Chapter 7: Atmospheric Scales, Circulations, and Global Wind Patterns in Meteorology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the four main scales of atmospheric motion?
Microscale, mesoscale, synoptic scale, and macroscale.
What is microscale motion in atmospheric phenomena?
Eddies with diameters of a few meters that last only a few minutes.
What characterizes mesoscale motion?
Circulations ranging from a few to hundreds of kilometers, lasting minutes to a day.
What is synoptic scale motion associated with?
Circulations around high- and low-pressure areas, lasting days to weeks.
What does macroscale motion involve?
Wind patterns observed at the planetary scale combined with synoptic scales.
What is an eddy in atmospheric terms?
A whirl of air that forms on the downwind side of an object when wind strikes it.
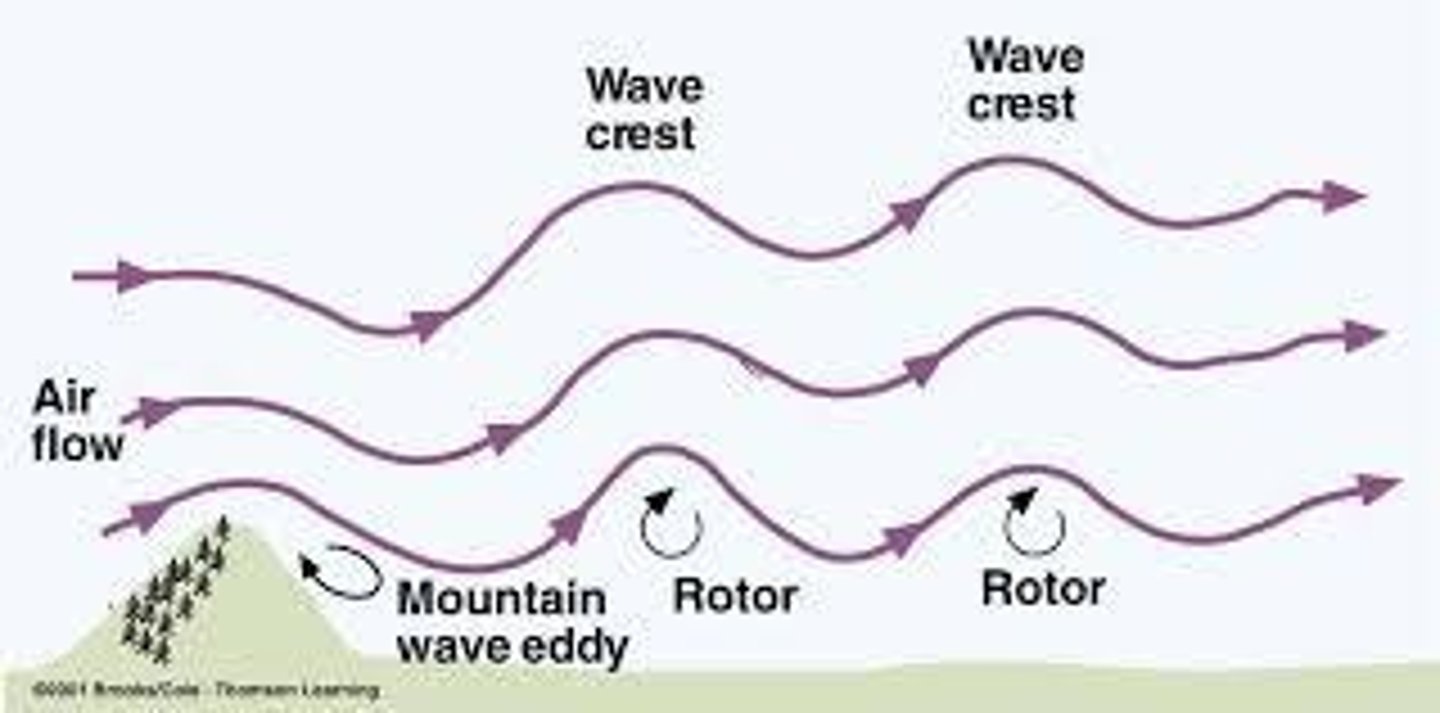
What are thermal circulations?
