History - Spring 2023 - Midterm
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Last updated 7:11 PM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
Congressional Military Reconstruction Act - 1867
* South divided into 5 military districts
* Majority of Southerners had to swear allegiance to US, then would get civilian government back
* Pass the 14th Amendment
* Majority of Southerners had to swear allegiance to US, then would get civilian government back
* Pass the 14th Amendment
2
New cards
Hiram Revels
First African American man to serve in congress. Filled a vacant seat in 1870
3
New cards
Black Codes
Restricted African Americans ability to own property, conduct business, buy and lease land, and move freely through public spaces
4
New cards
Scalawag
White southerner who collaborated (aided) with northern Republicans during Reconstruction for profit
5
New cards
Carpetbagger
A person during Reconstruction who moved from a northern to southern state in order to gain profit
6
New cards
Compromise of 1877
An informal, unwritten deal that disputed the 1876 election. Republican Rutherford B. Hayes would become president if he would remove the federal troops from SC, FL, and LA
7
New cards
Battle of Little Bighorn AKA Custer’s Last Stand
Decisive Native American victory and worst US Army Defeat in the Long Plains Indian War. The Sioux and Cheyenne had won the Battle of the Little Bighorn, killing Custer and every one of his men
8
New cards
Massacre of Wounded Knee
The slaughter of approximately 150–300 Lakota Indians by United States Army troops in the area of Wounded Knee Creek in southwestern South Dakota. The massacre was the climax of the U.S. Army's late 19th-century efforts to repress the Plains Indians
9
New cards
Chief Joseph
A leader of the Wallowa band of the Nez Perce Tribe, who became famous in 1877 for leading his people on an epic flight across the Rocky Mountains
10
New cards
13th Amendment
Abolished slavery
11
New cards
14th Amendment
Granted citizenship to all persons "born or naturalized in the United States"
12
New cards
15th Amendment
Granted African American men the right to vote
13
New cards
16th Amendment
Gives the Federal Government the power to levy an income tax on all income earners in the United States
14
New cards
17th Amendment
Allows voters to cast direct votes for US Senators
15
New cards
18th Amendment
Prohibition - Alcohol becomes illegal
16
New cards
19th Amendment
Granted women the right to vote
17
New cards
Civil Service Act - 1883
Guaranteed the rights of all citizens to compete for federal jobs without preferential treatment given based on politics, race, religion or origin
18
New cards
Carlisle School
Point was to remove indigenous children from the families and communities to assimilate them and stop the passing-on of indigenous culture
19
New cards
Dawes Severalty Act - 1887
Authorized the President to break up reservation land, which was held in common by the members of a tribe, into small allotments to be parceled out to individuals
20
New cards
Gilded Age
A period of economic growth as the United States jumped to the lead in industrialization ahead of Britain
21
New cards
Political Machines
A party organization that recruits its members by the use of tangible incentives—money, political jobs—and that is characterized by a high degree of leadership control over member activity.
22
New cards
Boss Tweed
He was convicted for stealing an amount estimated by an aldermen's committee in 1877 at between $25 million and $45 million from New York City taxpayers from political corruption, but later estimates ranged as high as $200 million. (Political Machine)
23
New cards
Haymarket Square Riot
A bomb detonates in Chicago after police arrive to break up a rally in support of striking workers.
24
New cards
Homestead Act
Enacted during the Civil War in 1862, provided that any adult citizen, or intended citizen, who had never borne arms against the U.S. government could claim 160 acres of surveyed government land
25
New cards
Pullman Strike
The most famous and far reaching labor conflict in a period of severe economic depression and social unrest - With the government working to the General Managers' Association's ends, Debs felt the only way to force the this company into arbitration was reaching out to other labor groups to join in a general strike, but his efforts did not succeed. The boycott dissolved in mid-July, and the ARU was defeated
26
New cards
Chinese Exclusionary Act
The first significant law restricting immigration into the United States - Only affected the Chinese
27
New cards
Plessy v. Ferguson
This person was arrested and brought to court for arraignment before Judge John H. ___ of the U.S. District Court in Louisiana. He then attempted to halt the trial by suing Ferguson because the segregation law was unconstitutional. His lawyers argued that the Separate Car Act violated the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Amendments. The judge found that Louisiana could enforce this law insofar as it affected railroads within its boundaries. He was convicted
28
New cards
Populist
A person, especially a politician, who strives to appeal to ordinary people who feel that their concerns are disregarded by established elite groups
29
New cards
Laissez-Faire
Abstention by governments from interfering in the workings of the free market
30
New cards
Progressives
They were interested in establishing a more transparent and accountable government which would work to improve U.S. society. These reformers favored such policies as civil service reform, food safety laws, and increased political rights for women and U.S. workers.
