Health midterm study guide (WITH DIAGRAMS)
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Organelles are _________ __________ of the cell
metabolic machinery
Dorsal body cavity
houses the organs of the upper central nervous system, including the brain and the spinal cord
Cranial cavity
houses the brain
spinal cavity
houses the spinal cord
ventral body cavity
in the anterior (front) aspect of the human body. It is made up of the thoracic cavity, and the abdominopelvic cavity.
Thoracic cavity
houses heart and lungs
Abdominopelvic cavity
Houses digestive system and most urinary system organs
Body cavity definition
Empty space that something is going to fit
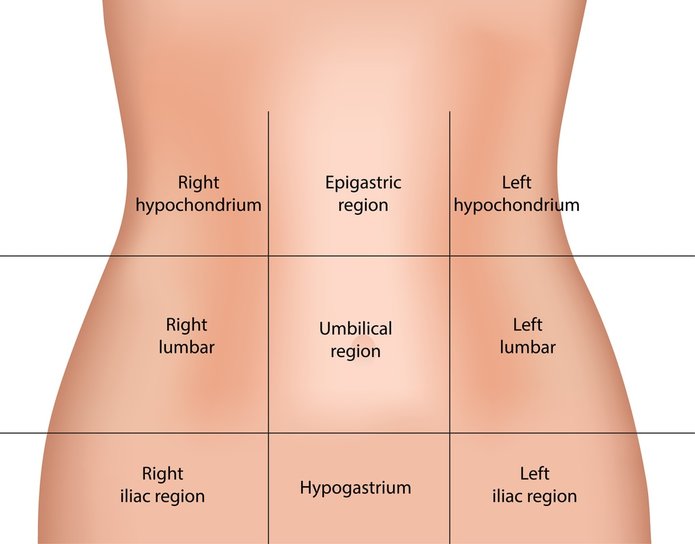
fill in the regions
regions filled in
Endocrine gland secretes products directly into the
bloodstream
Endocrine includes
Female ovaries, male testes, thyroid, and adrenal glands
Prolactin, FSH, TSH
The exocrine gland Secretes substances into a ______ system to an _______
ductal system to an epithelial surface
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from a concentration gradient
Facilitated diffusion
Transport substances across a membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Simple diffusion
A process that allows diffusion through a semipermeable membrane down their concentration gradient
Osmosis
Movement/Diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane from high water potential to low water potential
Mitosis
Division of the nucleus
Results in formation of two daughter nuclei
Cytokenisis
Division of the cytoplasm
Begins when mitosis is near completion
Results in the formation of two daughter cells
Prophase
First part of cell division, nuclear envelope breaks down and disappears
Metaphase
Chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell on the metaphase plate
Anaphase
Chromosomes are pulled apart and toward the opposite ends of the cell
Cell begins to elongate
Telophase
Spindles break down and disappear, chromosomes uncoil to become chromatin
Mitosis in order
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase,
Bone is also called
osseous tissue
Bone is composed of _____
bone cells in lacunae
Bone has large numbers of _______
collagen fibers
bone function
Functions to protect and support the body
Hyaline cartilage
Most common types of cartilage composed of abundant collagen fibers, rubbery matrix
Hyaline cartilage locations
Larynx, fetal skeleton prior to birth
hyaline cartilage functions
Functions as a more flexible skeletal element than bone
Elastic cartilage
Provides elasticity
Elastic cartilage location
Location: Supports the external ear
Fibrocartilage is
Highly compressible
Fibrocartilage location
Location: Forms cushion-like discs between vertebrae
Outer ear
Auricle/Pinna
Dense connective tissue has
Main matrix element is collagen fiber
Locations of dense connecrtive tissue
Tendons, Ligaments, Dermis
Dense connective tissue in tendons
Tendons: Attach skeletal muscle to bone
Dense connective tissue in ligaments
Ligaments: Attach bone to bone at joints
Dense connective tissue in dermis
Dermis: Lower layer of the skin
ADipose tissue
areolar tissue in which fat globules predominate
Many cells contain large lipid deposits
adipose tissue functions
Insulates the body, Protects some organs, Serves as a site of fuel storage
Vascular tissue
Blood
Blood cells surrounded by fluid matrix called
blood plasma
blood Functions at the transport vehicle for
materials
Synovial membrane
Connective tissue only
Secretes a lubricating fluid
Fluid alleviates pain
Nerve cells
Composed of neurons and nerve support cells
nerve cells function
Function is to send impulses to other areas of the body