Air movements caused by variations in air temperature, where warmer air rises and colder air sinks.
What are sea and land breezes?
Local winds that occur due to temperature differences between land and water.
What is a valley breeze?
A gentle upslope wind that occurs when heated air rises from the valley.
What are katabatic winds?
Strong down slope breezes typically found in elevated snow-covered plateaus.
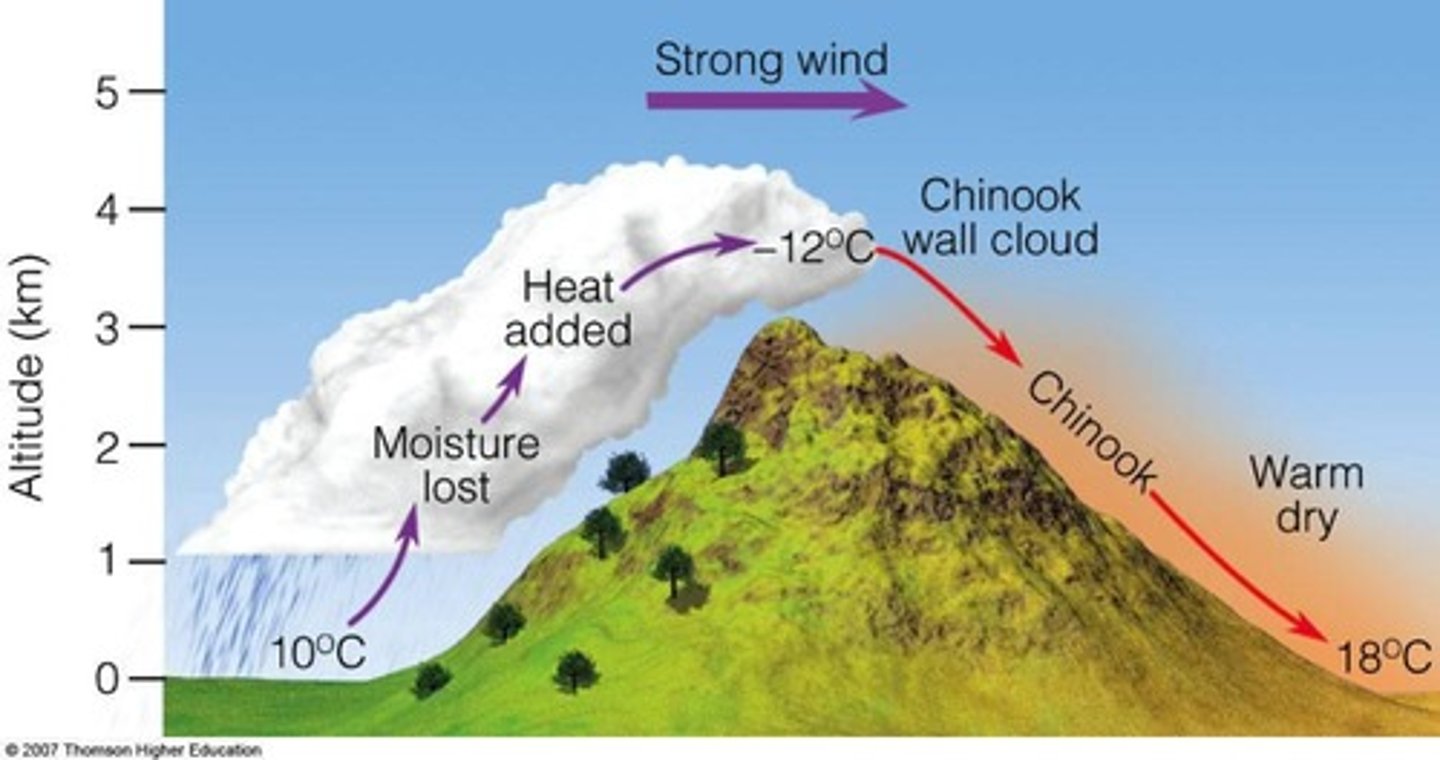
What are Chinook winds?
