4. pulpal and periapical pathology and inflammatory lesions of the jaw
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
what are the seven main categories of pathologies discussed this lecture?
periapical inflammatory disease
pulpal inflammatory disease
osteomyelitis
osteoradionecrosis
bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis
pericoronitis
soft tissue inflammation
what are some terms relevant to inflammatory lesions?
periapical inflammatory disease
rarefying and sclerosing osteitis
periodontal disease
pericoronitis
osteomyelitis
what is periapical inflammatory disease?
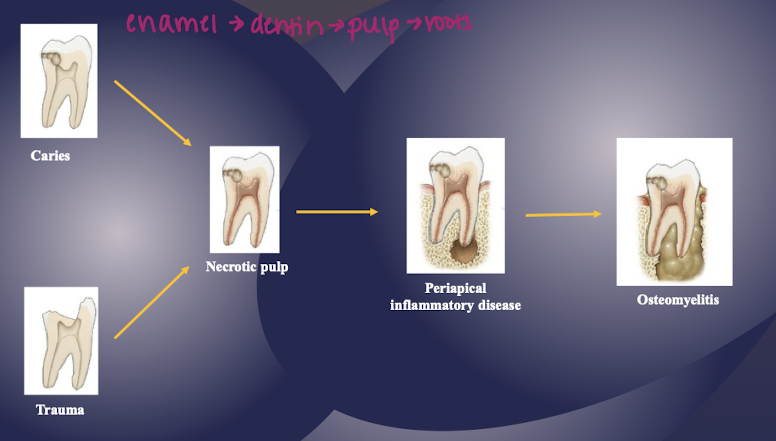
inflammatory response to pathogenic microorganisms and necrotic pulp (caries, trauma)
which is restricted to root apex?
periapical inflammatory disease
what inflammatory lesions are extension of inflammation into the bone from soft/gingival tissue?
periodontal disease, pericoronitis, osteomyelitis
which inflammatory lesion involves the supporting structures of the teeth?
periodontal disease
which inflammatory lesion involves crown of a partially erupted tooth?
pericoronitis
which inflammatory lesion involves extension of inflammation into bone marrow?
osteomyelitis
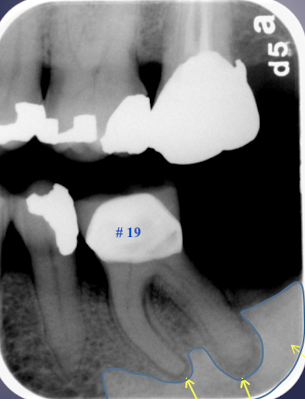
describe the flow of the following: caries and trauma, necrotic pulp. periapical inflammatory disease, osteomyelitis
inflammatory disease mechanism
apical vs periapical
apical: more tip itself vs periapical: broader term
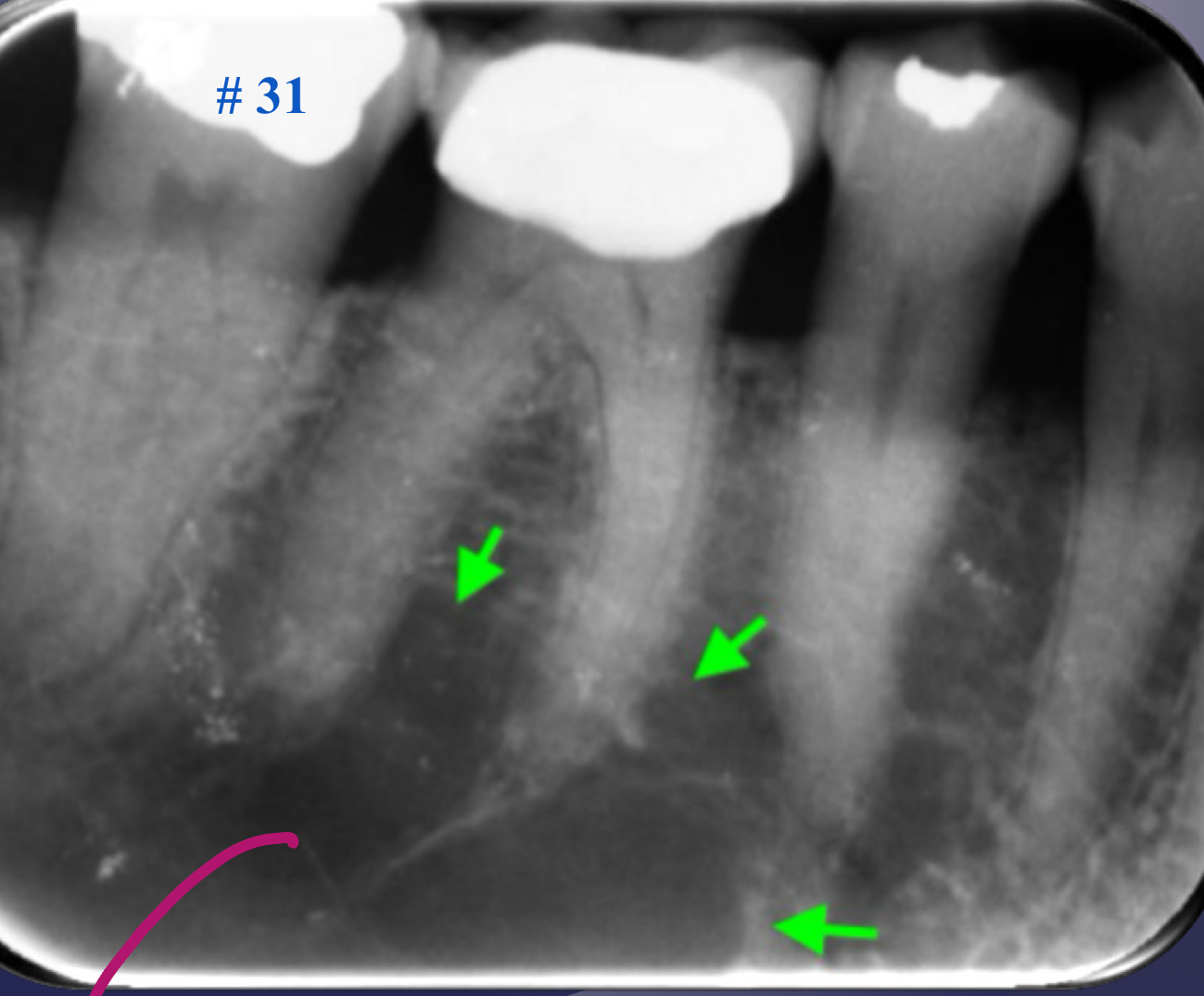
radiographic signs:
widened PDL space
loss of lamina dura
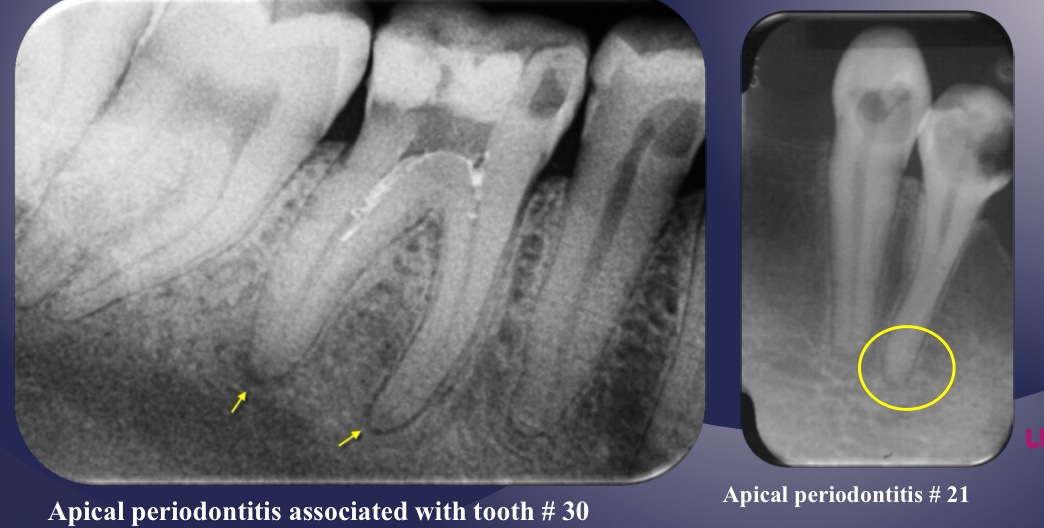
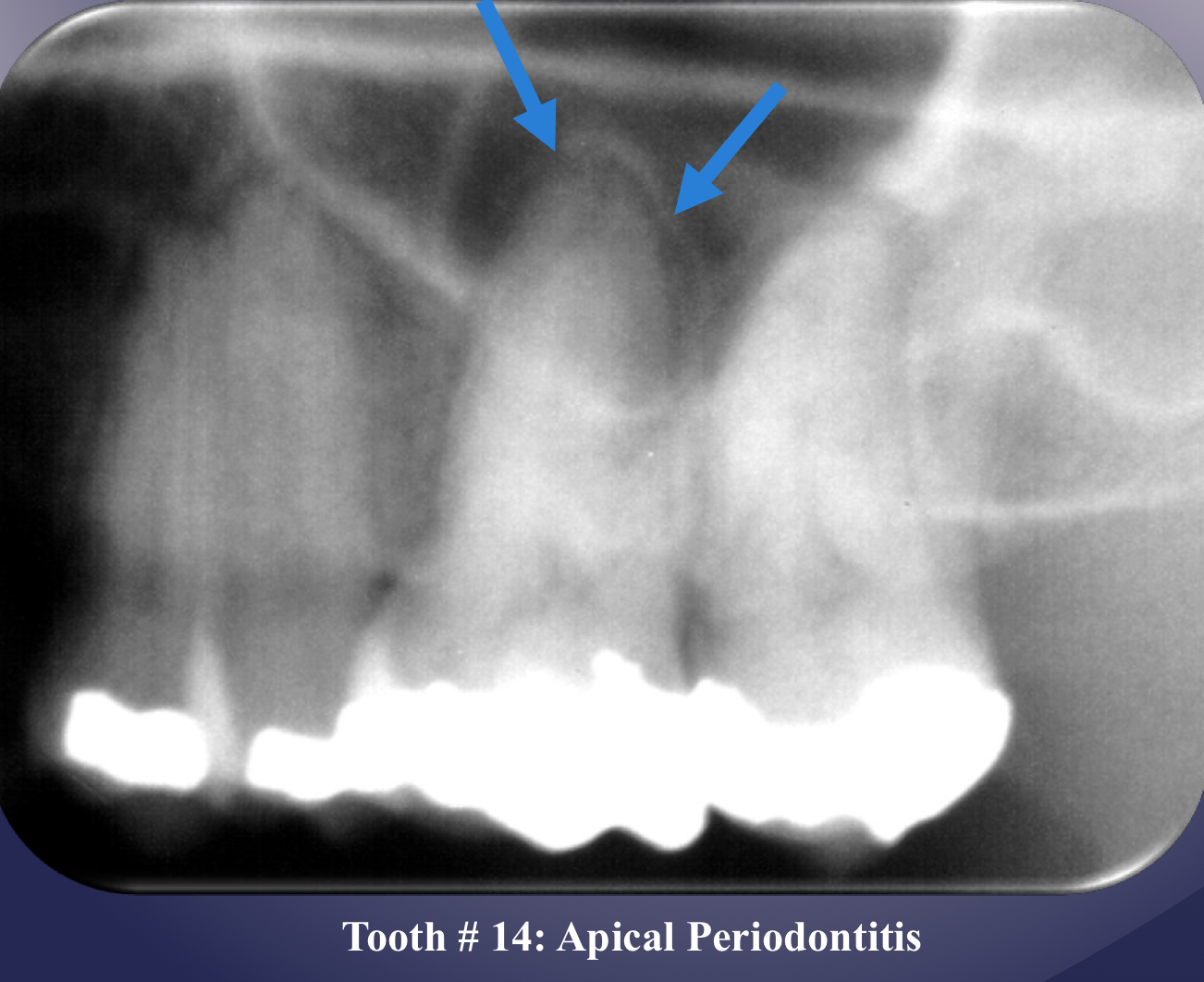
apical periodontitis
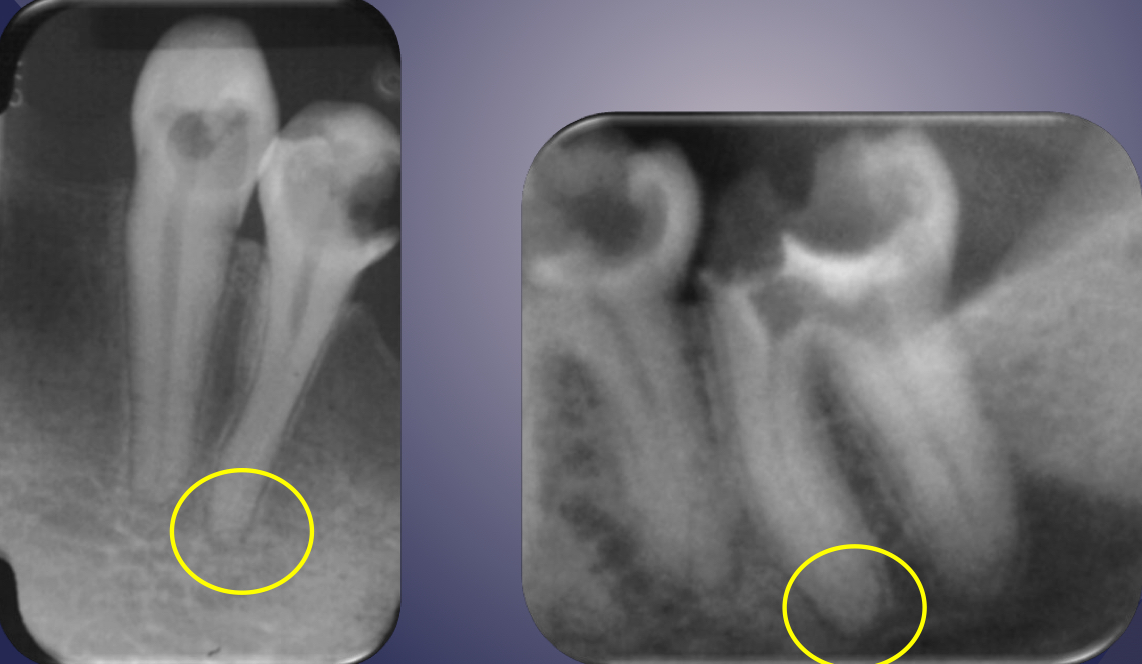
lack of continuous lamina dura, initial sign
apical periodontitis
rarefaction
loss of bone mineral
osteitis
bone inflammation
rarefaction + osteitis = ?
