IS-0200.c Basic Incident Command System for Initial Response, ICS 200 latest updated questions and answers
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Describe the course objectives and summarize basic information about the Incident Command System (ICS)
standardized management tool for meeting the demands of emergency or nonemergency situations
Describe the National Incident Management System (NIMS).
Resource Management
Command and Coordination
Communications and Information Management
Unity of Command
means that each individual has a designated supervisor to whom they report to at the scene of the incident
Unified command
When no one jurisdiction, agency, or organization has primary authority and/or the resources to manage an incident on its own, Unified Command may be established. There is no one "Commander." The Unified Command can allocate resources regardless of ownership or location.

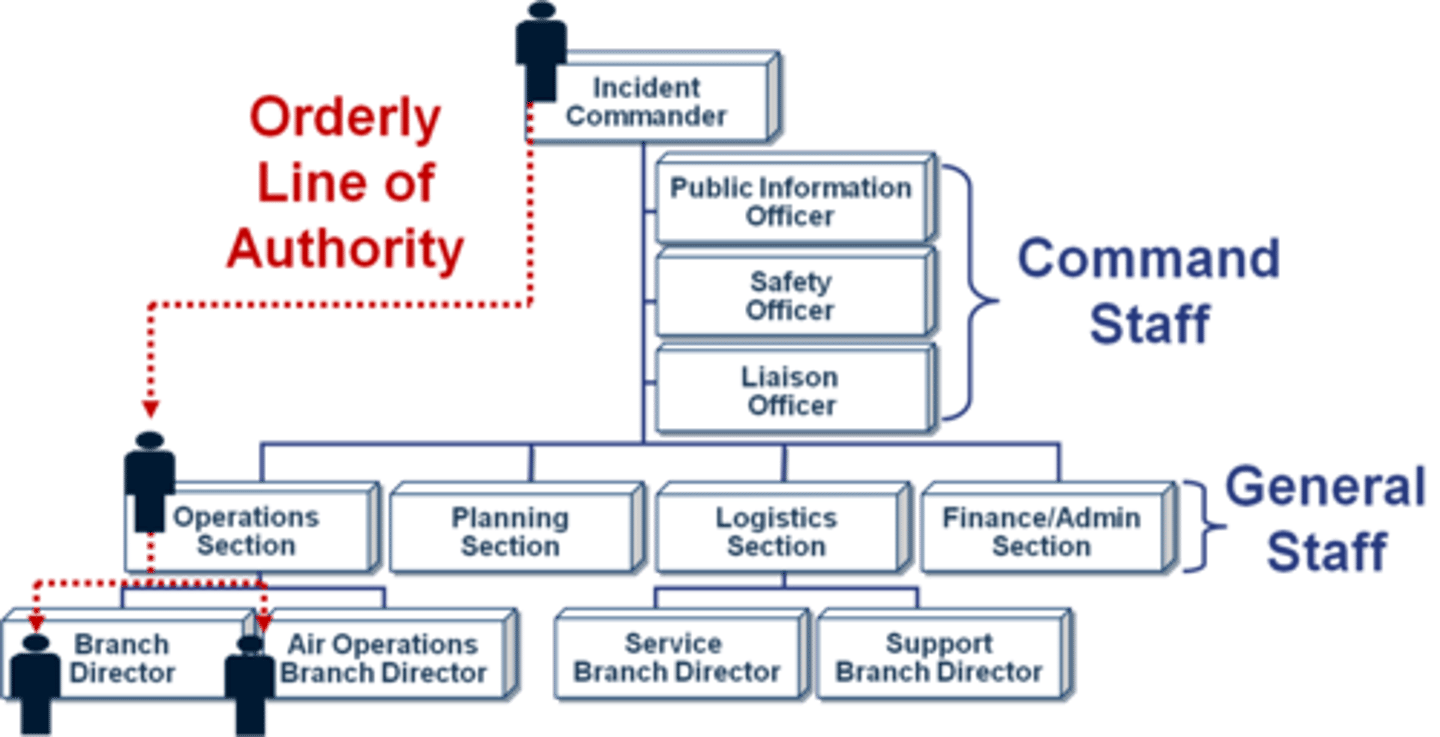
Chain of command
refers to the orderly line of authority within the ranks of the incident management organization.
The command function must be clearly established from the beginning of an incident. When command is transferred, the process must include:
A briefing that captures all essential information for continuing safe and effective operations.
The optimal span of control for incident management is
one supervisor to five subordinates; however, the 1:5 ratio is only a guideline and effective incident management often calls for different ratios.
When a supervisor's span of control becomes unmanageable, they can assign subordinate supervisors or redistribute subordinates to manage portions of the organization in order to regain a manageable span of control.
