Anxiety- Krysiak
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What is anxiety?
just recognize
an emotional state caused by the perception of real or perceived danger that threatens the security of an individual—> can produce uncomfy feelings

According to DSM-V what are the 5 classifications of anxiety?
generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
panic disorder (± agoraphobia)
social anxiety disorder (SAD)
posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)

What are a characteristic features of ALL CLASSES of anxiety?
anxiety and avoidance behavior—> fear and worry
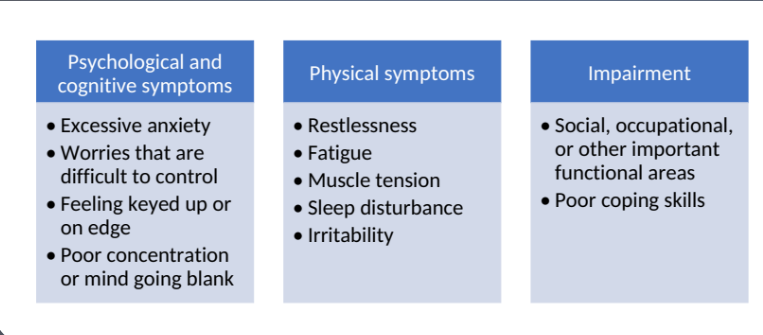
Diagnosis of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
persistent symptoms for most days for at least 6m
the anxiety is accompanied by at least 3 psychologic or physiologic symptoms:
restlessness or feeling on edge
fatigue
difficulty concentrating or mind going blank
irritability
muscle tension
sleep disturbances
Symptoms of GAD:
Noradrenergic Model of Anxiety Pathophysiology:
Hypersensitivity of the autonomic nervous system—> where the locus ceruleus (LC) serves as an alarm system—> releases norepinephrine (NE) and stimulates sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
GABA Receptor Model of Anxiety Pathophysiology:
GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter, has a strong regulatory or inhibitory effect on the 5-HT, NE, and DA systems. Benzodiazepines enhance the inhibitory effects of GABA.
Serotonin Model of Anxiety Pathophysiology (lack evidence):
5HT normally inhibitory
dysfunction at presynaptic auto receptors—> serotonin reuptake transporter site or postsynaptic receptors may play a role in anxiety
GAD treatment is a combination of what 2 therapies?
psychotherapy + drug therapy
Nonpharm for GAD?
psychoeducation
counseling/stress management
psychotherapy
CBT most effective
mediation
exercise
WHAT ARE THE 1st line, 2nd line, and alternative drugs for GAD?
1st line:
duloxetine
escitalopram
paroxetine
sertraline
venlafaxine XR
2nd line:
benzos
buspirone
imipramine
pregabalin
Alternative:
Hydroxyzine
Quetiapine
What is the adequate trial period for antianxiety response? Following an adequate trial and good response, treatment should be continued for at least how long?
adequate trial: 4-6w
following adequate trial, good response—> continue tx for 1 year
If benzodiazepines are the most frequently prescribed medications for acute treatment of anxiety, why are they not 1st line tx for GAD?
good for acute anxiety, however not recommended for long-term use
benzos are also not for depressive symptoms and should not be used with substance abuse disorders
antidepressants however—> can be used for acute and chronic anxiety, as well as for depressive symptoms (duh the name)
overall: GAD is mostly a long term disorder hence why antidepressants are 1st line
PRACTICE:
A 34 YO female is looking to start treatment for her ACUTE anxiety. She also has a history of depression. Would Duloxetine or Lorazepam be a better option for managing her anxiety? Why?
Duloxetine—> Why? Duloxetine is 1st line for acute anxiety and anxiety with depression but also Lorazepam is NOT recommended for depressive symptoms and may contribute to depression long term
REVIEW:
MOA and names of benzodiazepines:
Potentiation of the inhibitory activity of GABA by binding to GABAA receptors
names:
Alprazolam
Chlordiazepoxide
Clonazepam
Clorazepate
Diazepam
Lorazepam
Oxazepam
Which benzos are lipophilic? result?
Which are NOT lipophilic? result?
diazepam and clorazepate= rapidly absorbed and distributed
lorazepam and oxazepam= slower absorption and onset
Benzos undergo what 2 primary metabolic processes?
hepatic oxidation (CYP3A4) and glucuronide conjugation
Most benzos are converted into the metabolize DMDZ. What is the result of this conversion?
a. increases absorption
b. lengthens half-life
c. increased side effect risk
d. enhanced sedation
b.