increased radiolucency
loss of bone mineral + osteitis = increased radiolucency
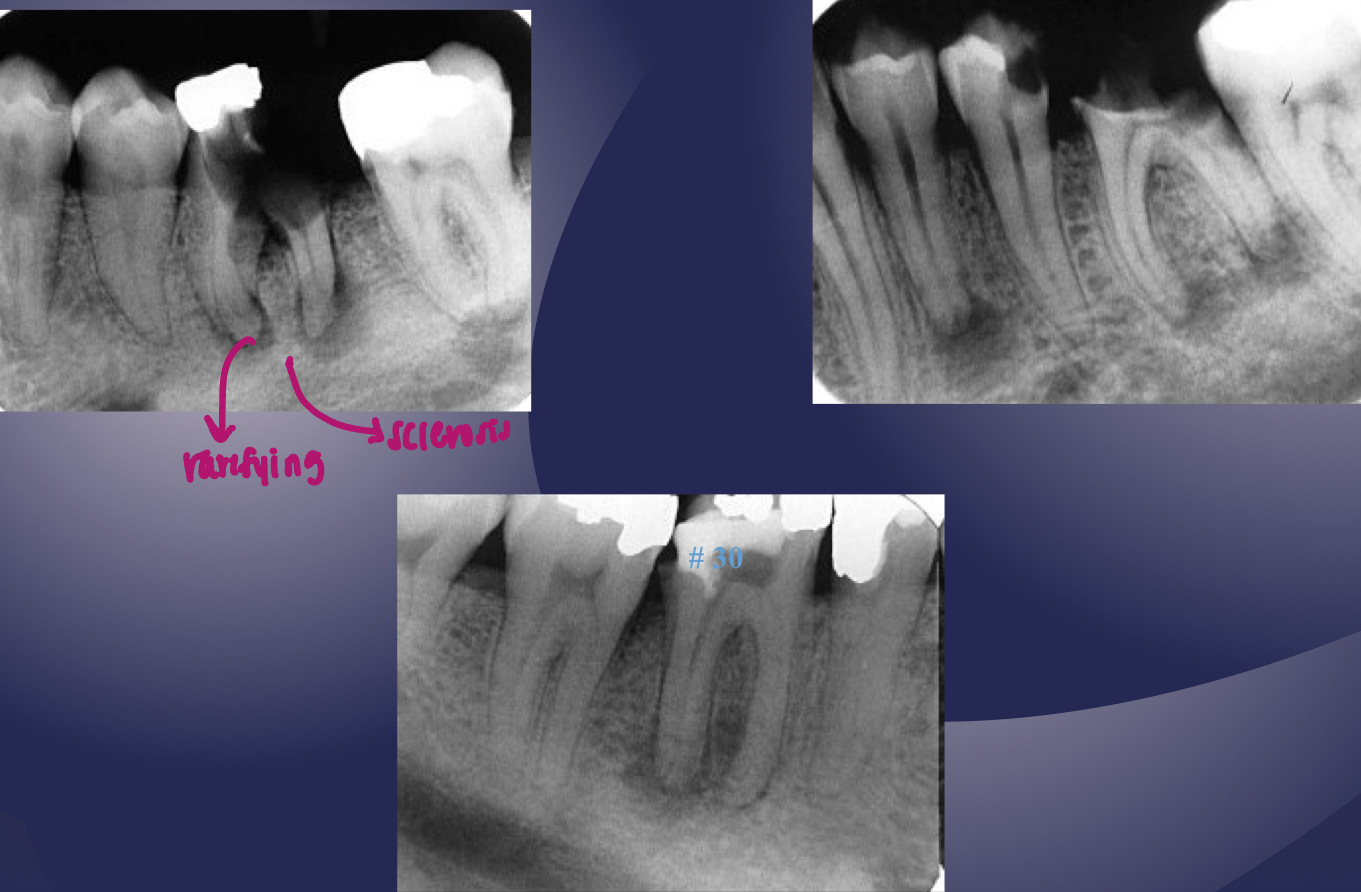
rarefying osteitis
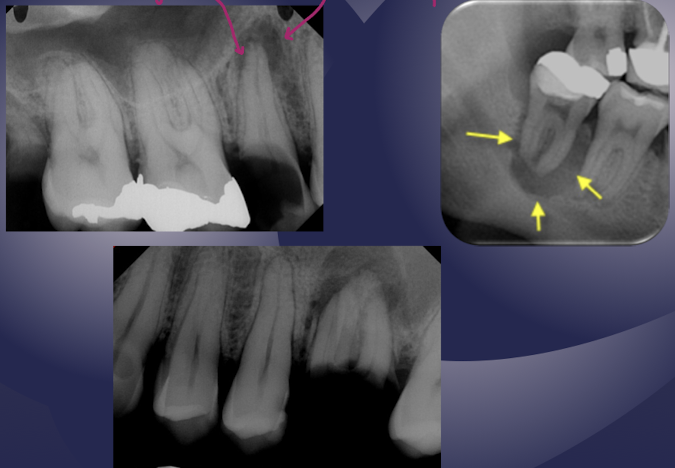
rarefying osteitis (LD gone and radiolucency)
chronic inflam with a non-vital tooth
radiolucent due to removal of bone
sequelae of acute episode
includes abscess, granuloma, or radicular cyst (these three have no distinction radiologically)
rarefying osteitis
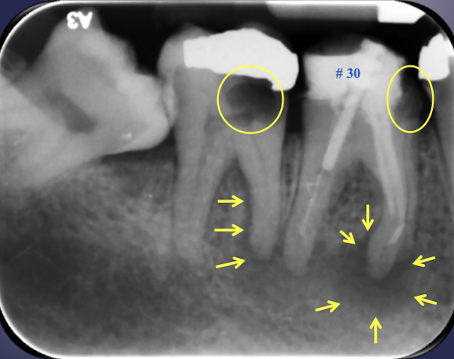
rarefying osteitis
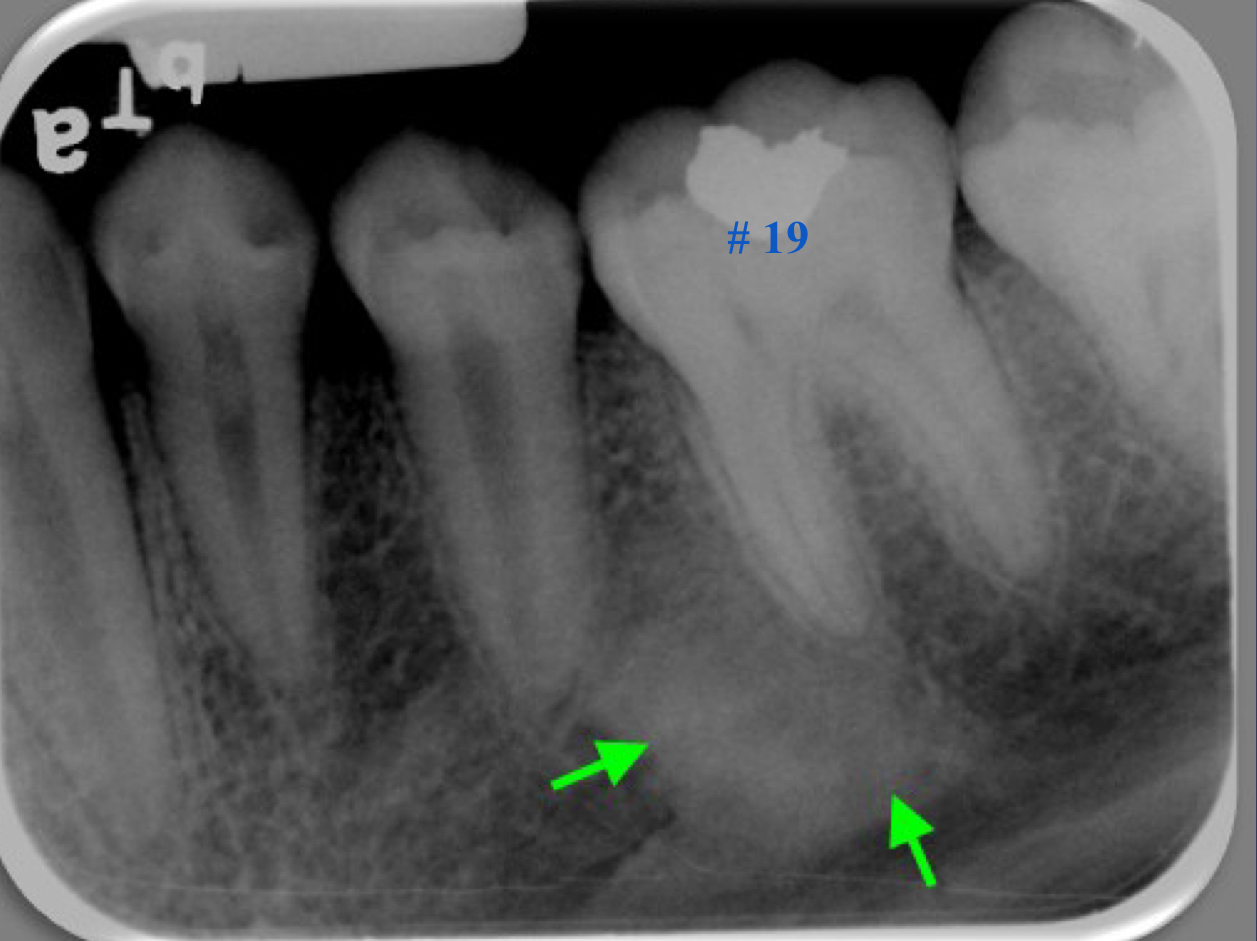
what are other terms for sclerosing osteitis?
