AP World History Chapter 5: Society and Inequality in Eurasia/North Africa, 600 B.C.E. - 600 C.E.
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Han Dynasty
(202 BCE-220 CE) This dynasty of China continued the centralization of the Qin Dynasty, but focused on Confucianism and education instead of Legalism.
Wu Di
Probably the most important emperor of the Han Dynasty; he started China's first civil service system c. 124 BCE to help oversee the day-to-day business of running the government.

Wang Mang
A reformist official in 9 CE who was troubled by the plight of the peasants seized power from the Han court and declared the foundation of the Xin dynasty (New dynasty). He was assassinated in 23 CE, probably due to his radical reform movements.

Yellow Turban Rebellion
A massive Chinese peasant uprising inspired by Daoist teachings that began in 184 C.E. with the goal of establishing a new golden age of equality and harmony.
Caste System
The system in old India that separated the people into social categories, but based mostly on colour with the Aryans always on the top of the social pyramid.
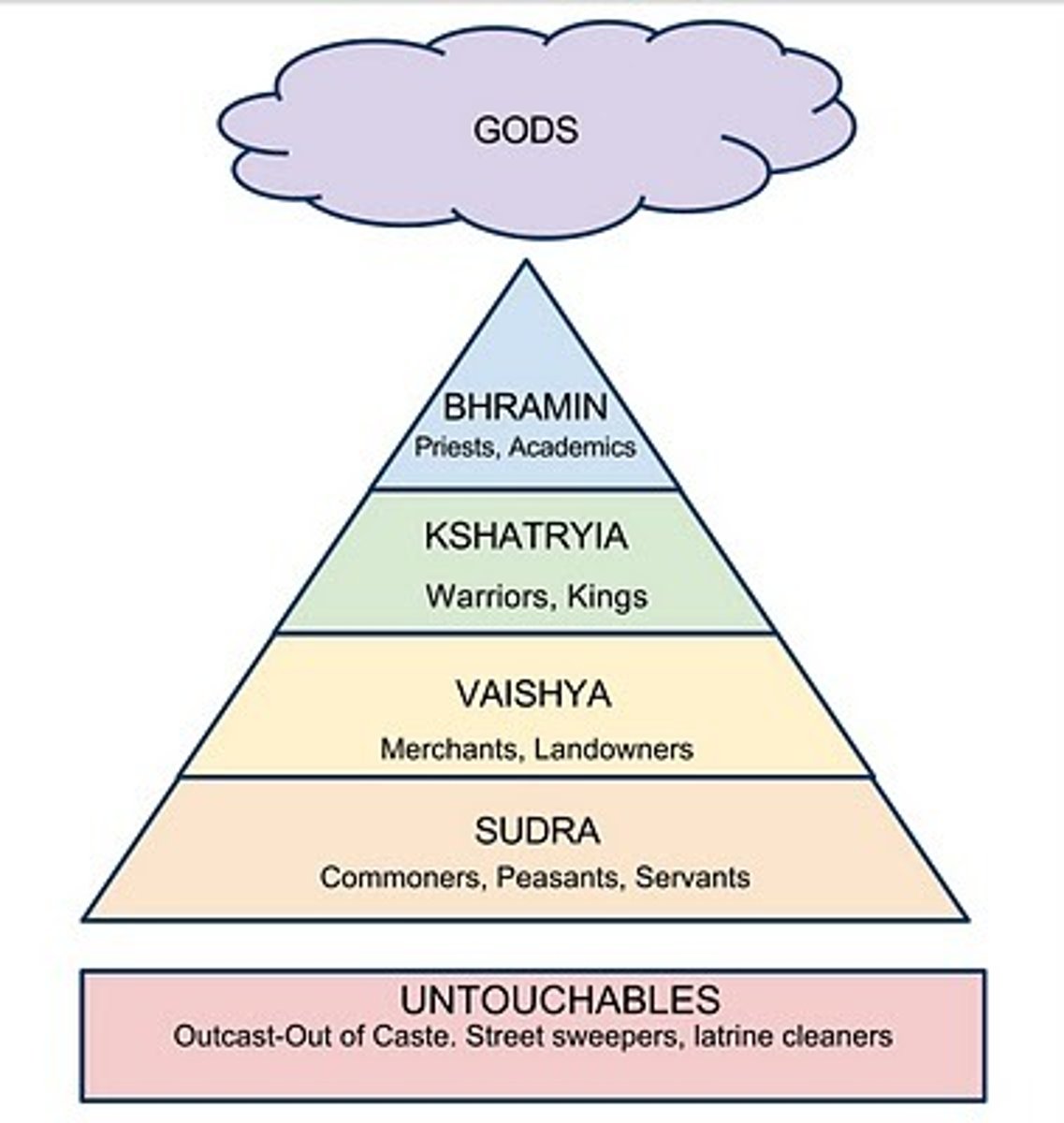
Varna
The four major social divisions in India's caste system: the Brahmin priest class, the Kshatriya warrior/administrator class, the Vaishya merchant/farmer class, and the Shudra laborer class.

