Anatomy Cells Textbook
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/229
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
230 Terms
1
New cards
Cytology
study of cellular structure and function
2
New cards
Who helped start cytology
Robert Hooke and Antony van Leeuwenhoek
3
New cards
what are major components of cells
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Organelles
Inclusions
Cytosol
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Organelles
Inclusions
Cytosol
4
New cards
Plasma Membrane (cell membrane)
The membrane that encloses a cell and controls the traffic of molecules into and out of the cell.
5
New cards
what is the largest organelle
nucleus
6
New cards
Cytoplasm
The contents of a cell between its plasma membrane and its nuclear envelope
7
New cards
the cytoplasm consists of
cytosol, organelles, inclusions, and the cytoskeleton
8
New cards
cytoskeleton
a supportive framework of protein filaments and tubules
9
New cards
organelles
diverse structures that perform various metabolic tasks for the cell
10
New cards
inclusions
accumulated cell products such as lipids and pigments or internalized foreign matter such as dust and bacteria
11
New cards
cytosol
A clear, featureless, gelatinous colloid in which the organelles and other internal structures of a cell are embedded.
12
New cards
cytosol is also called
intracellular fluid (ICF)
13
New cards
intracellular fluid (ICF)
The fluid contained in the cells; one of the major fluid compartments.
14
New cards
Extracellular (ECF)
Any body fluid that is not contained in the cells;
15
New cards
where are some locations where ECF is located
blood, lymph, and tissue fluid
16
New cards
ECF is located between the cells is also called
tissue fluid
17
New cards
what is the most useful unit of measurement for designating cell sizes
micrometer (um)
18
New cards
How wide are most human cells
10 to 15 um
19
New cards
what are the longest human cells and how long
nerve cells
meter long
muscle cells
30 cm long
meter long
muscle cells
30 cm long
20
New cards
cells cannot attain ____ size
unlimited
21
New cards
What will happen when a cell grows to big
too large it would rupture; could not diffuse from place to place fast enough to support its metabolism
22
New cards
what is an advantage of having many small cells instead of a few large ones
death of one or a few cells is of less consequence to the structure and function of the whole organ
23
New cards
what are examples of physiology takes place at the cell surface
binding of signal molecules such as hormones, the stimulation of cellular activity, the attachment of cells to each other, and the transport of materials into and out of cells
24
New cards
plasma membrane defines the ____ of a cell and governs its ____ with ____ ___
boundary
interactions with other cells
interactions with other cells
25
New cards
plasma membrane also controls and maintains
the passage of materials into and out of the cell and maintains differences in chemical composition between the ECF and ICF
26
New cards
the term plasma membrane refers to
exclusively to the cell surface
27
New cards
description of plasma membrane
oily, two-layered lipid film with proteins embedded in it
28
New cards
how much of lipid molecules are phospholipids
75%
29
New cards
phospholipids
composes most of the molecules of the plasma membrane and other cellular membranes.
30
New cards
phospholipids are
amphipathic
31
New cards
phospholipids have a ____ phosphate head and two _____ fatty acid tails
hydrophilic
hydrophobic
hydrophobic
32
New cards
phospholipids are not ___ but ___
stationary but highly fluid
33
New cards
How much of lipid molecules is cholesterol
20%
34
New cards
cholesterol
A steroid that functions as part of the plasma membrane and as a precursor for all other steroids in the body.
35
New cards
cholesterol affects
membrane fluidity
36
New cards
What happens is too much cholesterol
inhibits the action of enzymes and other proteins in the membrane
37
New cards
what happens is too little cholesterol
plasma membranes become excessively fragile
38
New cards
How much of lipids is glycolipids
5%
39
New cards
glycolipids
A phospholipid molecule with a carbohydrate covalently bonded to it, found in the plasma membranes of cells.
40
New cards
Proteins give membranes
specific abilities
41
New cards
Protein contribute greatly
to the functional differences between cell types
42
New cards
peripheral proteins
proteins that only adhere to the inner surface of the plasma membrane
43
New cards
Integral proteins
protein that penetrates all the way through
44
New cards
glycoproteins
A protein molecule with a smaller carbohydrate covalently bonded to it
45
New cards
channel protein
A protein in the plasma membrane that has a pore through it for the passage of materials between the cytoplasm and extracellular fluid
46
New cards
channel proteins act as ____ that ___
gates that open or close to allow material to pass through only at specific times
47
New cards
Gates are important for
timing of heart's pacemaker, conduction of nerve signals, and contraction of muscles
48
New cards
Other functions of proteins
actively bind to chemicals in the ECF or ICF, such as glucose, amino acids, and inorganic ions, and transport them through the membrane
act as receptors for hormones and other chemical messengers from other cells
enzymes that carry out chemical rxns at the cell surface
act as receptors for hormones and other chemical messengers from other cells
enzymes that carry out chemical rxns at the cell surface
49
New cards
Receptor function
a receptor that binds to chemical messengers such as hormones sent by other cells
50
New cards
Enzyme function
an enzyme that breaks down a chemical messenger and terminates its effect
51
New cards
Channel function
a channel protein that is constantly open and allows solutes to pass into and out of the cell
52
New cards
Gated channel function
a gate that opens and closes to allow solutes through only at certain times
53
New cards
cell-identity marker function
a glycoprotein acting as a cell identity marker distinguishing the body's own cells from foreign cells
54
New cards
cell-adhesion molecule (CAM) function
a cell-adhesion molecule (CAM) that binds one cell to another
55
New cards
All cells are covered with a fuzzy carbohydrate coat called the
glycocalyx
56
New cards
gyclocalyx
A layer of carbohydrate molecules covalently bonded to the phospholipids and proteins of a plasma membrane; forms a surface coat on all human cells.
