Systems Components flashcards
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
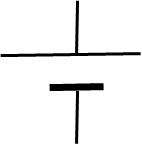
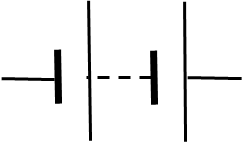
Purpose of Variable DC power supply
Easily adjust the output voltage and somtimes the current

Purpose of AC power supply
Supplies alternating currant to an electronic device

Purpose of a resistor
Limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in an electronic circuit
variable resistor,
potentiometer,
voltage divide
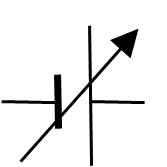
Purpose of a potentiometer
Measure the unknown voltage by comparing it with a known voltage
Purpose of a voltage divider
Scale down very high voltages so that it can be measured by a volt meter
variable resistor
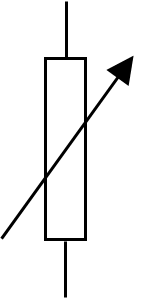
Purpose of a variable resistor
Adjust the value of current or voltage
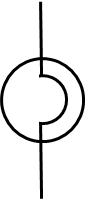
light-dependent resistor (LDR)

Purpose of a Light dependent resistor
Indicate the presence or absence of light, or to measure the lights intensity
Thermistor
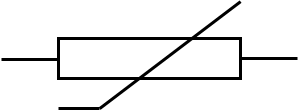
Purpose of the thermistor
Changed resistance as temperature changes
Fuse

Purpose of a fuse
Melts with too much current flows through, protects the circuit from too much current
(non-polarised) capacitor
Pass AC and block DC IN A SERIES CIRCUITA, filters power supplies
variable capacitor
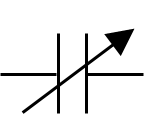
Purpose of a variable capacitor
To allows for change in capacitance, set a resonance frequency
polarised capacitor,
electrolytic capacitor
Filter power supplies

iron-cored transformer
(one secondary winding)
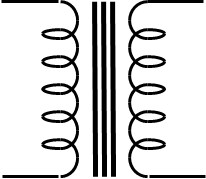
iron-cored transformer
(one secondary winding –
centre-tapped)
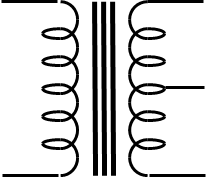
iron-cored transformer
(two secondary windings)
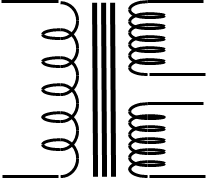
Purpose of Transformer
Transfer electric energy from one alternating current circuit to one or more other circuits, either increasing (stepping up) or reducing (stepping down) the voltage
junction diode
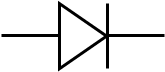
Purpose of junction diode
also known as a PN junction it allows current to flow more easily in one direction than another
Zener diode
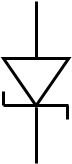
Purpose of a Zener diode
Voltage references or to regulate the voltage across small circuits
photo diode
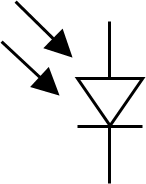
Purpose of a photo diode
The exact measurements of the intensity of light in science and industry, faster and more complex than normal PN junction diodes
light-emitting diode (LED)
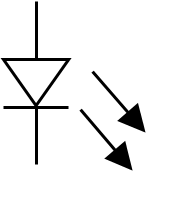
diode bridge
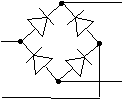
purpose of a diode bridge
Rectifying an alternating current into a direct current or pulsating current
npn transistor
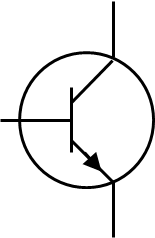
Purpose of NPN transistor
Amplifies weak signals that enter into the base and produces strong signals at the collectors end
pnp transistor
Increase voltage or current of signals, can be used as a switch
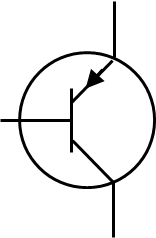
What is the difference between PNP and NPN transistor
PNP have a lower turn on voltage NPN have higher current carrying capacity
n-type junction field effect transistor (NJFET)
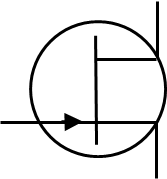
purpose of n-type junction field effect transistor (NJFET)
Switches and Amplifiers
p-type junction field effect transistor (PJFET)
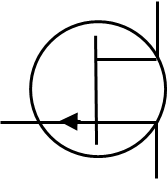
Purpose of p-type junction field effect transistor (PJFET)
Switches and Amplifies 2
integrated circuit (IC)
What kinds of Integrated circuits are there
Amplifier, timer, counter, logic gates, computer memory, micro controller and processor
single pole, single throw (SPST) switch