Warm, dry down slope winds that lead to rapid temperature increases and humidity drops.
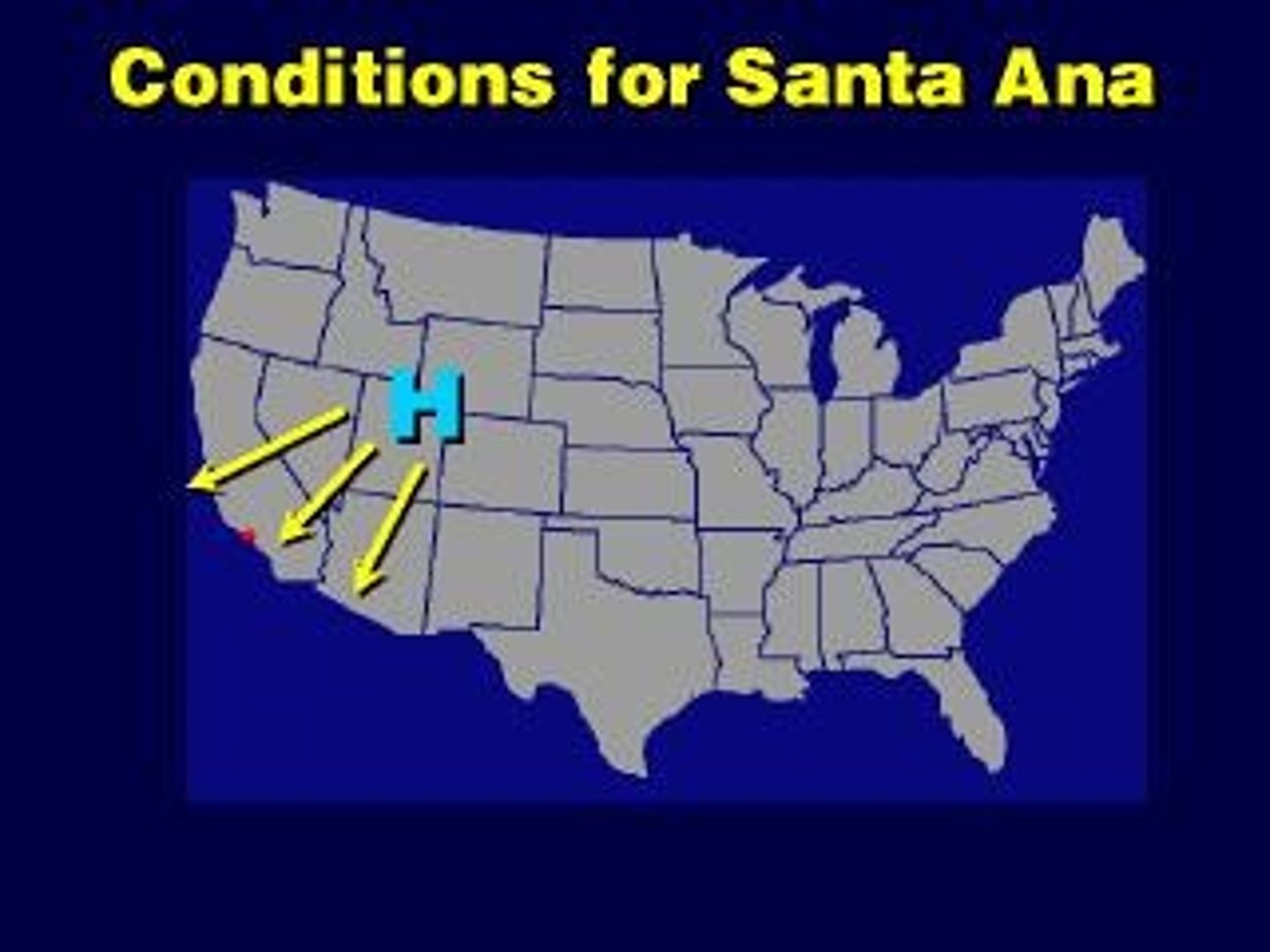
What are Santa Ana winds?
