chem kinetics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Chemical change
Involves a chemical reaction to produce a new product (def)
Chemical bonds are broken and reformed to make new molecules
Eg. Baking a cake, cooking an egg, burning a candle
Some are reversible
Physical change
A change in matter that alters its form but not its chemical identity , size and shape can change but no chemical reaction occurs , mostly reversible
Eg. Breaking a water , boiling water , melting an ice cube
Signs of chemical reaction
Temperature change
Light
Colour change
Bubbling (effervescence)
Odour
Formation of precipitate
To distinguish chemical and physical change
Whether there is a new substance that wasn’t there before
Chemical reaction = chemical change
Kinetics studies of chemical reactions provides information on
How fast a Chemical reaction occurs (rate of reaction)
How economically a product can be made
Collision theory
The rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the frequency of defective collision
Conditions for collision theory
Reacting particles must collide with each other
Must collide with sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy of the reaction
Correct orientation
all of these = effective collision
To find rate of a reaction
Measuring the amount of products formed per unit time = amount of products / time
Measuring the amount of reactants used up per unit time = amount of reactants used up / time taken
Steepest gradient means
Fastest rate of reaction (gentlest gradient =slowest rate of reaction)
Gradient is always steepest at the start
Over time, why does the rate of reaction decrease
The concentration of reactants decrease over time as the reaction progress .When the rate of reaction is 0, all the limiting regent has been used up
If the graph does not end at 0
There is still some excess reactant left
If a reaction gives off gas , how do you find the rate of reaction
Use a gas syringe to measure the volume of gas given off at regular time intervals
What does it mean when the graph is horizontal?
No more gas is produced , reaction has stopped
To increase rate of reaction involving acid
Use an acid that produces more h+ ions , eg sulfuric acid and not hydrochloric acid
(If the reactant stays the same and only the acid is changed to something similar , the similarity between both experiments is that the same vol of gas will be produced)
Factors affecting rate of reaction
Concentration
Pressure (gaseous reactants only)
Particle size (solid reactants only)
Temperature of the reacting mixture
Catalyst

Concentration of reactants
Increasing the conc = increasing the number of reactants per unit volume
when the concentration of the reactants increases , the number of reacting particles per unit volume increases , so they collide more often. As a result, the frequency of effective collision increases, hence an increase in rare of reaction
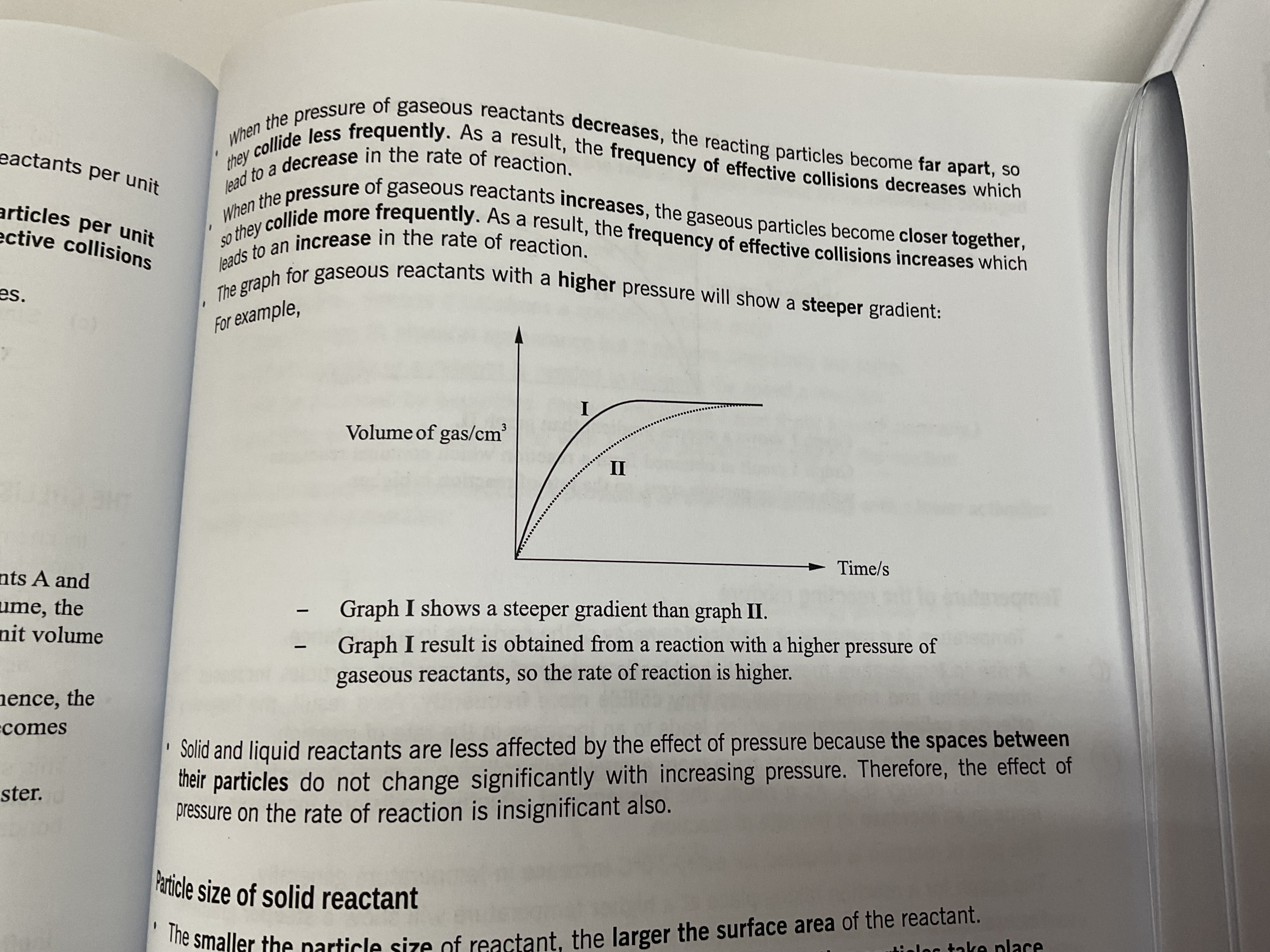
Pressure of gaseous reactants
As pressure of gas increases, gas particles are forced closer so they are able to collide more . This increases the number of gas particles per unit volume, increasing the frequency of effective collision between the gas particles, increasing the overall rate of reaction.
