BIOL10011 - Key Words
1/276
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
277 Terms
haploid
single set of chromosomes in an organism’s cell(s)
ecosystem collapse
ecosystem collapse when loss of life and ecosystems disrupted
IUCN assesses risk of ecosystem collapse using criteria that can be applied to any ecosystem
declining distribution
degradation of abiotic environment
quantitative risk a
nardoo hills nature reserve
threat of reduced water, higher temperature and predation
dieback of trees after drought, so seeds planted from another region where the species is more drought-tolerant —> climate-ready restoration
bittern and rice crop
bringing water in early
additional habitat
less predators
community action and merri creek
used to be a very biodiverse location but it was then overtaken by the city
community action to help restore it
community action responses
development of strategic plans
Visiting specialists
Running advocacy campaigns in the local media
Used community people to describe what’s needed
Lobbied councillors and members of government
Visits to schools and informational talks
Written grant applications
genetic rescue
the process where inbred populations receive genes from another population such that their overall genetic diversity increases
per capita growth rate
how much the population is increasing or decreasing in proportion to the population itself
lowland rainforest of subtrorpical Australia
flying foxes
extensively cleared for agriculture and grazing
intrinsic growth rate (r)
the number of births minus the number of deaths per generation time—in other words, the reproduction rate less the death rate
geographical scales
The bogong moth spends its larval stage in the plains of QLD and NSW and then adults migrate to the alpine zone (more than 1,000 km away)
They’re an important food for mountain pygmy possums
Coevolution and antagonistic relationships between species
Newts produce neurotoxin, which Garter snakes have evolved resistance to
Resistance is higher in regions where newts are and lower in regions which don’t have newts due to coevolution forces
pottoroo, truffles and mycorrhizae
potoroos feed on truffles so they are an important disperser of spores —> ecosystem engineers
potoroos have a high extinction rate, along with other small Australian mammals.
this may have a problematic influence on mycorrhizae networks in ecosystems
succession at Wilson’s promontory
Changes in vegetation over time
Invasion of coastal tea-tree into the coastal grassy woodland
may have already been at climax, with the tea tree an invasive species
now there’s increased management of fire and grazing to restore the woodland
vector transmitted parasites
carried by other organisms between their hosts
they are microparasites
mosquitoes are the most common vectors
genetic rescue and the mountain pygmy possum
possums found in 3 populations which are very genetically isolated
captive breeding unsuccessful
males from a nearby population at Mt Hotham released into the Mt Buller population
population increased significantly after that
demography
the study of the birth and death rates of populations and how they change over time
parasitoids
insects which eventually kill their hosts
e.g. parasitoid wasps
eggs grow and hatch in the host and eventually emerge from it
micropredators
attack several hosts, usually feeding on their blood
leeches, mosquitoes, flies, fleas and ticks
lampreys, vampire bats
ecosystem services of mountain ash forests
world’s largest forest carbon store
trees live a very long time ~350 years
help provide clean drinking water
Melbourne water supply at risk due to collapse of forests after logging
ecosystem collapse when loss of life and ecosystems disrupted —> moving toward acacia system which uses more water
provide tree hollows for bird and possum species e.g. the greater glider
banksia woodlands of the swan coastal plain
honey possum, honey eater, banksias, western ring tailed possum, moaning frog
honey possum threatened by habitat loss so now there is a tree-planting effort
threats of clearing, mining, fragmentation
living sea walls
reduce the impact of storm surges
protect coastal settlements and ecosystems
provide ecological niches to enhance marine biodiversity
Baw Baw frog conservation
affected by chytrid fungus
conservation focuses on breeding programs
Victorian volcanic plain conservation
striped legless lizards, growling grass frog
species face threats including: urban development, invasive species (weeds), changed disturbance regimes
large housing developments reducing habitat
assessment that 4,500 ha of grassland will be lost to housing, so new grassland reserves are being created to offset this loss
however this only represents a possible gain as the grassland reserves were never delivered and wetlands for growling grass frog habitat not built
effect of indigenous land burning
reduced landscape fuel loads
reduced vertical connectivity of fuels
protection of fire sensitive ecosystems
connection to country
tropical savannah and fire
most fire-prone environment on earth
either side of the equator
prolonged dry seasons leads to high biomass buildup
lightning ignites huge, canopy-destroying fires
burns in late dry season when fuel load is high and dry
long dry season and intense wet season (lots of growth)
changing fire timing helps offset emissions
Indigenous helping to manage fire timing and approach —> restoration the health and wellbeing of the forest and Aboriginal people
insect mouthparts (5)
chewing — beetles
piercing — mosquitoes
carving — flies
siphoning — butterflies
sponging — flies
urban flooding and rain gardens
if rain is directed directly into waterways this results in more pollutants and can end up in flash flooding when there is too much water
creating rain gardens can help to capture water as more water is absorbed into the soil — this helps to reduce flooding
the extinction of experience
loss of contact between people and nature
loss of willingness of people to protect nature
—> hampers conservation efforts
eating large prey
dragonfish and dragonfly larvae
hinged mouthparts, able to open mouth very wide (fish has space behind brain for head to tip back)
tooth comb
used for bark scraping (lemur)
introduced Australian species
Rabbits are the most destructive — lead to declines in native animals, change in habitat structure
Feral cats have the largest impact on native animal numbers — eat billions of native animals
heterothermic ectotherm
heterothermic = variable temp, ectotherm = body temp varies with ambient temperature
body temperature increases with the ambient temperature in 1:1 relationship
metabolic rate will increase with ambient temperature in an exponential-style relationship where it is much higher when hotter (behaviours to reduce heat)
bony fish movement
swim bladder for buoyancy (related to lungs)
fins of rays or bone or bone lobes
precursors to legs
conflict between offspring and parents
Conflict if parents produce offspring in subsequent years, and need to balance between caring for current and past offspring.
