Chemistry - Unit 1-7
1/370
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
371 Terms
Exothermic reaction
a reaction that releases energy in the form of heat
Endothermic reaction
a reaction in which energy is absorbed
Neutralisation: endo- or exo-?
exothermic
Combustion: endo- or exo-?
exothermic
Examples of exothermic reactions [3]:
neutralisation
combustion
respiration
Thermal decomposition: endo- or exo-?
endothermic
calcium carbonate thermal decomposition
calcium carbonate --> calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
Uses of exothermic reactions [2]:
hand warmers
self-heating coffee
Uses of endothermic reactions:
cold packs
Disposable hand warmer [2]
iron + sodium chloride --> iron (III) oxide
lasts for hours
Reusable hand warmer [5]
often sodium ethanoate (CH3COO-Na+)
supersaturated solution of dissolved salt
crystallises when metal disc is pressed
put in boiling water to re-dissolve
lasts about 30 minutes
Self-heating can reaction:
calcium oxide + water --> calcium hydroxide
Instant cold packs [3]
ammonium nitrate and water
when dissolved, takes in energy
lasts about 20 minutes
Exothermic reaction profile
High bar, curve, low bar
Endothermic reaction profile
Low bar, curve, high bar
Energy change during reaction =
difference between products and reactants
Activation energy
minimum energy needed to get a reaction started
Activation energy =
reactants to peak of curve
Bond breaking: endo- or exo-?
endothermic
Bond making: endo- or exo-?
exothermic
Bonds in exothermic reactions
making bonds > breaking bonds
Bonds in endothermic reactions
making bonds < breaking bonds
Bond energy
the amount of energy that will break a bond between two atoms
To calculate the energy change for a chemical reaction:
how much energy is needed to break the bonds
how much energy is released when bonds are formed
If the overall energy change is negative, the reaction is...
...exothermic
To find the overall energy change:
add the energy required to break bonds and the energy released by their formation
Alkaline fuel cell: hydrogen half equation
H₂ + 2OH⁻ → 2H₂O + 2e⁻
Alkaline fuel cell: oxygen half equation
O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
Acidic fuel cell: hydrogen half equation
H₂ → 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
Acidic fuel cell: oxygen half equation
O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
Alkaline fuel cell: full equation
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Acidic fuel cell: full equation
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Advantages of hydrogen fuel [3]:
no electrical recharging
no pollutants
range of sizes
Disadvantages of hydrogen fuel [3]:
highly flammable
produced by non-renewable resources
difficult to store
Electrolysis
the decomposition of a substance by an electric current
Cathode
negative electrode
Anode
positive electrode
Electrolyte
an ionic compound whose aqueous solution/molten form conducts an electric current
Anion
negative ion
Cation
positive ion
Why can't solid ionic compounds conduct electricity?
ions are held in place by strong electrostatic forces of attraction
Which electrode has electrons?
cathode
Substances are ... at the cathode
reduced
Substances are ... at the anode
oxidised
... become ... at each electrode
ions, atoms
Water molecule ionising
H₂O ⇌ H⁺ + OH⁻
Which product of ionised water goes to the cathode?
H⁺
Which product of ionised water goes to the anode?
OH⁻
Hydrogen is produced at the cathode if...
the metal is more reactive than hydrogen
Electrodes should be made from ... materials
inert (unreactive)
In the electrolysis of aqueous solutions, ... is usually produced at the anode (positive electrode)
oxygen, O₂
Half equation: anode: aqueous solutions
4OH⁻ → O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻
Half equation: cathode: (some) aqueous solutions
2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂
Order of discharge at anode
halide ion > hydroxide > all other negatively charged ions
Oxygen is released at the anode unless...
the solution contains a halide ion
Uses of aluminium (and its alloys) [7]:
- pans
- overhead power cables
- aeroplanes
- cooking foil
- drink cans
- window and patio door frames
- bicycle frames and car bodies
What compound is electrolysed to procure aluminium?
aluminium oxide, Al₂O₃
Where is aluminium oxide found?
bauxite ore
Aluminium oxide melting point
2050°C
How do we reduce the melting point of aluminium oxide?