focal sclerosing osteitis, condensing osteitis
hardening of the bone; bone deposition increase in radiopacity of bone (plus widened PDL)
sclerosing osteitis
sclerosing osteitis
describe how caries and trauma could lead to periapical abscess vs periapical granuloma
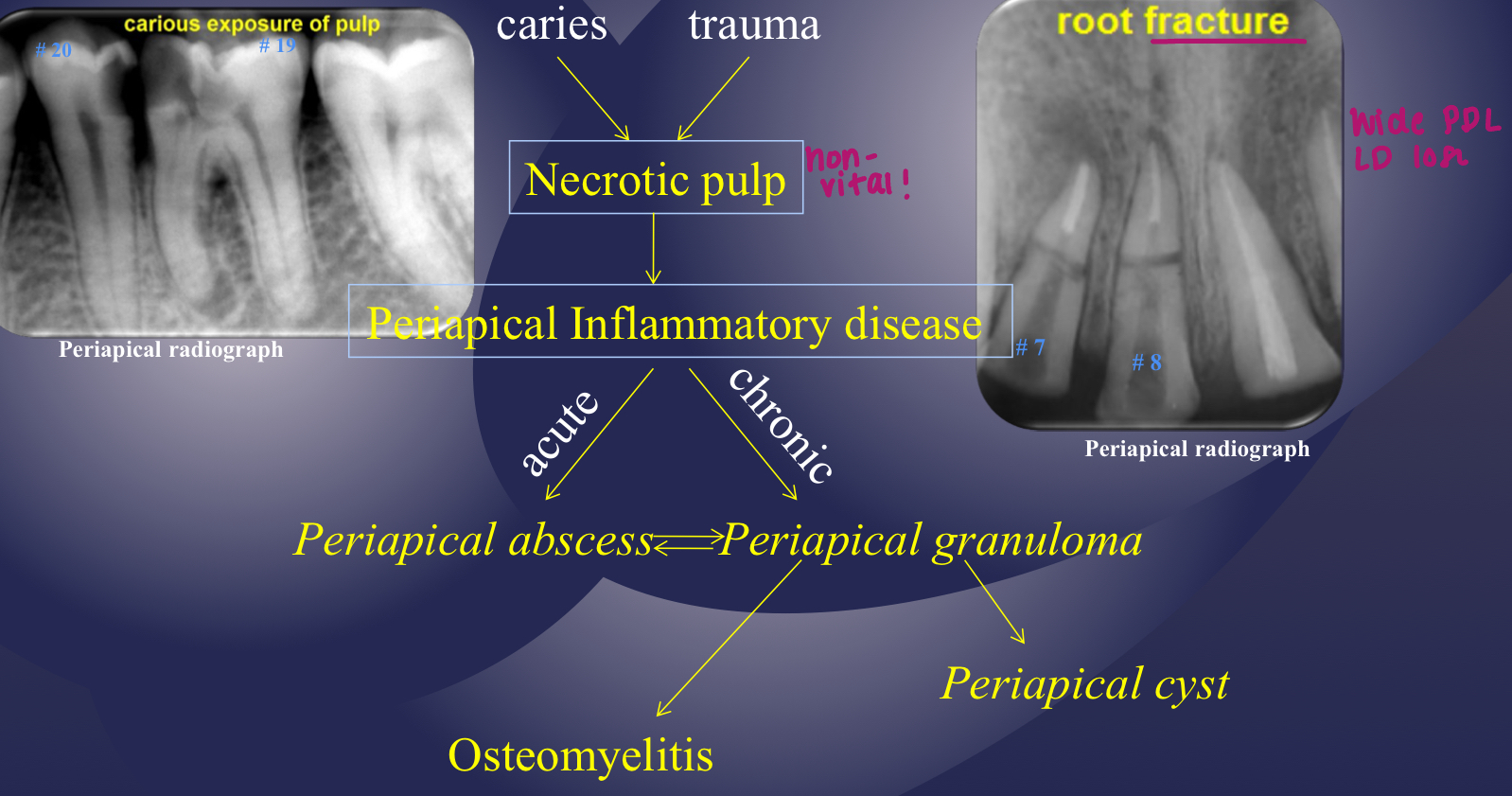
osteomyelitis and periapical cyst can arise from
periapical granuloma (chronic periapical inflammatory disease)
early periapical lesion
widening of PDL space, thickening of LD
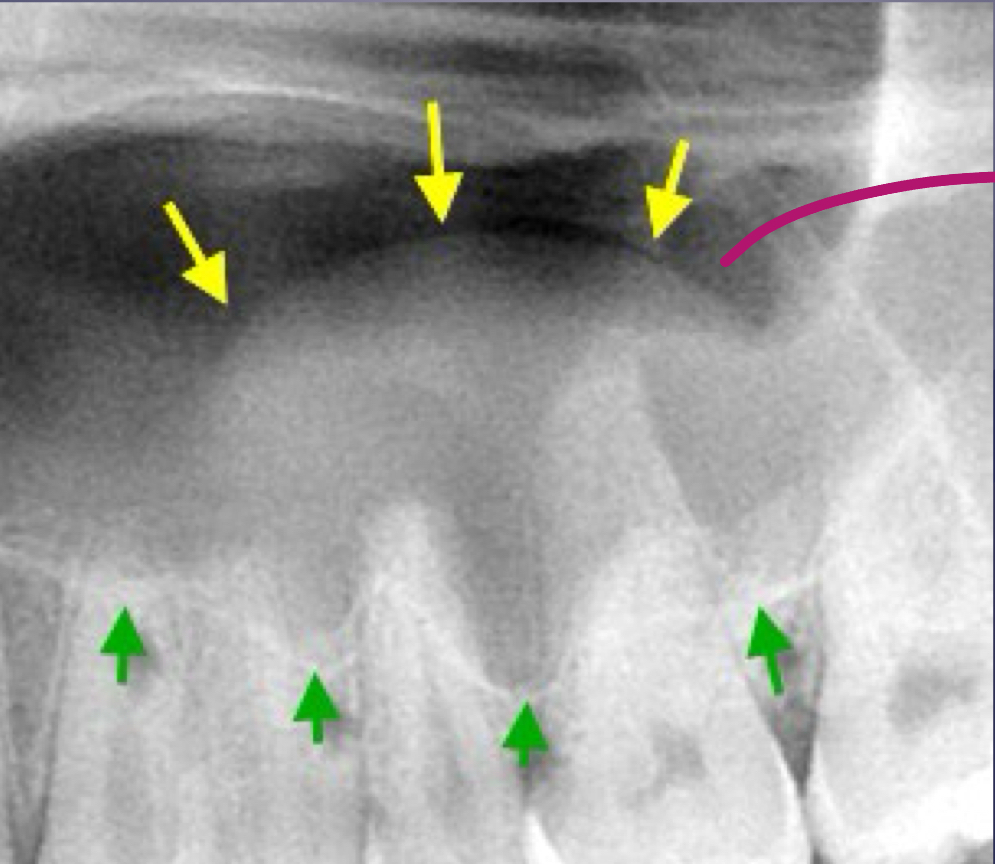
in maxillary M lift floor of max sinus!
what is the location of periapical inflammatory disease?
apical to root apex, adjacent to accessory canal/root fracture. perforation
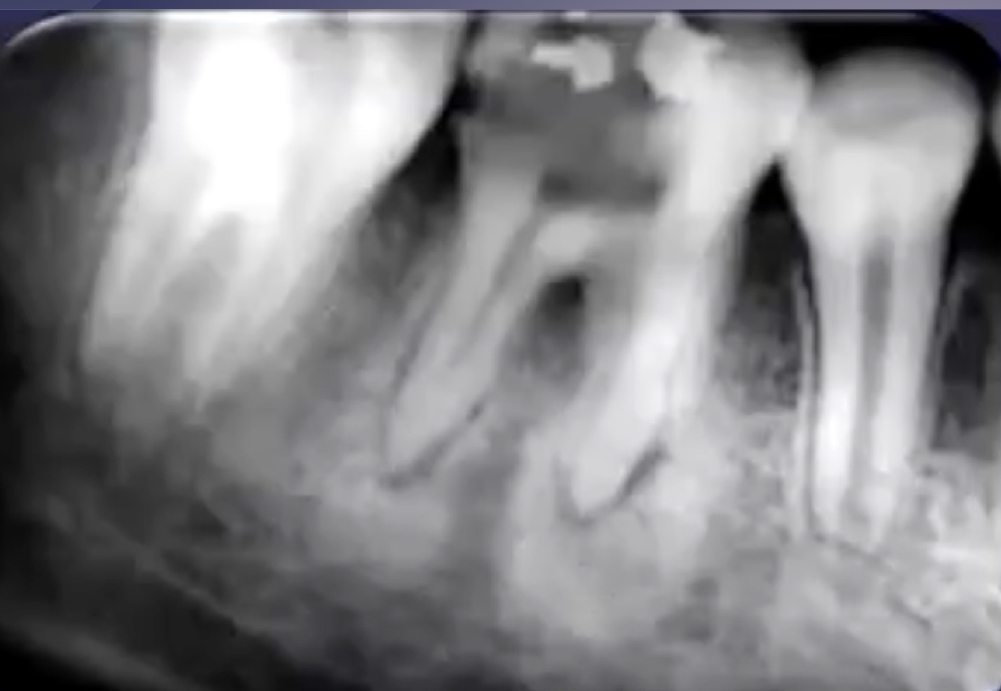
bone deposition around area of rarefaction
sclerosing osteitis + radiolucency
what are the alterations in trabecular bone pattern and marrow spaces of periapical inflammatory diseases?
thicker trabeculae and increase in number
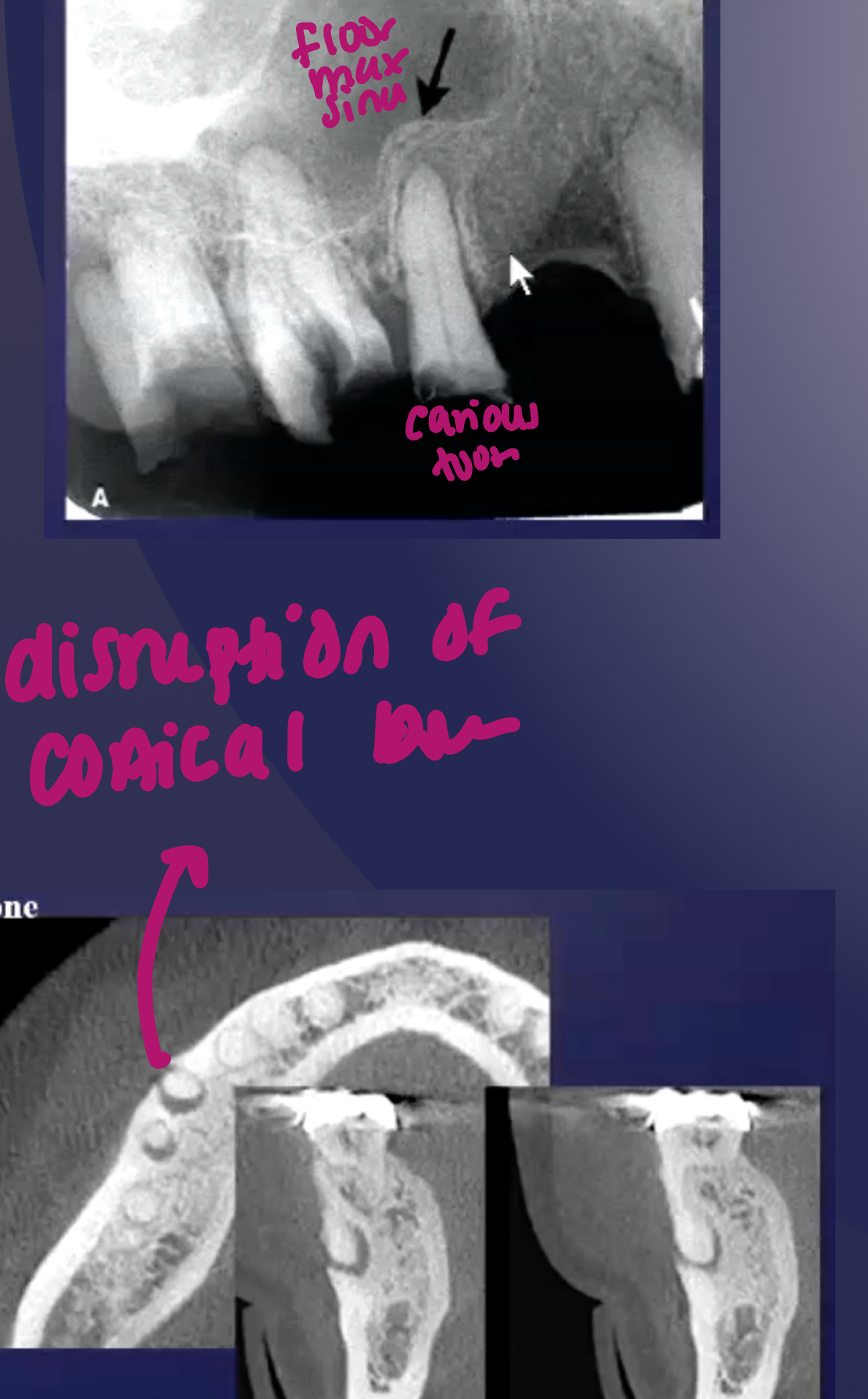
what are some effects of periapical inflammatory disease on surrounding structures?