pressure increase = rate of reaction increase
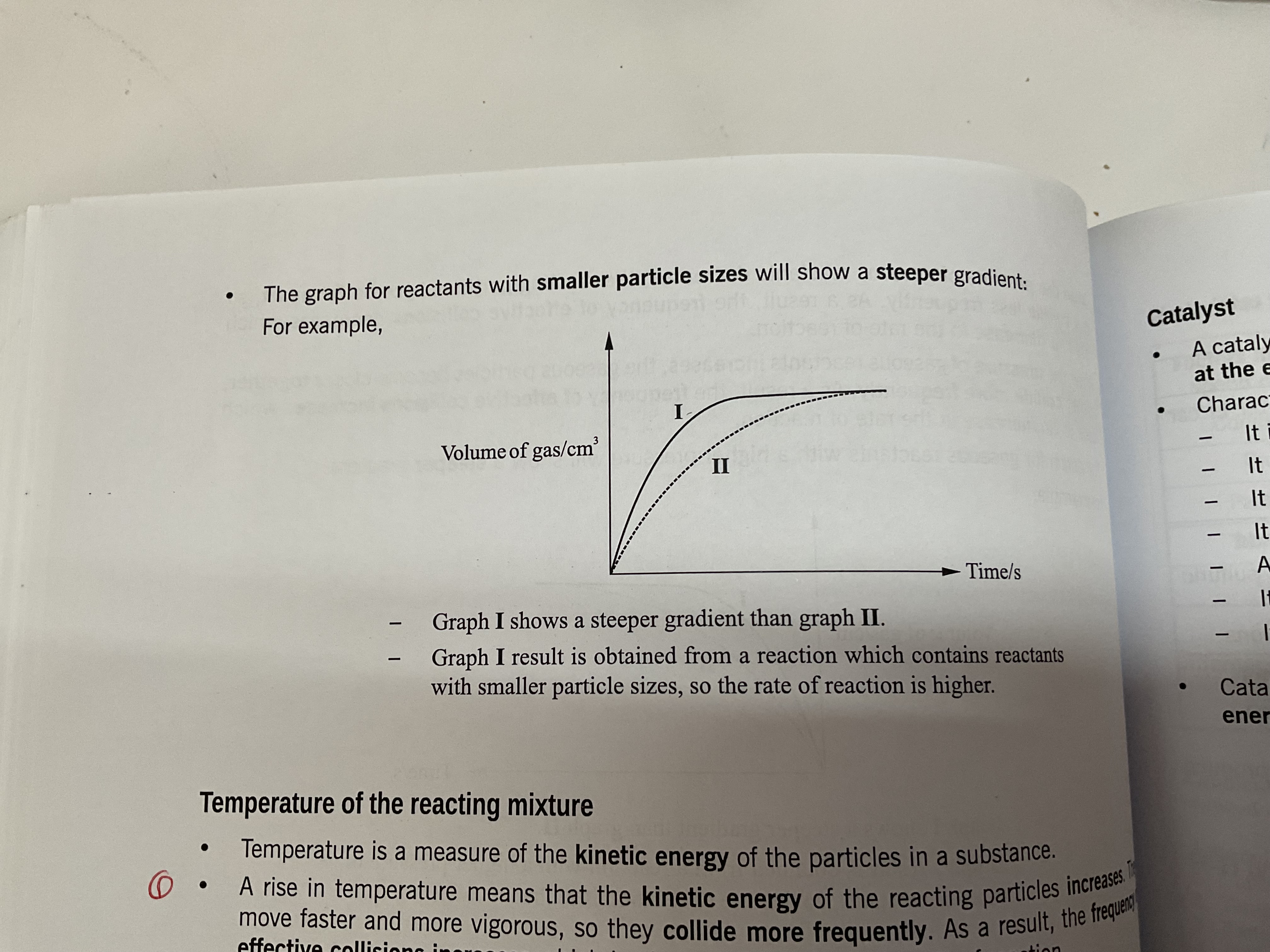
Particle size of solid reactant
Smaller the particle size = larger the surface area= faster rate of reaction
a large substance has a smaller surface area as the collisions are only limited to the outer surface
When the particle size decreases, the total surface area at any given time for reaction to take place increases, as a result, the frequency of effective collision per unit time increases which leads to an increase in the rate of reaction
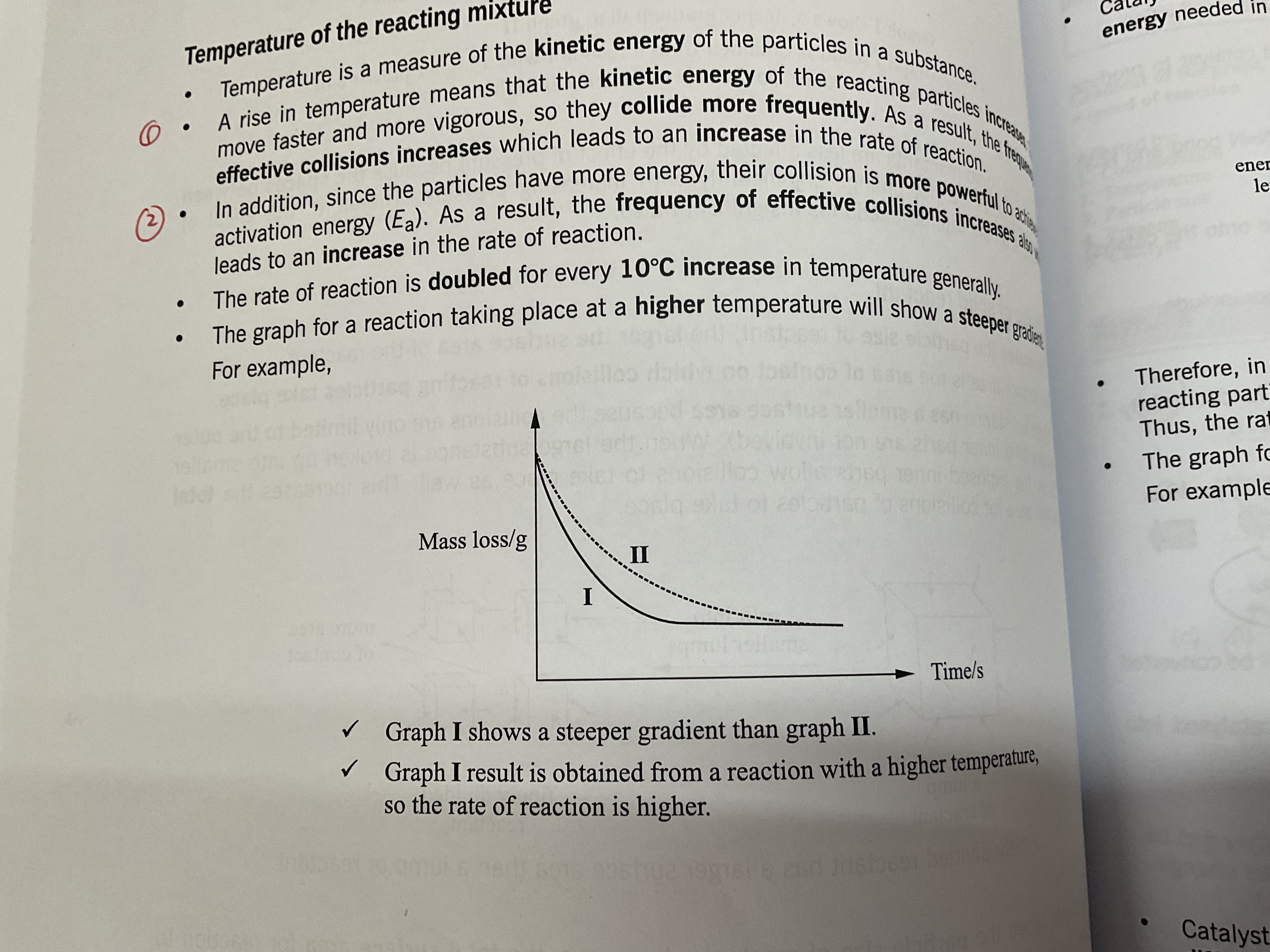
Temperature of the reacting mixture
an increase in temperature means that the kinetic energy of the reacting particles increases, they move faster and more vigorously so they collide more often. More particles have energy that is more than or equal to the activation energy . As a result, the frequency of effective collision increases, increasing the rate of reaction

Catalyst
In a catalysed reaction, more particles will have energy that is more than or equal to the activation energy. Hence, increasing the frequency of effective collision and rate of reaction
Only change rate not the yield of the experiment
Catalyst def
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction . It remains chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction and provides alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy
Which factors affect the frequency of collisions
Everything but catalyst ( temp, conc , pressure , particle size )
What affects energy of collsion
Only temp and catalyst