final exam health dev
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
1
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by vomiting?
metabolic alkalosis
2
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by myasthenia gravis (weakeness in the upper extremities, including chest muscles)?
respiratory acidosis
3
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by COPD?
respiratory acidosis
4
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by pneumonia?
respiratory acidosis due to excessive mucus that causes a decrease in respirations
5
New cards
What education should be provided an obese client before a surgical procedure?
* healthy diet
* increase activity levels
* increase activity levels
6
New cards
What education should be provided to an individual after a gastrectomy?
* maintain a semi-fowlers position
* report any new or unusual bleeding from surgical site
* do not manipulate NG tube, care for it
* start on clear liquid diet, advance as tolerated
* report any new or unusual bleeding from surgical site
* do not manipulate NG tube, care for it
* start on clear liquid diet, advance as tolerated
7
New cards
What are the s/s of a duodenal ulcer?
Pain 1.5 hours after meals
Pain @ night when food is digesting
Relieved by food consumption
Well-nourished because they are still able to eat foods
Pain @ night when food is digesting
Relieved by food consumption
Well-nourished because they are still able to eat foods
8
New cards
What are the s/s of a gastric ulcer?
Pain 30-60 mins or immediately after eating
Pain during daylight hours (eating hours)
Relieved by exacerbating food (vomittiing)
Malnourished/thin due to not being able to keep food in
Pain during daylight hours (eating hours)
Relieved by exacerbating food (vomittiing)
Malnourished/thin due to not being able to keep food in
9
New cards
What are the s/s of GERD?
* dyspepsia
* jaw, chest, and throat pain
* pyrosis (burning in throat)
* odynophagia (pain by swallowing)
* dental cares due to acid rubbing on teeth
* jaw, chest, and throat pain
* pyrosis (burning in throat)
* odynophagia (pain by swallowing)
* dental cares due to acid rubbing on teeth
10
New cards
What education should be provided to an individual post op gastric bypass?
* educate about s/s of infection & hemorrhage
* strict I&Os
* follow clear liquid diet with 6 small meals a day
* educate about exercise
* strict I&Os
* follow clear liquid diet with 6 small meals a day
* educate about exercise
11
New cards
What complication can be caused by a duodenal ulcer?
* bleeding/hemorrhage
* pernicious anemia
* dumping syndrome
* pyloric obstruction
* pernicious anemia
* dumping syndrome
* pyloric obstruction
12
New cards
What is the method of action for GI medications?
reduce gastric acid
13
New cards
How do we diagnose a gastric ulcer?
esophagogastroduodenscopy (EGD)
14
New cards
What are the common problems associated with chronic gastritis?
* gastric bleeding
* gastric obstruction
* dehydration
* dumping syndrome
* pernicious anemia
* h. pylori
* gastric obstruction
* dehydration
* dumping syndrome
* pernicious anemia
* h. pylori
15
New cards
Describe post-op care for a client after a Billroth II (gastrojejunostomy) procedure?
eat small 6 meals a day
sit upright while eating
increase fluids before or after meals but not during
sit upright while eating
increase fluids before or after meals but not during
16
New cards
___ is the severing of the vagus nerve to reduce gastric acid by diminishing cholinergic stimulation or reduce gastric acid secretion. It is specifically used as a therapeutic procedure in treating gastritis.
vagotomy
17
New cards
What is the treatment plan for a tension headache?
apply heat or ice to forehead
18
New cards
What are some migraine triggers caused by food a patient with a history of migraines need to avoid?
foods high in tyramine such as aged cheese, beer, and chocolate
19
New cards
What education should be provided to an individual prescribed cardidopa- levodopa?
“You should not be concerned if you excrete dark or orange fluids because this is a side effect from the medication.'“
20
New cards
What nursing interventions should be provided for an individual with a hemorrhagic stroke?
