biology double science edexcel igsces units 1,2 and parts of 3 an 5
What is MRS C GREN?
The 8 characteristics all living organisms share
What does the M in MRS C GREN stand for?
Movement
What does the R in MRS C GREN stand for?
Respiration
What does the S in MRS C GREN stand for?
Sensitivity
What does the C in MRS C GREN stand for?
Control
What does the G in MRS C GREN stand for?
Growth
What does the R in MRS C GREN stand for?
Reproduction
What does the E in MRS C GREN stand for?
Excretion
What does the N in MRS C GREN stand for?
Nutrition
Give 4 different types of eukaryotic organism
Animal, Plant, Fungi, Protoctist
Give 3 differences between plant and animal cells
Plant cells have a cell wall whereas animal cells do not, Plant cells have a permanent vacuole whereas animal cells do not and Plant cells have chloroplasts and are able to photosynthesise whereas animal cells do not
Describe the structure of fungi
Chitin cell wall, Often multinucleated and they contain a mycelium which is made of hyphae threads
How do fungi feed?
They are saprotrophic so they secrete enzymes that break down their food outside of their cells and then they absorb the nutrients
Are prokaryotic cells multicellular or unicellular?
unicellular
Give 5 features of bacterium cells
Cell membrane, Cell wall, Cytoplasm, Plasmid loops of DNA, No nucleus but large DNA loop instead
What is a pathogen?
A disease-causing microorganism
Give 4 different types of pathogen
Bacteria, fungi, viruses, protoctists
Describe the structure of a virus
Protein husk, Contain nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
Give 3 examples of viruses
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Influenza
Give two different species of bacteria
Lactobacillus bulgaricus which is used in the production of yoghurt. Pneumococcus which is bacterium that causes pneumonia.
Define tissue
A group of cells working together to carry out a specific function
Define organ
A group of tissues working together to carry out a specific function
Define organ system
A group of organs working together to carry out a specific function
How is the labour divided within a cell?
Within a cell, labour is divided between the organelles
Name 5 parts of an animal cell
Nucleus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm
Name 8 parts of a plant cell
Nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, cell membrane, cytoplasm, permanent vacuole, chloroplasts, cell wall
State 2 functions of the nucleus
Controls the cell, Contains genetic material (in the form of chromosomes)
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
It is where most of the cell’s chemical reactions take place.
State the function of mitochondria
They are the site of aerobic respiration
State the function of ribosomes
They are the site of protein synthesis
What is the function of the cell wall and what is it made of?
It provides strength and support. It is made of cellulose
What is the function of the permanent vacuole and what does it contain?
It supports the cell and contains cell sap (a solution of sugars and salts)
What is the function of chloroplasts?
They are the site of photosynthesis
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Controls what enters and leaves the cell, Separates the cell from its environment
What chemical elements are present in carbohydrates?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What chemical elements are present in lipids?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What chemical elements are present in proteins?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur
What are complex carbohydrates like starch and glycogen made up of?
Simple sugars
What are proteins made up of?
Amino acids
What two molecules are lipids made up of?
Glycerol and fatty acid tails
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts that increase the rate of metabolic reactions
State 4 factors that affect enzyme function
Temperature, pH, Substrate concentration, Enzyme concentration
Describe the effect of temperature on the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction
As the temperature increases, so does the rate of reaction. Once the temperature exceeds the optimum, the enzyme denatures and the rate of reaction decreases
Why does the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction increase when the temperature increases?
As the temperature increases the particles have more kinetic energy. This increases the chance of collisions between molecules being successful and leading to a reaction
If temperature increases above the optimum, how does this affect enzyme function?
The active site will be distorted as the enzyme denatures and so it will no longer fit the substrate
Describe the effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction
The rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction is fastest at the optimum pH. If the pH is too high or low, the enzyme will work less efficiently and the active site may be denatured at extremes of pH
Define diffusion
The net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration down their concentration gradient
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
As the temperature increases, so does the rate of diffusion as the particles have more kinetic energy and move faster
How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion
How does the surface area of the membrane affect the rate of diffusion?
As the surface area increases so does the rate of diffusion as there is more space for the particles to move through.
Define osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a high water potential to a low water potential down their water potential gradient across a partially permeable membrane.