57
New cards
Glycocalyx functions
cell-adhesion molecules that bind cells together and precent tissues from falling apart
cushions that plasma membrane and protects it form physical and chemical injury
cushions that plasma membrane and protects it form physical and chemical injury
58
New cards
Glycocalyx are chemically ___ and act like an ___ ___
unique
identification tags
identification tags
59
New cards
What is determined by the glycocalyx
human blood types and transfusion compatibility
60
New cards
List surface extensions of cells
microvilli
cilia
flagella
pseudopods
cilia
flagella
pseudopods
61
New cards
what do surface extensions do for cells
aid in absorption, movement, sensory processes, and phagocytosis
62
New cards
microvilli
extensions of the plasma membrane that serve primarily to increase its surface area
63
New cards
what cells are best for microvilli
cells specialized for absorption such as epithelial cells of the small intestine and kidney tubules
64
New cards
How much more surface area can microvilli give a cell
40 times more absorptive surface area
65
New cards
cilia
hair like process that are supported by a core of microtubules
66
New cards
What are microtubules equipped with and what does it do
little motor proteins that produce the beating motion of cilium
67
New cards
How many cilia do the respiratory tract and uterine (fallopian) tubes typically have
50 to 200
68
New cards
What does cilia do in the respiratory tract
moves mucus from the lungs and trachea up to the throat where it is swallowed
69
New cards
what does cilia do in the uterine tubes
move an egg or embryo toward the uterus
70
New cards
primary cilium
nonmotile, solitary cilia in which nearly every cell has
71
New cards
primary cilium function
Serves as antenna for monitoring nearby conditions
play roles in the senses of motion and balance; in the retina of the eye. form light-absorbing part of sensory cells, and in kidney tubules the monitor fluid flow
play roles in the senses of motion and balance; in the retina of the eye. form light-absorbing part of sensory cells, and in kidney tubules the monitor fluid flow
72
New cards
flagellum
resembles a long solitary cilium
73
New cards
what is the only functional flagellum in humans
whiplike tail of a sperm cell
74
New cards
Kartagener syndrome
a hereditary disease in which cilia and flagella lack the motor protein and therefore cannot move
75
New cards
pseudopods
A temporary cytoplasmic extension of a cell used for locomotion (ameboid movement) and phagocytosis
76
New cards
pseudopods can change
shape continually
77
New cards
what uses pseudopods and for what
white blood cells- use pseudopods to crawl about in the tissues, and when they encounter a bacterium or other foreign particles
Macrophages-snare bacteria with thin filamentous pseudopods and reel them in to be digested by the cell
Macrophages-snare bacteria with thin filamentous pseudopods and reel them in to be digested by the cell
78
New cards
macrophages and white blood cells keep
our tissues cleaned up and defend us against bacteria and other invaders
79
New cards
cellular junctions
cells linked to one another and to the extracellular environment
80
New cards
cellular junctions enable cells to
grow and divide normally, resist stress, and communicate with each other
81
New cards
Three principal types of connections
tight junctions
desmosomes
gap junctions
desmosomes
gap junctions
82
New cards
tight junction
completely encircles an epithelial cell near its upper end and joins it securely to adjacent cells
83
New cards
Tight junctions are formed by
the fusion of the plasma membrane of neighboring cells, and seal off the intercellular space
84
New cards
in a tight junction substances are restricted
from passing between the epithelial cells, but rather must pass through them, ensuring that the epithelial cells chemically process materials that travel across
85
New cards
desmosome
A patchlike intercellular junction that mechanically links two cells together
86
New cards
desmosome keep cells
from pulling apart and thus enable a tissue to resist mechanical stress
87
New cards
Desmosomes are common
in tissues as the epidermis and cardiac muscle
88
New cards
gab junction
A junction between two cells consisting of a pore surrounded by a ring of proteins in the plasma membrane of each cell
89
New cards
gap junction function
allows solutes to diffuse from the cytoplasm of one cell to the next, thereby serving for cell-to-cell electrical and chemical communication in tissues such as cardiac and smooth muscle
90
New cards
Cellular membranes list
epithelia
plasma membranes
intracellular membranes
plasma membranes
intracellular membranes
91
New cards
epithelia
(sheet of cells) that line the blood vessels, digestive and respiratory tracts, and other surfaces
92
New cards
plasma membranes
form the outer boundaries of all cells
93
New cards
intracellular membranes
various organelles
94
New cards
membranes cannot be ____ but must allow _______
impenetrable
chemicals to pass through
chemicals to pass through
95
New cards
these membranes are all ___ ___, allowing some substances to pass through while excluding others
selectively permeable
96
New cards
pemphigus vulgaris
desmosomes are destroyed
launches a misguided attack on the desmosome proteins, especially in the skin
launches a misguided attack on the desmosome proteins, especially in the skin
97
New cards
filtration
A process in which hydrostatic pressure forces a fluid through a selectively permeable membrane (especially a capillary wall).
