2ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY - LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Transes
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
250 Terms
Immune System
Lymphatic System is also known as the
Fluid Recovery or Balance, Lipid Absorption, Immunity of Defense
3 Functions of the Lymphatic System
Lacteals
_________ in small intestine absorb dietary lipids
Immune Cells
stand ready to respond to foreign cells or chemicals encountered.
Lymph
Clear, colorless fluid, similar to plasma but much less protein.
Lymphatic Capillaries
Closed at one end
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Lymphatic Capillaries is composed of
Protein Filaments
Lymphatic Capillaries is tethered to surrounding tissue by
Prevent backflow
What is the main function of the valves?
CNS, Bone Marrow, Tissues without Blood Vessels
Lymphatic capillaries found in almost all tissues of the body except
Edema
the collection of fluid in the interstitial spaces.
Skin
the primary line of defense.
F, low
T OR F:
Lymph flows at high pressure and speed.
Lymphatic Vessels
Passageway for the lymph
Tunica Interna, Tunica Media, Tunica Externa
Larger Lymphatic Vessels are composed of 3 layers:
Tunica Interna
inner most layer; endothelium and valves
Tunica Media
middle layer; elastic fibers, smooth muscle
Tunica Externa
thin outer layer.
(1) Contraction of surrounding skeletal muscle during activity, (2) Periodic contraction of smooth muscle in the lymphatic vessel wall, (3) Pressure changes in the thorax during respiration
Three (3) factors cause compression of Lymphatic Vessels
helps propelling the lymph for it to move throughout the vessels and the body
Importance of the Contraction of the Lymphatic Vessels
Lymphatic Capillaries, Collecting Vessels, Lymphatic Trunk, Collecting Duct (Right Lymphatic and Thoracic Duct),
Route of Lymph Flow
Collecting Vessels
course through many lymph nodes
Lymphatic Trunks
drains major portions of body
Right Lymphatic Duct
receives lymph from R arm, R side of head and thorax; empties into R subclavian vein
Thoracic Duct
larger and longer, begins as a prominent sac in abdomen called cisterna chyli;
Thoracic Duct
receives lymph from below diaphragm, L arm, and L side of head, neck and thorax; empties into L subclavian vein.
Cisterna Chyli
Thoracic Duct begins as a prominent sac in abdomen called
Cervical (Neck), Axillary (Armpit to Breastbone), Inguinal (Groin)
The most palpable nodes in our body are
infection or inflammation
When you have ____________ or ____________, the nodes are more palpable, obvious, and painful to touch.
congregate
The nodes ____________ which is why it is more palpable.
Mechanical, Hematogenous, Lymphatic
Three (3) major ways of cancer cells spreading
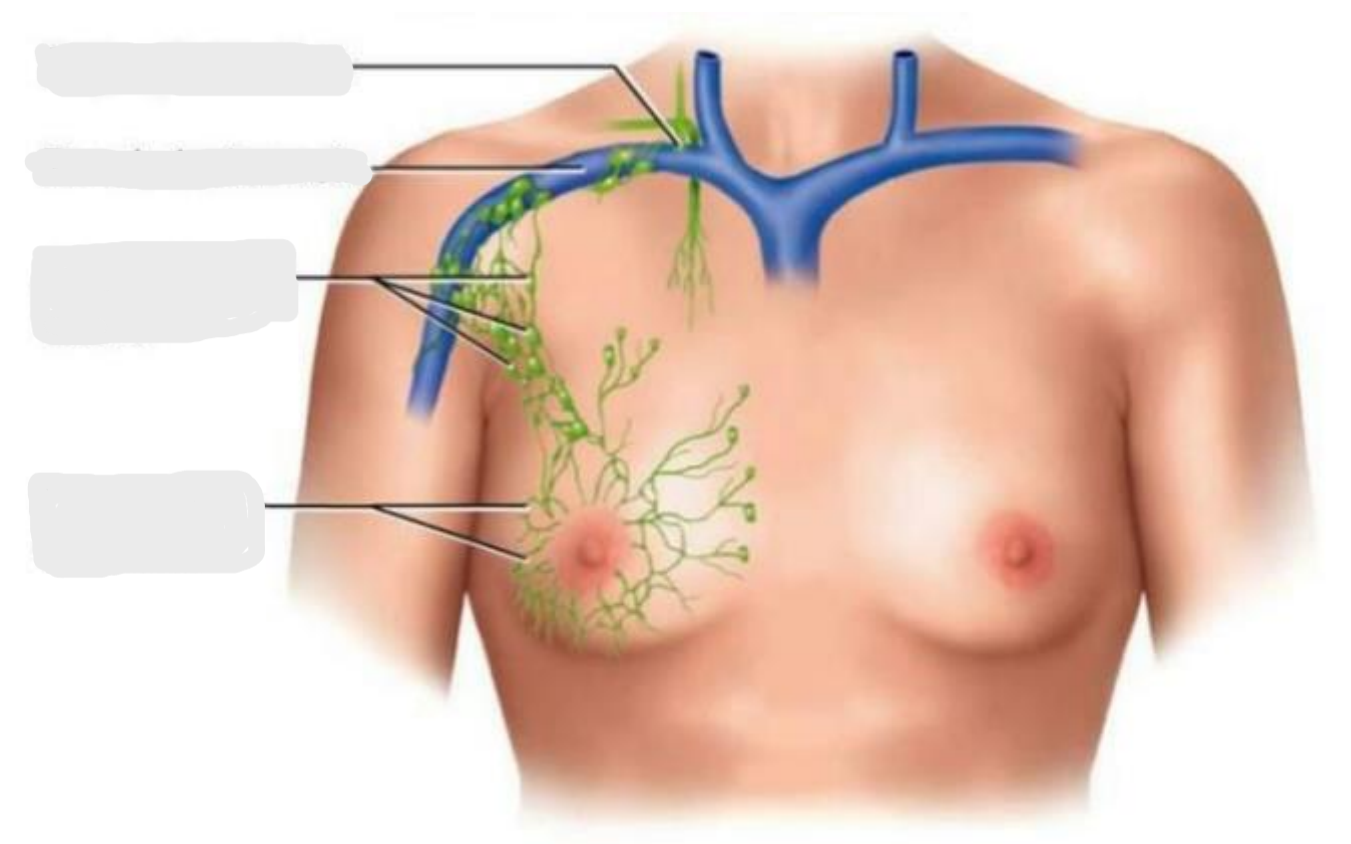
(1) Right Lymphatic Duct, (2) Right Subclavian Vein, (3) Axillary Lymph Nodes, (4) Lymphatics of Breast
Identify the parts
Epidermis, Cartilage
Tissues without blood vessels
Anchoring Filaments
keeps the lymphatic capillary in place.