* eat small but frequent meals, chew thoroughly
* eat with chin tucked in
* eat in a high-fowlers position
* remove all rugs/wires at home to avoid injury
* eat with chin tucked in
* eat in a high-fowlers position
* remove all rugs/wires at home to avoid injury
21
New cards
What is a TIA?
a neurological deficit that completely resolves in 24 hours that serves as a warning sign before a real stroke
22
New cards
What are the signs and symptoms of a stroke?
numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg (does not have to be bilateral)
sudden confusion or headache
aphasia (cannot understand speech receptive or expressive)
difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of balance
sudden confusion or headache
aphasia (cannot understand speech receptive or expressive)
difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of balance
23
New cards
What education should be provided for an individual with a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis?
Encourage the patient to do moderate exercises
Educate on a healthy diet to patient and caretakers
Manage fatigue by sleeping 8 hours and frequent rest periods
Educate on schedule bathroom times to encourage bowel/bladder program
\
Educate on a healthy diet to patient and caretakers
Manage fatigue by sleeping 8 hours and frequent rest periods
Educate on schedule bathroom times to encourage bowel/bladder program
\
24
New cards
What are the s/s of multiple sclerosis?
* ataxia
* paresthesia
* nystagmus
* Uhtoff’s sign
* paresthesia
* nystagmus
* Uhtoff’s sign
25
New cards
LEFT CVA clinical manifestations:
ataxia
aphasia (expressive, receptive, global)
slow cautious behavior,
right visual deficits and weakness
altered intellectual ability
aphasia (expressive, receptive, global)
slow cautious behavior,
right visual deficits and weakness
altered intellectual ability
26
New cards
What is the plan of care for an individual receiving tPA?
monitor for bleeding:
vitals such an low BP and cardiac arrhythmias
IV site
NG tube
stool/emesis
catheters
vitals such an low BP and cardiac arrhythmias
IV site
NG tube
stool/emesis
catheters
27
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by an NG tube?
metabolic alkalosis due to the risk of excessive suctioning of acidic secretions
28
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by an opiod overdose?
respiratory acidosis due to the low respiratory drive
29
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by diarrhea?
metabolic acidosis due to the base leaving the ass
30
New cards
What is the treatment plan for an individual experiencing respiratory alkalosis?
paper bag form hyperventilation
monitor calcium and potassium levels
oxygen therapy, reduce anxiety
monitor calcium and potassium levels
oxygen therapy, reduce anxiety
31
New cards
What acid base imbalance can be caused by hyperventilation?
respiratory alkalosis due to blowing off too much CO2
32
New cards
A patient with Fluid Volume Excess should report what to the physician?
2 pounds weight gain in 24 hours or 5 lbs in a week
33
New cards
What electrolyte imbalance is the patient most at risk for when taking Furosemide/Lasix?
hypokalemia
34
New cards
What electrolyte imbalances cause a positive Chvostek sign and positive Trousseau’s Sign?
hypocalcemia
35
New cards
What are the two major causes of hyperkalemia?
potassium sparing diuretics (Aldactone)
excess K+ intake
kidney failure bc it starts to retain everything
adrenal insufficiency
cellular movement of K+ (burns)
excess K+ intake
kidney failure bc it starts to retain everything
adrenal insufficiency
cellular movement of K+ (burns)
36
New cards
Tall, peaked T-waves are indicative of what electrolyte imbalance?
hyperkalemia
37
New cards
What are some examples of isotonic IV solutions? Remembered the
sodium chloride 0.9% (NS)
lactated ringers
Dextrose 5% Water (D5W)
lactated ringers
Dextrose 5% Water (D5W)
38
New cards
What are some examples of hypertonic IV solutions? \*more than 0.9% is hypertonic.
3% NaCL
5% dextrose in LR
5% dextrose in NS
5% dextrose in LR
5% dextrose in NS
39
New cards
What are some examples of hypotonic IV solutions? \*remember anything that is less than 0.9% is hypotonic.
0\.45% NaCl
0\.225% NaCl
0\.225% NaCl
40
New cards
A safe administration routes for potassium chloride is:
Potassium has to be administered slowly over at a IV rate of 10-20 meq/L but is to not excess 20 meq/L.