atmospheric O2 and insect size
when the oxygen concentration in the atmosphere is high, the insect needs smaller quantities of air to meet its oxygen demands.
The tracheal diameter can be narrower and still deliver enough oxygen for a much larger insect
mechanical isolation
reproductive parts do not fit
a type of pre-mating reproductive isolation
assumptions of the hardy-weinberg theory
no migration
no natural selection
no mutation
infinite population size (less genetic drift impact)
random mating
movement from quadruped to biped
big toe reduced
pelvis shortened
legs straightened
less robust arms
greater dexterity and tool use
cartilaginous fish
large liver with oil to remain buoyancy
cartilage lighter than bone, pectoral fins
diploid
two sets of chromosomes in an organism’s cell(s)
fission
division of a unicellular or multicellular organism into two or more separate daughter cells of equal size
binary and multiple fission
binary fission
division which results in two cells or organisms of equal size
meta communities
groups of local communities occupying a set of habitat patches that are linked by the dispersal of multiple, potentially interacting species
multiple fission
division which results in more than two cells or organisms of equal size
budding
the parent cell divides itself into two unequal parts
found in all domains and kingdoms, unicellular and multicellular organisms
fragmentation
where a fragment of a multicellular organism breaks off and forms a new organism
vegetative propagation
where a new plant grows from part of the parent plant
runners
stem which grows along the ground and branches into roots and branches along the nodes
bulbs
underground storage structure which can store a plant throughout its complete life cycle
tubers
grow beneath the soil, and look like a bulb branching off of the roots e.g. potatoes
suckers/basal shoots/root sprouts
a separate plant which grows from the meristem of a root at the base of the plant
parthenogenesis
when an unfertilised egg can develop into an individual, allowing the female organism to reproduce without a male
archaea
similar to bacteria, tend to live in extreme environments
domain
highest order of life: archaea, bacteria, Eukarya
kingdom
above phylum, below domain, five kingdoms (prokaryotes, protists, fungi, plants and animals)
dioecious
