Physiology 2
osmosis:: the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane up a solute concentration gradient
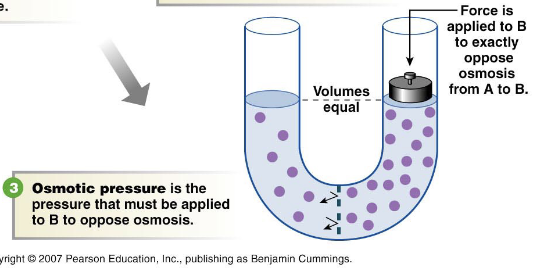 osmosis depends on:: the number of particles in a given volume of solution
osmosis depends on:: the number of particles in a given volume of solution
osmolarity:: = molarity * particles/molecule
hyperosmotic:: higher osmolarity in relation to another solution
hypoosmotic:: lower osmolarity in relation to another solution
isosmotic:: the same osmolarity in relation to another solution
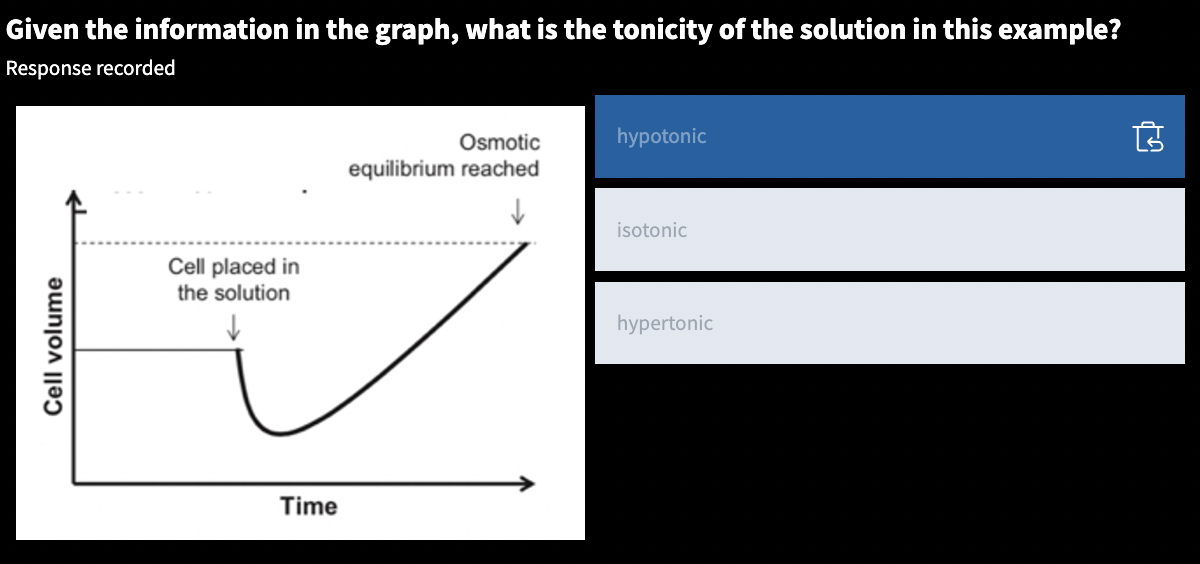
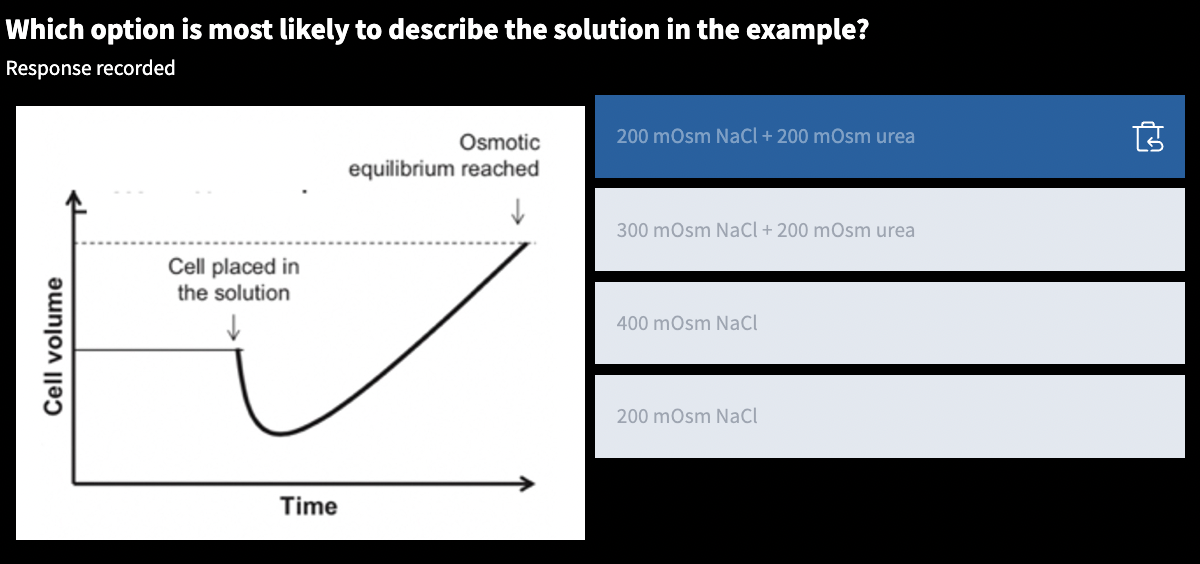
tonicity:: describes a solution based on its effects on the volume of a cell placed in the solution
hypertonic:: water diffuses out, shrinking
hypotonic:: water diffuses in, swelling
lysis:: a very hypotonic solution causes _
isotonic:: water diffuses normally, no effect to the cell
nonpenetrating solutes:: only solutes that effect osmolarity and tonicity


body fluid osmolarity:: 300 mOsm
 nonpenetrating:: assume that all intracellular solutes are _
nonpenetrating:: assume that all intracellular solutes are _