IB Chemistry HL Topic 10 & 20
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
homologous series
- successive members of a homologous series differ by a -CH2 group
- members of HS can be represented by same general formula
- members of homologous show a gradation in their physical properties
- members of a series have similar chemical properties
functional group
small group of atoms attached to a carbon atom in a molecule, giving characteristic properties to the compound
chemical properties
illustrated by sections that follow on different homologous series
physical properties
result of changes that occur in the strength of Van der Waals' forces w/ increasing molar mass and in some cases a change in molecular polarity
condensed structural formula
bonds are omitted, side chains put in brackets and repeated identical groups collected together
molecular formula
gives actual number of each type of atom in molecule
empirical formula
simplest whole number ratio
isomer
different compounds that have the same molecular formula
structural isomer
atoms joined in different order so that they have different structural formulae
stereo isomer
order the atoms are joined together is the same, but the molecules have a different arrangement of atoms in space and hence different 3D shapes
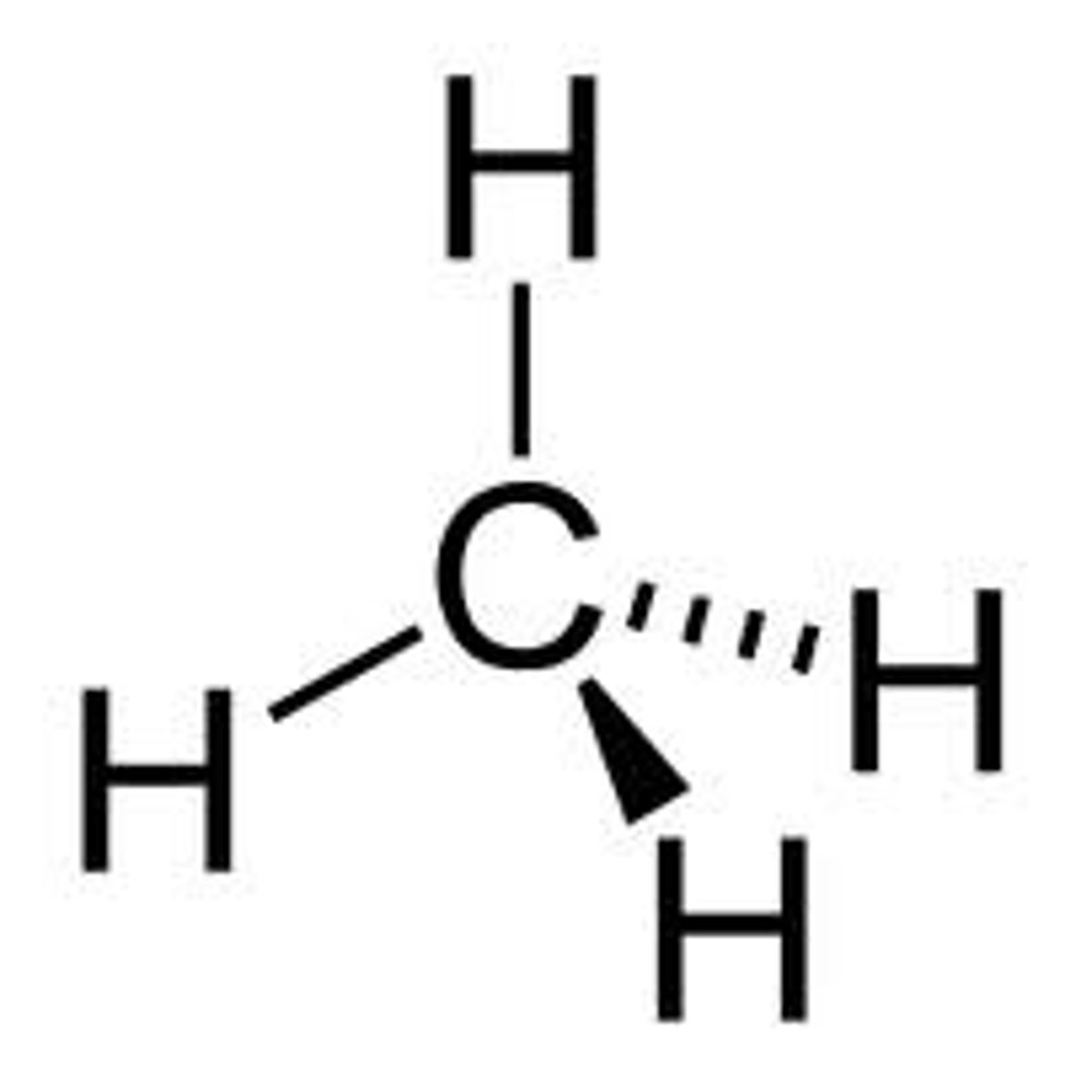
alkane
IPUAC name: -ane
- low chemical reactivity
- substitution: halogenation
alkene
IUPAC name: -ene
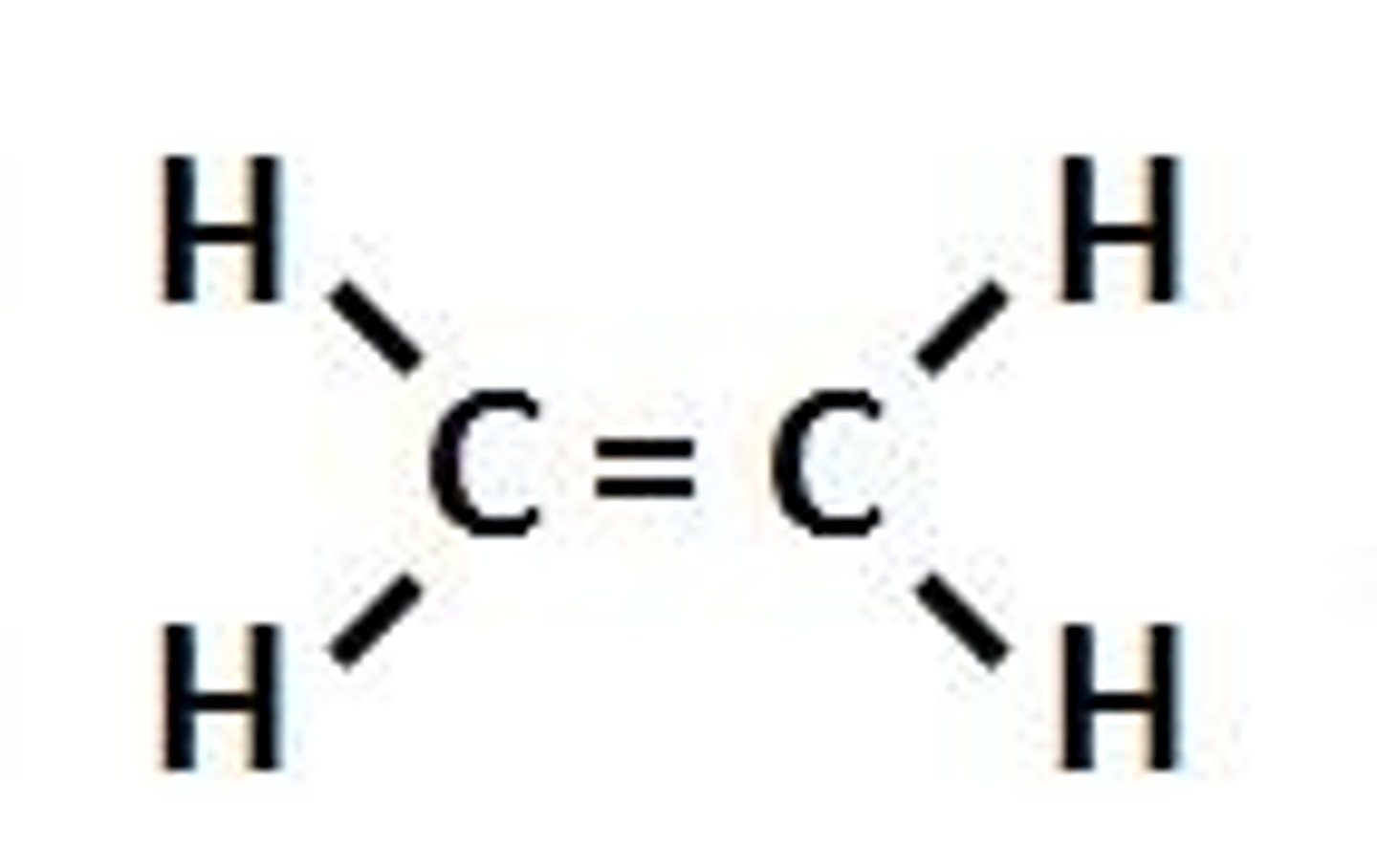
alcohol
IUPAC name: -anol

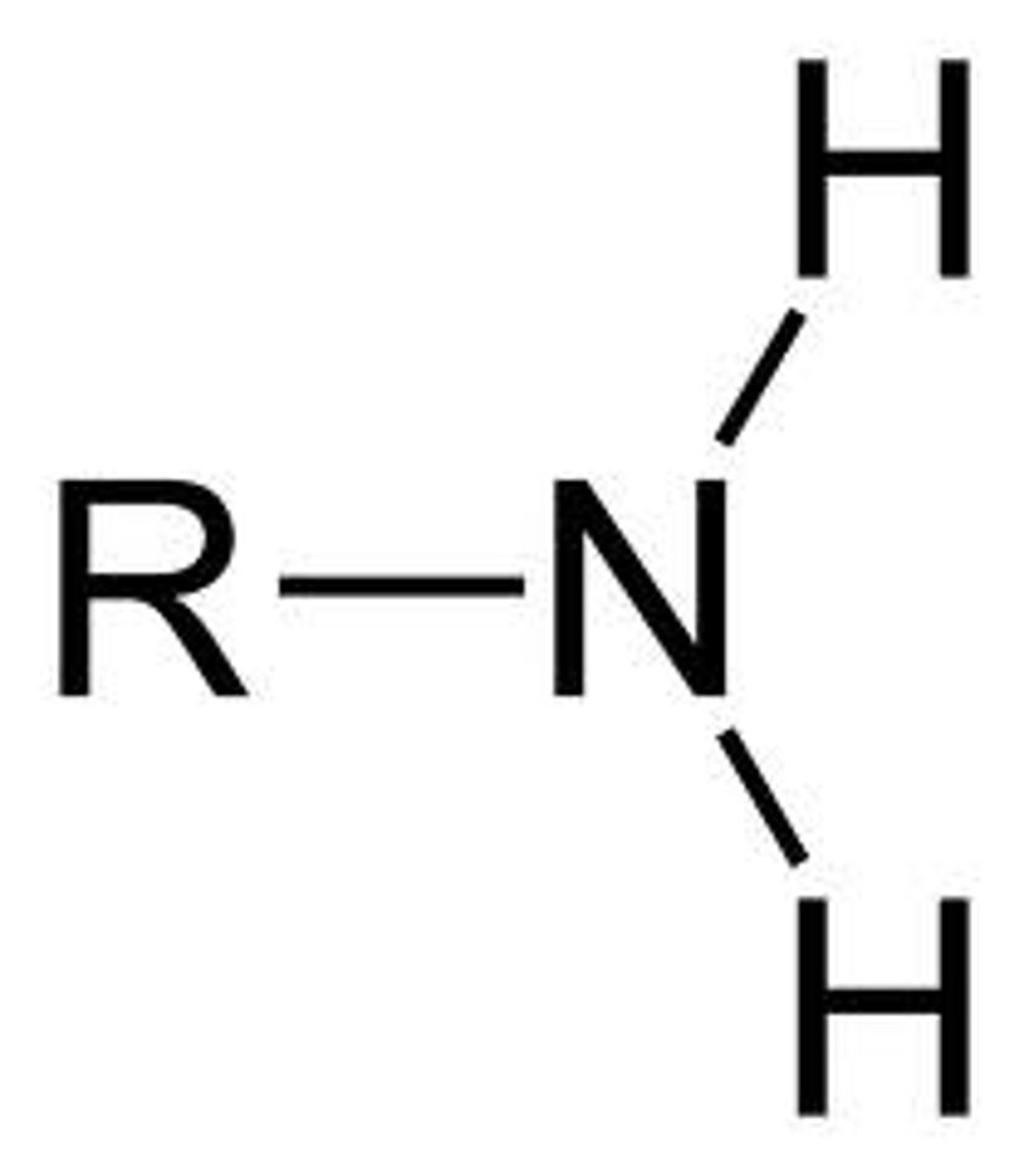
amine
IUPAC name: -anamine
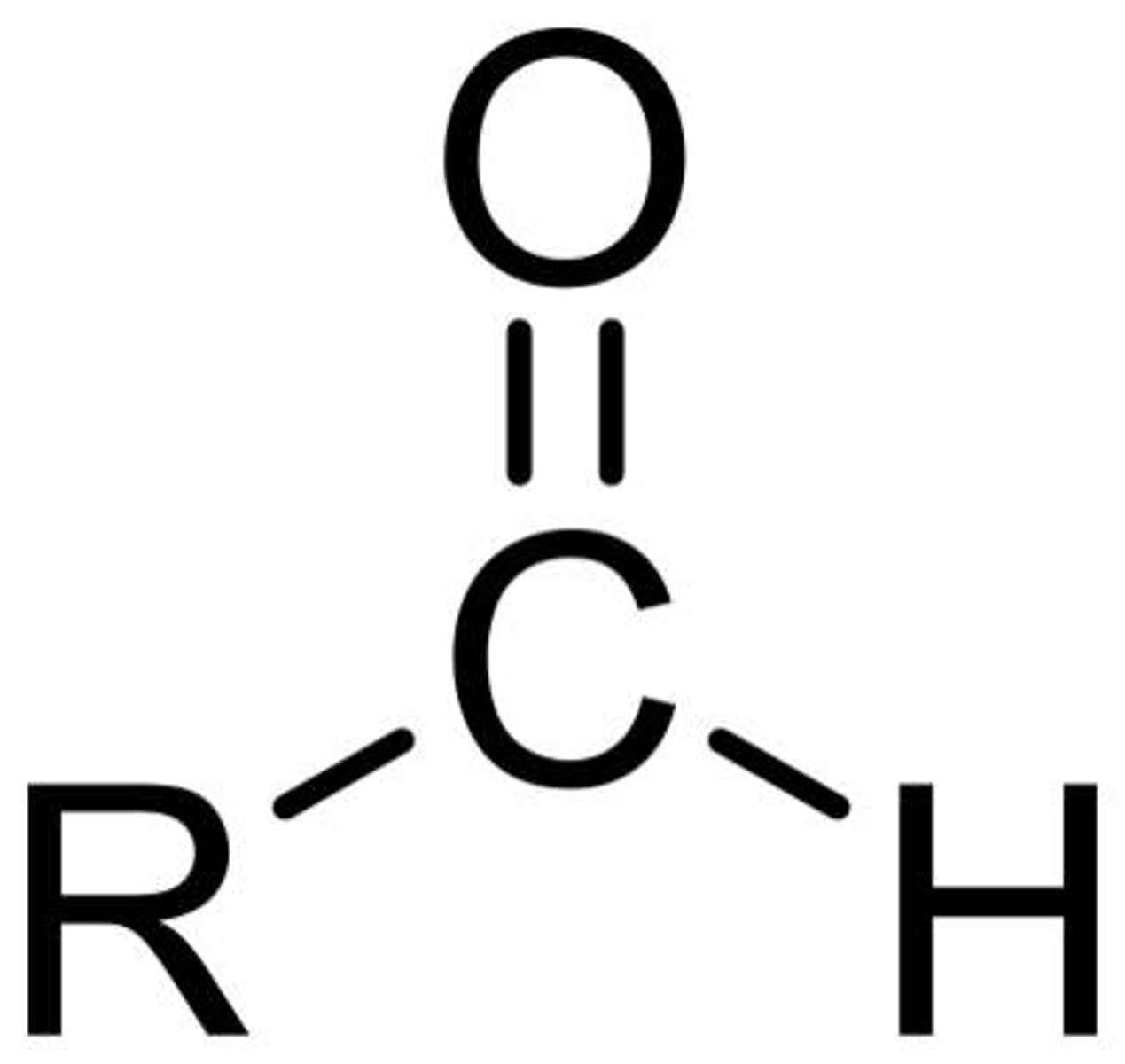
aldehyde
IUPAC name: -anal
ketone
IUPAC name: -anone