Warm, dry winds that blow downhill from the east or northeast into southern California.
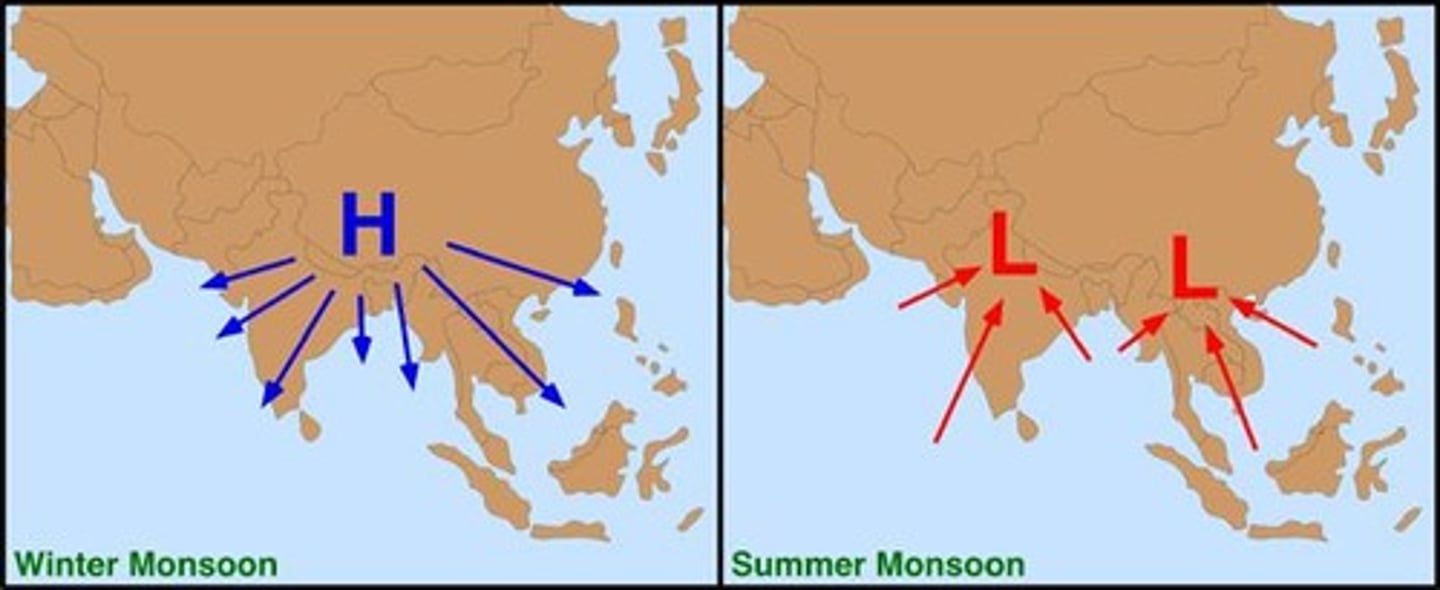
What characterizes monsoon winds?
Seasonally changing winds that shift direction between wet summers and dry winters.
What is the general circulation of the atmosphere?
The average wind patterns over a prolonged period across the globe.
What is the single-cell model of atmospheric circulation?
A theoretical model assuming a uniformly water-covered Earth with no rotation, containing one Hadley cell.
What is a Hadley cell?
A thermally direct cell driven by solar energy, where warm air rises at the equator and sinks at the poles.
What are the characteristics of jet streams?
Swift-flowing air currents that play a major role in heat transport, often exceeding 100 knots.