41
New cards
What should a nurse monitor for when administering K+ chloride safely?
phlebitis- look for any swelling, tenderness, warmness and redness
infiltration
infiltration
42
New cards
When a patient is receiving Potassium Chloride, administering ____ can be dangerous since hypokalemia increases the sensitivity to digitalis, predisposing one to digitalis toxicity at lower digoxin level. (therapeutic level of digi is 0.8-2.0 ng/mL).
digoxin
43
New cards
A person with a magnesium level greater than 2.6 mg/dL is at risk for what?
\
\
respiratory depression due to magnesium affecting the cardiovascular system by regulating BP
44
New cards
What is the most common cause of symptomatic hypomagnesemia?
excessive alcohol
45
New cards
What should be encouraged for a patient with Hypernatremia?
PO fluids
decreased sodium intake
anticipate hypotonic or isotonic IV solutions
decreased sodium intake
anticipate hypotonic or isotonic IV solutions
46
New cards
What should be restricted for a patient with Hyponatremia?
fluids bc they ordinally already have excess fluids
47
New cards
COPD is composed of what two diseases?
chronic bronchitis & emphysema
48
New cards
Which oxygen delivery system delivers the most precise amount of oxygen and which one delivers the most concentrated?
venturi mask & non-rebreather
49
New cards
What are your safety education points for a patient who is on oxygen at home?
* no smoking signs or smoking at all
* ensure all electric devices are secured and wired down
* know where the clothes fire extinguisher is
* cotton instead of synthetic material
* avoid use of acetone or alcohol containing products
* ensure all electric devices are secured and wired down
* know where the clothes fire extinguisher is
* cotton instead of synthetic material
* avoid use of acetone or alcohol containing products
50
New cards
What is the most effective way to assess oxygen therapy?
ABGs
51
New cards
What should the nurse do first if a chest tube is accidentally removed from the patient’s chest wall?
apply petroleum gauze with dry sterile gauze and tape over to secure
52
New cards
What should the nurse do first if a chest tube is accidently removed from the chest tube drainage system?
immerse the end of the tube in sterile water to provide temporary water seal
53
New cards
Which medications should be withheld prior to a PFT?
bronchodilators should be withheld 4-6 hours before to prevent a false reading
54
New cards
What education should you give a patient prescribed Guaifenesin, a mucolytic that helps clear the airway and clearing chest congestion thus making it breath easier?
educate patient to increase fluids to help thin secretions
55
New cards
What are complications of a bronchoscopy?
pneumothorax, infection, aspiration
56
New cards
What assessment findings indicate a pneumothorax?
absent or restricted movement of affected side
pleuritic pain
dyspnea
pleuritic pain
dyspnea
57
New cards
Bubbling in the water-seal chamber of a chest tube system indicates what?
an air leak, bubbling should only be present in the 3rd chamber
58
New cards
A patient with pneumonia who is sent home on a prescription of antibiotics should be educated to call the physician if what happens?
if there is a change in secretions and change in color sputum
59
New cards
What symptoms of indicative of Pneumonia?
* crackles
* pleuritic chest pain
* yellow-tinged sputum
* dull chest percussion
* decreased O2 sat
\*accompanied by fever, chills, SOB
* pleuritic chest pain
* yellow-tinged sputum
* dull chest percussion
* decreased O2 sat
\*accompanied by fever, chills, SOB
60
New cards
A patient brought up to the PACU after undergoing a vagotomy. What complications does the nurse need to monitor for?
* dumping syndrome
* diarrhea
* gastritis
* diarrhea
* gastritis
61
New cards
The PACU nurse is preparing to insert a NG tube to a post-op patient that has underwent a Billroth II procedure. What does the nurse need to make sure to do if the NG needs to be manipulated in any way?
has to call HCP before doing so
62
New cards
The patient complains of a sore throat and states “I cough up some blood earlier this morning.” The nurse knows the patient has just underwent an EGD. What is the best response from the nurse?
“Minor bleeding accompanied by a sore throat is common after an EGD since a tube was inserted down your esophagus.”