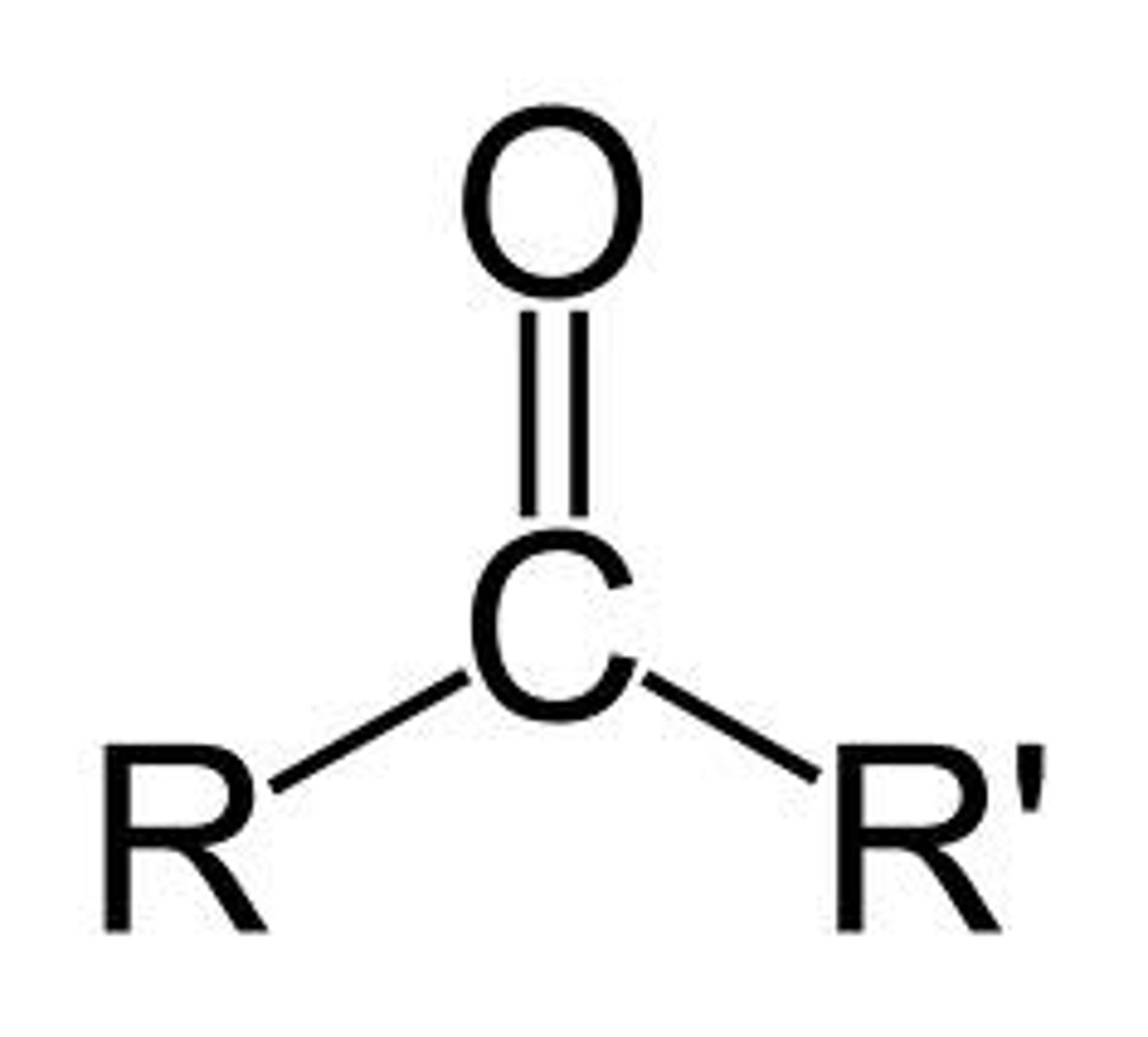
carboxylic acid
IUPAC name: -anoic acid
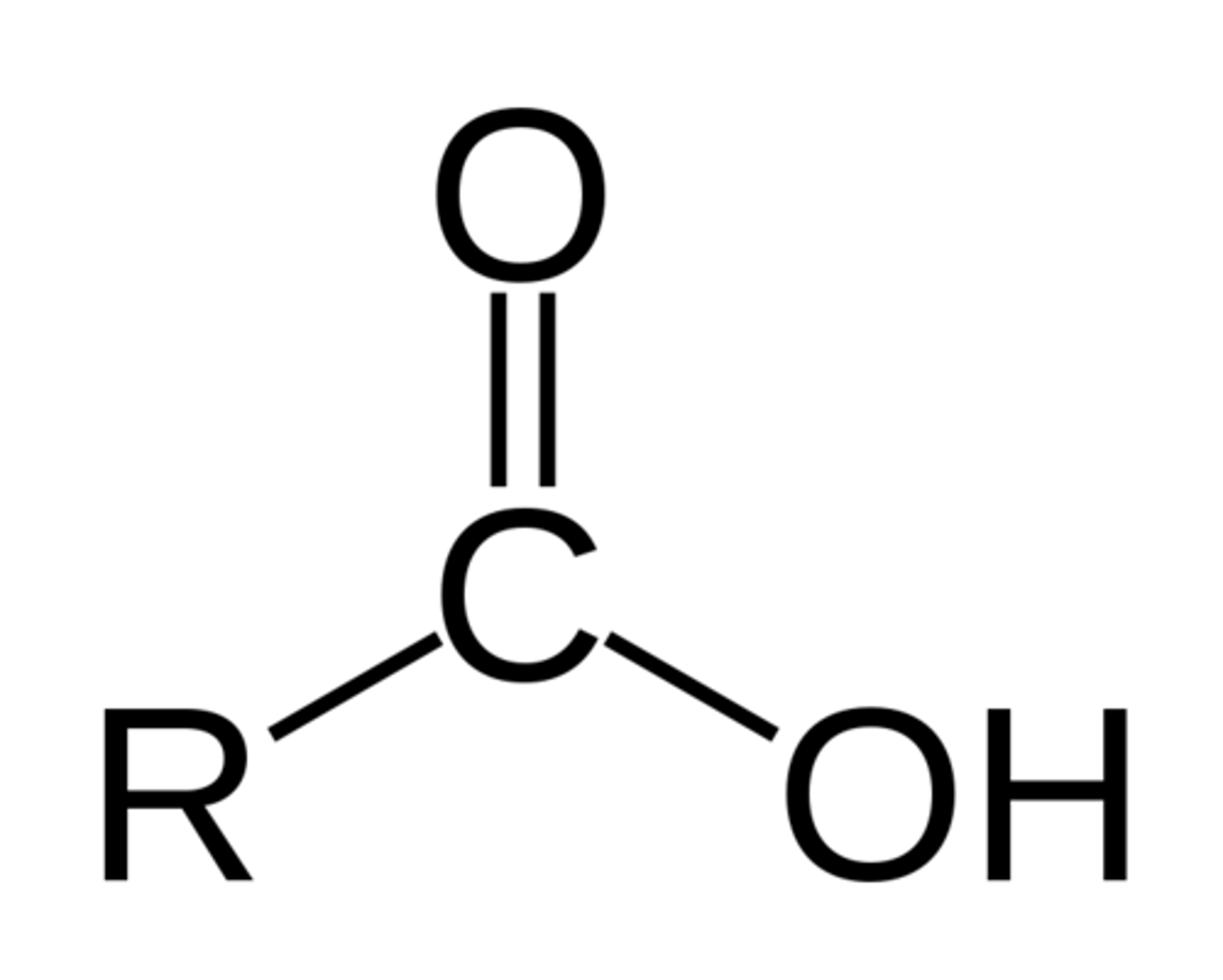
amide
IUPAC name: -anamide
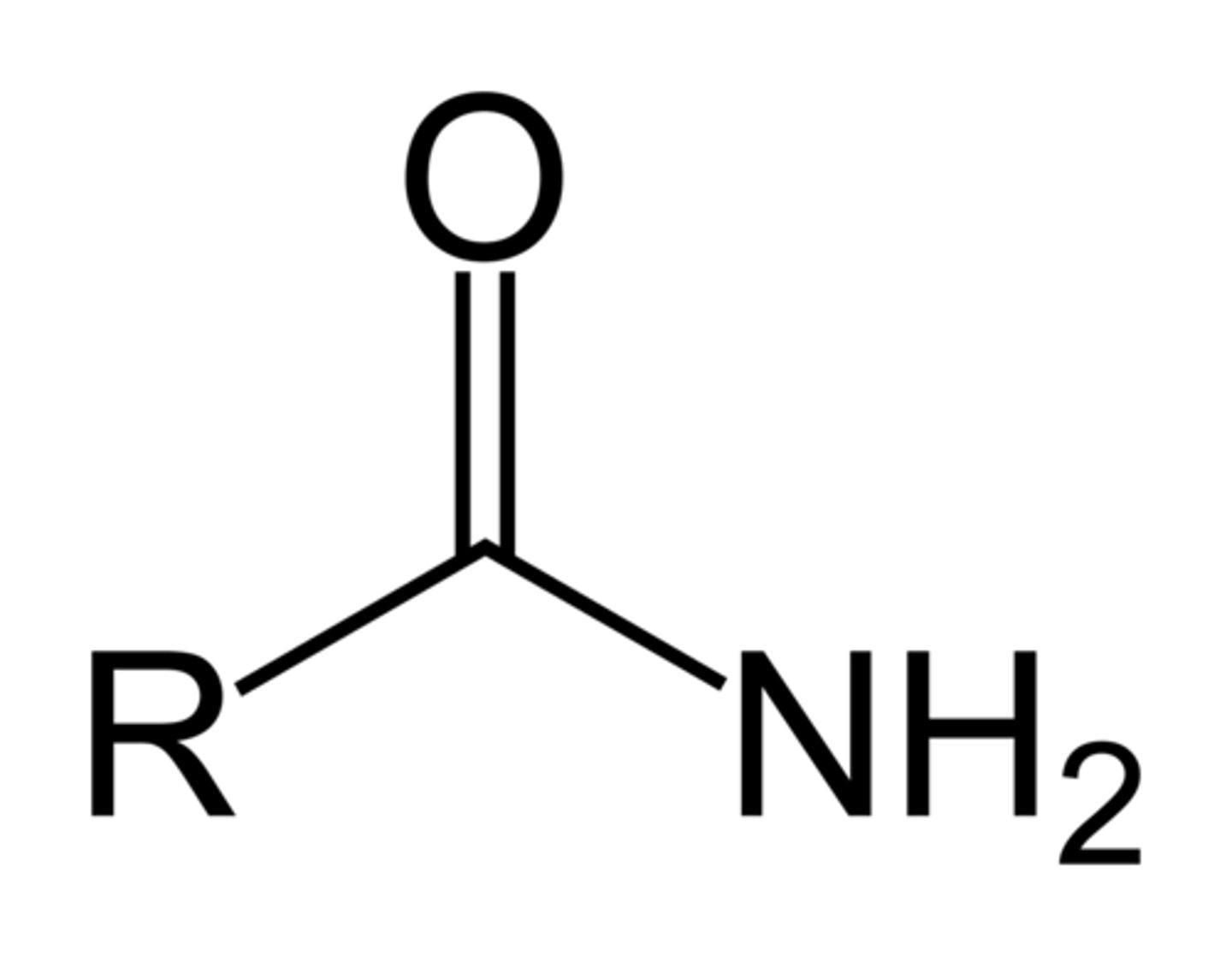
ester
IUPAC name: -anoate
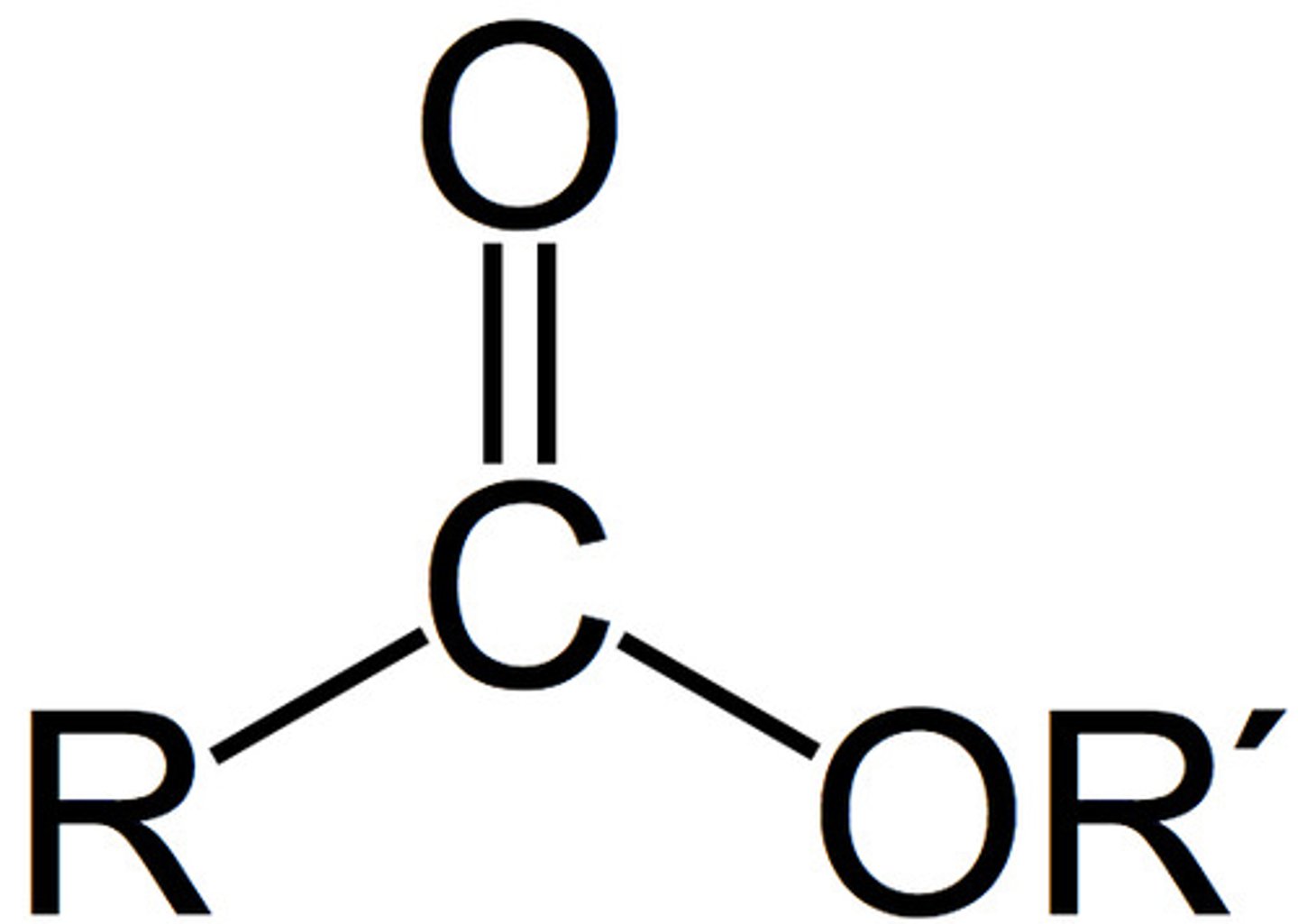
nitrile
IUPAC name: -anenitrile

saturated reactant
compounds which only contain single bonds
unsaturated reactant
compounds which contain double or triple bonds
electrophile
- electron-deficient species which is attracted to parts of molecules which are electron rich
- positive ions or have partial positive charge
nucleophile
