AP Biology Unit 1 Chemistry of Life
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab and Notes from Unit 1 of AP Biology, Chemistry of LIfe.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Monomers
The building blocks of polymers.
Dehydration Synthesis
One monomer forms a covalent bond to another monomer and releases a water molecule.
Hydrolysis
A covalent bond is broken by adding a water molecule (one molecule gains “H” and the other gains “OH”
Composition of Carbs
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Monosaccharaide
The building block/monomer of carbohydrates.
Simple sugar, contain 3-7 carbon atoms (ex. glucose, fructose galactose, all are isomers of each other (differ in organization of their atoms)).
Disaccharide
Form when two monosaccharides bond via dehydration synthesis (ex lactose, maltose, sucrose)
Polysaccharide
Long chains of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds (the chain may be branched or linear)
ex. starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
Starch
stored form of sugars in plants
Glycogen
storage form of glucose in humans
Primary Structure of Proteins
sequence of amino acids
Secondary Structure of Proteins
This structure refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone. (The backbone just refers to the polypeptide chain apart from the R groups – so all we mean here is that secondary structure does not involve R group atoms.)
The most common types beta plates and alpha helices, which are held in shape by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary Protein Structure
This is due to interactions of side chains. It is the overall 3D shape of the protein and often minimalizes free energy. Various types of bonds and interactions stabilize the protein at this level. Most proteins become functional at this level.
Quaternary Protein Structure
(more than one polypeptide), arises from the interactions of multiple polypeptide units. Some proteins aren’t functional until this stage, such as hemoglobin.
Nucleotides
Building blocks/monomers of nucleic acids.
Amino Acids
Building block/monomers of proteins
Fatty acids or glycerol
building blocks of lipids (not really monomers)
Function of carbohydrates
Quick/short term energy, source of dietary fiber
Lipids
These are fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water.
Specialized BLANKS (phospho-) contain hydrophilic polar heads (phosphate group) and hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails made of fatty acids to form the double BLANK bilayer. If it’s unsaturated, it causes a kink, increasing the spacing between cell membrane components and preventing dense packing while promoting fluidity within the cell membrane. The fat is unsaturated if it has at least 1 double bond.
BLANKs provide energy storage and support cell function (cholesterol). Some form the cell membrane. Steroids are lipids.
Proteins
Provide cell structure, send chemical signals, speed up chemical reactions (enxymes), C
CHNOPS in Proteins
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Sulfur, (only sometimes phosphorus)
CHNOPS in Nucleic Acids
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, not Sulfur
CHNOPS in Carbs
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (ratio 1:2:1)
CHNOPS in Lipids
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, sometimes phosphorus.
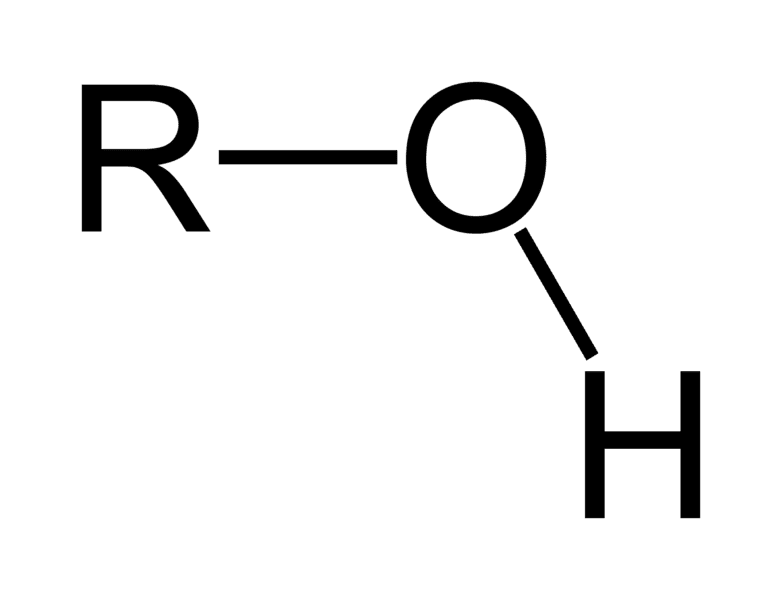
Hydroxyl group
OH (polar)
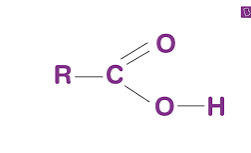
Carboxyl Group
COOH (acidic)
Methyl Group
CH3 (nonpolar)
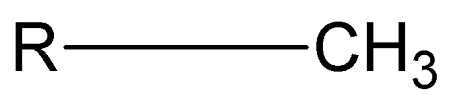
Carbonyl Group
CO (double bond) (polar)

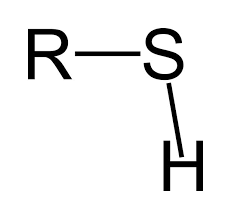
Sulfhydryl Group
SH (polar)
Amino
NH2 (basic)

Polypeptide
a continuous, unbranched chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds.
Amino Acid
Consists of an amino (NH2) and a carboxyl (COOH) and an R group which dictates its’ polarity and properties (size and structure). A protein is synthesized at the Carboxyl terminus.
R-Group CH3
Hydrophobic, nonpolar
R-Group CH2-OH
Hydrophilic, polar
R-Group CH2-COOH
Ionic, polar
Nucleic Acid Makeup
5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base.
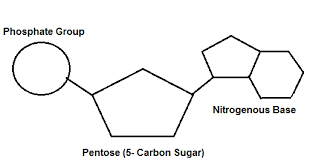
Ribose
The sugar in RNA
Deoxyribose
The sugar in DNA
AGCT
Nitrogenous bases of DNA
AGCU
Nitrogenous bases of RNA
Glycosidic Bond
is a type of ether bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Structure of DNA
Antiparallel, double helix, runs 5’ to 3’ one one side and 3’ to 5’ on the other.
Structure of RNA
Single strand
2 hydrogen bonds
There are BLANK holding together Adenine and Thymine in DNA.
3 hydrogen bonds
There are BLANK holding together Guanine and Cytosine in DNA.