Mastectomy
removal of the breast
Total Radical Mastectomy
not only you remove the breast and the tissue but also the lymph nodes.
Natural Killer Cells
Responsible for immune system surveillance.
T Lymphocytes
produced in red bone marrow and travels and mature in the thymus.
Thymus
site of maturation of your T lymphocytes.
B Lymphocytes
produced in the bone marrow.
Proliferation
Activation B lymphocytes causes ___________ and differentiation into plasma cells that produce.
B Lymphocytes
Help in the production of your antibodies.
B Lymphocytes
When you lack __________________, you also lack antibodies. If you lack antibodies, you can say that your immune system is not functioning optimally or it bugged down.
Antigen Presenting Cells
are macrophages from monocytes.
Macrophages
They are capable of engulfing larger particles considered as invading pathogens
Dendritic Cells
found in the epidermis, mucous membranes and lymphatic organs.
Reticular Cells
also contribute to stroma of lymph organs.
Phagocytes
causes the destruction of your invaders.
Cytotoxic T Cells, Helper T Cells, Suppressor T Cells
Subtypes of T Lymphocytes
Cytotoxic T Cells
bind to the surface of the antigen and directly destroys the cell membrane afterwards will enter phagocytosis.
Secrete Lymphokins
prevents migration of antigens, they call other lymphocytes
Helper T Cells
divide and mature into plasma cells and begins the secretion of Immunoglobulins
IgA
depend the stimulation of the helper t-cells
Helper T Cells
Primary targeted/ attacked by the HIV
Suppressor T Cells
decreases the production of Immunoglobulins
B Lymphocytes
Where the immunoglobulin and antibodies are produced and found
B Lymphocytes
Comes from plasma cells and memory cells when it has been exposed to antigens.
Plasma Cells
secretes Immunoglobulins and antibodies which binds and destroys specific antigens.
Redness-Tubor, Increase in Heat-Calor, Pain-Dolor, Inflammation-Tumor, Loss of Function-Functo Laesa
Signs of inflammation
Immune Response
the body’s action plan to combat invading pathogens and substances.
Antigen
any foreign substance which enters the body
Immunogen
if an antigen is easily or readily destroyed
Allergen
causes allergic reaction
Proteins
Mostly the one that causes allergic reaction are your
Bone Marrow
This is where T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes are produced.
Spleen
filters the blood and it serves as the graveyard of your dead RBC.
Spleen
After 120 days, the dead RBC will be sequestered to the
IgM
reaches at adult levels at approximately 1 year of age
IgG
becomes present at 4 years old.
IgG
could be passed on from the mother to the fetus via the placenta.
IgA
reaches its peak during adolescence.
IgA
abundant in your breast milk.
Breast Milk
rich in immunoglobulin A and antibodies but poor in iron.
Colostrum
first breast milk that comes out from the mother.
IgE
the one responsible for allergic reactions and hypersensitivity responses
MALT
prevalent in passages open to exterior.
MALT
point of entry of microorganism.
MALT
When the pathogen enters the body, the _____ will act as a protection.
Lymphatic Nodules
Dense oval masses of lymphocytes and congregate in response to pathogens.
Lymphatic Nodules
When there is a pathogen that enters and invades the body, the __________ ____________ will congregate. Meaning, they will gather and crowd, then it would become palpable.
Peyer Patches
more permanent congregation clusters found at junction of small to large intestine.
Lymphatic Organs
Are found at well-defined sites.
Primary Lymphatic Organs
site where T and B cells become immunocompetent.
Immunocompetent
mature enough to fight against the pathogens.
Secondary Lymphatic Organs
Immunocompetent cells populate these tissues.
Lymph Node
Only organ that filters the lymph
Capsule
composed of dense connective tissue surrounding each lymph node.
Trabeculae
subdivide lymph nodes into compartments containing lymphatic tissue and lymphatic sinuses.
Lymphatic Tissues
found inside trabeculae and consists of lymphocytes and other cells that can form aggregations of tissue.
Lymphatic Sinuses
spaces between lymphatic tissue
Lymphatic Sinuses
contains macrophages on a network of fibers.
Lymphadenopathy
Collective term for all lymph node diseases
Lymphadenitis
when the lymph nodes are swollen, painful, and responding to foreign antigen
Lymph Nodes
common sites for metastatic cancer.
Metastatic Cancer
cancer cells spread through other parts of the body other than the point of origin.
Tonsil
Covered by epithelium.
Palatine Tonsils
pair at posterior margin of oral cavity
Palatine Tonsils
stays behind tonsillar pillars.
Lingual Tonsils
Pair at root of tongue
Pharyngeal Tonsil
single tonsil on wall of pharynx.