- electron-rich species which is attracted to parts of molecules which are electron deficient
- nucleophilies have a lone pair of electrons and may also have a negative charge
combustion reaction
Complete combustion: C8H18 + O2 --> CO2 + H2O
Incomplete combustion: C8H18 + O2 --> CO + H2O + C + CO2
- these products w/ other minor products of hydrocarbon combustion and residue of lead compounds, are major sources of air pollution
addition reaction
- occurs when 2 reactants combine to form a single product
- characteristic of unsaturated compounds
- (i.e. C2H4 + Br2 --> C2H4Br2)
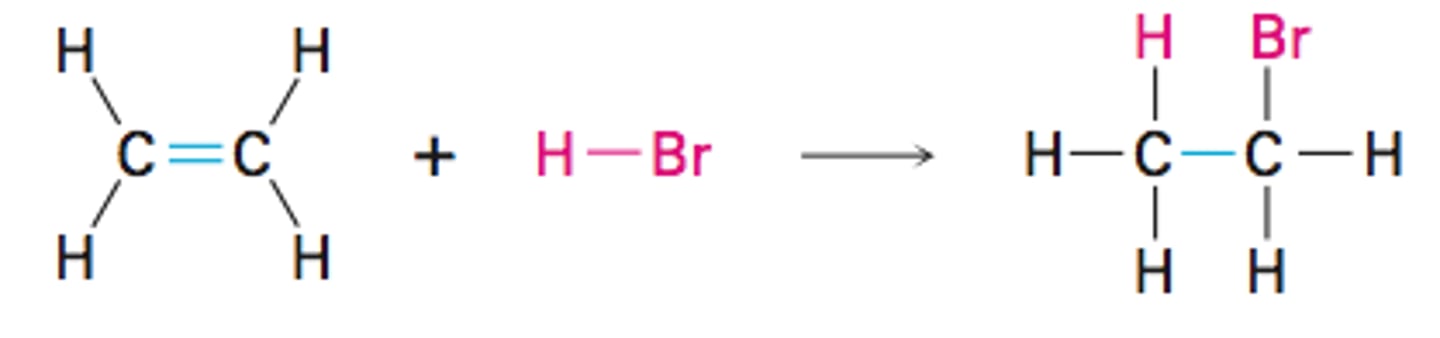
halogenation reaction
- occurs when one atom or group of atoms in a compound is replaced by a different atom or group
- characteristic of saturated compounds and aromatic compounds
- (i.e. CH4 + Cl2 --> CH3Cl + HCl)
- initiation, propagation, termination
elimination reaction
- occurs when a small molecule is lost from a larger compound
- usually results in the formation of a double or triple bond
- when H2O is the eliminated molecule -- reaction is dehydration
- (i.e. C2H5OH --> C2H4 +H2O)