Define active transport
The movement of molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration against their concentration gradient using energy
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process where some organisms are able to turn light energy into chemical energy.
What type of organisms use photosynthesis to make their own food?
Producers
What type of reaction is photosynthesis?
Endothermic
Where does photosynthesis take place?
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
What is the symbol equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Explain the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
As temperature increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis. Once the temperature exceeds the optimum, the rate of photosynthesis decreases as enzymes begin to denature
Explain the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
As the light intensity increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis.
What is the inverse square law?
As the distance from the light source doubles, the light intensity quarters. Light intensity ∝ 1 / distance2
Explain the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis
As the concentration of carbon dioxide increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis.
What is a limiting factor?
A factor that limits the rate of a reaction when there is not enough of it.
Describe the structure of leaf tissue
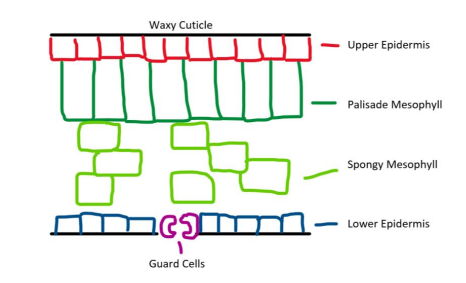
Give 3 ways leaves are adapted for photosynthesis
They are thin which provides a short diffusion distance, The spongy mesophyll layer has lots of air spaces for efficient gas exchange, Palisade mesophyll cells have lots of chloroplasts for photosynthesis
What are mineral ions used for in a plant?
Growth
Give 2 common ions in plants
Magnesium ion (Mg2+), Nitrate ion (NO3-)
What are magnesium ions used for in plants?
chlorophyll
What are nitrate ions used for in organisms?
Amino acids
Why is a balanced diet important?
The body needs different substances in different proportions to function properly, too much or too little of different things can be harmful.
What 7 groups are needed for a balanced diet?
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids (fats), vitamins, minerals, water and dietary fibre.
What is the function of carbohydrates in the diet?
The body’s main source of energy.
What are the functions of proteins in the body?
structural or metabolic roles in the body and are used as hormones, enzymes, antibodies etc
What are the functions of lipids in the body?
Energy storage, Cell membranes, Buoyancy, Insulation
What is vitamin A used for?
Keeping the skin healthy, Improved vision in the dark, Strengthening the immune system
What is vitamin C used for?
Growth and repair
What is vitamin D used for?
The absorption of calcium
What is calcium used for in the body?
Strengthening bones and teeth
What is iron used for in the body?
Haemoglobin to transport oxygen in the blood.
What is water used for in the body?
A reaction medium, Temperature control, Transport
What is dietary fibre used for?
It helps keep everything flowing through the digestive system.
Compare the energy requirements of more and less active people
The more active a person is, the greater their energy requirement
Describe how energy requirements change as we age
Adults generally require more energy than children
What is the alimentary canal?
The complete tube that food passes through as it passes through the body.
What is the difference between the alimentary canal and the digestive system?
The alimentary canal involves the tubes that the food passes through whereas the digestive system also includes digestive glands.
Describe the passage of food through the alimentary canal
Mouth to oesophagus to stomach to small intestine to large intestine to rectum
What is the function of the mouth?
To chew and break down food and To secrete digestive enzymes
What is the oesophagus?
The tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach
What does the stomach do?
A muscular sac containing acid that pummels the food and breaks it down further
What role does the pancreas play in digestion?
The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine
What are the two parts of the small intestine called?
Duodenum and ileum
What is the function of the duodenum?
To receive food directly from the stomach and uses enzymes and chemical digestion to break the food down
What is the function of the ileum?
Most nutrients are absorbed from the food in the ileum into the blood
How is the ileum adapted to absorption?
It’s lined with villi which provide a large surface area for reabsorption
How are villi adapted for absorption?
Thin walls, Large surface area, Good blood supply close to the surface
What is the function of the large intestine (colon)?
Water is reabsorbed into the blood in the large intestine
What is the function of the rectum?
The rectum stores faeces before egestion
How does peristalsis work to push food through the gut?
Muscles contract in a wave like fashion which pushes food along.
What enzymes break starch down to glucose?
Maltase and amylase
What group of enzymes break proteins down into amino acids?
Proteases