The Atmosphere, The Water Cycle & Ocean Currents
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Where is most of Earth’s water found?
The Ocean
Where is most of Earth’s freshwater found?
Glaciers and ice caps
Glaciers
Land covered with ice that makes up much of the earth’s fresh water
Groundwater
Water held underground in layers of rock & sediment
surface water (Lakes, rivers, and ponds)
When the earth’s surface dips below the groundwater level
Aquifers
A layer of rock & sediment that can holds usable groundwater.
The Water Cycle
The continuous movement of water within the Earth and atmosphere. It is driven by energy from the sun and the force of gravity
Evaporation
The transfer of water from the earth’s surface to the atmosphere
Liquid state → gaseous state
Transpiration
The evaporation of water from plants through small pores (stomata) on the leaves/stems of plants/trees
Condensation
Occurs when the air cools and cannot hold anymore water vapor. The water will be released in the form of precipitation.
gaseous state → liquid state
Precipitation
Water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail
Infiltration
Water soaks into the Earth’s surface moving into the pores and cracks of rocks.
Surface runoff
Water from precipitation that flows over the ground’s surface. This occurs when the ground is already too saturated for excess storm water, snow melt or impervious surfaces
Impervious surface
a hard, constructed surface that does not allow water to seep into the ground
Groundwater/Subsurface Flow
The movement of water underneath the Earth’s surface. This typically happens after precipitation has infiltrated the soil.
Accumulation (collection)
The process of water collecting in Earth’s oceans, rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water.
What are ways humans alter and affect the Water Cycle?
Redirect rivers
Build dams to store water
Drain water from wetlands for development
We use water for infrastructure and agriculture
pollution
climate change
Ocean current
the continuous, predictable, and directional movement of seawater
Salt vs Fresh water
The salt water is more dense because of the added salt (adds mass without really changing the volume). As a result the salt water sinks
Warm vs. Cold water
Warm water is less dense because the molecules are moving faster and spread out more so the warm water rises/floats
Ocean Conveyor Belt
A constantly moving system of deep-ocean circulation driven by temperature and salinity. The great ocean conveyor moves water around the globe.
How does the Ocean Conveyor Belt form?
Water at the poles cools and freezes
Sea ice forms
But the salt is left behind
Water that does not form ice is left saltier and colder than before
This water is more dense and sinks
Warmer water rushes in to fill its place
Current has formed
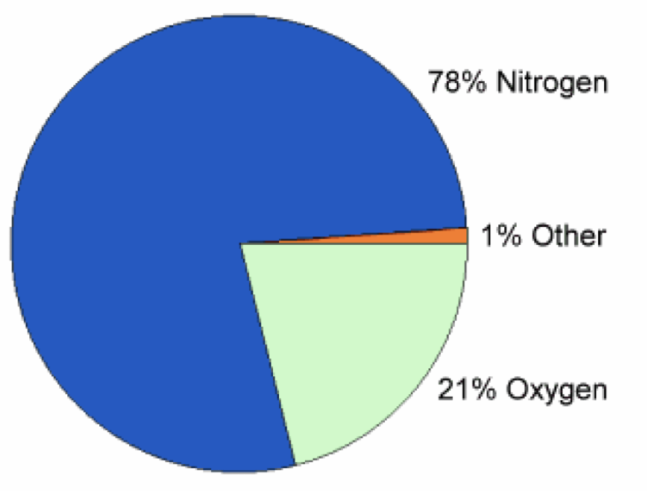
What makes up air?
78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% Other. Solids, liquids, and gases…but mostly gases!
Air density
the amount of air molecules in a given area
Low density → low pressure → high temp.
High density → high pressure → low temp.
Air pressure
the amount of force exerted by air molecules. It is caused by gravity acting on the molecules.
Fewer molecules will exert less pressure
More molecules will exert more pressure
Wind
Wind is air flowing from high to low pressure.
It is air in motion
How do hot air balloons work?
When air is warmed, the molecules in it will move apart and the air becomes less dense. Air pressure also decreases because fewer molecules are in the same place.
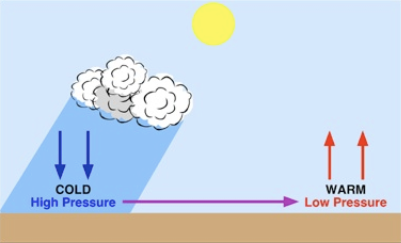
How does wind form?
Wind is caused by the unequal heating of the Earth’s surface. Because Earth is curved, the sun’s rays strike the equator more directly than the poles.
Why is the atmosphere important?
Protects organisms from the sun’s harmful rays
Without the atmosphere, days would be extremely hot and nights would be extremely cold
Winds transport clouds, precipitation, and particles (like seeds) across the Earth
Troposphere
Closest to the Earth’s surface
contains 75% of the atmosphere’s mass
weather, clouds, mountain tops
Troposphere distance
thinnest layer
0-20 km
Troposphere temperature trends
Warmed by the Earth’s surface
As the altitude increases, the temp decreases
Stratosphere
2nd layer
Contains the ozone layer
protects Earth from UV rays
less dense than the troposphere
Because the Ozone absorbs the UV rays, the temperature increases as the altitude increases
Planes fly at the bottom of the Stratosphere
Stratosphere distance
20-50 km
Stratosphere temperature trends
Because the Ozone absorbs the UV rays, the temperature increases as the altitude increases
Mesosphere
3rd layer
This layer does not absorb energy from the sun
meteoroids burn up because of lots of friction
Mesosphere Distance
50-85 km
Mesosphere temperature trends
the coldest layer
the temperature decreases as the altitude increases
Thermosphere
4th layer
Solar radiation hits here first! The few particles get tons of energy
The International Space Station
Aurora Borealis
Thermosphere distance
85-600 km
Thermosphere temperature trends
hottest layer (over 1,000° C)
feels cold because there isn’t enough matter to transfer the heat
the temperature increases as the altitude increases
Exosphere
5th and outermost layer which gradually fades out to space
satellites orbits and spaceships travel here
Exosphere Distance
600-10,000 km
Exosphere temperature trend
the temperature changes drastically