addition-elimination reaction
- occurs when two reactants join together and in the process a small molecule is lost
- reaction occurs b/w a functional group in each reactant
- also known as -- condensation reaction
- (i.e. RNH2 + R'COOH --> R'COHNR + H2O)
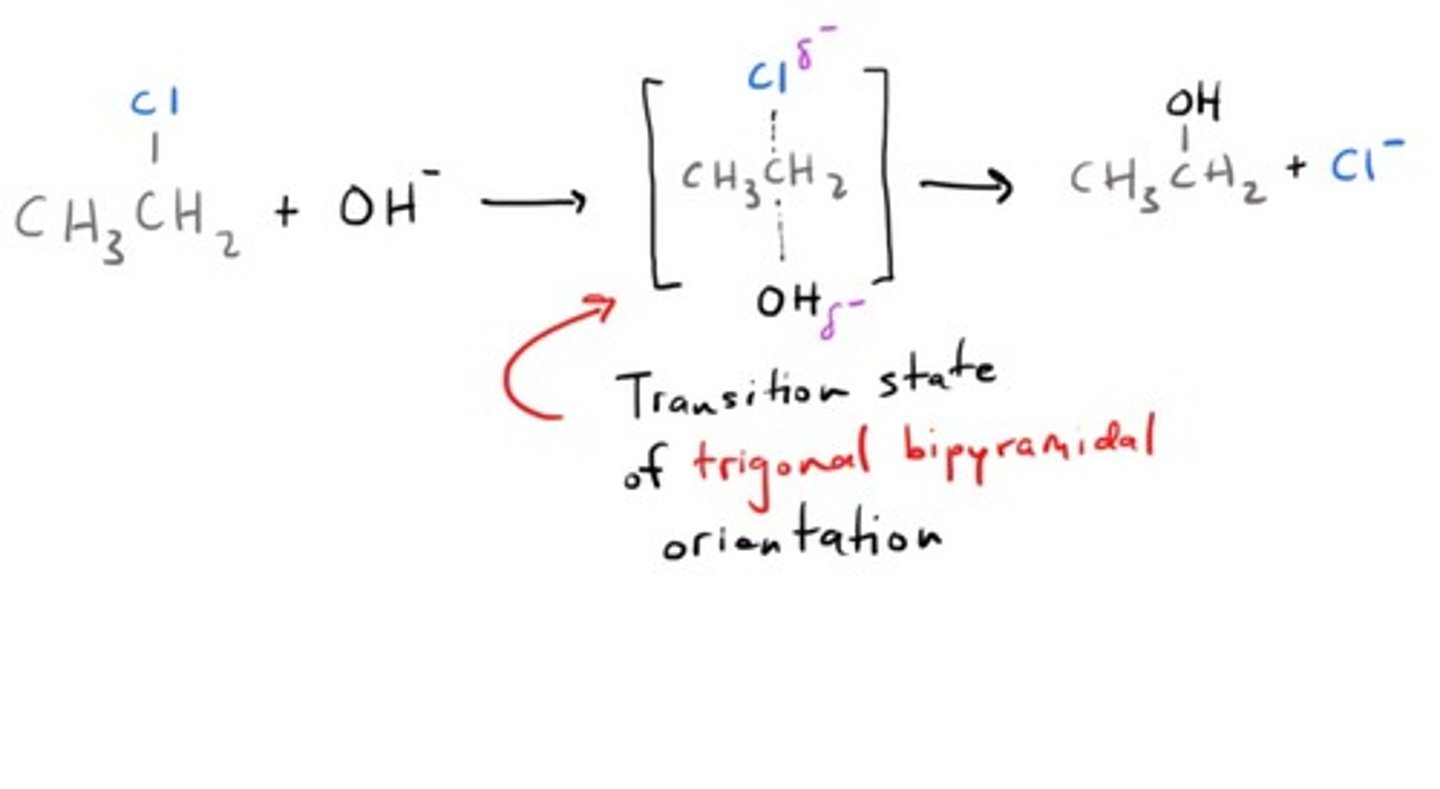
nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2)
- Primary halogenoalkanes: SN2 mechanism
--> one-step mechanism dependent on concentration of both halogenoalkane and hydroxide ion
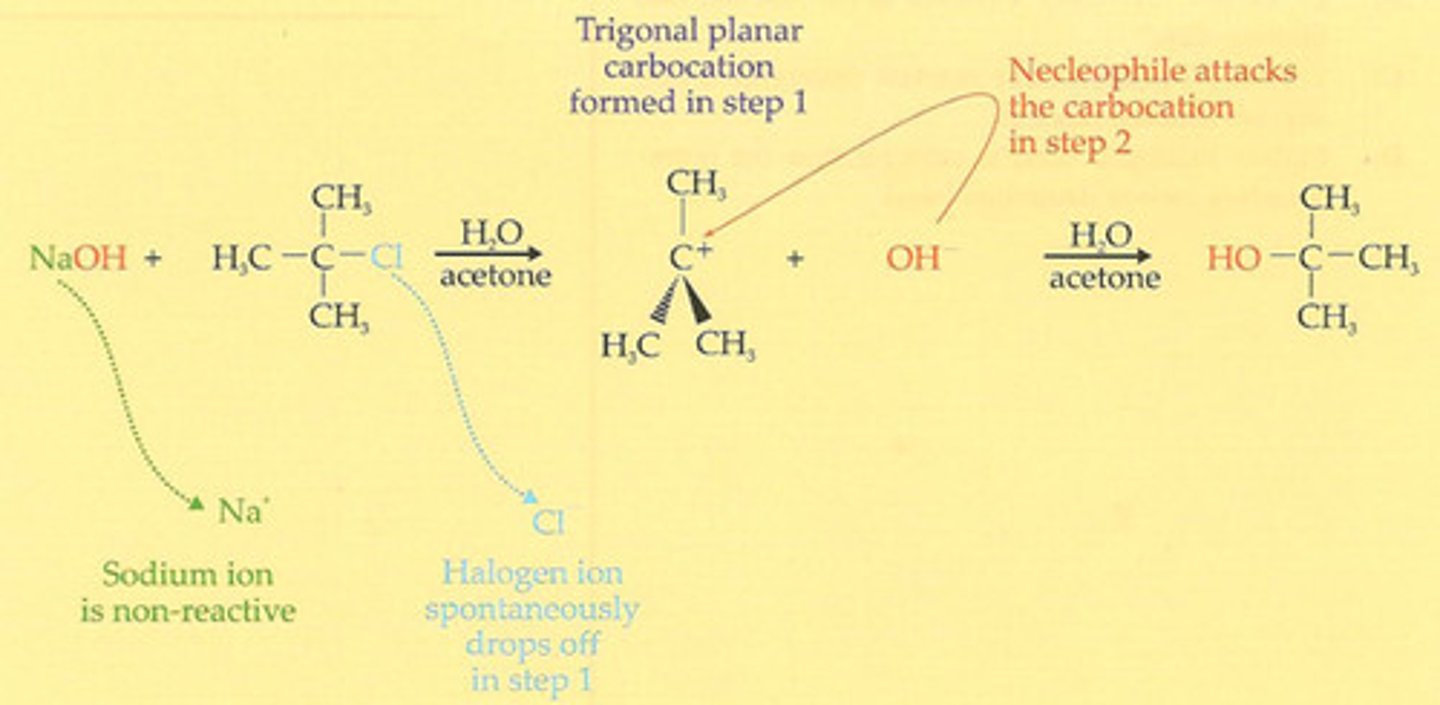
nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN1)
- Tertiary halogenoalkanes: SN1 mechanism
--> two-step mechanism
--> 1st step: halogenoalkane ionizing by breaking its carbon-halogen bond heterolytically
--> 2nd step: carbocation intermediate is attacked by nucleophilie to form new bond
homolytic fission
when covalent bond breaks by splitting the shared pair of electrons b/w two products
- produces two free radical each w/ unpaired electron
heterolytic fission
- when a covalent bond breaks with both the shared electrons going to one of the products
- produces two oppositely charged ions