bone deposition
alteration in trabecular bone pattern and marrow spaces
periosteal new bone formation
perforation of bone border
halo sign
elevation/displacement of floor f maxillary sinus
maxillary posterior teeth
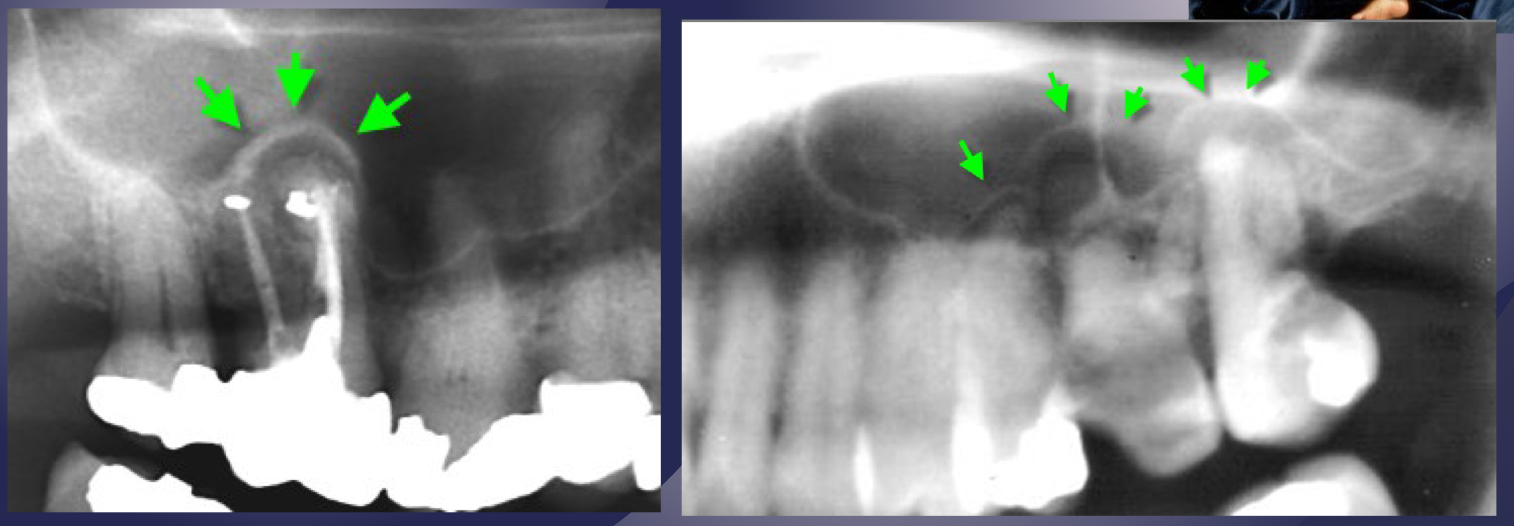
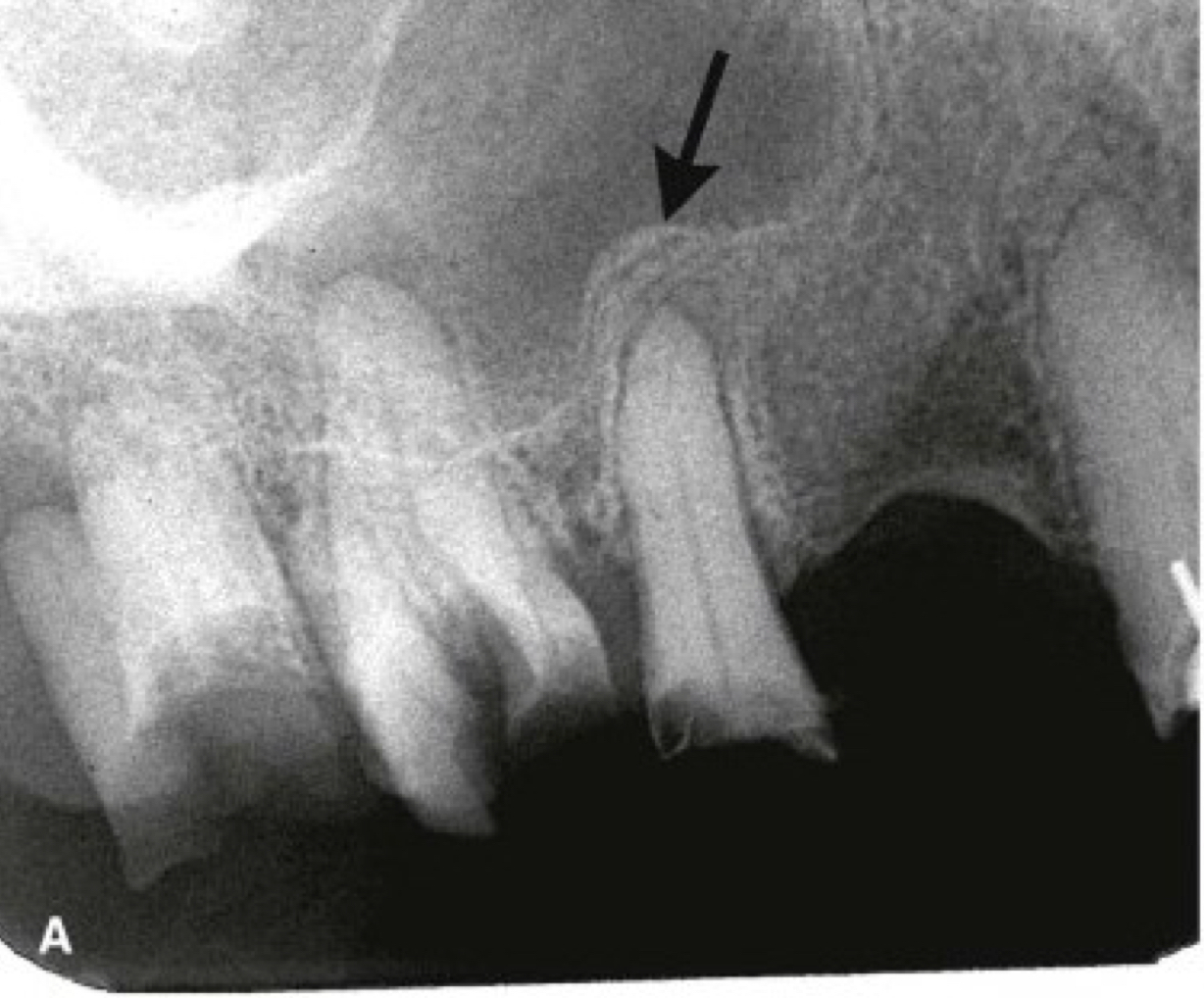
periostitis/onion skin
periostitis, onion skin
periosteal bone formation in floor of maxillary sinus
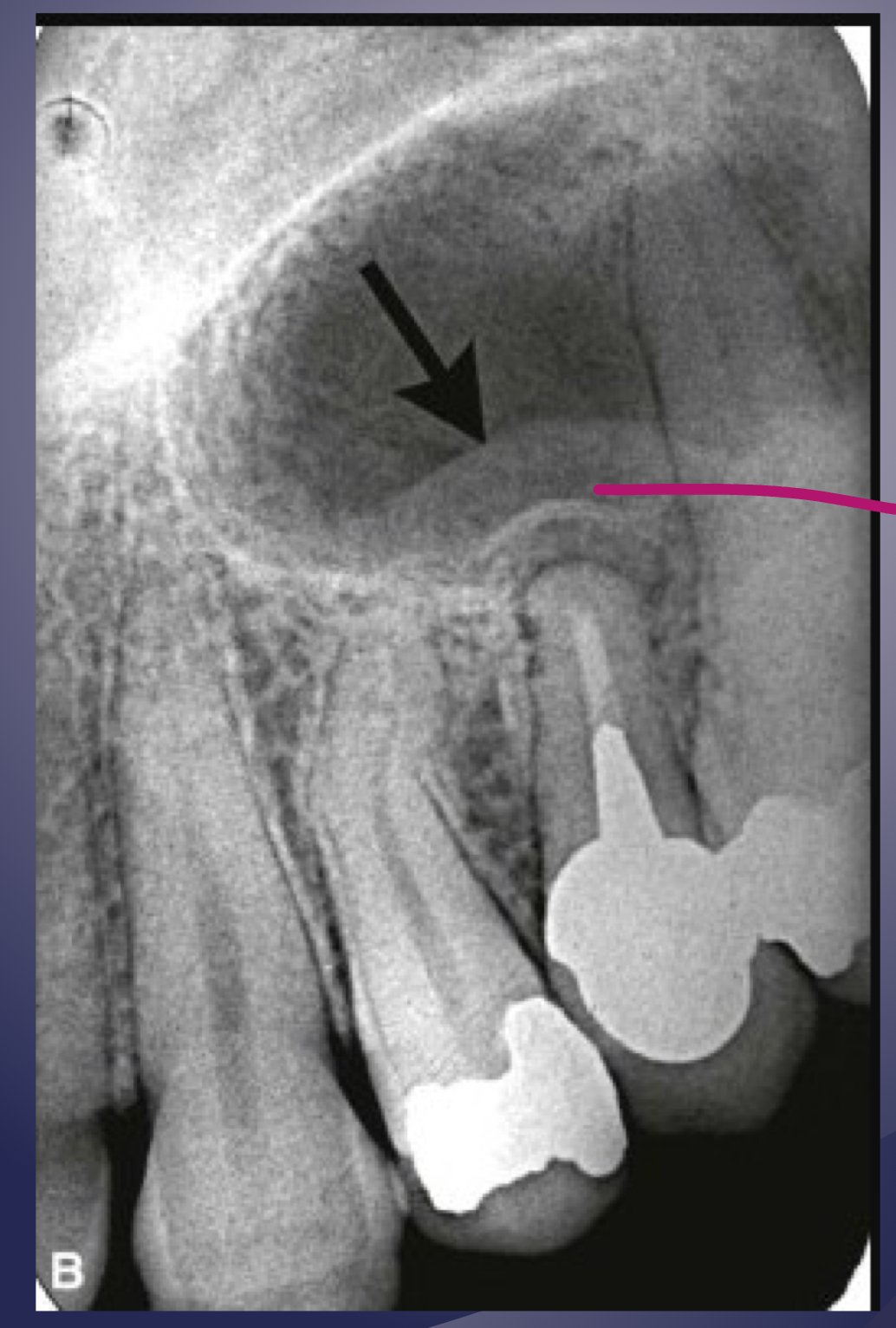
periostitis and mucositis
mucosal thickening
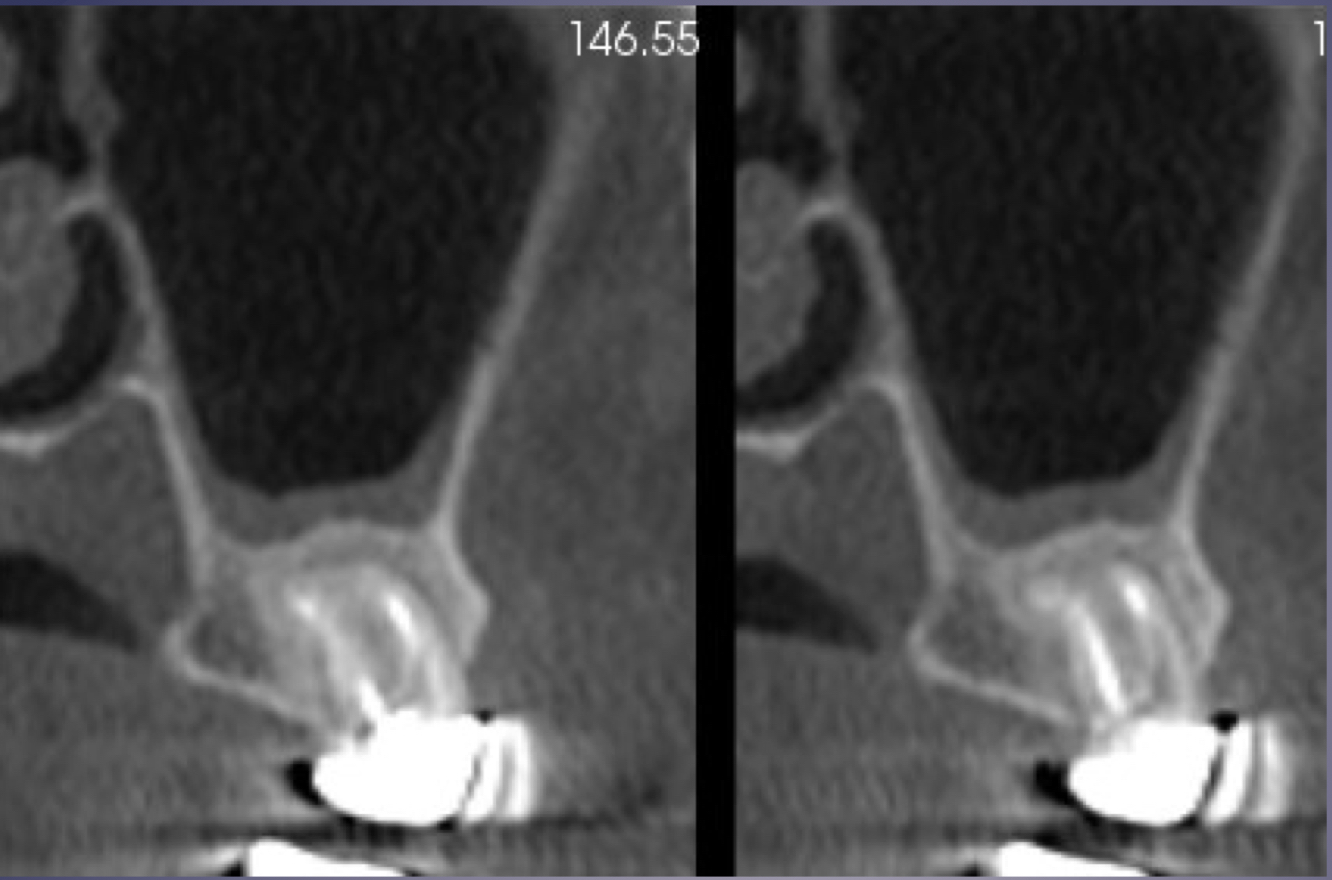
mixture of rarefying and sclerosing osteitis
no pathology, submandibular gland fossa
dense bone island of vital tooth, no widening of PDL; inositiosis just extra bone w/in two plates of cortical bone
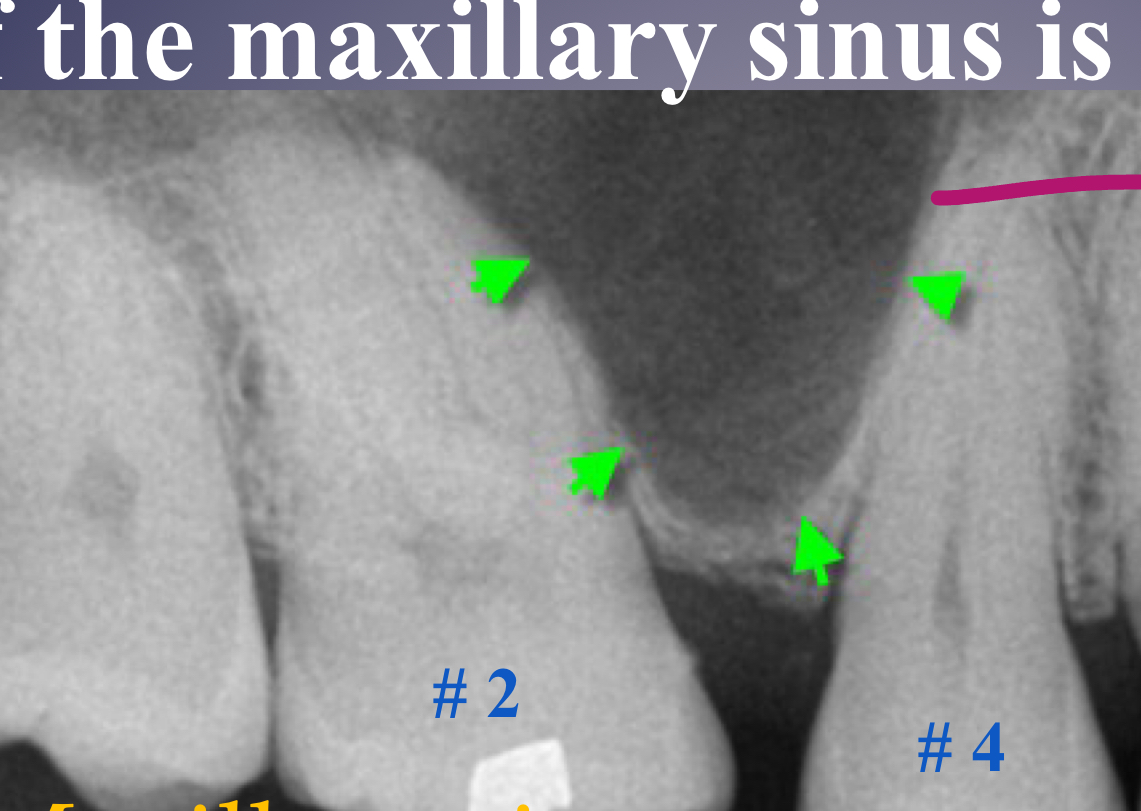
maxillary pneumatization
mucus retention cyst
what are some potential results of periapical inflammation that all present identically radiographically?