Which of the following is true:
A. The ICS intelligence function is limited to national security or other types of classified information.
IB. n ICS, modular organization means that the Incident Commander must activate complete, intact teams to staff the different functional areas.
C. Resources include personnel, tools, and equipment available, or potentially available, for assignment to incidents.
D. The use of radio codes (10-codes) is the most efficient means of communicating within an ICS organization.
C. Resources include personnel, tools, and equipment available, or potentially available, for assignment to incidents.
Chain of command
formal communication
assignments, resources and progress checks
informal communication
info about incident
qualities in a good leader
Take command.
Balance response initiatives with safety concerns.
Motivate responders.
Communicate clear directions.
Size up the situation and make rapid decisions.
Assess the effectiveness of tactics/strategies.
Be flexible and modify plans as necessary.
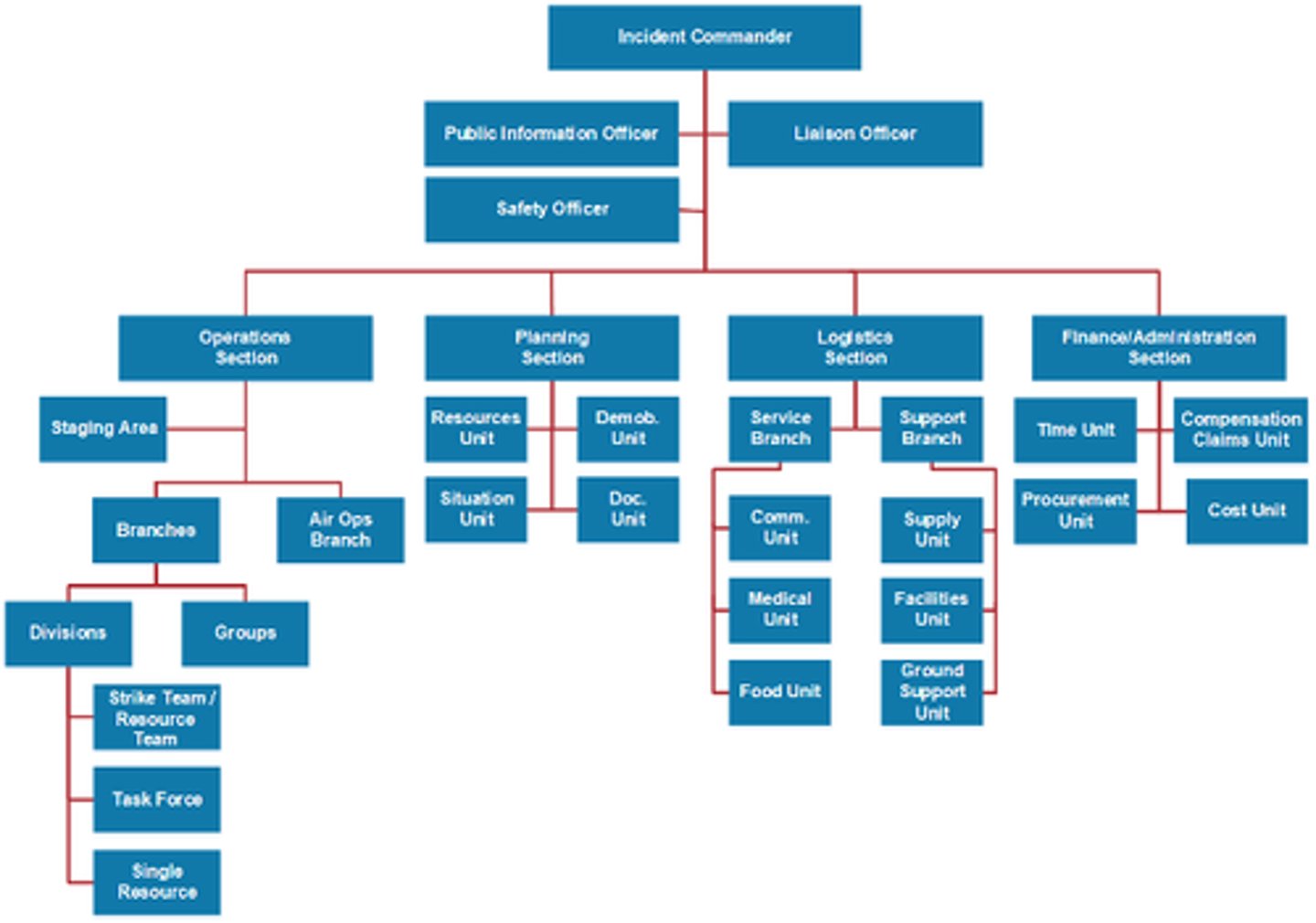
ICS organization five major functional areas:
Command, Operations, Planning, Logistics, and Finance/Administration
Liaison Officer
the point of contact for representatives of other governmental agencies, nongovernmental organizations, and/or private entities
Planning Section
collects, evaluates, and disseminates incident situation information and intelligence
Logistics Section
responsible for all support requirements needed to facilitate effective and efficient incident management, including ordering resources from off-incident locations
Finance/Administration Section
perform cost analysis and contracting services
Public Information Officer
handles media and public inquiries, emergency public information and warnings, rumor monitoring and response, and media monitoring, and coordinates the dissemination of information in an accurate and timely manner
Safety Officer
responsible for monitoring incident operations and advising the Incident Commander on all matters relating to operational safety, including the health and safety of emergency responder personnel
Strike Team
composed of specified combinations of the same kind and type of resources, with common communications and a Leader
Task Force
-is a group of resources with common communications and a leader that may be preestablished and sent to an incident, or formed at an incident.