63
New cards
A patient who is 1 hour post op from an EGD complains of a “sharp, retrosternal pain.” What is the nurse’s next action?
call HCP to request a CT scan
64
New cards
The nurse knows that the most important nursing intervention after an EGD is to monitor the patients ____ due to the possibility of puncturing a lung during the procedure or the stomach.
respiratory status
65
New cards
A nurse must assess the ___ before the patient can resume a tolerable diet after an EGD.
gag reflex
66
New cards
A nurse is assessing a post-op patients vital signs after an EGD procedure. The patients vitals are the following: BP of 96/70; HR of 110; 101 degrees temp. What is the nurse’s priority action?
contact HCP because esophageal perspiration is suspected
67
New cards
What patient education is essential pre-op of an EGD procedure?
NPO 6-8 hours before & remove objects such as dentures
68
New cards
GERDs medications include the following:
* PPIs (“azoles”)
* antacids
* histamine receptor antagonist (rantidine)
* prokinetics (metoclopramide)
* antacids
* histamine receptor antagonist (rantidine)
* prokinetics (metoclopramide)
69
New cards
___ is the GERD medications that controls nausea and vomiting by blocking dopamine & serotonin receptors increasing GI motility (increasing the tone of lower esophageal sphincter)?
metoclopramide (in the prokinetics drug class)
70
New cards
What GERD medication suppresses gastric acid and lowers hydrogen ions?
ranitidine
71
New cards
Antacids reduce gastric acid and protect the mucosal lining. What if the patient is taking magnesium hydroxide or calcium carbonate?
The nurse must educate that long term use of magnesium antacids causes diarrhea and long term use of calcium causes constipation.
72
New cards
What complication due to chronic gastritis can cause or lead to the other complications that can occur with the diease?
pyloric stenosis
73
New cards
The normal pH is __.
7\.4
74
New cards
The normal CO2 level is ___.
35-45
75
New cards
The normal CO3 (bicarb) is ___.
22-28
76
New cards
Anything less than ___ is considered acidic. Anything more than 7.45 is __.
acidic; alkalotic
77
New cards
The first line of maintenance of acid-base balance is the chemical and protein buffers. What is the last?
kidney buffers because they either excrete or retain electrolytes
78
New cards
The biggest indicator of respiratory acidosis upon assessment is ___.
diminished lung sounds
79
New cards
When the patient cannot fully expand the lungs, they are retaining acid, causing respiratory acidosis. What are common causes of this acid-base imbalance?
Drugs (anasethesia)
Edema in the lungs
Pneumonia due to excess mucus (chronic)
Respiratory center of the brain is damaged (stroke)
Sac elasticity of alveoli is impaired (COPD, Emphysema, bronchitis)
Edema in the lungs
Pneumonia due to excess mucus (chronic)
Respiratory center of the brain is damaged (stroke)
Sac elasticity of alveoli is impaired (COPD, Emphysema, bronchitis)
80
New cards
A patient experiencing respiratory acidosis will have a lack of O2, more CO2 (acidic). What clinical manifestations occur with acid base imbalance?
* bradypnea (lungs cannot full expand)
* confused, drowsy, HA (no O2 to brain)
* hyperkalemia due to acidity
* EKG changes with a peaked T wave
* pale or cyanotic
* confused, drowsy, HA (no O2 to brain)
* hyperkalemia due to acidity
* EKG changes with a peaked T wave
* pale or cyanotic
81
New cards
A patient is being treated for respiratory acidosis when suddenly he experiences a respiratory rate of 10. What is the nurse’s next action?
prepare the pt for intubation
82
New cards
The most important nursing intervention when a patient is experiencing respiratory alkalosis is ___.
having the patient breath into a paper bag
83
New cards
Respiratory alkalosis can be caused by anything that makes the body works too hard, or hyperventilate, and makes the body expel too much CO2 (acidic). What are some causes?