parulis aka gum boil
periapical granuloma
periapical cyst
periapical abscess
condensing osteitis
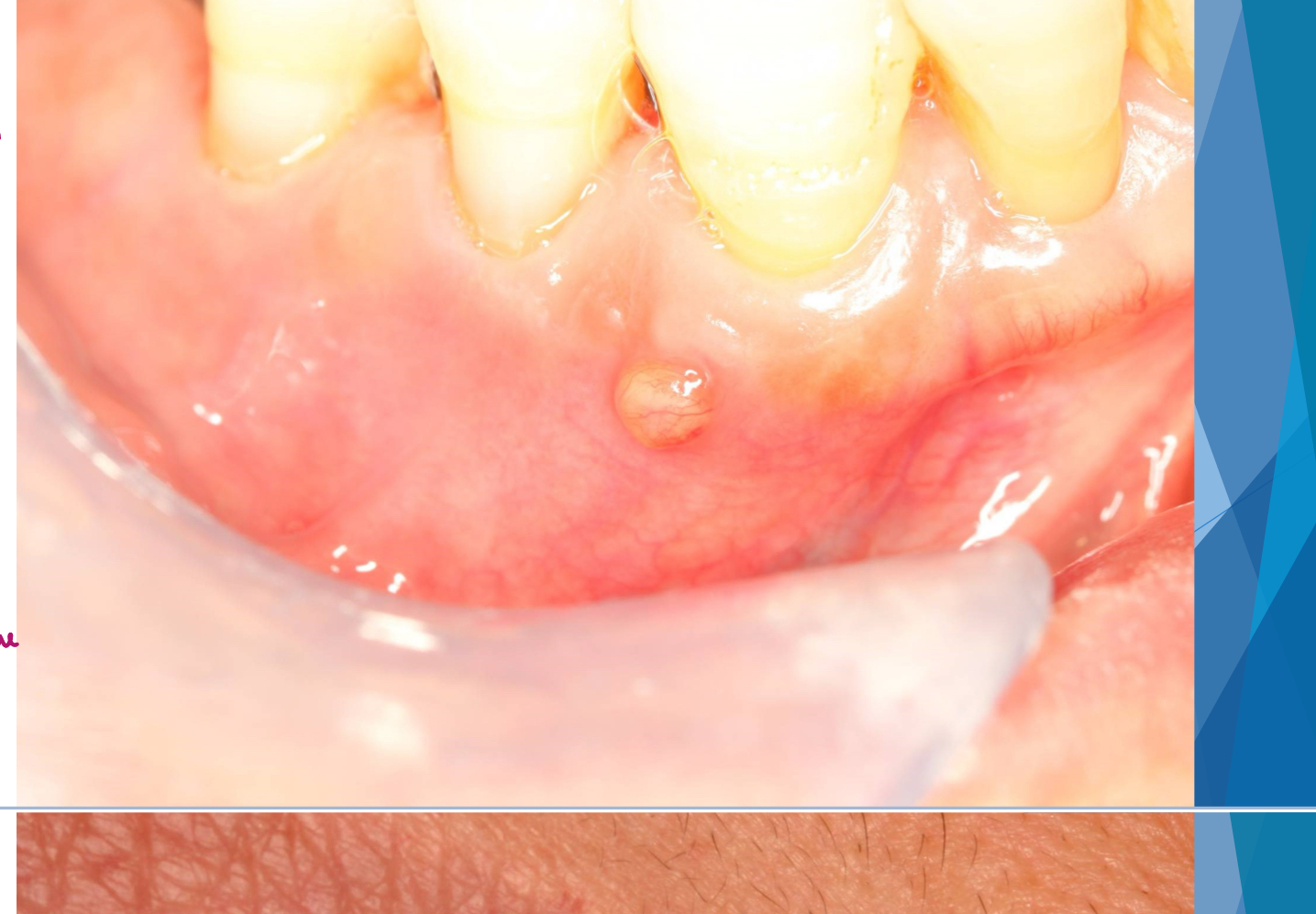
gum boil
parulis
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
inflamed granulation tissue at intraoral opening of sinus tract
classically dome-shaped yellow-pink papule; rarely hyperplastic soft tissue mass that may mimic pyogenic granuloma or other pathology ie exophytic hyperplastic perulis on adj tooth assocxiated w non-vital tooth
usually on gingiva facial to non-vital tooth
may or may not exhibit active suppuration
parulis
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
parulis
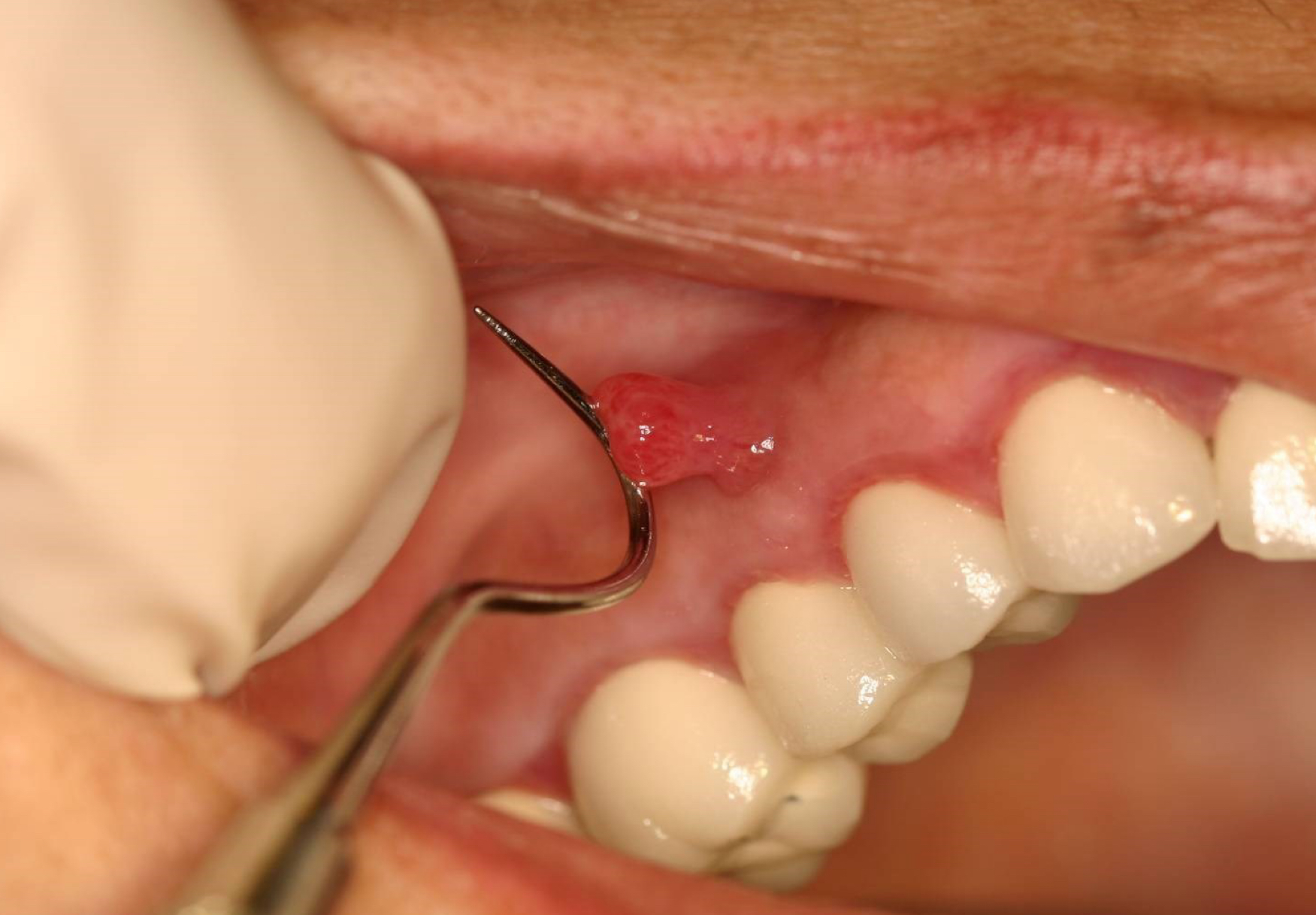
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
parulis; not easy to pulp test teeth that are equidistant to this sinus tract extrusion

what is the problem with the naming of periapical granuloma?