Jati
A sub-varna in the caste system of India that gave people of sense of community because they usually consisted of people working in the same occupation.
Dharma
In Hindu belief, a person's religious and moral duties "It is better to do one's own duty badly than another's well."
Classical Labor Systems
Slavery & Wage labor in the Greco-Roman world, Caste in India, Peasant farming in China (along with the persistence elsewhere of sustenance farming, pastoral nomadism, and hunting/gathering).
Delos
Greek island sacred to Apollo that was the namesake for the Delian League (basically the empire of Athens). Home to a slave-trading network during the Roman empire.
Saint Paul
Missionary of Christianity who compared followers of God to "slaves of Christ."
Saint Augustine
Christian theologian who describes slavery as God's punishment for sin.
Latifundia
Huge estates owned by wealthy families in the Roman Empire that utilized slave labor for production.
Manumission
A grant of legal freedom to an individual slave (a common practice in the Greco-Roman world that would not be accompanied later in the Trans-Atlantic slavery world).
Spartacus
A Roman gladiator who led the most serious slave revolt in Roman history from 73 to 71 B.C.E.

Appian Way
A major road connecting Rome to southern Italy built by the Romans (home to thousands of crucified slaves after the revolt of Spartacus).
Patriarchy
A form of social organization in which males dominate females (gender hierarchies of the Classical Era).
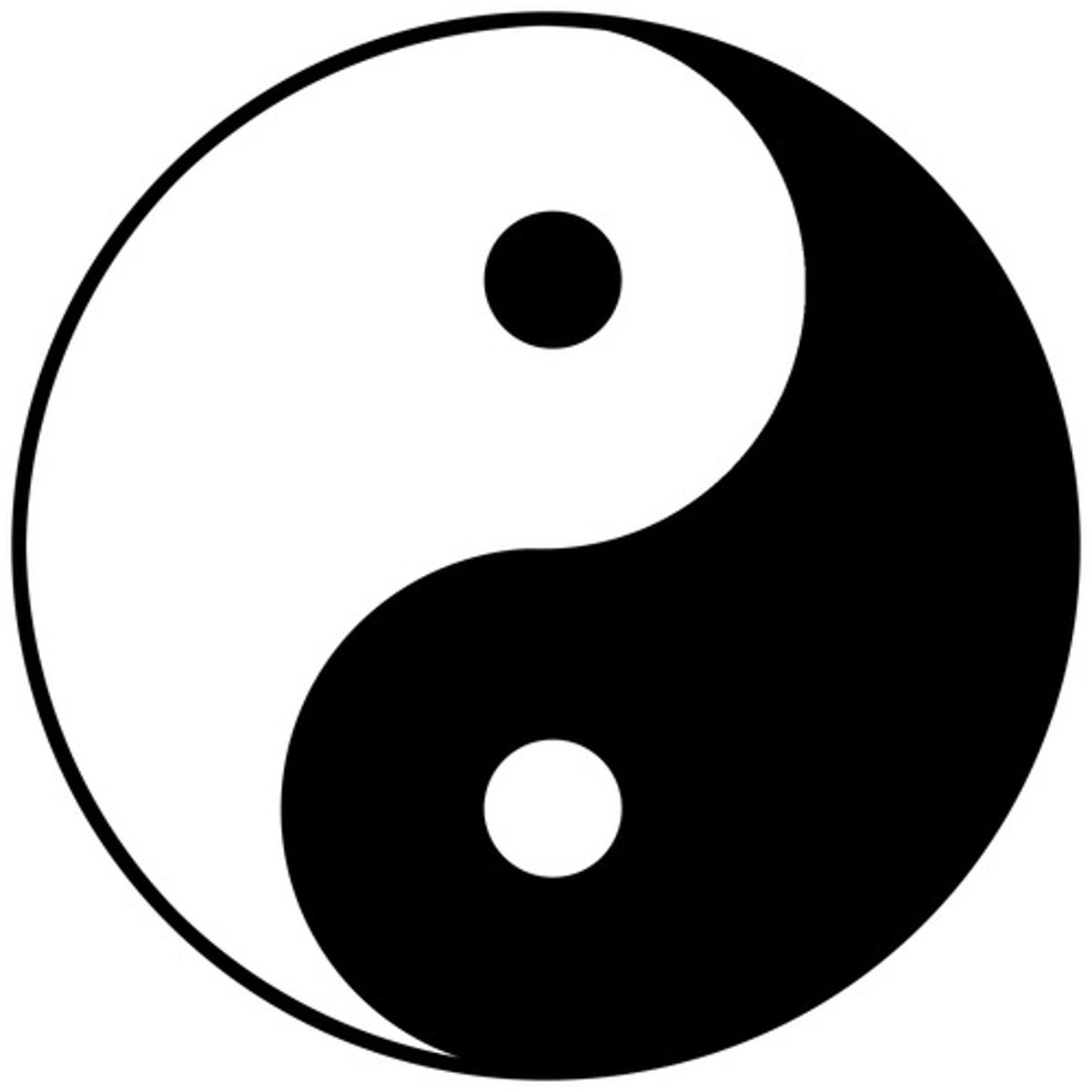
Yin and Yang
In Daoist belief, complementary factors that help to maintain the equilibrium of the world. One is associated with masculine, light, and active qualities while the other with feminine, dark, and passive qualities.