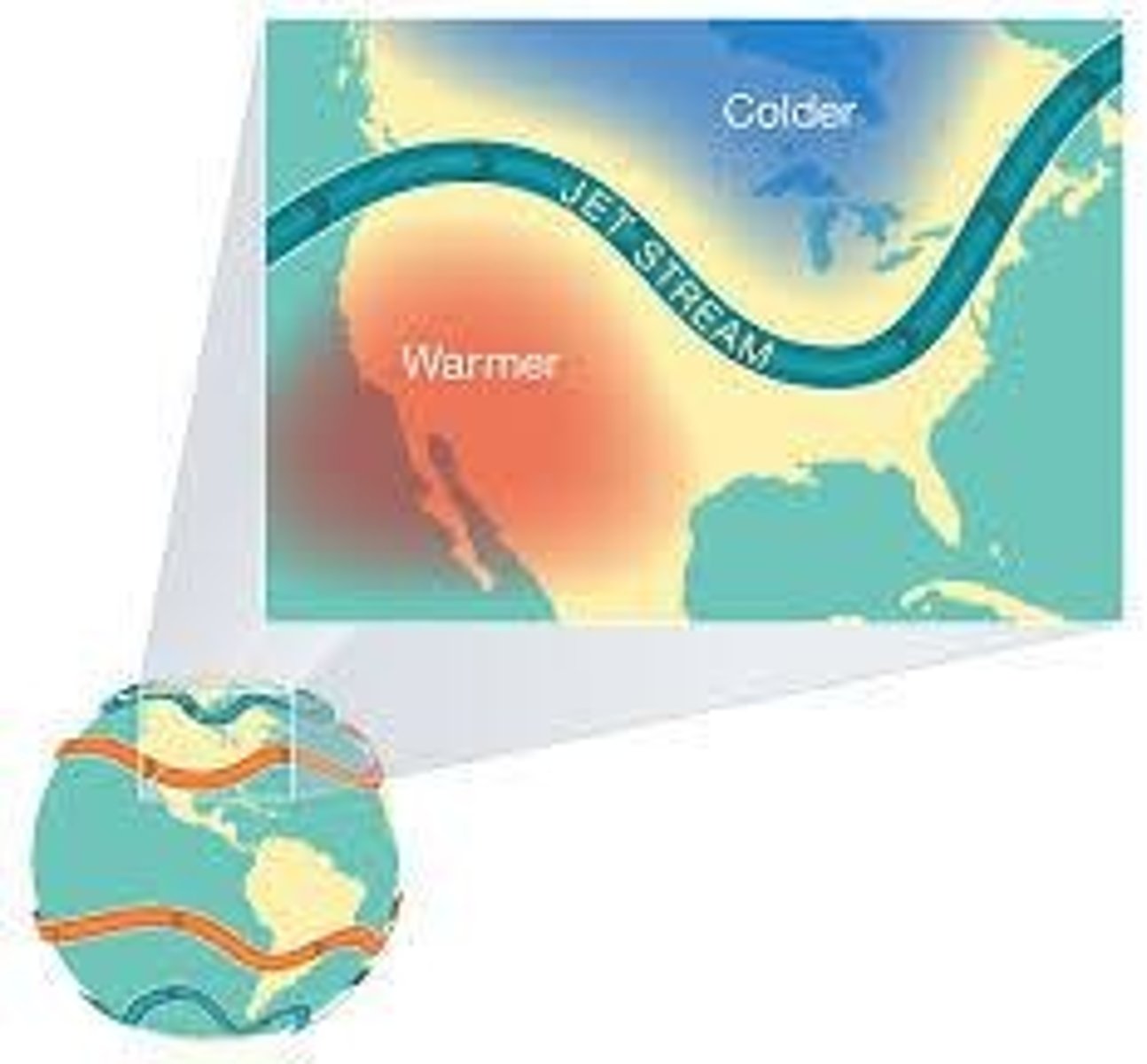
What causes the formation of jet streams?
Horizontal differences in air pressure.
What are the two main types of jet streams?
Polar jet streams and subtropical jet streams.
What is the role of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)?
It brings high rainfall during summer when it shifts to bring moist air from the ocean.
What is the significance of subtropical highs?
Regions of high pressure that contribute to dry weather and desert formation.
What happens to precipitation patterns between the equator and 30° latitude?
High rainfall occurs in the tropics, while low precipitation is found near 30° and polar regions.
What are the four regions of semipermanent highs/lows in the Northern Hemisphere?
Bermuda high, Pacific high, Icelandic low, and Aleutian low.