Benzodiazepine ADRs:
biggest complication: abuse, dependence, tolerance
CNS: drowsy, sedation, psychomotor impairment, disorientation, depression, confusion, irritability, impairment of memory and recall
Benzos have a risk of tolerance to some side effects but not others.
What side effects does tolerance develop in?
What side effects do NOT develop a tolerance?
tolerance: sedative, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant effects
no tolerance: anxiolytic or antipanic effects
WHAT IS THE RECOMMENDED DURATION FOR BENZOS?
only 2-4 weeks for acute anxiety
Why is Buspirone (Buspar) considered second-line?
inconsistent efficacy for long term use
delayed onset
lack of efficacy for concurrent depressive or anxiety disorders
Unlike Benzos, Buspirone is effective for what symptoms of anxiety?
Buspirone effective for PSYCHIC symptoms of anxiety (Worry, rumination, apprehension)
Helpful tip: I think of it like this— buspirone treats the "mind" of anxiety (thoughts), while benzos treat the "body" (physical symptoms)
Answer the following about Buspirone:
dosing of Buspirone is __-__ times a day. Affect on adherence?
drug interactions?
when will we see a therapeutic benefit?
2-3 times a day—> negatively affects adherence
D/I: CYP3A4 INHIBITORS INCREASE LEVELS, MAOI
ex: rifampin can lower levels of buspar x10
with an MAOI, buspar can cause hypertensive crisis
full benefit might not be seen for 4-6 weeks
For monitoring outcomes of GAD:
initially patients should be monitored every __ weeks
initial pharm therapy with an _____ will not lead to remission
following an adequate trial/good response, tx should be continued for at least __ year(s)
initially patients should be monitored every 2 weeks
initial pharm therapy with an SSRI will not lead to remission
following an adequate trial/good response, tx should be continued for at least 1 year(s)
What is Panic Disorder (PD)?
Begins as unexpected panic attacks involving intense, terrifying fear of life-threatening danger
followed by persistent concern about future attacks, worry about the consequences, or behavioral changes related to the attacks
About 70% of pts. with panic disorder develop Agoraphobia.
What is Agoraphobia?
anxiety about being in places or situations where escape might be difficult or where help might not be available in the event of a panic attack
as a result—> pts. may avoid specific situations in which they fear a panic attack may occur
Diagnosis of Panic Disorder (PD):
a discrete period of intense fear or discomfort in which ≥4 of the following symptoms develop and reach a peak within 10 minutes:
Palpitations/ increased HR
sweating
trembling/shaking
shortness of breath/ sensations
feeling of choking
chest pain/discomfort
nausea
dizziness/faint
derealization/depersonalization
fear of losing control
fear of dying
paresthesias
chills/hot flushes.
PD symptoms usually lasts between ___-___ with peak intensity of symptoms within the first 10 minutes.
20-30
PD treatment uses what kinds of therapies?
single or combo pharm therapy + psychotherapy OR psychotherapy followed by pharmacotherapy
Nonpharm for PD?
SAME AS GAD!!!!!!!!!!!
psychoeducation
counseling/stress management
psychotherapy
CBT most effective
mediation
exercise
WHAT ARE THE 1st LINE, 2nd LINE, and LAST LINE DRUGS FOR PD?
1st line
SSRIs (fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine approved)
SNRIs (Venlafaxine XR approved)
2nd line
Benzos (Clonazepam and Alprazolam approved)
TCAs (Clomipramine, imipramine not approved)
LAST LINE
MAOIs
At the start of therapy for PD, SSRIs can cause _________ syndrome.
activation syndrome (increased anxiety, jitters, shakes, agitation)
Phases of therapy for PD:
acute phase is __-__ months
alter therapy if no response after ___-___ weeks at max dose
pts. who respond to pharm therapy should continue at full dose for a least ___ year (s)
acute phase is 1-3 months
alter therapy if no response after 6-8 weeks at max dose
pts. who respond to pharm therapy should continue at full dose for a least 1 year
What is Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD):
characterized by intense, irrational, and persistent fear of being negativity evaluated or scrutinized in at least one social or performance situation
exposure to feared circumstance usually provokes a panic attack
the person recognizes that the fear is excessive/unreasonable
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) and Panic Disorder (PD) are difficult to differentiate sometimes. What is the difference between these two?
the RATIONALE behind the fear
fear of anxiety symptoms= PD
fear or embarrassment from social interaction= SAD
How does SAD present?
fear of being ____________-
ex’s of feared situations?
physical symptoms?
what are the 2 types?

What types of treatments are utilized in SAD?