31
New cards
Muckrakers
Any of a group of American writers identified with pre-World War I reform and exposé writing. The muckrakers provided detailed, accurate journalistic accounts of the political and economic corruption and social hardships caused by the power of big business in a rapidly industrializing United States
32
New cards
Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire
The Triangle Shirtwaist Company factory in New York City burned, killing 146 workers, on March 25, 1911. The tragedy led to the development of a series of laws and regulations that better protected the safety of factory workers
33
New cards
Sherman & Clayton Antitrust acts
This act is a law the U.S. Congress passed to prohibit trusts, monopolies, and cartels. Its purpose was to promote economic fairness and competitiveness and to regulate interstate commerce
\
This act addresses specific practices that the other act does not clearly prohibit, such as mergers and interlocking directorates
\
This act addresses specific practices that the other act does not clearly prohibit, such as mergers and interlocking directorates
34
New cards
Ida B. Wells
African-American journalist and activist who led an anti-lynching crusade in the United States in the 1890s
35
New cards
Janette Rankin
1917 - Representative of Montana became the first woman to serve in Congress
36
New cards
Alice Paul
One of the most prominent activists of the 20th-century women's rights movement
37
New cards
W.E.B Dubois
Well known as one of the foremost Black intellectuals of his era. Became director of publicity and research for the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). He attacked Washington's acceptance of racial segregation
38
New cards
Booker T. Washington
He chose to concentrate on what blacks could accomplish by focusing on learning industrial skills; he believed this would help his race secure economic self-reliance.
39
New cards
Yellow Journalism
This was a style of newspaper reporting that emphasized sensationalism over facts
40
New cards
Captain Alfred T. Mahan
In 1890, a lecturer in naval history and the president of the United States Naval War College, published The Influence of Sea Power upon History, 1660–1783, a revolutionary analysis of the importance of naval power as a factor in the rise of the British Empire
41
New cards
Open Door Policy
A major statement of United States foreign policy issued in 1899 and 1900 intended to protect the rights of all countries to trade equally with China and confirming multi-national acknowledgment of China's administrative and territorial sovereignty
42
New cards
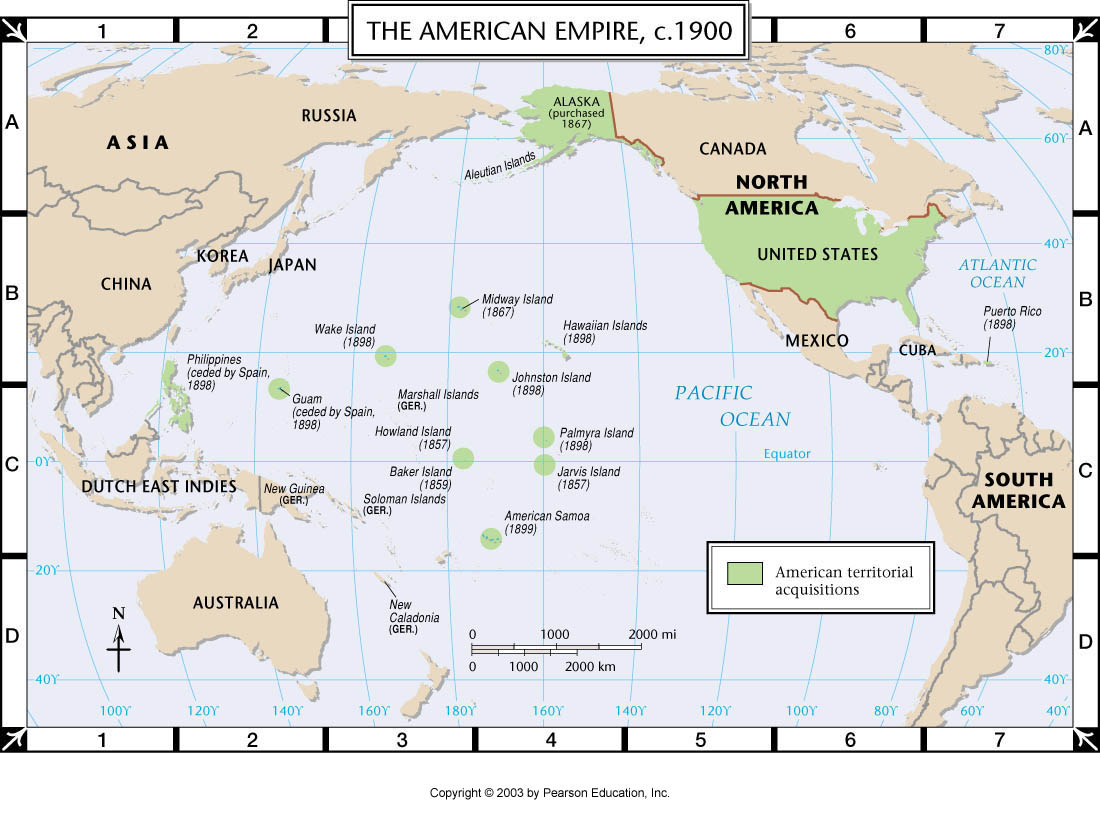
Map of US Imperialism
\:)
43
New cards
Spanish American War
An 1898 conflict between the United States and Spain that ended Spanish colonial rule in the Americas and resulted in the U.S. acquisition of territories in the western Pacific and Latin America - Puerto Rico, Guam, Philippines - Later Cuba (Spain surrendered)
44
New cards
Big Stick Policy
The corollary stated that not only were the nations of the Western Hemisphere not open to colonization by European powers, but that the United States had the responsibility to preserve order and protect life and property in those countries - Roosevelt “Speak softly and carry a big stick; you will go far.”