male and female reproductive organs found in separate individuals e.g. humans
monecious
an individual has both male and female reproductive systems
hermaphrodite
an individual has both male and female reproductive systems
oviparous
lay eggs
viviparous
embryo develops internally, live young
ovoviviparous
fertilised eggs remain in the parents’s body until they hatch but the offspring’s nutrients comes from the egg not the mother’s placenta
e.g. seahorses, some shark species
alternative generations
subsequent lifecycles alternate between diploid and haploid organisms
occurs in all land plants
plasmogamy
fusion of two cells brings together two compatible haploid nuclei, but they don’t fuse so two nuclei types are present
karyogamy
fusion of the two nuclei of haploid eukaryotic cells
dikaryotic
organisms which contain two genetically distinct cell nuclei in the same cell
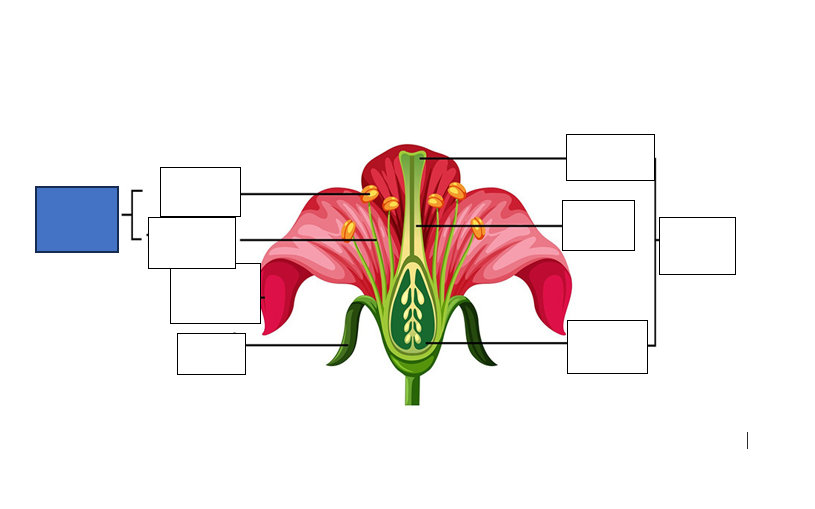
stamen — male reproductive part of the flower, long slender stalk with the anther at the tip
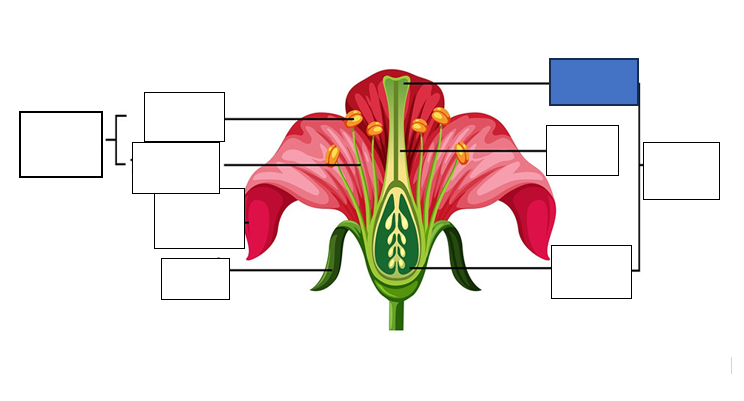
stigma — the tip of one or several carpels — the part at the highest point above the ovary)
actinomorphic flowers
more than one plane of symmetry
zygomorphic flowers
one plane of symmetry
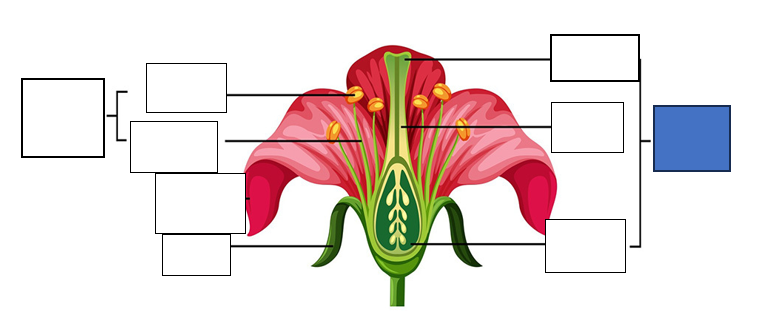
carpel — seed-bearing structure which includes the whole middle part of the flower
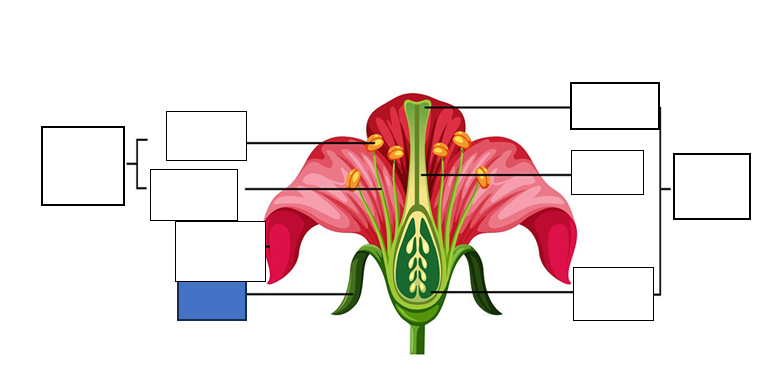
sepal — the little leaves at the bottom which protect the bud
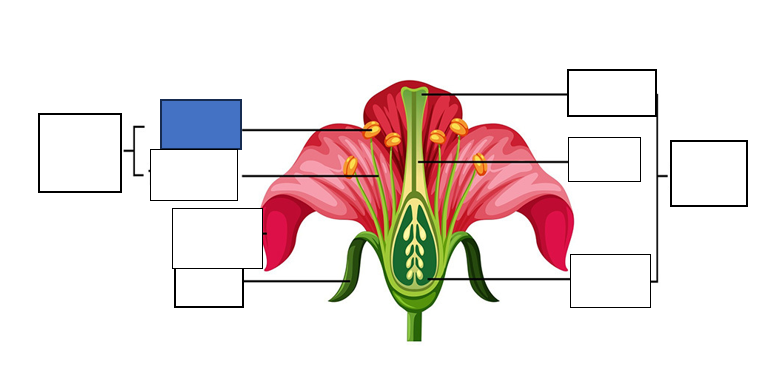
anther — the yellow part which holds the pollen for fertilisation of another flower
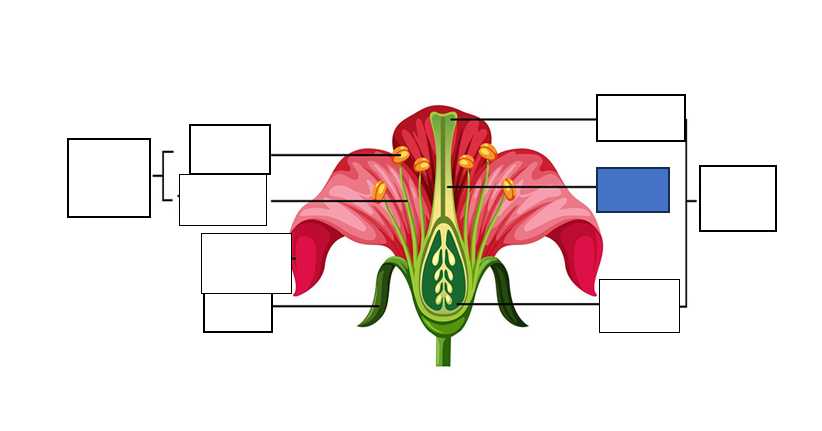
style — stalk which connects the stigma to the ovary. assists with fertilisation as it is the tube pollen follows to the egg.
anaerobic cellular respiration
organisms do not use oxygen to extract energy from food and use a different compound instead
when did respiration evolve
aerobic respiration evolved 3 billion years ago
(though anaerobic respiration evolved first)
obligate aerobic bacteria
cannot survive without oxygen
obligate anaerobic bacteria
cannot survive in the presence of oxygen
facultative anaerobic bacteria
can grow without oxygen but use oxygen if its present
hyphae
fungi in soil which absorb oxygen from air spaces in between soil particles
the main mode of vegetative growth in fungi