98
New cards
The most important example of filtration in human body
blood pressure driving water and small solutes through gaps in the walls of the capillaries, while holding blood cells and large molecules such as proteins in the bloodstream
99
New cards
Filtration is the mechanism by which
salts, nutrients, and other blood solutes are delivered to the cells of surrounding tissues, and how the kidneys selectively filter wastes from the blood
100
New cards
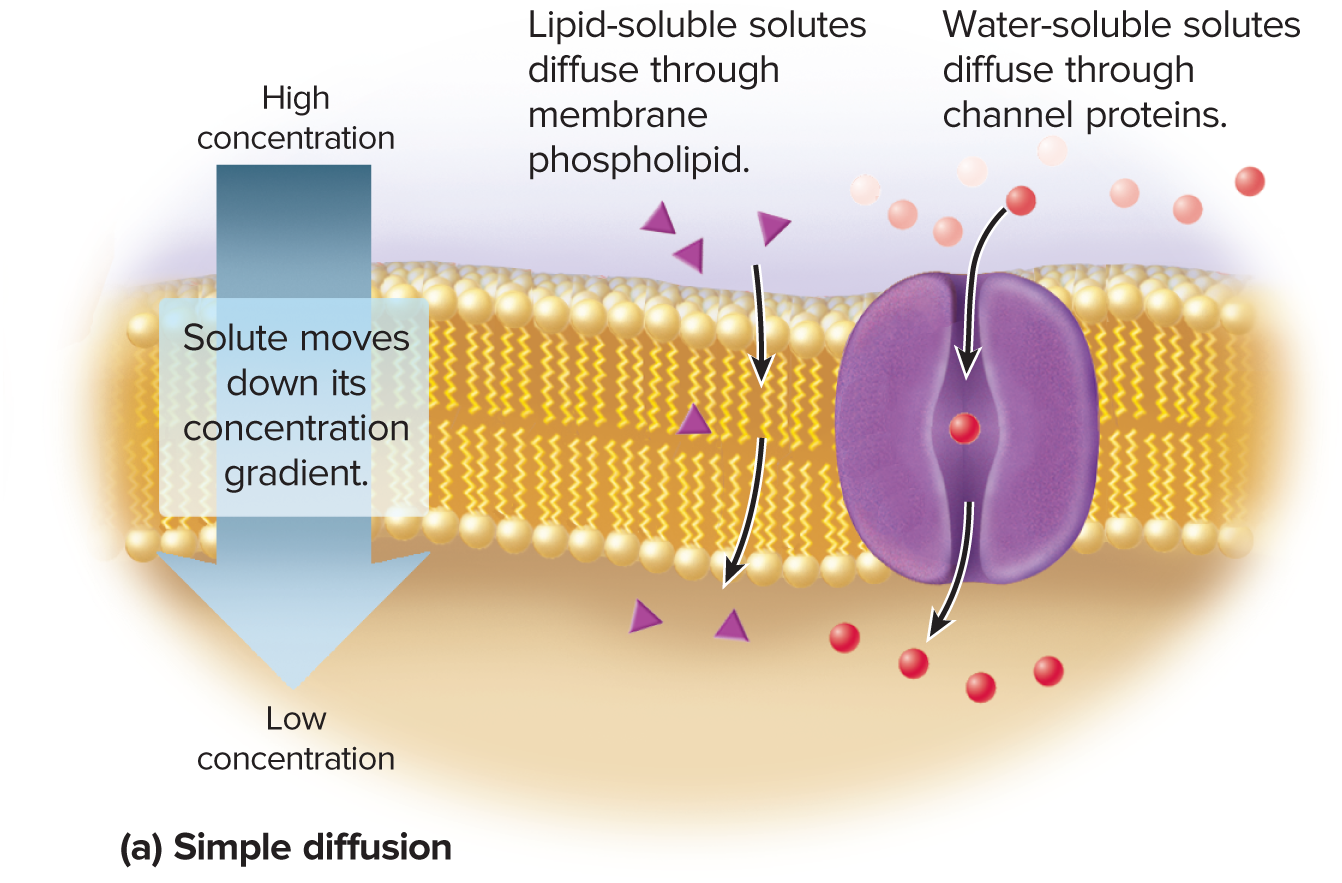
simple diffusion
the net movement of particles from a place of high concentration to a place of low concentration (down a concentration gradient)