what protects and supports nerve cells
neuroglia aka gilal cells insulate, protect, and support neurons
Skins functions
to protect the body, Aids in body heat loss or heat retention as controlled by the nervous system
Avascular
no blood supply
two dermis layers
Papillary and reticular
Reticular layer
Blood vessels
Sweat and gland oil
Deep pressure receptors
General term for sweat gland (sudoriferous gland)
Papillary layer
Projections called dermal papillae
Some certain capillary loops
Other house pain receptors and touch receptors
subcutaneous/hyperdermis
Anchors the skin, to underlying organs
Composed of mostly adipose tissue
stratum Basale
Deepest layer of epidermis
Lies next to dermis
stratum lucidum
Formed from dead cells of the deeper strata
Occurs only in thick, hairless skin of the palms of the hand and soles of feet
5th layer
epidermis layers
stratum Basale and sebaceous gland
5 epidermis layers in order
stratum Basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
melanin
Yellow, Brown, or black pigments
Carotene
Orange, yellow pigment from some vegetables
Hemoglobin
Red coloring from blood cells in dermal capillaries
Oxygen content determines the extent of red coloring
Redness
Erythema
Due to embarrassment, inflammation, hypertension, fever, or allergy
Pallor
Blanching
Due to emotional stress such as fear, anemia, low blood pressure, impaired blood flow to an area
Jaundice
Yellowing
Liver disorder
bruises
Hematomas
skin appendages
Hair
Hair follicles
Nails
Two types of suderficious glands
Apocrine and Eccrine
Apocrine
Ducts empty into hair follicles
Begin to function at puberty
Release sweat that also contains fatty acids and proteins (milky/yellowish color)
Eccrine
Open via duct to pore on skin surface
Produce sweat (clear)
Oil
Produce oil (sebum)
Lubricant for skin
Prevents brittle hair
Kills bacteria
Muscle tissue function
Function is to produce movement
Muscle tissue types (3 types)
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
Skeletal muscle
under voluntary control
Cardiac muscle
under involuntary control
smooth muscle
under involuntary control
Saggital section
Divides the body into right/left parts
Median/Midsaggital
Divides the body into EQUAL left and right parts
Frontal/Coronal
Divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
Transverse/Cross section
Divides the body into superior and inferior parts of the body
Plasma membrane
Barrier for cell components (bilayer)
Double phospholipid layer
membrane transport
Movement of substances into and out of the cell
Two basic modes of transport
Passive and Active
Passive transport
Passive processes: No energy is required
Active transport
Active Processes: Cell must provide metabolic energy (ATP)
Serous Membranes
Lines open body cavities that are closed to the exterior of the body
Specific Serous Membranes
Peritoneum, PLeura, Pericardium
Peritoneum
Peritoneum: Abdominal cavity
PLeura
Pleura: Around the lungs
Pericardium
Pericardium: Around the heart
body membranes
Cover body surfaces
Lines body cavities
Form protective sheets around organs
Epithelial membranes
Cutaneous membranes
Mucous Membranes
Serous Membranes
Mucous Membranes
Digestive, Reproductive, Respiratory)
Lines all body cavities that open to the exterior body surface
Often adapted for absorption or secretion
Connective tissue membranes
Synovial Membranes
Pleural Membrane
Pericardium
Peritoneum
Visceral covers hearts surface and is separated from parietal cardium by a small volume of fluid
How many bones in the adult body
206
Appendicular skeleton bones
126
axial skeleton bones
80
Another name for sternum
breastbone
another name for clavicle
collarbone