Temp
Aspirin toxicity
Controlled intubation
Pain/pregnancy
Anxiety, asphyxia, asthma
Aspirin toxicity
Controlled intubation
Pain/pregnancy
Anxiety, asphyxia, asthma
84
New cards
A patient with respiratory will have low calcium & low potassium due to losing acidity in the body, leaving it alkalotic. What assessment finding does the nurse expect to find?
positive Chvostek’s sign
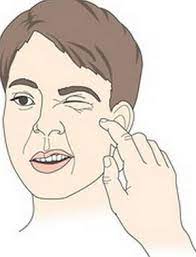
85
New cards
The hallmark sign of respiratory alkalosis is ____.
tetany with tingling and numbness
86
New cards
What vital signs will a patient experiencing respiratory alkalosis exhibit?
tachypnea, tachycardia
87
New cards
A patient comes into the ER with a flushed face and is throwing up. The nurse notices the patient is having Kussmaul respirations and notes a fruity/acetone breath. The nurse knows the patient is likely to develop what acid-base imbalance?
metabolic acidosis due to a DKA
88
New cards
Anything that causes the body to lose base out the ass results in metabolic acidosis. What are some specific causes?
Diarrhea
Ostomy drainage
Fistula
Alcoholism (liver cannot produce bicarb)
Ostomy drainage
Fistula
Alcoholism (liver cannot produce bicarb)
89
New cards
A patient experiencing metabolic acidosis. The nurse checks the ABGs results and the pH is 7.25. The nurse assess the patients vitals a notes Kassumal breathing with a decreased BP. The patient is confused and weak. What does the nurse prepare for?
intubation
90
New cards
metabolic acidosis s/s:
* tachypnea
* hyperkalemia
* cardiac dysthrymias
* nausea/vomitting to try to make the body alkalotic
* \
* hyperkalemia
* cardiac dysthrymias
* nausea/vomitting to try to make the body alkalotic
* \
91
New cards
metabolic alkalosis s/s:
* hypoventilation, bradypnea
* hypotension
* hypokalemia with EKG changes
* tremors
* tetany
* hypotension
* hypokalemia with EKG changes
* tremors
* tetany
92
New cards
To obtain an ABG:
\*must perform Allen test first\*
1. use heparin needle
2. APPLY PRESSURE FOR 5-10 minutes!!!
3. roll sample after drawing
4. put it in ice
5. monitor site for phlebitis
1. use heparin needle
2. APPLY PRESSURE FOR 5-10 minutes!!!
3. roll sample after drawing
4. put it in ice
5. monitor site for phlebitis
93
New cards
Partially compensated is when the pH, CO2 & CO3 are ___.
all out of range
94
New cards
Fully compensated is when the pH is _. The CO2 & CO3 are _.
normal; both outside expected range
95
New cards
What can trigger a migraine?
* environmental allergies
* bright lights
* odors
* alcohol
* stress/anxiety/ sleep deprivation
* bright lights
* odors
* alcohol
* stress/anxiety/ sleep deprivation
96
New cards
A nurse knows that a patient diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease is due to the loss of dopamine. What clinical manifestations does the nurse expect to see in the patient?
Tremors at rest “pill-rolling”
Rigidity “cogwheel” movement
Akinesia/bradykinesia
Postural instability “shuffling gait”
Rigidity “cogwheel” movement
Akinesia/bradykinesia
Postural instability “shuffling gait”
97
New cards
A nurse is assessing her patient in the ER that came in due to a hemorrhagic stroke when all of a sudden the patient begins to seize. What does the nurse do?
roll the patient to their side and do not put anything in their mouth
98
New cards
The patients complains of “on-going, excruciating pain” and pressure on one side of the eye and that doesnt seem to go away even with analgesia. What question should the nurse ask during the focused assessment?
“Do other members in your family get headaches often?”
“What coping skills do you practice when undergoing stress?”
“How many hours at night do you sleep?”
“Do you have seasonal allergies?”
“What coping skills do you practice when undergoing stress?”
“How many hours at night do you sleep?”
“Do you have seasonal allergies?”
99
New cards
The patient shouts “I have this headache that feels like the worst headache of my life!” The nurse is concerned because she suspects a hemorrhagic stroke. What is the nurse’s priority action?
obtain a CT/MRI
100
New cards
Increased ICP decreases cerebral perfusion which can increase the risk for a hemorrhagic stroke. What are the late signs of increased ICP?
cushing’s triad:
increased BP with pupillary changes
low RR with slurring speech
low HR with slow bounding pulse
increased BP with pupillary changes
low RR with slurring speech
low HR with slow bounding pulse