CBT + pharmacotherapy
WHAT IS THE 1st LINE, 2nd LINE, and ALTERNATIVES for SAD?
1st LINE
SSRIs (Paroxetine and Sertraline approved, Fluvoxamine not approved)
Venlafaxine XR
2nd LINE
Benzos (Clonazepam, Citalopram)
Alternatives
gabapentin
b-blockers (propranolol, atenolol)
During acute phase of tx for SAD, the patient should be seen on a _________ basis while drug dosage is being titrated.
a. weekly
b. biweekly
c. monthly
d. bimonthly
a.
What is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
Exposure to a traumatic event involving threatened death, serious injury, or harm, with a response of intense fear, helplessness, or horror.
How is PTSD diagnosed?
sorry in advance, this is so long :(
A. The person has been exposed to a traumatic event in which both of the following have been present:
The person experienced, witnessed, or was confronted with an event that involved actual or threatened death or serious injury, or a threat to the physical integrity of self or others
The person’s response involved intense fear, helplessness or horror
B. The traumatic event is persistently re-experienced in ≥ 1 of the following ways:
Recurrent and intrusive images, thoughts, perceptions or distressing dreams of the event
Acting or feeling as if the traumatic event were recurring
Intense psychological distress at exposure to internal or external cues that symbolize or resemble an aspect of the traumatic event
Physiologic reactivity upon exposure to internal or external cues that symbolize or resemble an aspect of the traumatic event
C. Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma and numbing of general responsiveness as indicated by ≥ 3 of the following:
Efforts to avoid thoughts, feelings, or conversations associated with the trauma
Efforts to avoid activities, places, or people that arose recollections of the trauma
Inability to recall an important aspect of trauma
Markedly diminished interest or participation in significant activities
Feeling of detachment or estrangement from others
Restricted range of affect (e.g. unable to have loving feelings)
Sense of foreshortened future (e.g. does not expect to have a career)
D. Persistent symptoms of increased arousal (not present before the trauma) indicated by at ≥ 2 of the following: difficulty falling asleep, irritability or outbursts of anger, difficulty concentrating, hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response
When is pharmacotherapy utilized for PTSD?
if symptoms persist for 3-4 weeks and is causing impairment—> pharmacotherapy ± psychotherapy
Nonpharm for PTSD?
psychotherapy—> CBT (extremely beneficial)
exposure therapy—> involves confronting trauma cues, best for pts. with mild symptoms or refuse meds
WHAT IS THE 1st LINE, 2nd LINE, and ALTERNATIVES for PTSD?
1st LINE
SSRIs (Sertraline and paroxetine FDA approved)
Venlafaxine XR
2nd LINE
TCAs
Alternatives
Mirtazapine
Nefazodone
Phenelzine
Anticonvulsants
atypical antipsychotics (risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine)
adrenergic inhibitors (prazosin, clonidine)
WHAT CLASS OF MEDICATIONS SHOULD NOT BE USED IN PTSD?
BENZOS
To be diagnosed with OCD a person has to have what?
obsessions, compulsions, or both
Define obsessions:
Define compulsions:
(recognize the differences between them)
obsession: recurrent persistent ideas, thoughts, impulses or images that are experienced as intrusive and inappropriate and produces marked anxiety
the person attempts to ignore/suppress the thoughts, impulses, images with something else (like a compulsion)
compulsion: repetitive behaviors or mental acts that the person feels driven to perform in response to an obsession
In OCD, the obsessions or compulsions take more than ___ hour(s) a day.
1
What should be offered to every patient with OCD?
CBT —> it is the TREATMENT OF CHOICE in adolescents and adults with mild OCD
WHAT IS THE 1st LINE and alternative drugs for OCD?
1st LINE
SSRIs (Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline)
Alternatives
CLOMIPRAMINE (after failing 2 SSRIs)
Venlafaxine XR (use clomipramine before trying, not FDA approved)
What is the place of antipsychotics in OCD tx?
evidence does not support monotherapy, however agents may be helpful for augmentation after failure of 2+ antidepressants
can use: Ladol, Risperidone, Aripiprazole
First line drug therapy should be for at least ___ weeks and CBT should be for at least ___ weeks before concluding inadequate response.
First line drug therapy should be for at least 12 weeks and CBT should be for at least 13 weeks before concluding inadequate response.
For OCD, pharm therapy should be continued for ____ years before tapering because relapse rates are very high.
1-2 years
Review:
For all anxiety disorders, except OCD the duration of treatment is at least __ years.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
a. 1 (OCD is 1-2 years)