Purpose of single pole, single throw (SPST) switch
Basic ON/OFF function
single pole, double throw (SPDT) switch
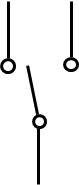
Purpose of single pole, double throw (SPDT) switch
Connects a single line conductor to either of 2 possibilities
double pole, single throw (DPST) switch
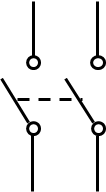
Purpose of double pole, single throw (DPST) switch
Connect 2 source terminals to their respective output terminals (NEVER TO EACH OTHER)
double pole, double throw (DPDT) switch
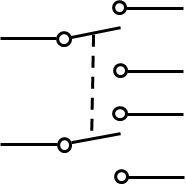
Purpose of double pole, double throw (DPDT) switch
Connect 2 independent signals to two possibilites in tandem
normally open
(NO) switch

Purpose of a normally open switch
Allows no current to flow unless altered
normally closed (NC) switch

Purpose of normally closed switch
Allows current to flow until altered
Relay
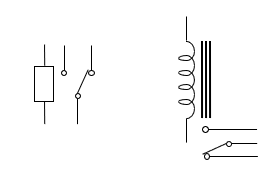
Purpose of a relay
Control one circuit by opening and closing contacts in another circuit
Ammeter

Purpose of ammeter
Measure amps (current)
Voltmeter
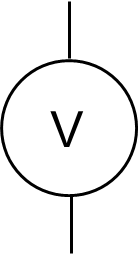
Purpose of voltmeter
Measure volts
Galvanometer
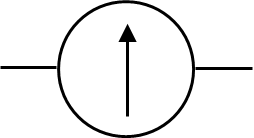
Purpose of a Gavanometer
Measure the direction and intensity of electrical current
cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO)
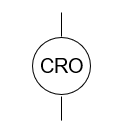
Purpose of a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO)
Displaying measuring and analyzing waveforms (DC or AC) and other electrical phenomena
voltage amplifier
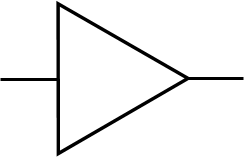
Purpose of a voltage amplifier
Accept input voltage and produce an accurate replica of this voltage as an output voltage
operational amplifier (op amp)
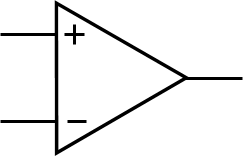
Purpose of a operational amplifier (op amp)
Amplify and output the voltage difference between two input pins
Motor
Microphone
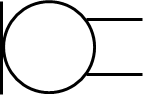
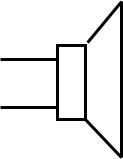
NOT gate or inverter
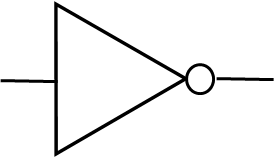
Purpose of a NOT gate
Inverts the input signal eg. 1 = 0
OR gate
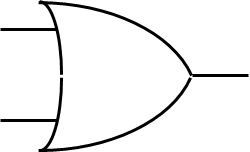
Purpose of an OR gate
Will produce an on signal is at least one pin is on
XOR (exclusive OR) Gate
The inputs must be different to produce an ON signal
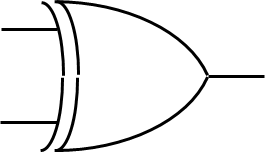
NOR Gate
If at least one pin is ON it will produce an OFF signal

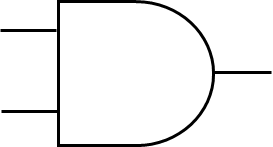
AND Gate
A ON signal will only be produced is both of the pins are ON
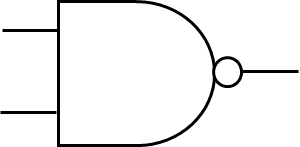
NAND Gate
A OFF signal will only be produced if both pins are ON
T (toggle) flip-flop
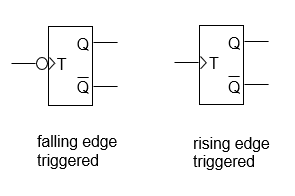
Purpose of a T (toggle) flip-flop
Changes or toggles its output based in the input state
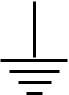
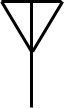
What is an Aerial
Antenna
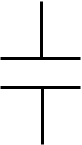
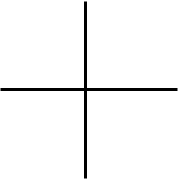
non-connected leads
connected leads
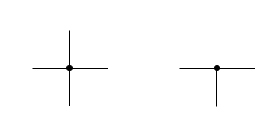
dot for junction of connected leads

Watts =
volts X Amps
What is a analogue signal
It is a continuous signal with constant fluctuations
What is a digital signal
A signal with only two voltages 1 and 0, which is high and low respectively
What does variable mean
A factor or condition which can be measured, altered or controlled
What type of motion is used in resonance
oscillation
what is the difference between Non and polarized capacitors
Capacity how much voltage they can store, Non-Polarized capacitors can run much higher frequencies
What is resonance
A phenomenon that occurs when objects match the vibrations of another object increases the amplitude of an objects oscillations
What are the 4 forces
Compression, Tension, Shear, Torsion, bending