Three Obediences
A notion in some Eastern cultures that a woman owes subordination first to her father, then to her husband, and third to her son.
Ban Zhou
The first female Chinese historian who wrote about the Han dynasty in the first and second centuries CE. (45-116 CE)

Empress Wu
(690 - 705 C.E.) Tang ruler who supported Buddhist establishment; tried to elevate Buddhism to state religion; had multistory statues of Buddha created.
Tang Dynasty
(618-907 CE) The Chinese dynasty that was much like the Han, who used Confucianism. This dynasty had the equal-field system, a bureaucracy based on merit, and a Confucian education system.
Aristotle
(384-322 BCE) Greek philosopher who wrote about social relationships including arguing that slavery for some people was "by nature" and argued that women were inferior to men as a sort of "inadequacy."

Aspasia
A well-educated woman who helped shape Athenian politics as an adviser to Pericles (an exception in Athens). She was frequently referred to as a prostitute in Athenian discourse and poetry.
Pericles
(495? BCE-429? BCE) Athenian statesman. He was the central ruler of Athens during its golden age. He was the central patron behind many of their achievements. He was also a very skilled speaker.

Helots
Slaves in the Spartan polis.
Plutarch
Greek biographer of the first to early second century CE. Author of Parallel Lives which compared famous men of classical Greece and republican Rome.
Xenephon
(430 - 354 BCE) Athenian writer and student of Socrates known for his account of the final years of the Peloponnesian War and writings about his teacher.
When was the Imperial Academy for Chinese official training built, and by whom?
124 BCE, by Emperor Wu Di (enrolled 30,000 students)
Poetry of Buddhist Nuns set into writing
100 BCE
Spartacus Slave Rebellion
73 BCE
Laws of Manu Established
1-200 CE
Emperor Wang Mang in power
100 CE
Ban Zhao life
45-116 CE
Vesuvius Eruption
79 CE
Yellow Turban Rebellion Period
184 CE
Slavery replaced by serfdom in Rome
500 CE
Empress Wu Reign
690-705 CE
Merchants in China
Typically oppressed and exploited, since they "contribute nothing" directly, but occasionally become very wealthy and raise respectable sons.
Brahmin (Caste: colour, Purusha part, Duties)
1st: White/Spirituality, Head, Priests/Teachers
Kshatriya (Caste: colour, Purusha part, Duties)
2nd: Red/Courage, Shoulders, Warriors
Vaisya (Caste: colour, Purusha part, Duties)
3rd: Yellow/Wealth, Thighs, Farmers
Sudra (Caste: colour, Purusha part, Duties)
4th: Black/Ignorance, Feet, Labor
Untouchables (Caste: colour, Purusha part, Duties)
N/A (5th): -, -, polluted labor
Percentage of slaves as Roman population
33-40%
Which job were slaves restricted from serving in?
Military service
Slaves often worked as these prominent professions...
Doctors, teachers, business agents, entertainers, actors, skilled artisans
Menander
Quoted as saying that teaching women to read and write is like feeding a vile snake on poison.
Differences in Spartan and Athenian Patriarchy
Women had a more active role in Sparta, since they were the ones that would produce Sparta's army. They were not seen as required to stay in the house.
Why did Spartan women exercise more authority in the house?
Men were often away at war.