this is not a true granuloma
granuloma: collection of immune cells around foreign body/infection
granulation tissue: newly formed tissue around injury
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
histopathological features:
granulation tissue surrounded by fibrous CT
tissue from apex of non-vital tooth socket
lymphocytic infiltrate may be intermixed w neutrophils, plasma cells, histiocytes, and occasionally mast cells or eosinophils
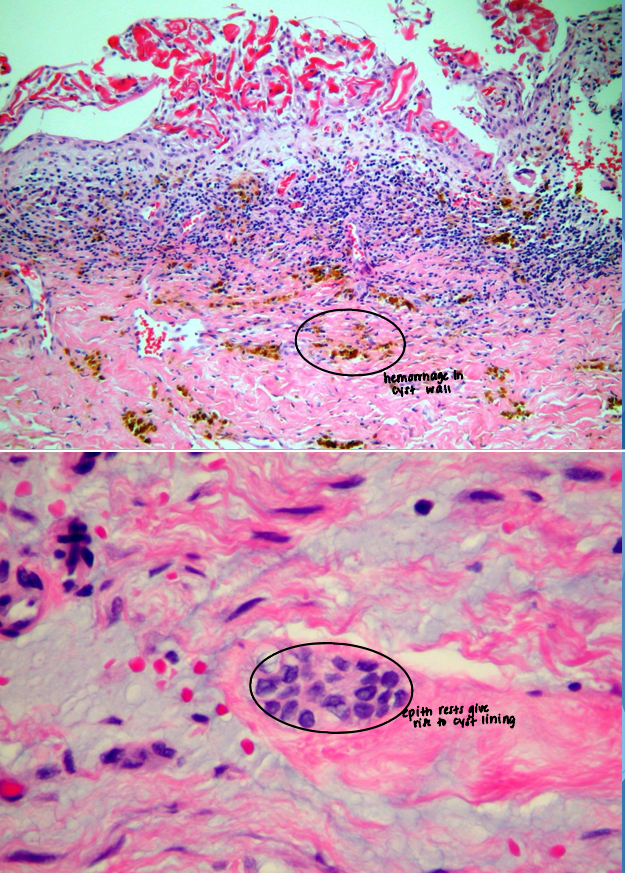
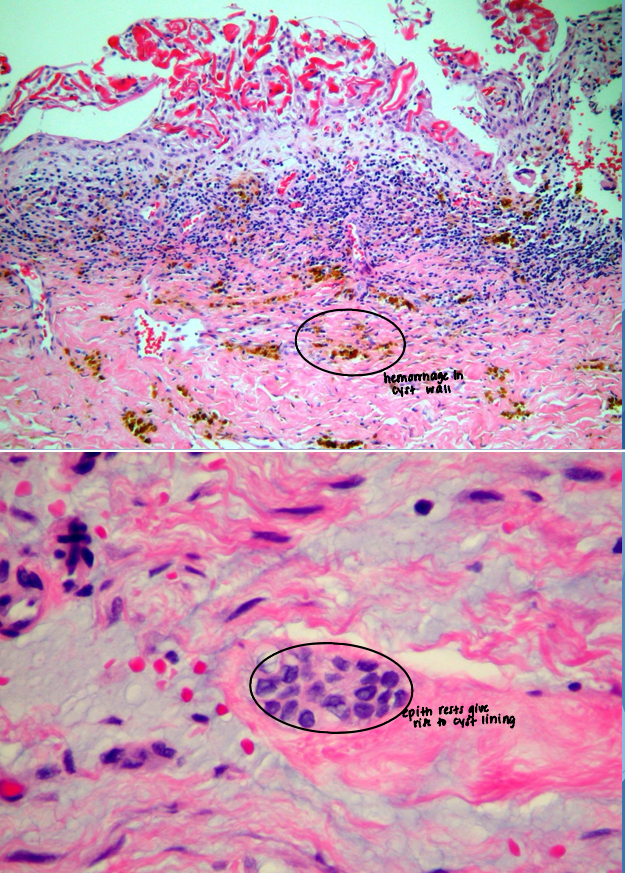
periapical granuloma
apical radicular cyst aka
periapical cyst
define a cyst
pathological cavity lined by epithelium

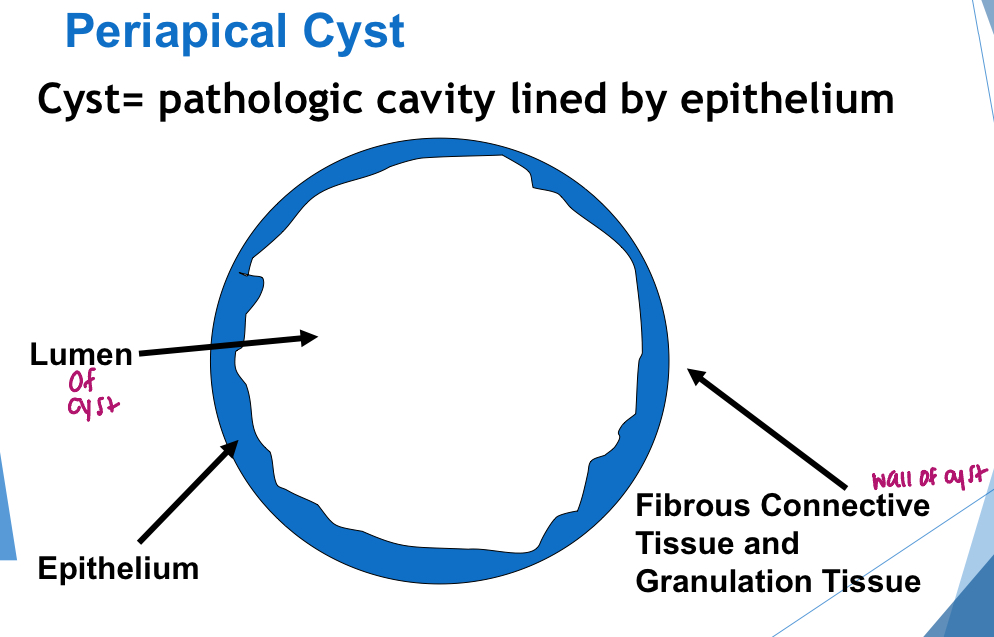
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
most common odontogenic cyst
epithelium at apex of non-vital tooth may be stimulated to form cystic lining
usually derived from rests of Malassez
lateral variant may develop along lateral aspect of root at orifice of accessory canal (necrotic root)
mimics lateral periodontal cyst
may give rise to residual (BLANK)
periapical cyst
which is the most common odontogenic cyst?
periapical cyst
what are rests of Malassez?
clusters of epithelial cells in the periodontal ligament that are remnants of the Hertwig's epithelial root sheath left over from tooth development; maintain health of perio tissue health
usually develop at apex but a lateral accessory canal could lead to lateral tooth root growth (necrotic root)
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
histopathological features:
lining of cyst composed of stratified squamous epithelium
wall of cysts consists of dense fibrous tissue w inflammatory infiltrate
periapical cyst
what is the only thing that can differentiate periapical cyst from periapical granuloma?
presence of epithelium
which potential result of periapical inflammation shows acute symptoms?
periapical abscess unlike cyst and granuloma
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
accumulation of acute inflammatory cells at the apex of non-vital tooth