- are mixed resources assigned for specific tasks rather than divided by areas
divisions
typically organized by geographical location.
Groups
are typically organized by function rather than by geography. Using Groups would mean separating teams by specific tasks (e.g., rescue, medical aid), which could complicate evacuation efforts in geographically defined areas
modular development
is the process of dividing a program into separate modules that can be developed and tested separately and then integrated into a single program.
Delegation of authority:
A delegation of authority is needed when an incident scope is complex or beyond existing authorities.
Grants authority to carry out specific functions.
- Is issued by the chief elected official, chief executive officer, or agency administrator in writing or verbally.
- Allows the Incident Commander to assume command.
- Does NOT relieve the granting authority of the ultimate responsibility for the incident..
steps you would take to keep the agency executives involved
- Get approval of strategic goals for the incident.
- Conduct periodic briefings to keep executives informed.
- Inform executives of critical issues and unanticipated changes.
- Work with the executives to manage external relations.
At noon a sudden, severe windstorm strikes the city, uprooting trees and trapping several commuters in their vehicles. Power is out to half of the city. Traffic is gridlocked. The storm has passed as quickly as it began.
What are the objectives?
Identify life-safety priorities and initial resource needs.
Begin rescue operations.
Clear traffic jams and reroute traffic flow.
Restore power within 2 hours.
what is an Incident objectives?
they state what will be accomplished.
EX. Objective: Stop the spread of hazardous materials from a tractor-trailer accident into the river by 1800 today.
What is strategy?
establish the general plan or direction for accomplishing the incident objectives.
EX. Strategy: Employ barriers.
what is a Tactic?
specify how the strategies will be executed.
For example:
EX. Tactic: Use absorbent damming materials to construct a barrier between the downhill side of the accident scene and Murkey Creek
Elements of an Incident Action Plan
What must be done
Who is responsible
How information will be communicated
What should be done if someone is injured
An agency or organization providing personnel, services, or other resources to the agency with direct responsibility for incident management is called a(n
Assisting agency
An ___________ is an individual assigned to an incident from an assisting or cooperating agency.
Agency Representative
where are resources kept?
ICS Structure and Staging Area Management
Field Briefings
Incident Objectives: Clear statement of the immediate goals and tasks.
Assignments: Specific duties and responsibilities for each team member or unit.
Safety Protocols: Information on potential hazards, PPE requirements, and safety measures.
Communication Plan: Frequencies, channels, and call signs to ensure effective communication.
Logistical Needs: Any equipment, supplies, or support required to complete tasks.
Staff Briefings
Incident Overview: Current situation, recent developments, and any changes in incident status.
Incident Objectives and Priorities: Outline of the strategic objectives set by the Incident Commander.
Section-Specific Updates: Each Section Chief may provide updates on their area (Operations, Planning, Logistics, Finance/Administration).
Coordination Needs: Information on coordination between sections or external agencies.
Resource Status: Overview of resource availability, including personnel, equipment, and supplies.
Safety Concerns: Broad safety issues that apply across the incident.
Planning for Next Operational Period: Any preparation for future shifts or changes in operational strategy.
Section Briefings/Meetings
Section Objectives: Key goals and expectations specific to the section.
Role Assignments: Specific tasks assigned to individuals or units within the section.
Updates from Other Sections: Relevant information from other sections that may impact the section’s work.
Resource Requirements: Review of current resources and identification of any additional needs.
Safety and Risk Management: Section-specific hazards and safety protocols.
Communication and Reporting: Instructions on communication, reporting structure, and check-in points.
Next Steps: Outline of immediate actions and any preparatory work for the next operational period.
Explain how the modular organization expands and contracts.
ICS expands by adding sections, branches, or units as an incident grows in complexity. It contracts by deactivating these roles as the incident's needs decrease, keeping the response efficient and right-sized.