mix it with cryolite
Cryolite-aluminium oxide mixture melting point
850°C
Aluminium oxide electrolysis reaction
2Al₂O₃ → 4Al + 3O₂
Aluminium forms at the ... electrode
negative
Oxygen is produced at the ... electrode
positive
Aluminium electrolysis cell [4]
- lined with carbon negative electrode
- molten aluminium is tapped or siphoned off
- carbon dioxide and oxygen gas emitted from anodes
- steel case
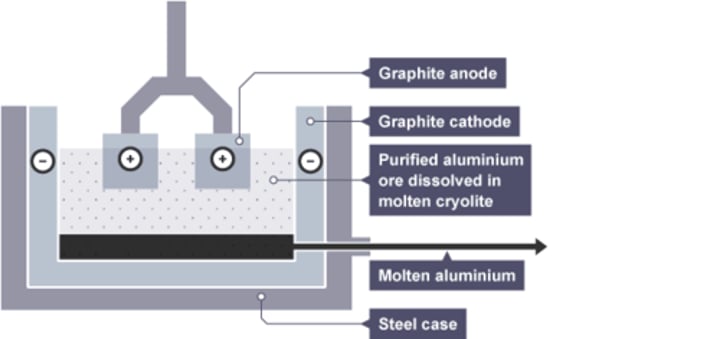
At the cathode (aluminium extraction):
Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al
At the anode (aluminium extraction):
2O²⁻ → O₂ + 4e⁻
Reaction of oxygen with hot carbon anodes:
C + O₂ → CO₂
... have to be replaced regularly
Carbon anodes
Brine
water saturated with salt (sodium chloride)
Products of electrolysis of brine [3]
- chlorine gas
- hydrogen
- sodium hydroxide
At the anode (brine electrolysis):
2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
At the cathode (brine electrolysis):
2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂
What is left after brine electrolysis?
sodium hydroxide, NaOH
Alkali
a soluble hydroxide
Base
substance that can neutralise acids
Acid
any compound that forms H⁺ ions in solution
Neutral
neither acidic nor alkaline
Dissolving sodium hydroxide in water
sodium hydroxide (water→) sodium ions(aq) + hydroxide ions(aq)
Indicators [4]:
- litmus paper
- universal indicator
- phenolphthalein
- methyl orange
Litmus paper [3]
acid: red
neutral: no change
basic: blue
Universal indicator
an indicator with a different colour for each pH value.
Phenolphthalein [3]
acid: colourless
neutral: colourless
basic: pink
Methyl orange [3]
acid: red-orange
neutral: yellow
basic: yellow
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14

Neutral solution + universal indicator
green
Acidic solution + universal indicator
red - yellow
Basic solution + universal indicator
blue - purple
pH meter
a device used to measure the pH of a solution

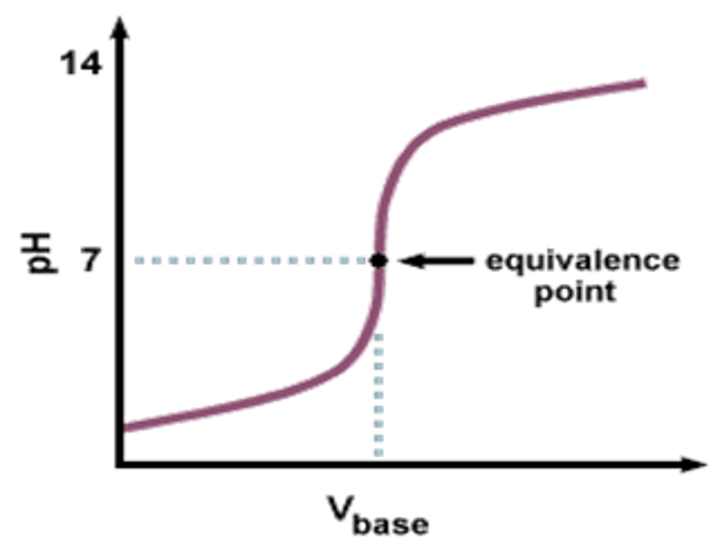
Equivalence point
the point in a titration where the number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of moles of hydroxide ions (middle of vertical drop)
Ionise
the reaction of a molecular substance with a solvent to form ions in solution.
Acids are classed as strong or weak depending on how they...
ionise in water
In aqueous solutions, acid molecules...
ionise and release H⁺ ions
Strong acids ... in aqueous solutions
fully ionise
How can we tell if an acid is weak?
it is a reversible reaction
Weak acids ... in aqueous solutions
partially ionise
Carbonic acid
H₂CO₃
Ethanoic acid
CH₃COOH
Citric acid
C₆H₈O₇
As the pH scale decreases by one unit...
the concentration of hydrogen ions increases by ten times