may arise as initial form of pathosis or fro acute exacerbation of chronic periapical inflammatory lesion (phoenix abscess)
phoenix abscess
a sudden, painful flare-up of a long-standing, often silent, dental infection. It occurs when a chronic periapical abscess, which may be asymptomatic, becomes acute, presenting with symptoms like severe pain, swelling, and pus
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
clinical features:
non-specific symptoms may include headache, fever, malaise, chills
tenderness of affected tooth
abscess may spread through bone (osteomyelitis) or perforate cortex and spread through soft tissue (cellulitis)
periapical abscess
T or F: periapical abscesses are typically fluctuant, meaning you can displace with finger
true
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
histopathological features:
acute inflammatory cells, cellular debris, necrotic material, and bacterial colonies
phoenix may include soft tissue component
periapical abscess
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
treatment and prognosis:
drainage
elimination of infection
antibiotics for medically compromised patients
periapical abscess
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
localized area of bone sclerosing
condensing osteitis
condensing osteitis
aka focal sclerosing osteitis (radiopaque)
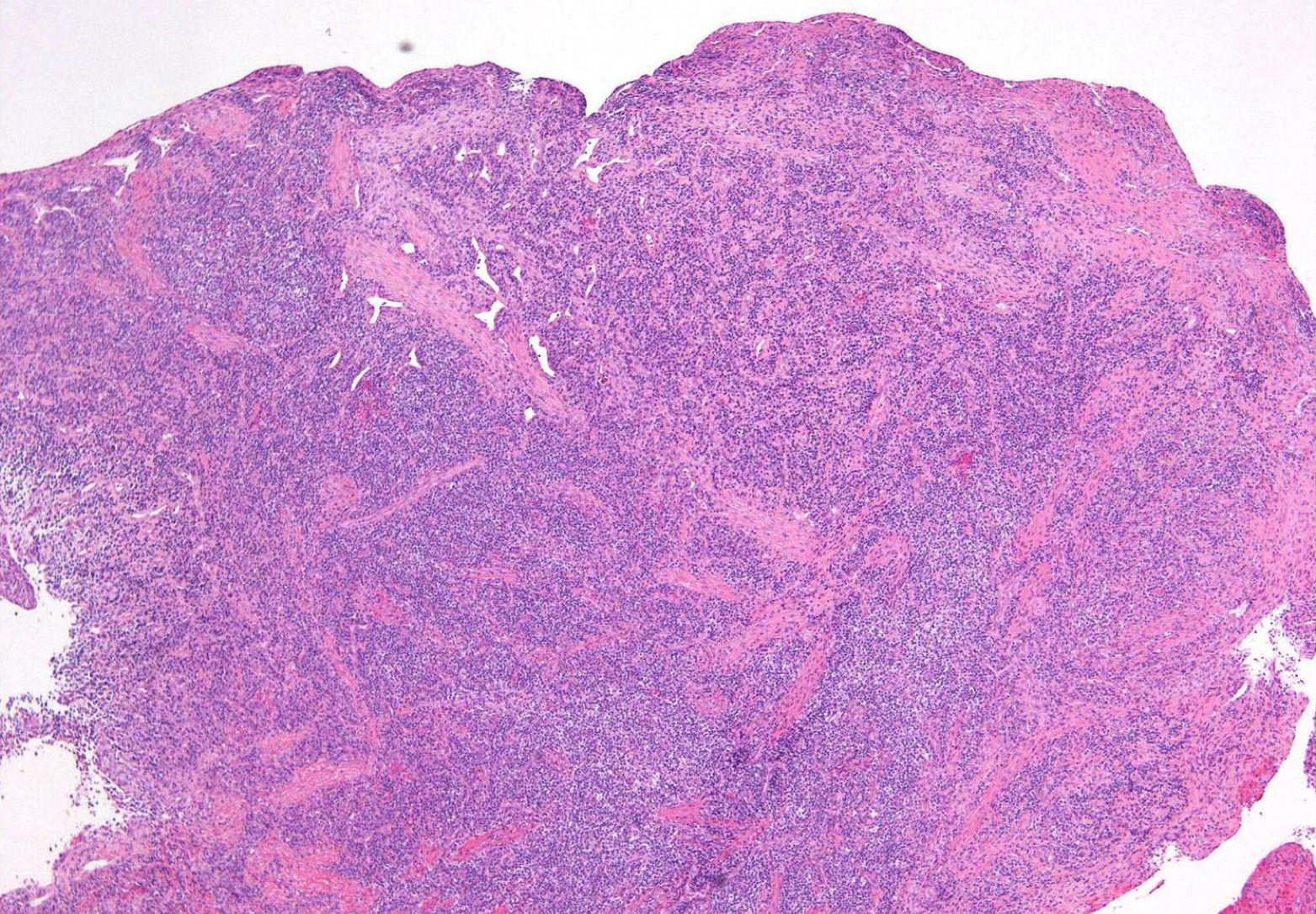
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
periapical granuloma; granulation tissue w neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, vascular channels
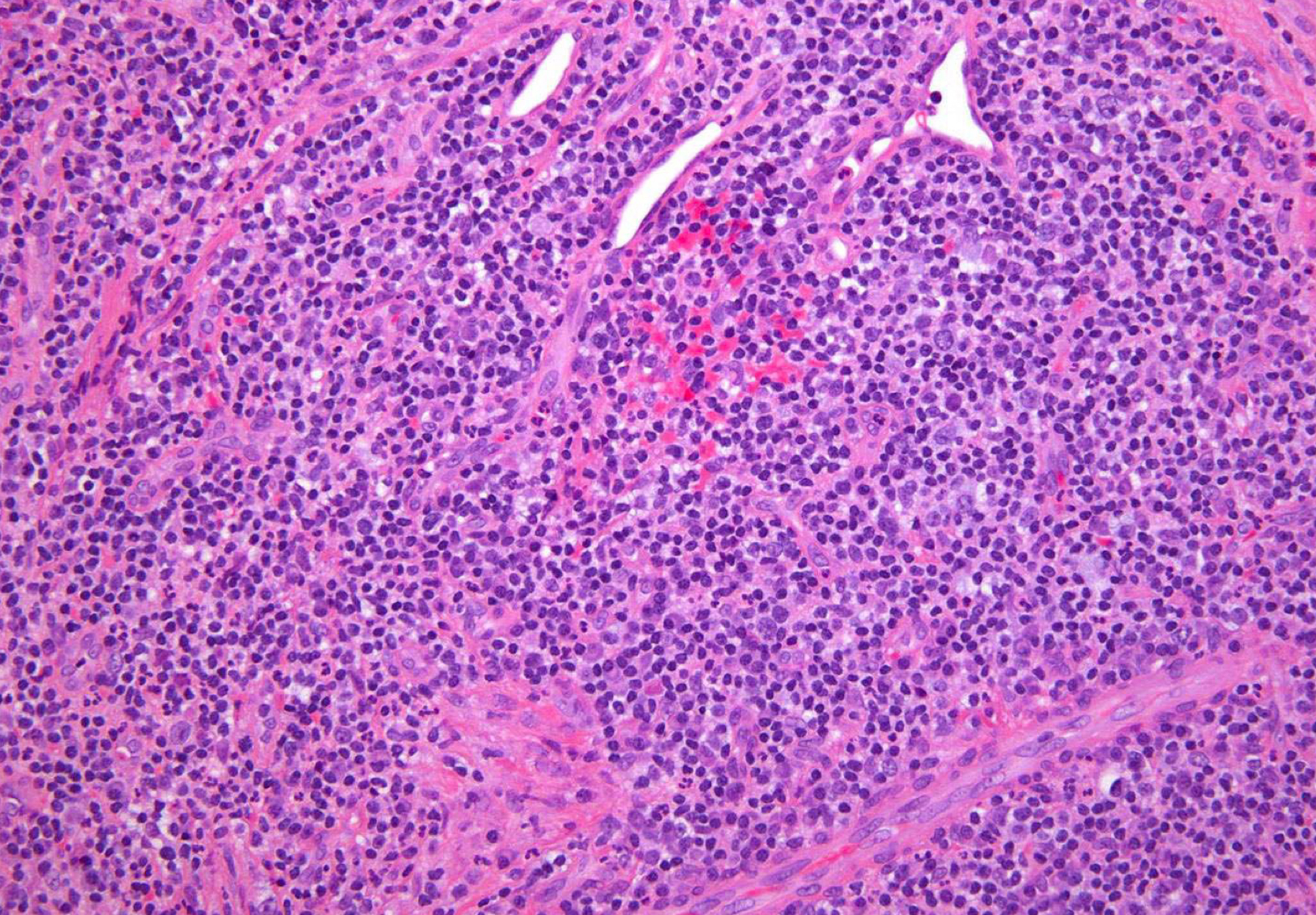
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
periapical granuloma; fibroblasts
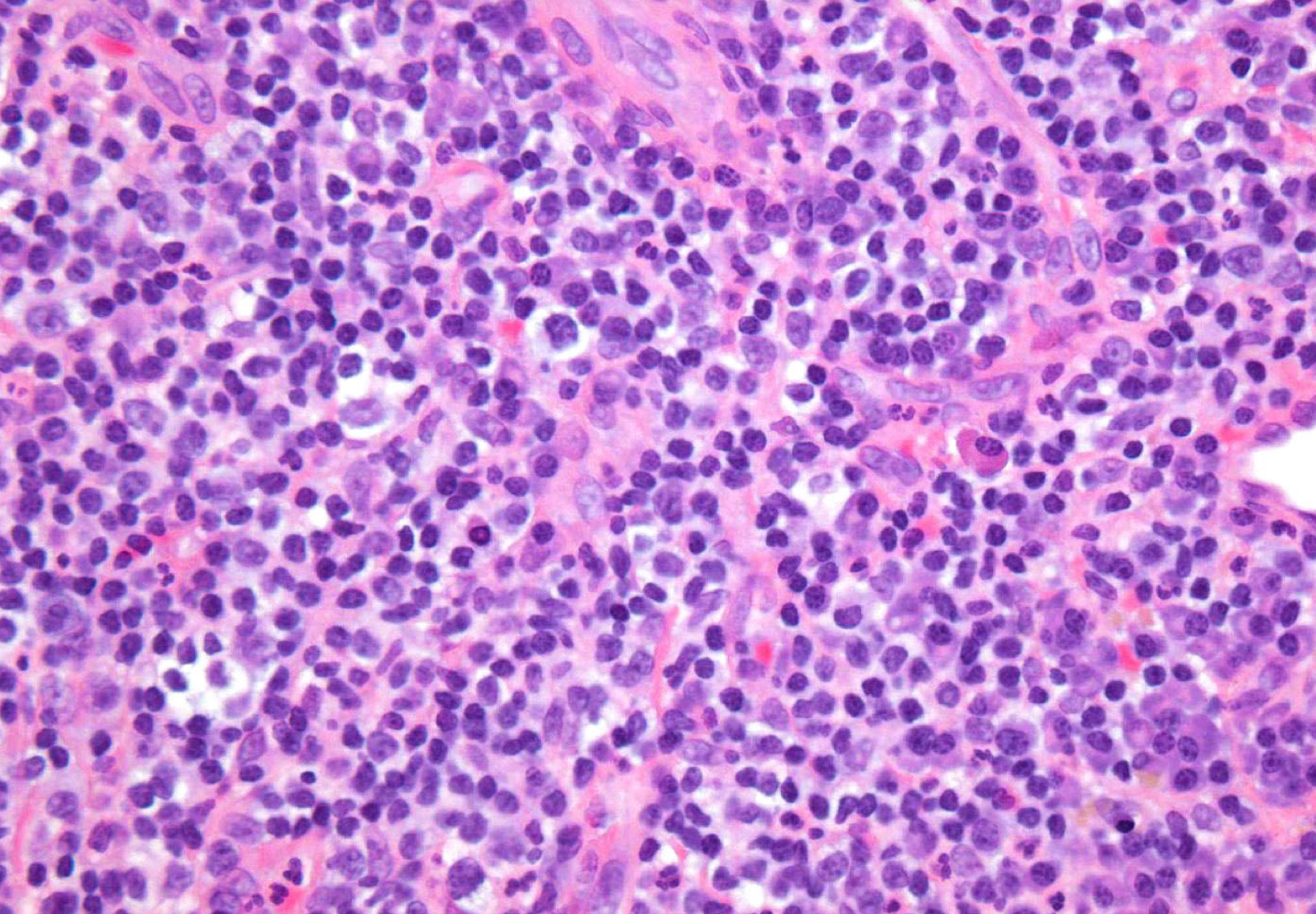
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
periapical granuloma; lymphocytes
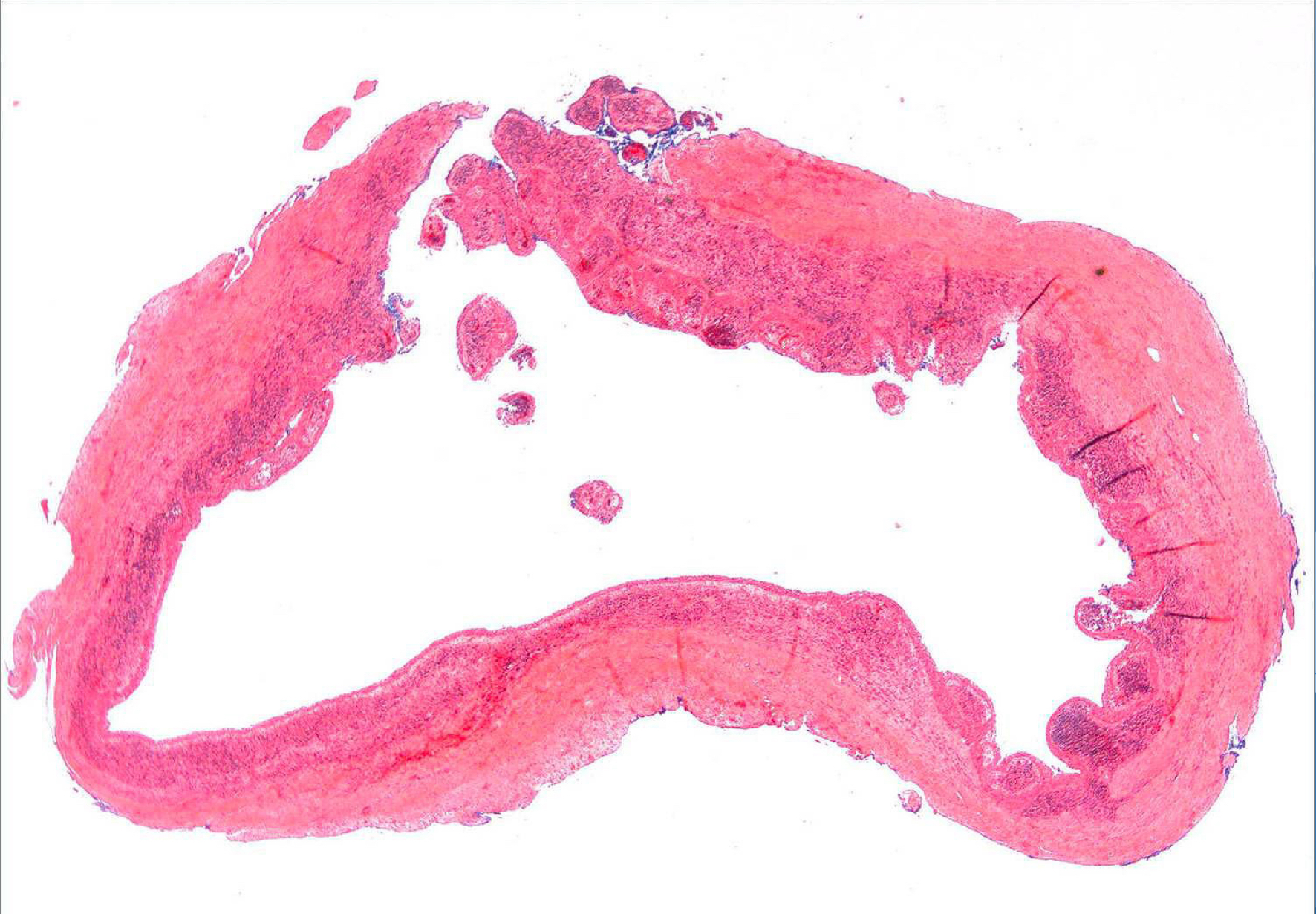
periapical cyst
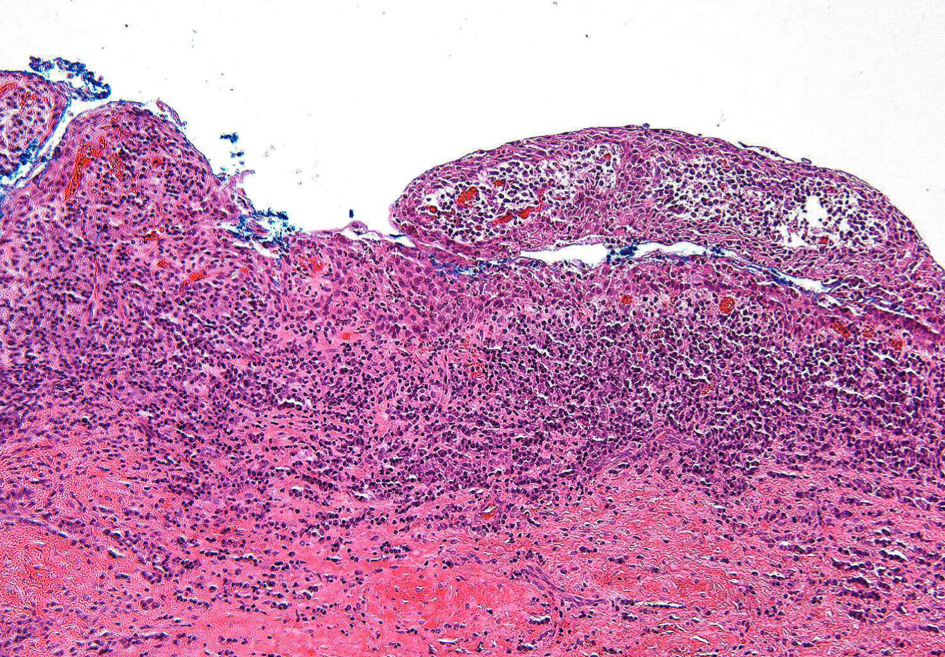
periapical cyst
periapical cyst
what gives rise to lining of a cyst?