45
New cards
Dollar Diplomacy
The use of a country's financial power to extend its international influence
46
New cards
Moral Diplomacy
The system in which support is given only to countries whose beliefs are analogous to that of the nation
\
A major idea behind this was to force countries to pursue democracies. If a country was willing to align with the values seen as moral by the American government, then they were supported. If not, they were harmed economically by the U.S.'s lack of support
\
A major idea behind this was to force countries to pursue democracies. If a country was willing to align with the values seen as moral by the American government, then they were supported. If not, they were harmed economically by the U.S.'s lack of support
47
New cards
Panama Canal
This joined the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, changing international trade forever.
\
* Colombia buy for $10 million, yearly lease of $250,000
* Legislature turned it down
* US backed a “revolt” by Panama
* Hay/Bunau-Varilla Treaty
* US right to build canal
\
* Colombia buy for $10 million, yearly lease of $250,000
* Legislature turned it down
* US backed a “revolt” by Panama
* Hay/Bunau-Varilla Treaty
* US right to build canal
48
New cards
Events affecting US Neutrality
* German resumption of unrestricted submarine warfare
\
* Zimmerman Telegram - Germany asks Mexico to invade US, Mexico would get southwest US back, distract US from WWI
\
* Zimmerman Telegram - Germany asks Mexico to invade US, Mexico would get southwest US back, distract US from WWI
49
New cards
US Agencies created during WWI
* War Industries Board (WIB)
* Fuel Administration
* Food Administration
* Fuel Administration
* Food Administration
50
New cards
Espionage Act - 1917
This act prohibited obtaining information, recording pictures, or copying descriptions of any information relating to the national defense with intent or reason to believe that the information may be used for the injury of the United States or to the advantage of any foreign nation
51
New cards
Sedition Act - 1918
Made it a crime for American citizens to "print, utter, or publish... any false, scandalous, and malicious writing" about the government
52
New cards
Woodrow Wilson’s 14 Points
1. Open diplomacy without secret treaties
2. Economic free trade on the seas during war and peace
3. Equal trade conditions
4. Decrease armaments among all nations
5. Adjust colonial claims
6. Evacuation of all Central Powers from Russia and allow it to define its own independence
7. Belgium to be evacuated and restored
8. Return of Alsace-Lorraine region and all French territories
9. Readjust Italian borders
10. Austria-Hungary to be provided an opportunity for self-determination
11. Redraw the borders of the Balkan region creating Roumania, Serbia and Montenegro
12. Creation of a Turkish state with guaranteed free trade in the Dardanelles
13. Creation of an independent Polish state
14. Creation of the League of Nations
53
New cards
Treaty of Versailles
This forced Germany to surrender colonies in Africa, Asia and the Pacific; cede territory to other nations like France and Poland; reduce the size of its military; pay war reparations to the Allied countries; and accept guilt for the war
54
New cards
Great Migration
One of the largest movements of people in United States history. Approximately six million Black people moved from the American South to Northern, Midwestern, and Western states roughly from the 1910s until the 1970s
55
New cards
Problems in the US following WWI
Economic problems, labor unrest, racial tensions, and the intensity of the antiradicalism they helped create—all combined in the years immediately following the war to produce a general sense of disillusionment