Hyphae secrete digestive enzymes which break the substrate down making it easier to absorb.
lenticels
act like stomata by moving air through the stems of woody plants and some roots

aerial roots
useful in environments with anoxic or waterlogged soils e.g. mangroves
aerenchyma
small air pockets in plant tissue which allow for exchange of gases from exposed parts of the plant to submerged parts e.g. mangroves
direct diffusion as respiration
small animals (<1mm diameter) can obtain O2 from diffusion across body surface
integumentary exchange
skin as gas exchange surface where gasses diffuse directly into circulatory system
e.g. earthworms and amphibians
only works in moist environments
trachea
tubes in insects which provide oxygen through living material e.g. body and wings
some insects ventilate the tracheal system with muscle contractions
open to the environment through spiracles
separate to circulatory system
spiracles
the openings to trachea — opened and closed when needed

gills
found in a cavity or externally
highly branched and folded filaments which water passes over and oxygen rapidly diffuses into the circulatory system or coelomic fluid
many gills use a counter current system to gain oxygen and lose CO2
amphibian lungs
simple sac like lung
reptile lungs
sac-like, sometimes subdivided
chemoautotrophs
bacteria which synthesise their own organic molecules using the oxidation of inorganic compounds rather than sunlight
photoautotrophs
manufacture their organic molecules from simple inorganic molecules using sunlight as the energy source for photosynthesis
anoxygenic photosynthesis
pathway which does not generate oxygen
Anoxygenic photoautotrophs use H2S as a source of electrons and have bacteriochlorophylls rather than chloroplasts
bacteriochlorophylls
hotosynthetic pigments found in some phototrophic bacteria and act similarly to chlorophylls
oxygenic photosynthesis
photosynthesis which generates oxygen (what we usually see today)
cyanobacteria
the earliest oxygenic photoautotrophs
scavengers
eat remains of food left by carnivores and herbivores
radula
structure in mollusc mouths for feeding which is a toothed, chitinous ribbon used for scraping or cutting food
labium
forms the floor of the mouth of an insect
labrum
helps hold food in position when the insect feeds