epithelial rests
periapical cyst
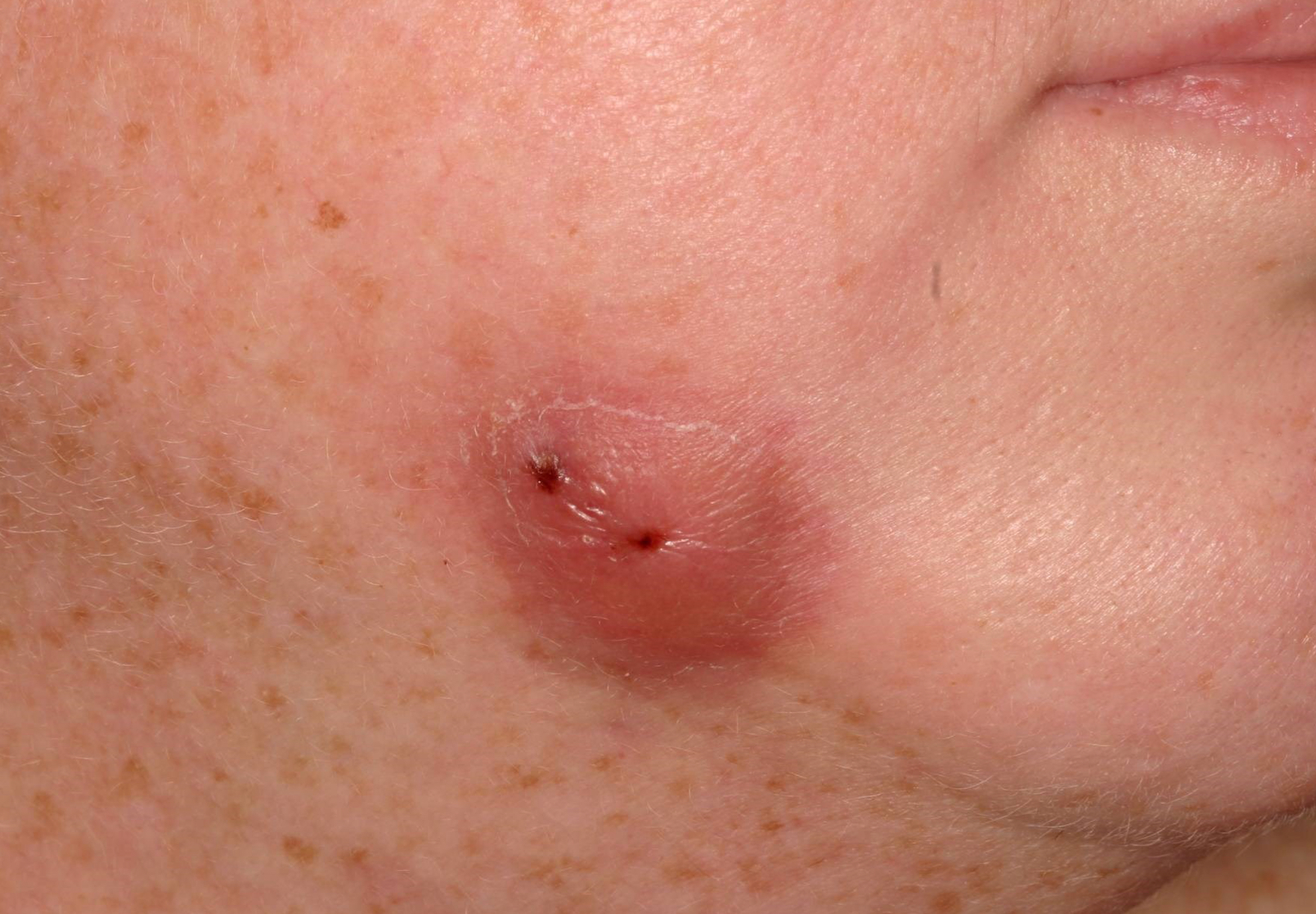
periapical abscess (sinus tract spread extraorally)
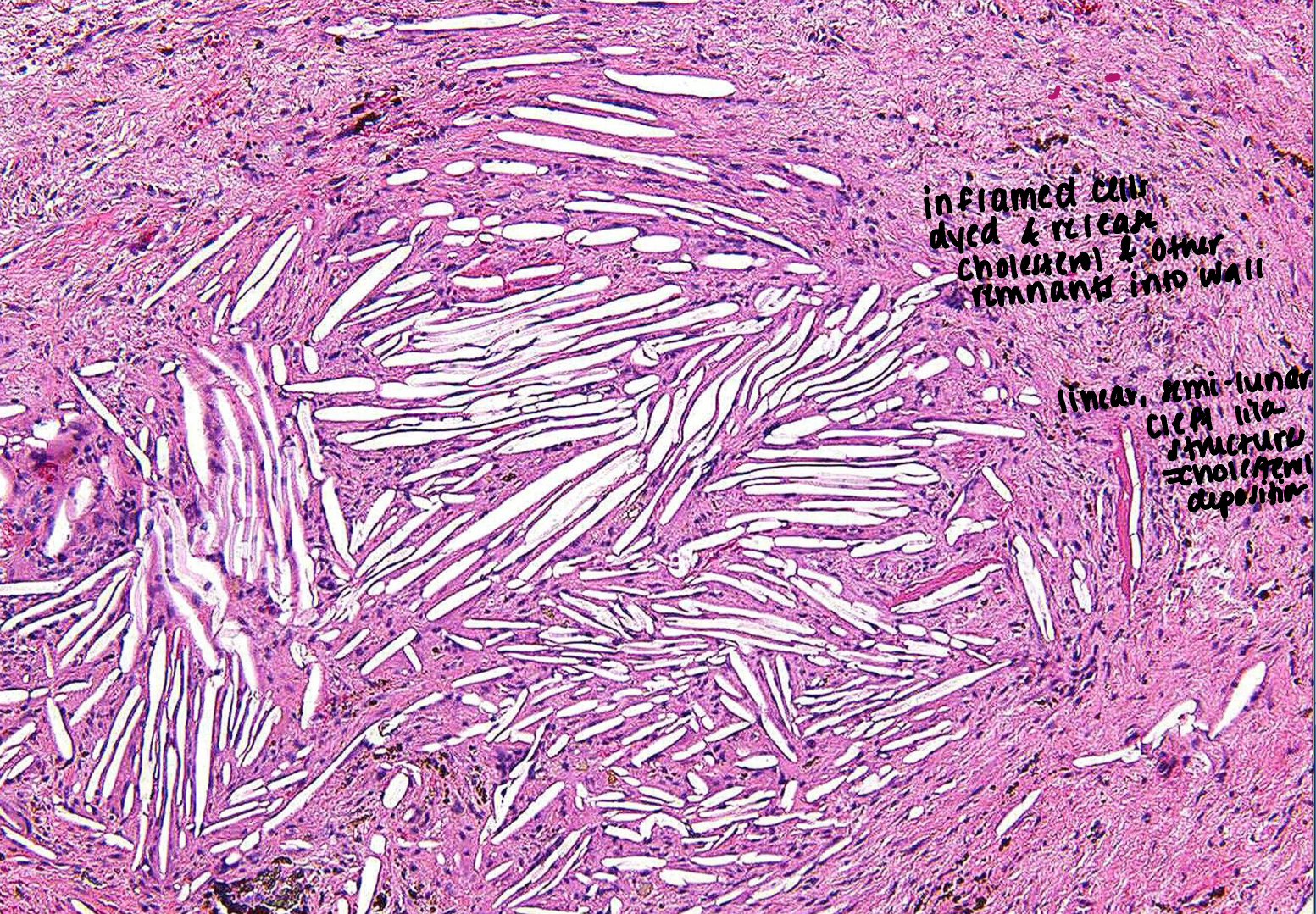
sclerotic bone = mineralized tissue vs granular tissue - less dense
condensing osteitis
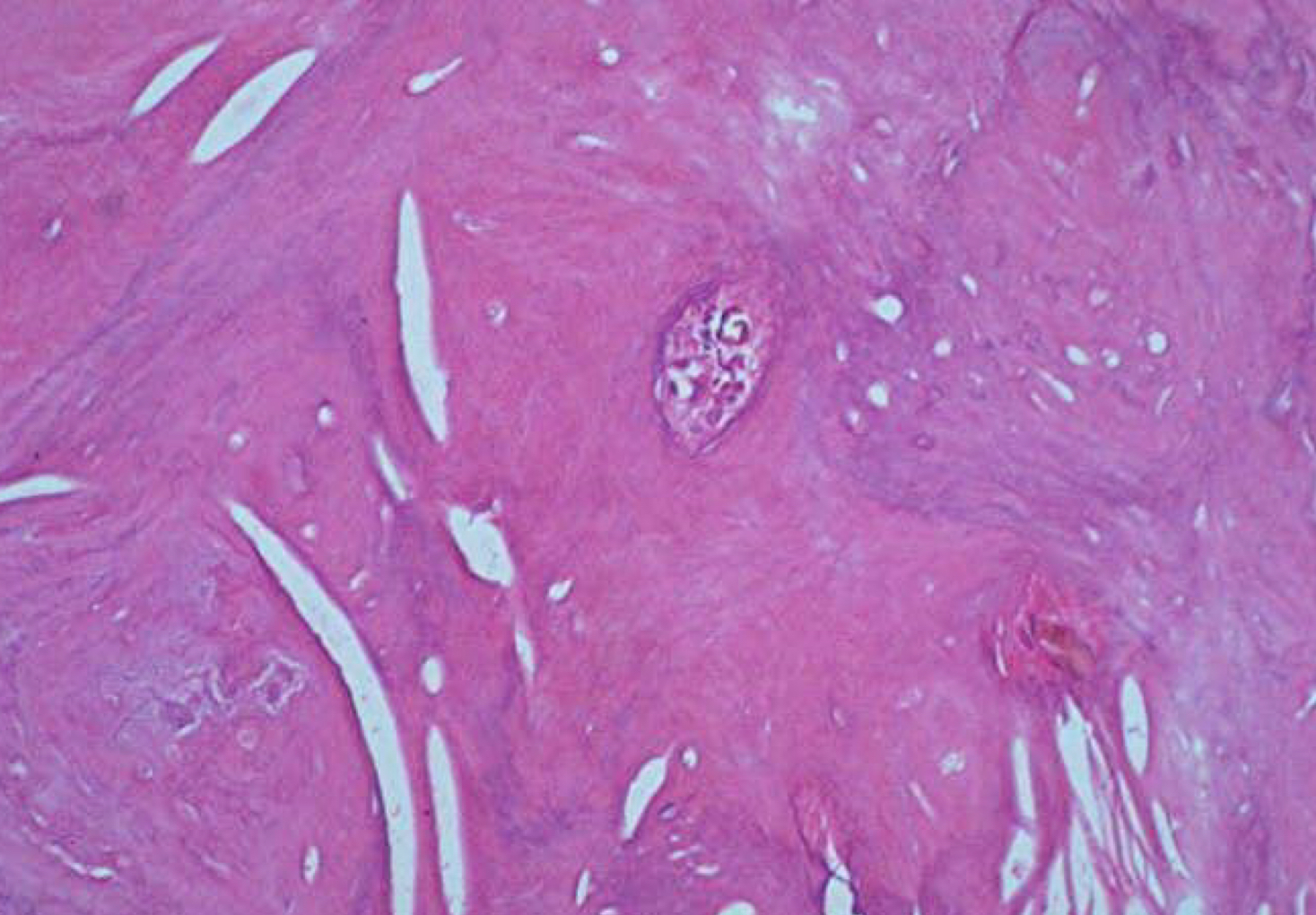
condensing osteitis
which potential result of periapical inflammation?
treatment:
endodontic therapy or extraction of offending tooth
85% of cases will resolve or regress
bone scar may result following resolution of inflammation
condensing osteitis
what are treatment options and possible prognosis for non-vital teeth?
root canal therapy
non-restorable teeth treated w extraction and curettage of apical tissue
periapical fibrous scar may form in area of defect, especially if cortical plates have been lost
rare recurrences
untreated cysts may give rise to squamous cell carcinoma
why choose root canal for treatment of non-vital teeth?
persistent lesions treated w periapical surgery and submission of tissue for microscopic examination
what is the rationale for treatment of all periapical pathology?
untreated cysts may give rise to squamous cell carcinoma
what is chronic hyperplastic pulpitis?
pulp polyp
unique pattern of pulpitis sometimes seen in children and young adults w large pulp exposures (usually primary molars)
hyperplastic granulation tissue extrudes from pulp chamber
asymptomatic
chronic hyperplastic pulpitis usually affects (primary) molars
true
chronic hyperplastic pulpitis is asymptomatic
true
treatment of chronic hyperplastic pulpitis?
endo or extraction
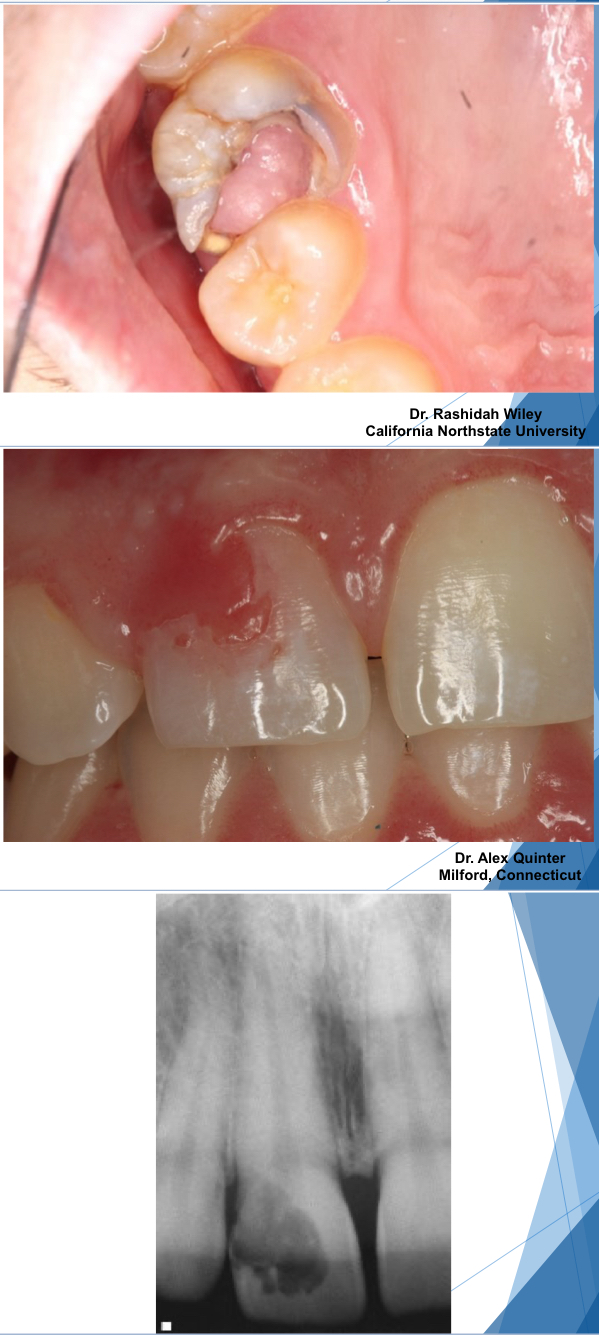
chronic hyperplastic pulpitis