8: Frauds and Errors
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
threats to AIS
natural and political disasters
software errors and equipment malfunctions
unintentional acts
intentional acts
fraud
any and all means a person uses to gain an unfair advantage over another person
corruption
dishonest conduct by those in power which often involves actions that are illegitimate, immoral, or incompatible with ethical standards
misappropriation of assets
theft of company assets by employees; this can include physical assets and digital assets
fraudulent financial reporting
intentional or reckless conduct, whether by act or omission, that results in materially misleading financial statements
nartual and political disasters
ability to destroy an information system and cause many companies to fail (ie. fires, floods, earthquakes, etc.)
unintentional acts
caused by human carelessness, failure to follow established procedures, and poorly trained or supervised personnel
intentional act
a deliberate destruction or harm to a system (ie. fraud, sabotage)
fraud traits
false statement, representation, or disclosure
a material fact, which induces a victim to act
an intent to deceive
a justifiable reliance by the victim on the misrepresentation
injury or loss was suffered by the victim
investment fraud
misrepresenting or leaving out facts in order to promote an investment that promises fantastic profits with little or no risk
auditor’s responsibility to detect fraud
understand fraud
discuss the risks of material fraudulent misstatements
obtain information
identify, assess, and respond to risks
evaluate the results of their audit tests
document and communicate findings
incorporate a technology focus
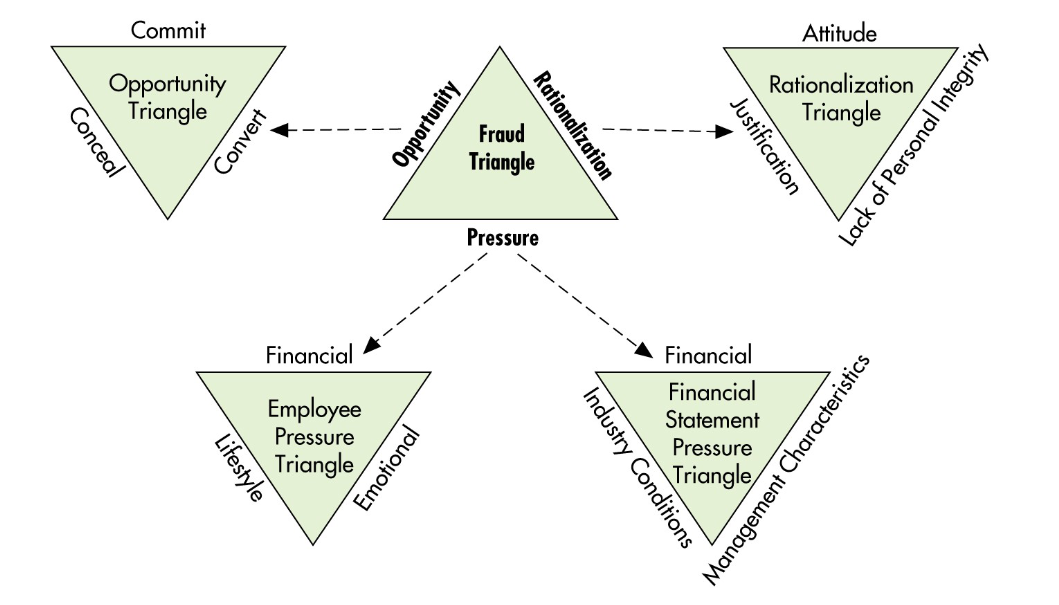
conditions of fraud
pressure: incentive or motivation for committing
opportunity: condition that allows a person to commit or conceal
rationalization: the excuse to justify action
fraud triangle
computer fraud
any fraud that requires technology to perpetrate it; categorized via the data processing model: input, processor, computer instruction, data, output
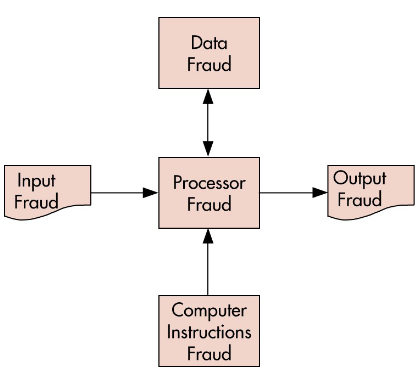
input fraud
the technique by which a perpetrator alters or falsifies computer input
processor fraud
unauthorized system use, including the theft of computer time and services
computer instructions fraud
involves:
tampering with company software,
copying software illegally,
using software in an unauthorized manner, and
developing software to carry out an unauthorized activity
data fraud
illegally using, copying, browsing, searching, or damaging company data
output fraud
the technique by which a perpetrator alters or falsifies computer output