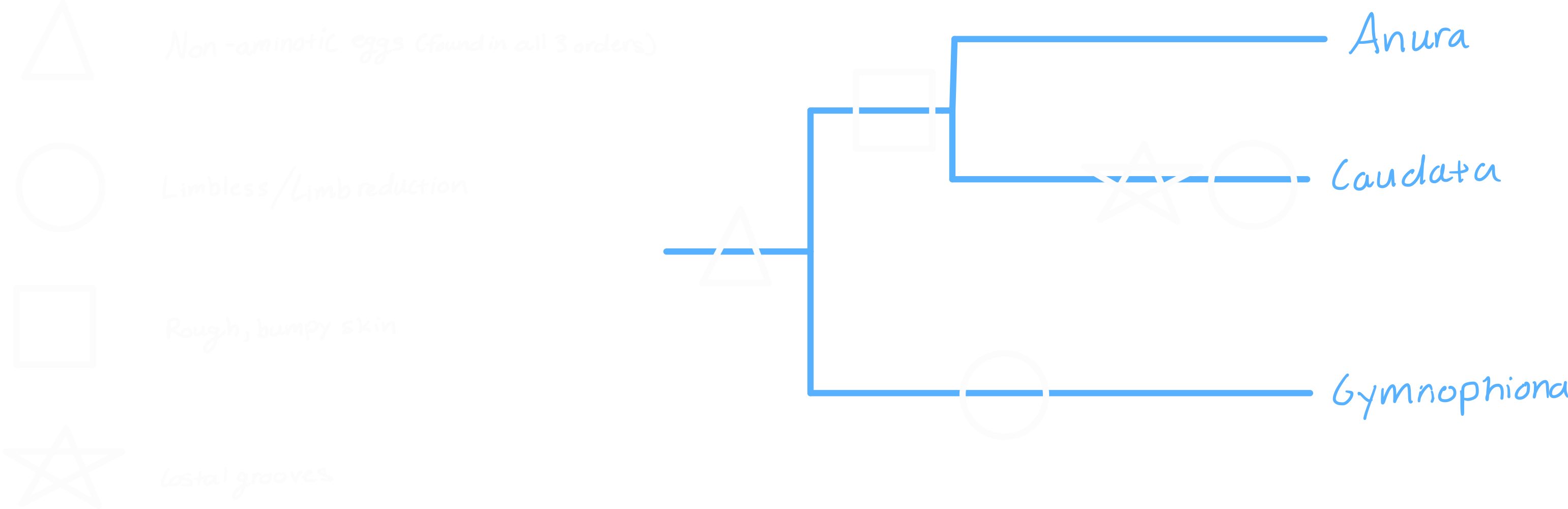
Amphibian evolution
Snakes
Class Reptilia
Order Squamata
Turtles
Class Reptilia
Order Testudines
Salamander Common Traits
Costal Grooves
- Located on the sides of the salamander body
- Look like rolls, bumps, or ribs poking out under the skin
- Evenly spaced bumps with a crease in between each segment
Tail Shape (2 types)
Rounded
- All or most of the tail is circular or tubelike in shape
- Would appear as a circle if a cross section cut was made
Keeled/Paddle
- All or most of the tail is vertically flattened
- Widest part of the tail is in the middle, becoming thinner at the top and bottom
- Would appear as an oval if a cross section cut was made
Nasolabial Groove
- Located in the space between the nose and mouth
- Grooves, that are channel-like which run from the nose down to the mouth
- One groove under each nostril, making 2 total on the face
Gills
- Located behind the head on either side of the body
- Leafy, frill-like, or branched structures that are in place of lungs
- On the juvenile form of aquatic salamanders
Frog Common Traits
Tympanum
- Located on the sides of the head, behind eyes
- Large round circles that range in color but are usually green or brown
Parotoid Glands
- Located on the sides of the head, behind eyes or behind tympanum
- Large raised bumps that are distinct from warts (if present)
- Can be oval or circular
- Can be the same color or different color that the rest of the skin
Dorsolateral Folds
- Located on the back, slightly to sides of the body
- Two long folds of skin that run in one line from the back of
the head to the end of the back
- Can be the same color or different color that the rest of the
skin
Boss
- Located on top of the head between the eyes
- Hard raised bump, (as if a cartoon was bonked on top of
the head)
- Feels like a round bone under the skin
Snakes Common Traits
Labial Scales
- Located around the mouth on the upper and lower "lips"
- Starts from nose and goes toward the back of the mouth
- Upper scales are large and distinctly shaped
- May have dark markings (bars) running vertically between each scale
Scale Types
Smooth
- Cover the whole body of the snake
- Smooth and soft to the touch
- Often diamond shaped and appear to not be overlapping
Keeled
- Cover the dorsum and sides of the body
- Rough to the touch
- A small raised line runs down the middle of each scale
- Individual scales often pointed at the tips
- May appear to be overlapping a little
Anal Scale (2 types)
Single
- Located on the ventrum or belly
- Separates the body from the tail
- Last belly scale (long, horizontal smooth scale)
- One single scale
Divided
- Located on the ventrum or belly
- Separates the body from the tail
- Last belly scale (long, horizontal smooth scale)
- Divided diagonally into two scales, one scale overlaps the other
Hemipenes
- Located on the ventrum or belly
- Between the torso and the tail
- 2 white phallic structures with frills at their ends splaying out from the last belly scale
- Often seen on preserved specimens in pairs
Lizards Common Traits
Gular fold
- Located on the ventral side of body
- Between head and torso
- Horizontal fold of skin that defines the neck area
Scale type
Mucronate
- Pointed, sharp
- Often keeled
- Rough to the touch
Cycloid
- Rounded
- Like fish scales
- Smooth to the touch
Granular/beaded
- Small, round
- Like lizard is covered in very small individual beads
- Bumpy but smooth to the touch
Dewlap
- Located on the ventral side of body
- Between head and torso
- Vertical fold of skin that expands perpendicular to the body
- Can expand or fold down (retract)
- Can be the same color as the body or different
Dorsal Crest
- Located on the dorsal side of body
- Can start on head and continue down body, sometimes to tail or...
- Can start behind head and continue down the body, sometimes to tail
- Can be covered in scales that cover the body or be uniquely spikey scales
- Can be the same color as the body or different
Turtle Common Traits
Carapace
- Located on/is the dorsum
- Often hard and slightly rounded structure with unique patterns
- Can have smooth or spiked edges
- Attached to the rest of the turtle
- Spine is fused to underside
Plastron
- Located on/is the ventrum
- Often hard
- Can have unique coloration or patterns
- Often large and covering most of ventrum
- Attached to the rest of the turtle
Scutes
- Located on dorsum (on top of carapace)
- Not all carapaces have scutes!
- Smooth, hard/durable scale-like structures
- Can have unique patterns or colors
Tubercules
- Located on neck, sometimes under chin
- Small protrusions
- Can be tentacle-like or spikey
- Often the same color as turtle skin